Science_T3_2022
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
a solution is
a mixture where a solute is solute is dissolves in a solvent
2
New cards
a solute is, a solvent is :
solute = substance being dissolves
solvent = liquid that does the dissolving
solvent = liquid that does the dissolving
3
New cards
a diluted solution is
a solution with very few solute particles, can dissolve a lot more solute
4
New cards
a concentrated solution is
a solution with lots of solute particles, can dissolve a little more solute
5
New cards
a saturated solution is
a solution with the maximum amount of solute, can't dissolve any more
6
New cards
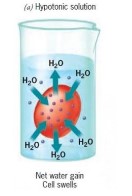
a hypotonic solution is ...
there is a higher concentration of water outside the cell vs in it, so the cell intakes water and swells
7
New cards
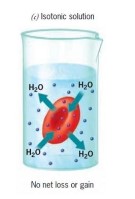
an isotonic solution is...
there is an equal concentration of water both in and out of the cell. the cell doesn't change.
8
New cards
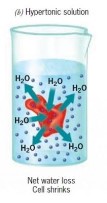
a hypertonic solution is...
there is a high concentration of water in the cell, but a low concentration of water outside the cell. the cell's water is sucked out of it by the outside, it shrinks.
9
New cards
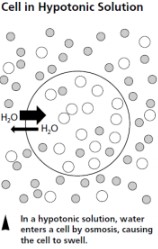
water entering a cell is called
osmosis. photo is an example of a hypotonic solution.
10
New cards
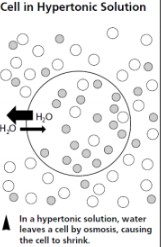
water leaving a cell is called
osmosis. photo is an example of a hypertonic solution
11
New cards
diffusion is
the movement of solute particles (nutrients or waste) moving down its concentration gradient
12
New cards
what is a concentration gradient
the difference in concentration inside and outside of a cell
13
New cards
diffusion works better in which type of organisms:
unicellular organisms
14
New cards
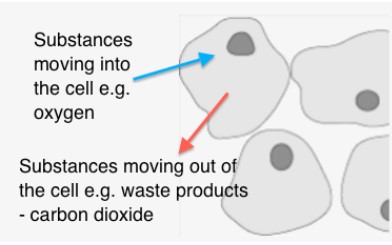
how does diffusion work in multicellular organisms?
it uses organ systems to move nutrients around the body.
15
New cards
why is diffusion inadequate for multicellular organims?
the low surface area to volume ratio. the surface area is where the particles diffuse, so the larger it is, the more particles can be exchanged.
humans are so big, and we have like zero surface area.
humans are so big, and we have like zero surface area.
16
New cards
define homeostasis
the process of maintaining a stable internal environment via constant adjustments
17
New cards
name some examples of homeostasis in humans
production of insulin after eating certain foods, sweating to regulate heat
18
New cards
how does homeostasis work in humans?
all of the cells, tissues, organs and systems working together. they communicate via the nervous and endocrine systems, which monitor functioning.
19
New cards
flowering plants rely on what kind of response for homeostasis
a coordinated response, involving everything working together
20
New cards
humans rely on what kind of response for homeostasis
an automatic response
21
New cards
why is the endocrine system important for homeostasis?
it secretes HORMONES that regular bodily activities
22
New cards
the respiratory system maintains homeostasis by
a high concentration of carbon dioxide (rather than oxygen) in the blood triggers faster breathing -> lungs exhale frequently -> removes CO2.
23
New cards
the excretory system maintains homeostasis by
low water level in blood -> kidneys retain more water -> they produce more concentrated urine -> less water is lost
24
New cards
the endocrine system maintains homeostasis by
high concentration of sugar in blood -> pancreas (endocrine organ) produces the hormone insulin -> helps cells absorb sugar out of blood
25
New cards
the regulation is done by WHAT KIND of loop?
a negative feedback loop
26
New cards
what is in a negative feedback loop?
stimulus ->
receptor (sense change) ->
signal (command from brain) ->
response (ie skin makes sweat) ->
does the response work? if not, negative feedback again back to receptor etc etc.
receptor (sense change) ->
signal (command from brain) ->
response (ie skin makes sweat) ->
does the response work? if not, negative feedback again back to receptor etc etc.
