Bio Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/156
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific method steps
1. Observation
2. Hypothesis
3. Test
4. Conclusion
2
New cards
Does data always prove hypothesis?
No. Conclusions reject hypothesis, accepts hypothesis, supports.
3
New cards
Inductive reasoning
Specific to general
Ex. One bacteria(specific) and all bacteria (all bacteria)
Ex. One bacteria(specific) and all bacteria (all bacteria)
4
New cards
Aspects of science
1. Repeatable
2. Can be verified and edited
3. Dynamic
4. Objective
5
New cards
Limitations of science
1. Some things can’t be tested
2. Equipment/ tech is limited or unavailable
3. People can’t accept or aren’t ready to accept hypothesis
6
New cards
Science creates
1. Model
2. Theory
3. Law
7
New cards
Chemistry
Deals with the composition and property of matter.
8
New cards
Matter
Anything that occupies space and has mass
1. Liquid
2. Solid
3. Gas
4. Plasma
1. Liquid
2. Solid
3. Gas
4. Plasma
9
New cards
Oxygen
Most in body of mass
10
New cards
Carbon
\#1 in all organisms by # of atoms
11
New cards
Hydrogen
\#1 in universe
12
New cards
Atom
(Un-cuttable)
Smallest unit of matter
Smallest unit of matter
13
New cards
Proton
\+1 charge
Mass of 1
Found in nucleus
Mass of 1
Found in nucleus
14
New cards
Neutron
0 charge
Mass of 1
Found in nucleus
Mass of 1
Found in nucleus
15
New cards
Electron
\-1 charge
No mass
Found in the space area energy levels
No mass
Found in the space area energy levels
16
New cards
Rutherford gold foil experiment
Particles went straight through the space of the atom
All positive charge was held in the common nucleus of the atom
