Antibody detection and ID
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Discovered antibodies against RBCs(nonABO) are usually
Unexpected (immune alloantibodies)
Expected antibodies are those against
ABO antigens
AHG is also known as
Coombs test
Screen cells and panel cells come from
Group O donors
Screen cells are either
2 or 3 cell panels
Ideally you want as many
Homozygous cells as possible
Panel cells contain
8-20 cells with known RBC phenotypes
Momozygous expression of antigens on screening cells is desirable because
Some antibodies show dosage
Common antibodies that show dosage
Rh (not D), Kidd, Duffy, MNSs, and Lutheran
Proper detection and ID of RBC antibodies is important for
Appropriate blood products, HDN, and hemolytic anemias
Check cells are
O positive RBCs coated with anti-d
Purpose of check cells
Used to ensure AHG tests with negative results are not false negatives
If CC test is negative
Washing method was inadequate and protein is bound to the red cells causing neutralization, or reagent was left out
When AHG is negative
There should be free AHG in the test tube
When CC are added
The free AHG should agglutinate the sensitized RBCs
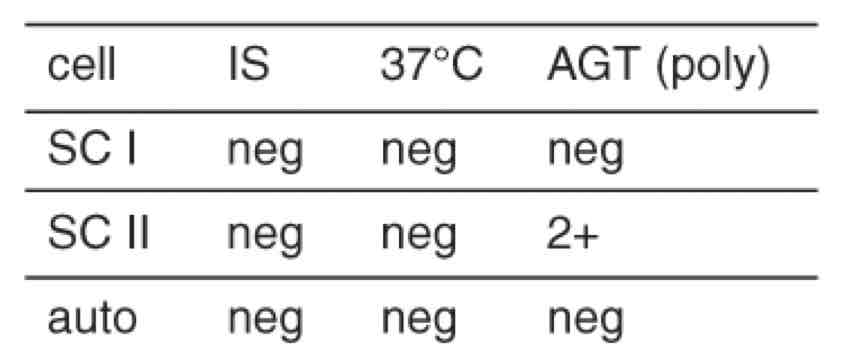
possible interpretations
Single alloantibody, two alloantibodies w ags on cell 2 only, probable IgGalloantibody
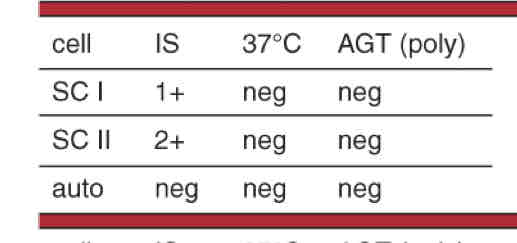
Possible interpretations
Single or multiple antibodies probably IgM
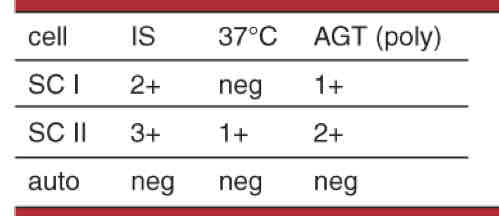
Possible interpretations
Multiple alloantibodies warm and cold, potent cold antibody binding complement at AHG
Cold or IgM insignificant antibodies
I, Lewis, M, N, P1, Lu a, K
Significant antibodies that react at or past 37
Rh, K, S,s, K, Kell, Duffy, Kidd, Lu b, Xg a
Auto control involves
Testing patient serum against pt cells
Positive auto control means
Positive DAT and free antibody in pt serum
Positive auto control does not
Rule out alloantibody possibility
Positive auto control is associated with
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, drug induced hemolytic anemia, HTR, or benign conditions
Follow up positive auto control with
DAT and elution
NEAT
No enhancement added test
PEG
Ur elves water molecules away and help ag/ab to get closer to bind
Zeta potential
Reduction of the electrical charged around the cells to allow the antibody to bind
Panel cells
Cells that have more antigen phenotypes than screen cells that allow the identification of antibody
Negative auto control means
Alloantibody
Sufficient evidence to prove suspected antibody
Testing pt serum w 3 antigen positive and 3 antigen negative
Patient should be negative for
The antigen for the antibody being tested for
Antigen typing on a patient can’t happen if
They have been transfused w/in 3 months
IgG DAT positive cells can cause
False positive reactions
How are IgG DAT positive cells treated
Glycine EDTA to strip antibody then perform DAT and antibody type (not with Kell)
When a patient has a significant antibody you must
Antigen type donor units for the antigen (not for IgM)
Cross match w antigen negative units must be
Carried through AHG even if the antibody is cold