27
New cards
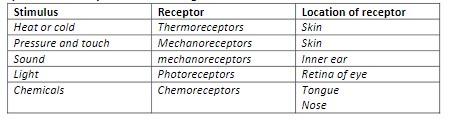
how many kinds of receptors are there?
four. thermo (heat - on skin), mechano (pressure/touch/sound - skin and inner ear), photo (light - retina of eye), and chemo (chemicals - tongue/nose).
28
New cards
what does our internal environment consist of?
body temperature, ion concentrations, water content, blood glucose levels
29
New cards
why is it so important for us to maintain homeostasis?
humans are delicate. we need to be in a narrow range of, say, temps to survive.
30
New cards
in the stimulus response model, what is the control center?
stimulus->receptor->control center->effector-> response
the control center is usually the BRAIN
the control center is usually the BRAIN
31
New cards
an example of an effector?
stimulus->receptor->control center->effector-> response
a classic one is MUSCLES. they move to a safer place, control blood pressure, or shiver to warm you up.
a classic one is MUSCLES. they move to a safer place, control blood pressure, or shiver to warm you up.
32
New cards
in a negative feedback loop, ie homeostasis, the body's response acts (AGAINST/FOR) the stimulus
AGAINST
33
New cards
in a positive feedback loop, ie childbirth, the body's response acts (AGAINST/FOR) the stimulus
FOR
the response AMPLIFIES the stimulus, ie childbirth or blood clotting.
the response AMPLIFIES the stimulus, ie childbirth or blood clotting.
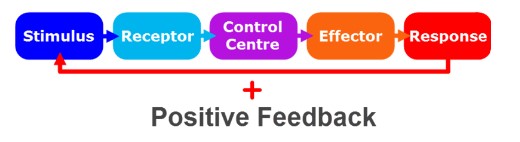
34
New cards
positive feedback loop example; childbirth
brain releases oxytocin->
uterus contracts->
baby moves through birth canal->
stretch receptors activate ->
et cetera.
uterus contracts->
baby moves through birth canal->
stretch receptors activate ->
et cetera.
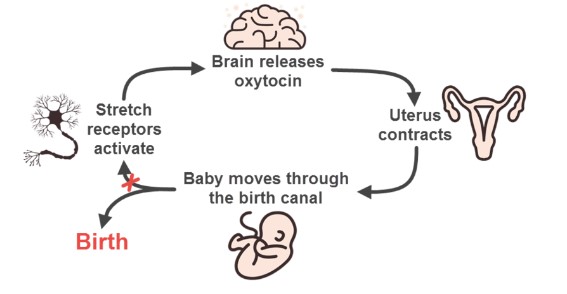
35
New cards
what are the parts of the nervous system
central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and neurons
36
New cards
the central nervous system is made up of
the brain and the spinal cord
37
New cards
what the the three sections of the brain
the cerebellum (balance and movement), the MEDULLA OBLONGATA (heartbeat, body temp, breathing rate), and cereBRUM (thinking, intelligence, memory, etc.)
38
New cards
what is the peripheral nervous system made up of
the sensory and motor neurons that connect to the central nervous system--including all the nerves and neurons that AREN'T part of the brain or spinal cord.
39
New cards
what are the three main types of neurons (nerve cells)?
sensory neurons, motor neurons, and relay neurons
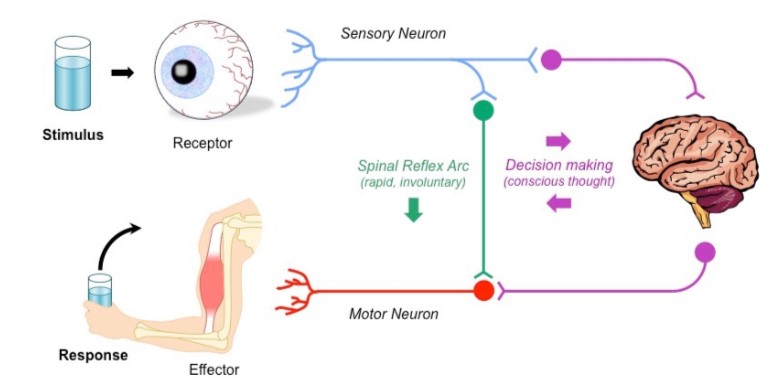
40
New cards
what do sensory neurons do?
carry information FROM the receptor to the CNS (central nervous system)
41
New cards
what do motor neurons do?
carry information FROM the CNS to the EFFECTOR
42
New cards
what do relay/connector neurons do?