Light charges repel
All positive charge was held in the common nucleus of the atom
Light charges repel
17
New cards
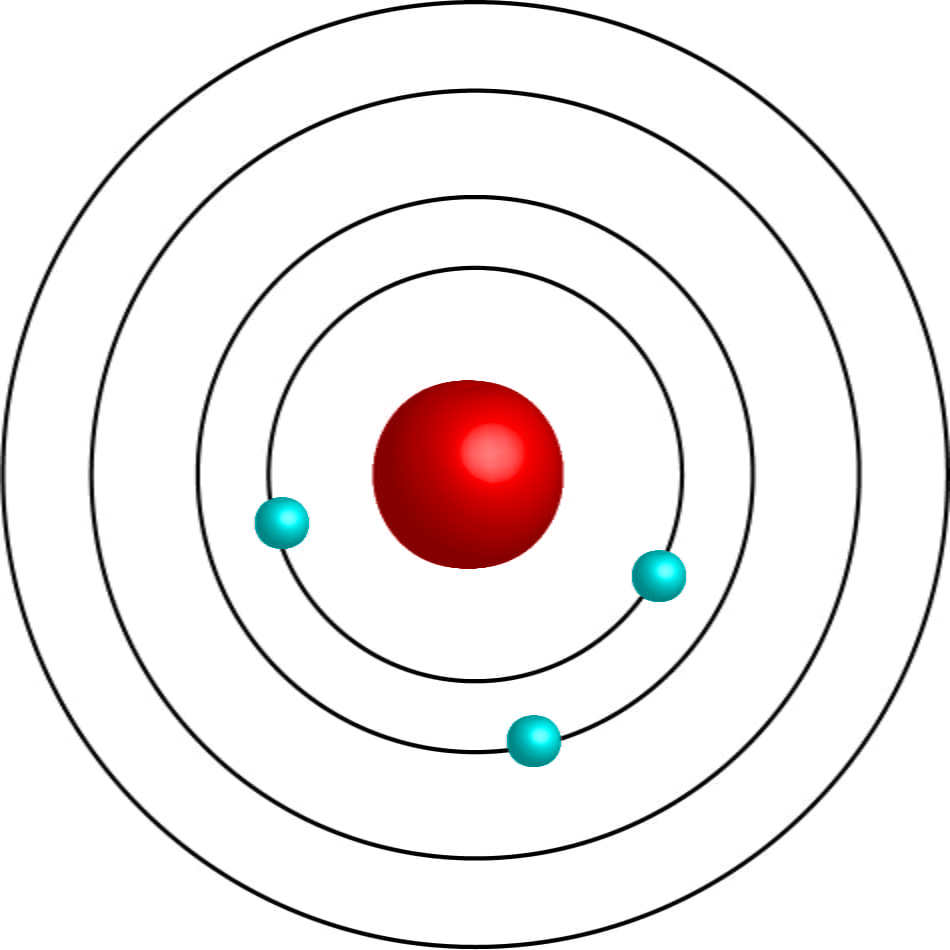
Bohr experiment
Heated elements
If electron displaces energy, it would show dissipating energy through singular color
If electron displaces energy, it would show dissipating energy through singular color
18
New cards
what is inside the nucleus ( atomic mass)
Neurons and protons
19
New cards
First level of atom
1. Lower level
2. Holds 2 electrons
20
New cards
Second level of atom
Holds 8 electrons
21
New cards
Third level of atom
Highest level
Can hold 18 electrons
Only 8 are involved with bonding
Can hold 18 electrons
Only 8 are involved with bonding
22
New cards
Isotopes
Same # protons, different # neutrons
23
New cards
unstable isotope
Carbon14
isotopes which radioactively decay to form new stable isotopes of the same element or a different element
isotopes which radioactively decay to form new stable isotopes of the same element or a different element
24
New cards
unstable isotopes examples
1. x-ray film
2. Geiger counter (through noise)
3. Scintillation medium (flashes of light)
25
New cards
Mendeleev
Arranged elements according to their atomic mass (P + N)
26
New cards
Mosely
Arranged elements according to atomic number (# of Protons)
27
New cards
atomic number
number of protons
28
New cards
atomic mass
number of protons and neutrons
29
New cards
how to find the number of neutrons
atomic mass - number of protons
ex:
Carbon:
12 - 6 = 6
Fluoride:
19 - 9 = 10
Chloride:
35 - 17 = 18
ex:
Carbon:
12 - 6 = 6
Fluoride:
19 - 9 = 10
