CPIM Module 1.1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
supply chain
the network of suppliers that deliver products from raw materials to end customers through either an engineered or transactional flow of information, goods, and money.
service industry
narrow definition: an organization that provides intangible goods
broad definition: all organizations except farming, mining and manufacturing
supply chain management
the design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging world-wide logistics, synchronizing supply with demand, and measuring performance globally.
upstream supply chain
moving to the direction of supplier of raw materials
downstream supply chain
moving to the direction of end customer
external influences on supply chains:
customer expectations
government regulations and/or sanctions
economic conditions
political and social environment
global and domestic competitors
MPC - manufacturing planning and control system
a closed-loop information system that includes the planning functions of production planning (S&OP), master production scheduling, material requirement planning (MRP), and capacity requirement planning - once the plan has been accepted as realistic, execution begins. The execution functions include input-output control, detailed scheduling, dispatching, anticipated delay report (department and supplier), and supplier scheduling
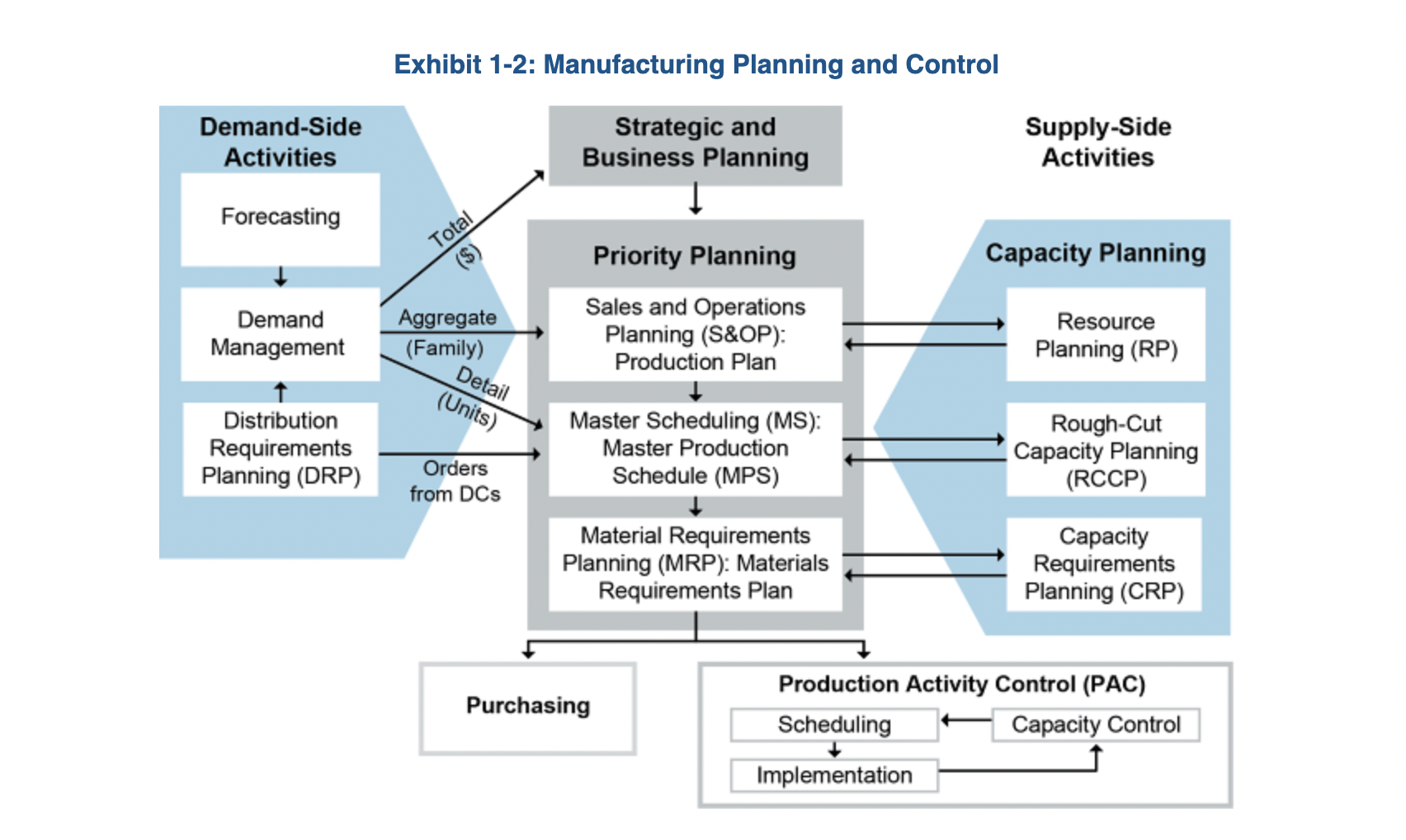
Key points about planning system:
top-down approach - every planning proces refers back to the business plan (see figure above)
closed-loop system - continuous improvements made based on the capacity contraints, feedback, unexpected events