COORDINATE the response within the CNS
43
New cards
what does a neuron do?
carry information from the nervous system as ELECTROCHEMICAL IMPULSES.
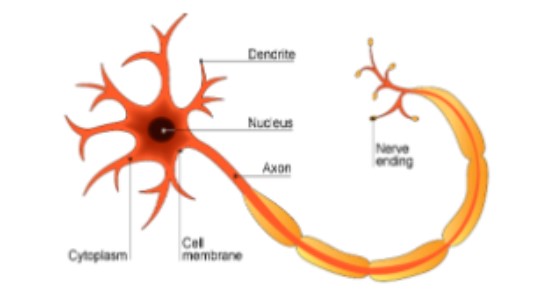
44
New cards
what are the six parts of the brain?
thalamus, brain stem, cerebellum, medulla, hypothalamus, cerebrum
45
New cards
what does the cerebrum do?
it controls all our conscious activities. it's the largest part of the brain.
46
New cards
what does the hypothalamus do?
it maintains a constant heart rate, body temperature, and sleep pattern. it also helps the pituitary gland.
47
New cards
what does the medulla do?
it controls automatic functions, i.e. respiration, digestive systems, sleep, and arousal, and it also processes sensory information, i.e. movement and vision. it's located at the bottom of the brain stem.
48
New cards
what does the cerebellum do?
maintains movement, balance, and coordination
49
New cards
what is the brain stem made up of?
it's made up of three parts--the MEDULLA, PONS, AND MIDBRAIN. it's the lower part of the brain.
50
New cards
what does the thalamus do?
process and carry sensory information, i.e. ears, nose, eyes, skin, and it sends these messages to the cortex
51
New cards
what is a stroke?
damage to the brain from interruption of its blood supply
52
New cards
what is a brain tumour?
a cancerous (or non-cancerous) mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain.
53
New cards
the endocrine system uses hormones to...
regulate growth and regular functioning, and maintain a stable internal environment
54
New cards
the endocrine system is made up of different WHATs that secrete hormones
glands
55
New cards
what are the 9 glands of the endocrine system?
the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, thymus, and the ovary/testis (depending on gender)
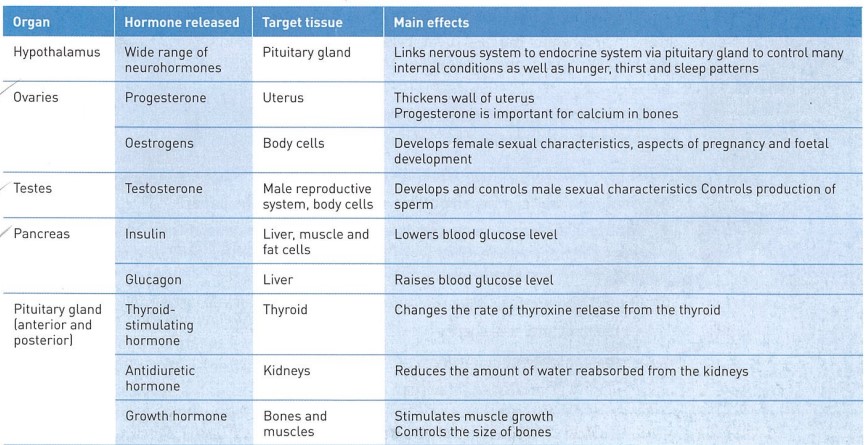
56
New cards
how to hormones know where to go to get to their target organ?
they have different three dimensional shapes, which bind to a target organ like a LOCK AND KEY. only the hormone whose EXACT shape matches the receptor can bind to it.
57
New cards
what does the pineal gland do?
it releases the hormone MELATONIN, which controls sleep patterns
58
New cards
what does the pituitary gland do?
it releases hormones to:
1. stimulate OTHER glands to release hormones i.e. thyroid, ovaries, testes.