Chloride:
35 - 17 = 18
30
New cards
Bonds
Atoms bond to become more stable
* forms molecules by filling outer energy level
* can bond by either gaining/ giving/ sharing
* forms molecules by filling outer energy level
* can bond by either gaining/ giving/ sharing
31
New cards
Ionic bond
gaining and giving up electrons
32
New cards
positive ion
cation (more protons)
33
New cards
negative ion
Anion (more electrons)
34
New cards
covalent bond
sharing of outer level electrons and can be shared in a nonpolar or polar manner
_______________
_______________
35
New cards
octet bond
when the rule of outer bonds of 8 is satisfied
36
New cards
nonpolar covalent bond:
equal sharing of electrons
37
New cards
polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons
hydrophobic (wa
hydrophobic (wa
38
New cards
hydrogen bond
the attraction of opposite partial charges.
causes pulling and tension
---------------
causes pulling and tension
---------------
39
New cards
PH scale
power of hydrogen measured.
water: 7
humans: 7.4
water: 7
humans: 7.4
40
New cards
buffer
molecule that resists a change in PH
41
New cards
natural state
homeostasis
42
New cards
buffer in body
bicarbonate and carbonic acid
43
New cards
Biochemicals
molecules of life and are all organic (contain carbon)
44
New cards
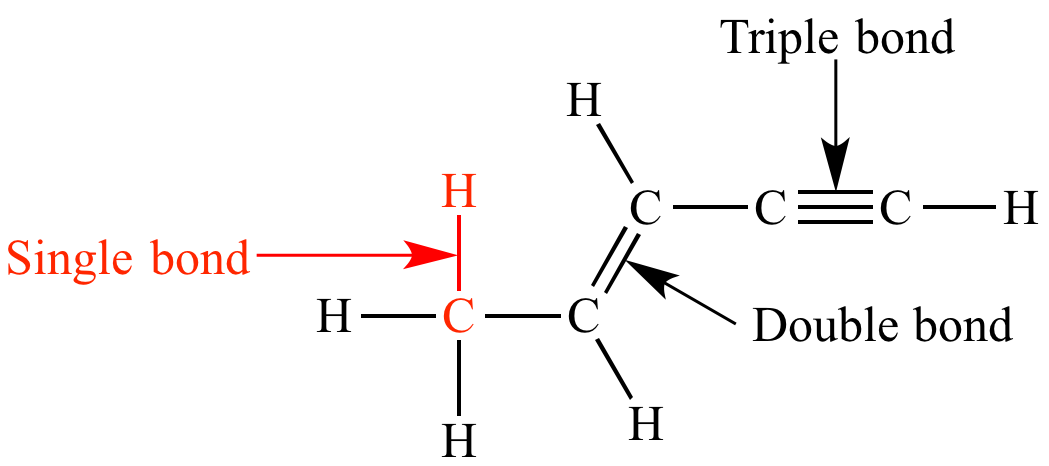
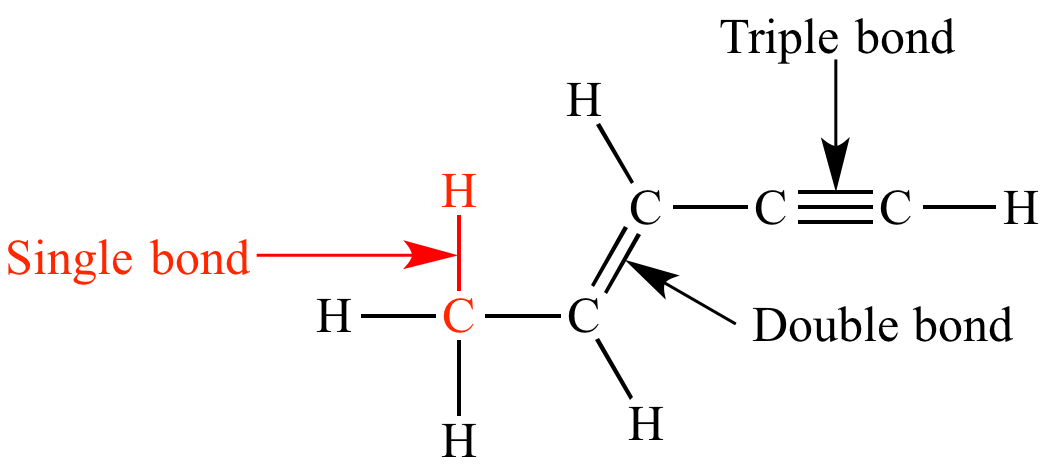
Single bond
chemical bond between two atoms involving two valence electrons.
Covalent bond
Covalent bond
45
New cards
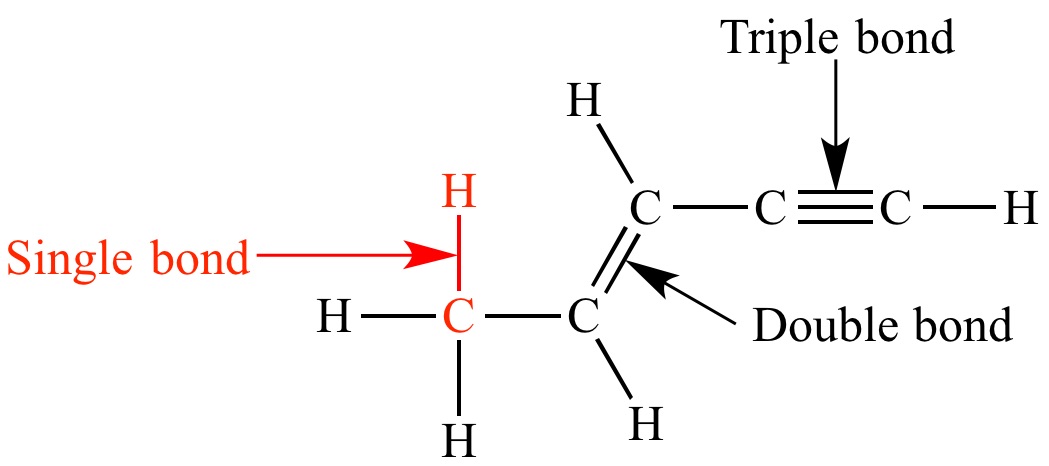
Double bond
1. a chemical bond in which two pairs of __electrons__ are shared between two __atoms__.
