Basic Cardiology Concepts
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is CO?
Heart rate x SV
What controls heart rate?
Sympathetic nervous system (IDK RW CHECK)
What can cause a low heart rate?
Sick sinus syndrome
3rd degree AV block
Excessive vagal tone
What affects stroke volume?
Preload
Afterload
What is preload?
Stretching pressure on the myocardium during diastole
What determines preload?
Volume delivered to ventricle
What does dehydration do to the heart?
Decreased preload, decreased SV, increase in HR
What does too much preload do?
Congestion (edema)
What controls preload long term?
RAAS
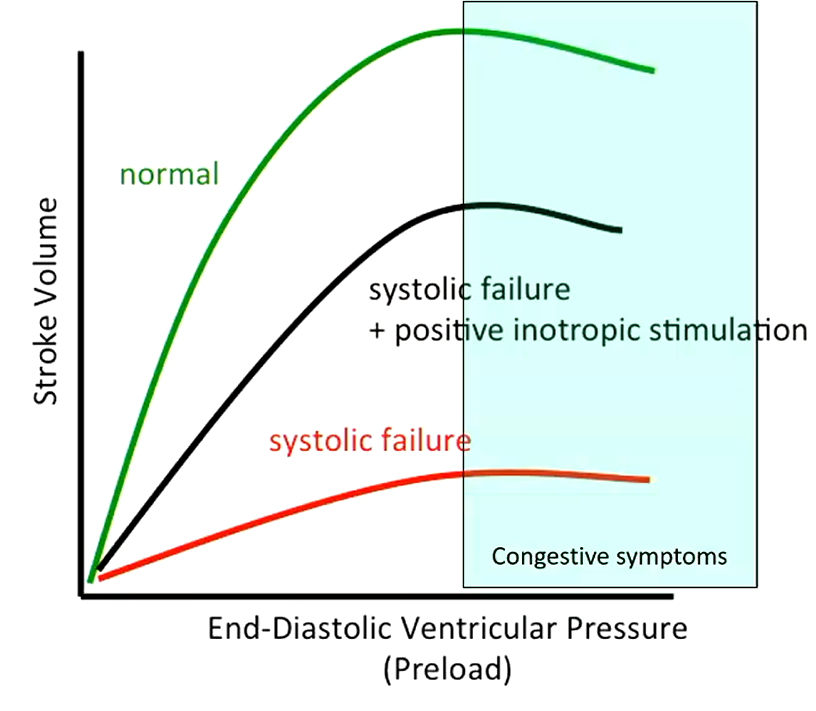
What does this tell you?
As pre-load increases, stroke volume will increase until it cannot anymore then congestion begins
How much of a diuretic do you want to give a patient with congestion?
Enough to eliminate congestion but not reduce pre-load
What is a side effect of too much diuretic?
Decreased pre-load leading to decreased CO and hypoxic kidneys
What can you do to combat excess preload?
Diuretics (get rid of fluid)
Venodilators (increase amount of blood veins can hold)
What is afterload?
Forces opposing ventricular contraction during systole
Factors that affect wall stress
What effects afterload?
Arterial blood pressure
Wall thickness (thinner the wall, the more wall stress)
Counter-productive consequences of RAAS/SNS
Secondary to other disease
What do you do if afterload is too high?
Arterial dilators (reduce BP)
Negative chronotropes like a beta blocker (improve relaxation time and helps the heart accommodate high afterload easier)
How do you calculate afterload (T)?
Systemic BP * radius of ventricle / 2 * wall thickness
What happens if we fail to compensate and get poor CO?
Anorexia, lethargy, weakness, syncope (more common if sudden decompensation)
How can you differentiate poor CO vs dehydration?
A dehydrated dog will eat
What stimulates the RAAS system?
Low Na, Cl
Arterial underfilling
SNS activation
Mechanoreceptors
What does the RAAS system do?
Vasoconstriction, increased Na resorption, aldosterone release, renal water retention, release of AVP, increase thirst
What can long term aldosterone cause?
Myocardial fibrosis and remodeling
If we have a dehydrated patient, but they are eating what does that tell you about CO?
It is good
Why is long term activation of RAAS bad?
It increases pre-load and afterload (pressure and volume overload)
What mechanoreceptors in the SNS sense underfilling?
Left ventricle
Carotid sinus
Aortic arch
Renal afferent arteriole
What does activation of the SNS do?
Increased contractility form B1
Tachycardia from B1 and B2
Arterial vasoconstriction from alpha 1s
What C/S can clue you into heart failure?
Coughing dog WITH tachycardia
Why does the atria love to dilate?
That is the only way they can compensate because they cannot contract
T/F atrial dilation lets you differentiate between pressure and volume overload?
False
What are the ways the ventricle can change?