2. control growth and development
3. regulate balance in childbirth + breast milk
1. stimulate OTHER glands to release hormones i.e. thyroid, ovaries, testes.
2. control growth and development
3. regulate balance in childbirth + breast milk
59
New cards
what does the thymus gland do?
release THYMOSIN, which stimulates WHITE BLOOD CELL production to fight infection.
60
New cards
what does the pancreas do?
release INSULIN and GLUCAGON, which regulate blood glucose levels.
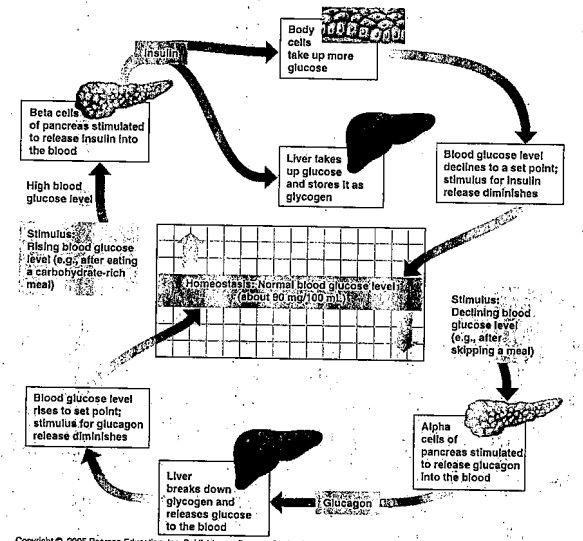
61
New cards
what do the ovaries do?
release oestrogen and progesterone. basically girl puberty.
62
New cards
what do the testes do?
release testosterone. basically boy puberty.
63
New cards
what do the adrenal glands do?
they release hormones i.e. ADRENALINE which increase heart rate and blood pressure. also increases amount of muscle energy.
64
New cards
what does the thyroid gland do?
release THYROXINE, which regulates CELL GROWTH and activity.
65
New cards
what do the parathyroid glands do?
release PARATHORMONE, which regulates blood calcium lvl -> BONE DEVELOPMENT
66
New cards
what does the hypothalamus do?
it links with the nervous system. controls REFLEX ACTIONS (breathing, heartbeat).
other hormones that control; body temp, hunger, thirst, sex drive, emotions.
CONTROLS THE PITUITARY GLAND.
other hormones that control; body temp, hunger, thirst, sex drive, emotions.
CONTROLS THE PITUITARY GLAND.
67
New cards
what does the uterus do
hold a fetus if a woman is pregnant
68
New cards
what do the ovaries do
produce the female's ova (eggs)
69
New cards
what does the vagina do
leads from the vaginal opening to the uterus
70
New cards
what do the fallopian tubes do
connect the ovaries to the uterus
71
New cards
what is the cervix
a ring of muscle at the opening of the uterus, after the vagina ends
72
New cards
what does the prostate gland do
secrete PROSTATE FLUIS which nourishes sperm and lubricates sperm ducts
73
New cards
what does the testes do
produce sperm
74
New cards
what does the scrotum do
regulate the temperature of sperm by holding it outside the body
75
New cards
what do the sperm ducts do
transport sperm to the urethra
76
New cards
what does the urethra do
carry either semen or urine out of the body
77
New cards
what does the penis do
deliver sperm into the vagina during sexual intercourse
78
New cards
what does IVF stand for
in-vitro fertilisation -- 'in glass' fertilisation
79
New cards
how does the egg stage of IVF go?
the woman has hormone injects to stimulate egg ripening in her ovaries. a hormone (LH) triggers ovulation, and the eggs are harvested with a needle.
80
New cards
how does the rest of IVF go?
the father produces a semen sample. it's then combined with the eggs, and monitored until an embryo develops, which will then be placed in the woman's uterus!
81
New cards
who was the first IVF/test tube baby?
Louise Brown, 1978.
82
New cards
what are some reasons a couple might not be able to have kids?
1. not enough sperm or ova
2. woman might have blockages in reproductive system
3. pregnancy cannot be maintained
2. woman might have blockages in reproductive system
3. pregnancy cannot be maintained
83
New cards
organisms that can't be seen with the naked eye are called
microbes
84
New cards
microbes live;
everywhere. on you. on your mum.