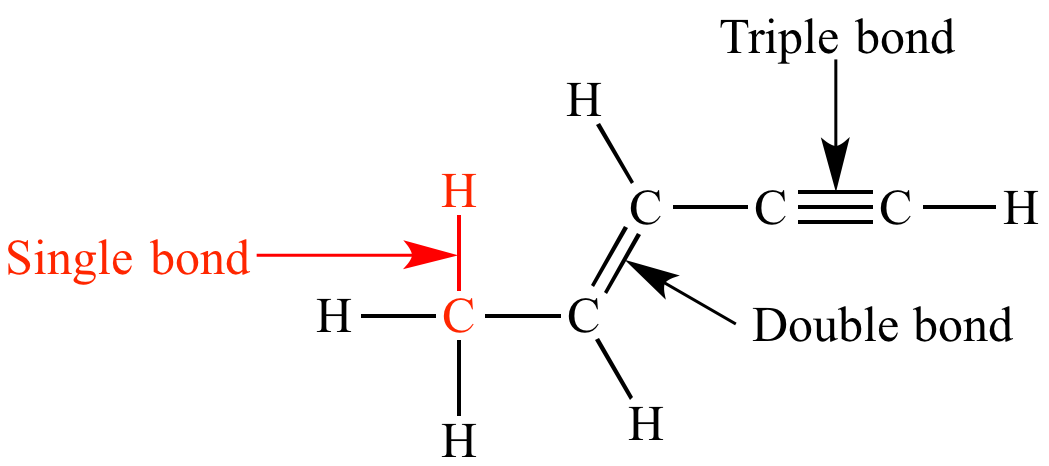
46
New cards
Triple bond
a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. T
L
L
47
New cards
4 classes of Biochemicals
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic acids
48
New cards
Carbohydrates
Sugars + starch
49
New cards
monosaccharide
Simple sugars and sweet
Monosaccharide and Disaccharide
Monosaccharide and Disaccharide
50
New cards
Monosaccharide examples
1. Glucose
2. Fructose
(Contains 5-6 carbon sugars)
51
New cards
Monosaccharide module
Chain and ring
52
New cards
Disaccharide examples
lactose, glucose, sucrose, Mattose
6 sided shape, house
6 sided shape, house
53
New cards
Hydrocarbon backbone
C-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-H
54
New cards
Alcohol
OH + c-c-c-c-
55
New cards
Amine group
C-c-c-c-c-c+ N-H+-H
56
New cards
Acid group
C-c-c-c-c-c+C=O + -OH
57
New cards
Ketone, aldehyde group
C-c-c-c-c-c-c+ =O
58
New cards
Phosphate group (DNA)
C-c-c-c-c-c-c+ -P-O-O=O
59
New cards
Polysaccharide
Complex carbohydrates
1. Starch
2. Cellulose
3. Glycogen
4. Chitin
1. Starch
2. Cellulose
3. Glycogen
4. Chitin
60
New cards
Starch is found in
Plants, energy storage
61
New cards
Cellulose
Makes up cell walls in plants
62
New cards
Glycogen
In animals, energy storage, liver muscle
63
New cards
Chitin
In insects, exoskeleton, fungi cell wall
64
New cards
Lipids
any of a class of organic compounds that are fatty acids or their derivatives and are __insoluble__ in water but soluble in organic solvents.
1. Energy storage
1. Energy storage
65
New cards
Triglycerides
\
C-C-C
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
C-C-C
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
66
New cards
Saturated f.a
C-C-C-C-C-C
All single bonds
Solid at room temperature
All single bonds
Solid at room temperature
67
New cards
Unsaturated f.a
C-C-C-C-C=C-C
At least one double bond
Liquid at room temperature
At least one double bond
Liquid at room temperature
68
New cards
polyunsaturated fatty acids
2+ double bonds
Omega-3 f.a
Anti-inflammatory
First double bond is found in 3rd fatty end
Omega-3 f.a
Anti-inflammatory
First double bond is found in 3rd fatty end
69
New cards
Omega-6 f.a examples
Corn
Peanuts
Peanuts
70
New cards
Omega-3 f.a
Fish, flax seed, walnut, leafy green, chia seeds
Essential to human diets
Essential to human diets
71
New cards
Trans fat
Product of hydrogenation process
Helps/ prevents polyunsaturated fats not go bad
Helps/ prevents polyunsaturated fats not go bad
72
New cards
CIS
process of hydrogenation process
bent on same sides
bent on same sides
73
New cards
transconfiguration
like an arrow down from opposite sides.