Concentric or eccentric hypertrophy
What causes concentric hypertrophy?
Pressure overload
Increased systolic wall stress
Valvular stenosis, arterial hypertesion
What causes eccentric hypertrophy?
Volume overload
Increased diastolic wall stress
Mitral regurgitation, dilated cardiomyopathy, patent ductus venosus
What does left heart disease cause?
Pulmonary edema
What does right heart disease cause?
Ascites
What is unique about cats?
They can have left sided heart disease and pleural effusion and pulmonary edema
T/F blood flows from high to low pressure areas?
True
What is the most reliable way to measure systolic BP?
Mitral regurgitation jet
What is the best way to measure pulmonary artery pressure?
Tricuspid regurg jet
What is normal blood velecity?
5 m/s
How do you determine blood pressure from velocity?
Measure first from mitral regurg jet then do P=4V²
How can you determine if a patient has heart disease?
Asymptomatic with murmur or arrhythmia, breed prevalence, coughing, respiratory rate and or effort, syncope, weakness and or exercise intolerance, abdominal distension
If a little dog is coughing and is fat, do you think heart disease?
No, probably respiratory disease
What is syncope?
Fainting or passing out
Why is there inspiratory dyspnea with heart diseaes?
Lungs will be heavy and wet and struggle to expand
What does expiratory dyspnea indicate?
Probably respiratory disease (asthma in cats)
What does ascites indicate?
Disease on the right side of the heart of pericardium
What does cyanosis tell you?
Uncommon, but suggests a serious problem with oxygen exchange or delivery
Probably severe pulmonary edema if this is present
What is required for syanosis?
5g/dL of hemoglobin must be deoxygenated (very hard)
Why cant extremely anemic patients be cyanotic?
They do not have enough hemoglobin to become cyanotic
T/F you should always feel the femoral pulse when you auscultate the heart?
True
What do weak pulses tell you?
Poor CO
What does femoral pulse quality tell you?
Difference between systolic and diastolic pressures
What will aortic regurgitation tell feel like?
Diastolic runoff will cause a “water hammer” pulse
Where does a normal jugular pulse extend?
1/3 up the neck
What do right heart disease do to the jugular?
Jugular distension or big pulses
What does really loud crackles without overt dyspnea imply?
Primary airway disease like chronic bronchitis
What should you look for?
BCS, respiratory effort, abdominal distension, mm color and CRT, pulse quality and synchrony, presence of jugular pulses, listen to lungs and heart
What valves can you hear on the left side?
Mitral, aortic, and pulmonic
Where do you listen to the mitral valve?
Apex of the heart on the left side under the ribs
Where do you listen to the aortic and pulmonary valve?
Base of the heart above the ribs on the left side
Where do you listen to the tricuspid valve?
On the right sight at the costocartilage junction
How do you listen to the PDA?
Cranial and dorsal to the apex of the heart
Where do you listen to cats?
Left and right parasternal
What is the S1 sound?
The lub where mitral and tricuspid valve closes
Systole
Where is the S1 sound heard best?
Apex of the heart
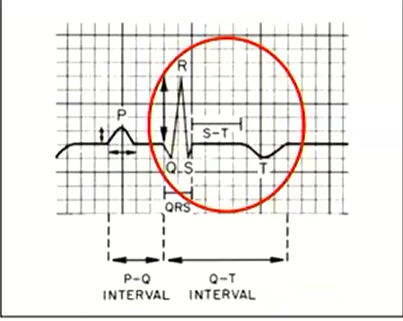
What is heart here?
S1 sound
What is the S2 sound?
The dub from closure of aortic and pulmonic valves
Diastole
Where do you hear the S2 sound?
Apex of heart
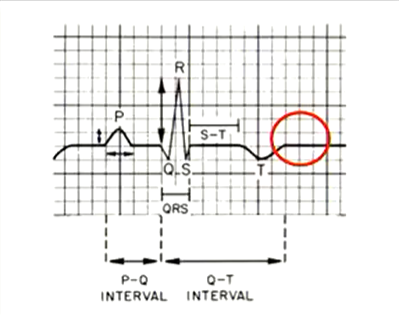
What is happening here?
S2
What does a split S2 of lub-BDUB mean?
Pathology
What is S3?
Lub DubUhW or ventricular gallop
What can cause an S3?
Severe mitral insufficiency
DCM
PDA
HCM
Systolic anterior motion of mitral valve with obstructive HCM
What is S4?
BuhLub Dub
Atrial gallop
What can cause an S4?
HCM
Concentric hypertrophy form systemic hypertension
DCM
What is it called when is speeds up and slows down with breathing?
Regularly irregular sinus arrythmia
What can cause chaotic rhythm?
Pulse deficits
Ventricular and supraventricular premature beats
A-fib