85
New cards
are all microbes harmful?
no.
86
New cards
how many kg of your bodyweight do microbes make up?
2kg
87
New cards
what causes infectious disease?
pathogens
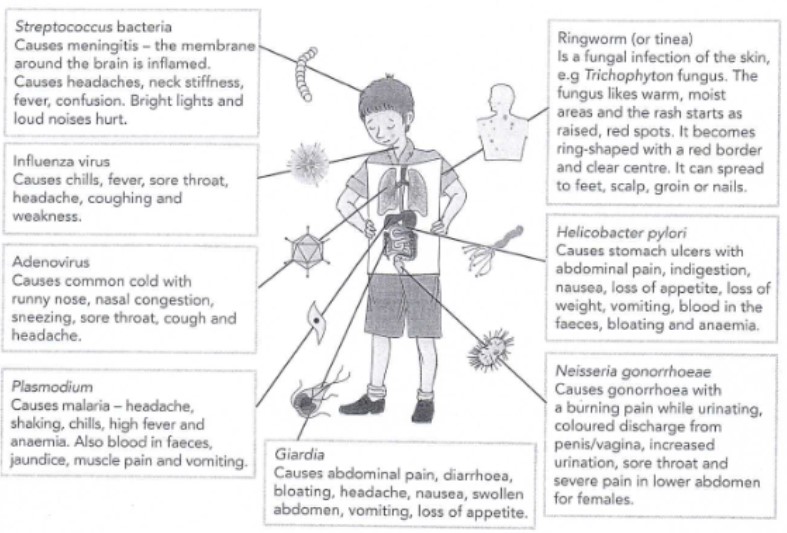
88
New cards
is bacteria unicellular or multicellular?
unicellular - but they don't have a nucleus!
89
New cards
are viruses living or non-living?
non-living - though this is controversial. it's made up of genetic material covered with a layer of protein/fact.
90
New cards
what are some examples of non-infectious diseases?
genetic disease, i.e. haemophilia (blood not clotting), nutritional i.e. anorexia, physiological malfunction i.e. diabetes, or environmental, i.e. skin cancer
91
New cards
what is the first line of defense made up of?
barriers to prevent infection - i.e. skin, tears/saliva/mucus, stomach acid, urine, and the cilia (hairs that line airways/nose hair ig)
92
New cards
what can barriers be classified as? hint: 2 categories
physical barriers and chemical barriers
93
New cards
mucus can be found in
the nose, lungs, and intestines
94
New cards
what are some physical barriers in the first line of defense?
skin, cilia, and urine flow
95
New cards
what are some chemical barriers in the first line of defense?
stomach acid, tears, saliva, and mucus
96
New cards
what is the only specific line of defense?
the third line of defense! the first and second are both non-specific.
97
New cards
what are some common parts of the second line of defense?
a fever, inflammation, or phagocytes/pus
98
New cards
a type of white blood cell that destroys pathogens?
phagocyte (dead phagocytes = pus)

99
New cards
increased core temperature that slows or kills pathogens
fever
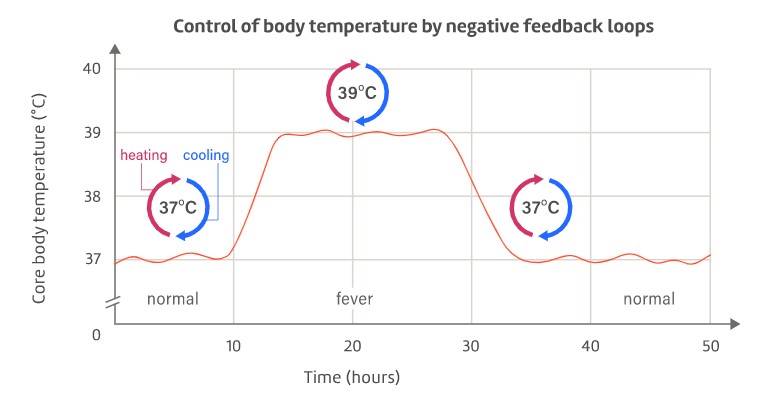
100
New cards
the second line of defense is only necessary when;
the pathogen has ALREADY entered the body