has a higher melting point
contributes to heart disease
has a higher melting point
contributes to heart disease
74
New cards
phospholipids
found in membrane structure
Phosphate grp + 2 f.a + 1 glycerol
Phosphate grp + 2 f.a + 1 glycerol
75
New cards
phospholipid head
polar and hydrophilic
76
New cards
phospholipid fatty acid tails
nonpolar and hydrophobic
77
New cards
sterols
cholesterol- in animal cell membranes
precursor to hormones
testosterones
vitamin D
estrogen
precursor to hormones
testosterones
vitamin D
estrogen
78
New cards
waxes
long chain of f.a + alcohol
coatings on leaves o prevent water loss or found in hair
coatings on leaves o prevent water loss or found in hair
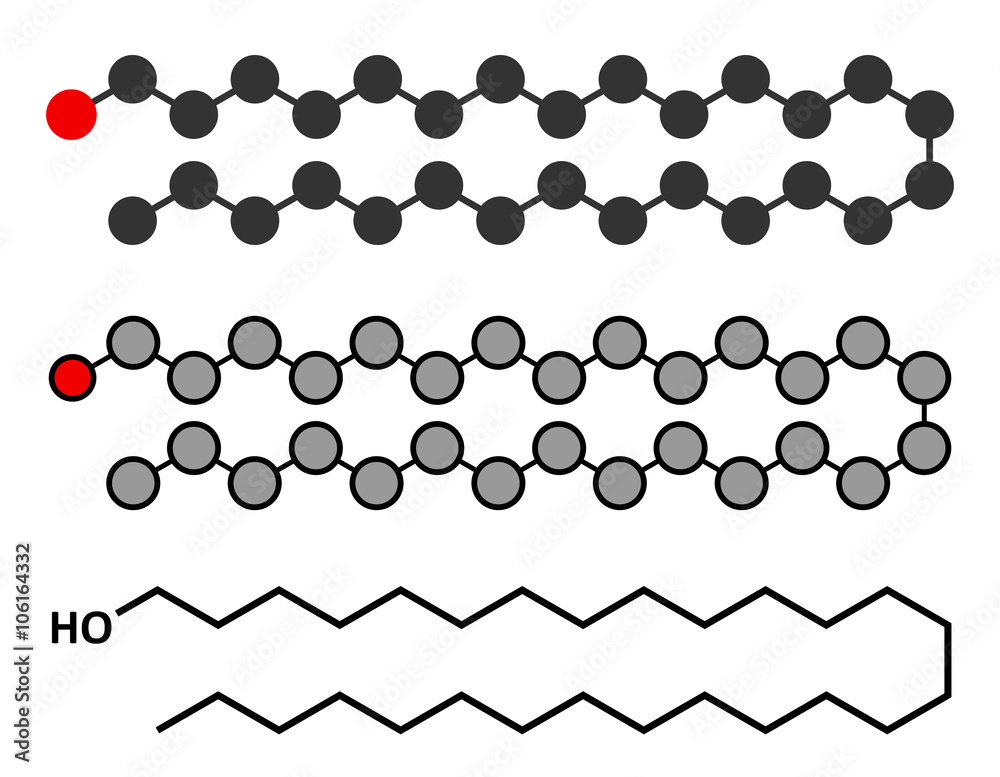
79
New cards
Proteins
enzyme, hormones, antibodies, structure, transport
* shape determines the function
* shape determines the function
80
New cards
Primary structure (protein)
Linked amino acids
81
New cards
peptide bond
bond between Amino acids and protein
82
New cards
secondary structure (Protein)
hydrogen bonding
* helix (coil)
* B-sheet (silk)
* helix (coil)
* B-sheet (silk)
83
New cards
tertiary structure
fold upon self (other bonds)
* globula (enzymes)
* globula (enzymes)
84
New cards
Quartiary structure (protein)
2 or more polypides
* hemoglobin
* hemoglobin
85
New cards
Denaturation
destroy of 3D shape
86
New cards
how is Denaturation done?
1. by heat
1. by changing of PH
87
New cards
Janssens
spectade makers, 2 lenses together
88
New cards
Galileo
improved on 1st microscope
89
New cards
Robert Hooke
corks made of compartments (cellule) (cells)
90
New cards
Anton Van Leewenhock
FATHER OF MICROSCOPY
* made fine lenses 270xs
* viewed animalcules
* made fine lenses 270xs
* viewed animalcules
91
New cards
Robert Brown
Nucleus- for development
92
New cards
Schleidon
all plants have cells
93
New cards
Schwann
all animals have cells
94
New cards
Rudolph Virchow
All cells came from pre-existing cells
95
New cards
Cell theory
the cell is the smallest unit of life, and they come from pre-existing cells.
96
New cards
Animal Cell
does not have a cell wall
does not have chloroplast
\
does not have chloroplast
\
97
New cards
plant cell
does not have a centriole
98
New cards
flagella
tails of bacteria that control locomotion
99
New cards
Prokaryotic
no nucleus
100
New cards
Eukaryotic
has a nucleus