Soaps - saponification
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
sources of fats and oils (lipids)
typically found from animals or plants
Animal fats= solid at room temp: saturated fats (all carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds)
plant oil: liquid at room temp = unsaturated fats (contain one or more double or triple C-C bond.
fats and oils
contain large non-polar (have no overall dipole in the molecule) molecules (triglycerides)
fats and oils are distinguished through their physical state at room temp.
being non-polar they are unable to form bonds with water - non-soluble
tryglycerides
synthesised by a condensation reaction between a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids
fatty acid
carboxylic acids with chain lengths of eight or more carbon atoms
have a carboxyl functional group attached to the hydrocarbon tail
glycerol
a small molecule with 3 hydroxyl functional groups
condensation reaction to form triglycerides;
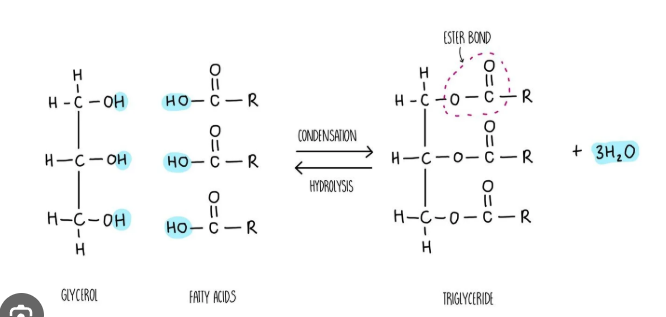
saponification
to form a soap the ester links in the triglyceride must be broken in a hydrolysis reaction (using a strong base such as NaOH)
by product is gycerol
all soaps are made up of a:
long hydrocarbon chain
carboxylate ion (COO-)attached to the hydrocarbon tail, is polar
a metal ion normally Na+ or K+
limitation of soaps
soap with form
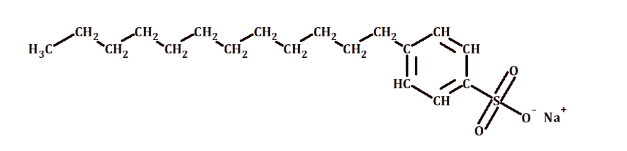
detergents
contain a hydrocarbon chain sourced from petroleum products, do not form insoluble salts with calcium or magnesium ions
anionic detergent
a type of detergent where the hydrophilic (water-attracting) part of the molecule carries a negative charge
cleaning action of soaps
non-polar tail dissolves into grease through dispersion forces, which are stronger than the dispersion forces in grease
ion-dipole and H-bonds are formed from the carboxylate group on the soap and water
interactions are stronger than the H-bonds in water therefore dissolving into water
through agitation grease and oil molecules are able to be removed in the form of micelles
how does soap work in water

how does soap clean oil off of a surface

structure of a detergent
why does soap not work in hard water?

what is hard water
water with a relatively high concentration of cations (Mg and Ca
why are soaps basic?
soaps are salts of long chain fatty acids formed from a strong base and a weak acid, therefore they are basic.