supply side priorities: feasibility and availability; demand side priorities: timing and order of work
Time horizon planning of:
Strategic and Business Planning
S&OP
Master Scheduling
Material Requirement Planning
Strategic and Business Planning - STRATEGIC
S&OP - TACTICAL - medium range
Master Scheduling - TACTICAL - medium to short range
Material Requirement Planning - OPERATIONAL - short range
Sales&Operations Planning (S&OP)
key output: a consensus set of numbers that the supply side of the organization commits to produce and that the demand side (marketing and sales) agrees to set as their goals
input on the aggregate family level
master scheduling
information on detail level for individual units (MTO - raw materials, ATO - components, MTS - finished goods)
input: S&OP
output: MPS - master production schedule (which units in which period)
MRP - Master Requirement Planning
involves calculating the dependent demand:
input: MPS + BOMs
output: calculations on when and how much of raw materials/components to order
Demand Side Activities:
quantities come from:
forecasts
demand management
distribution requirement planning (DRP)
Supply Side Activities
image
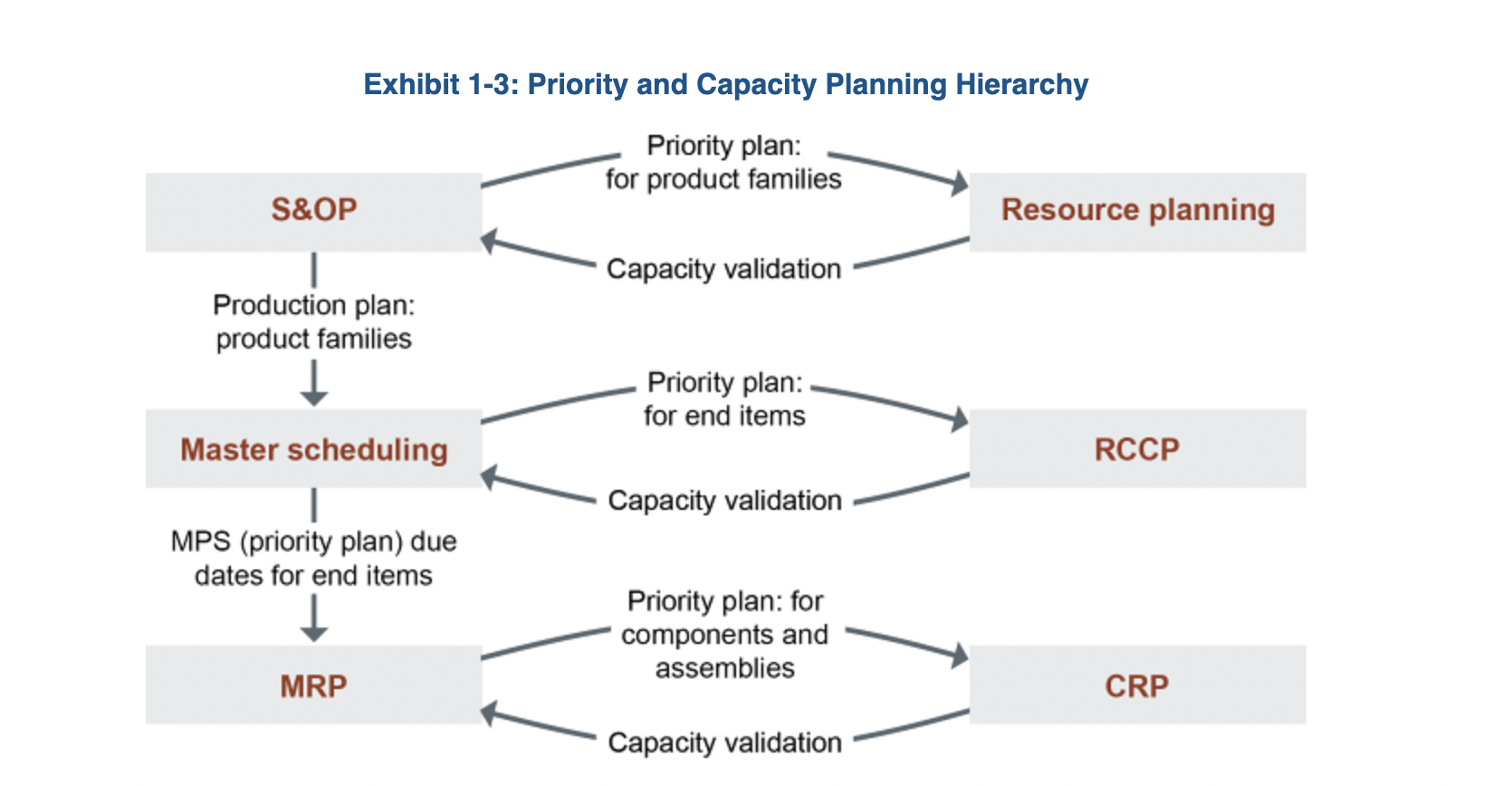
RCCP - Rough-Cut Capacity Planning
comparing required capacity from the MPS (master scheduling level) in key resources (checking on bottleneck work centers, labor, machines…)
CRP - Capacity Requirement Planning
detailed check of capacity based on the MRP - breaks down planned and released orders from MRP into specific workcenters and time-periods: calculates exact workload vs availability capacity
PAC - Purchasing and Production Activity Control
result of MRP; planning —> execution
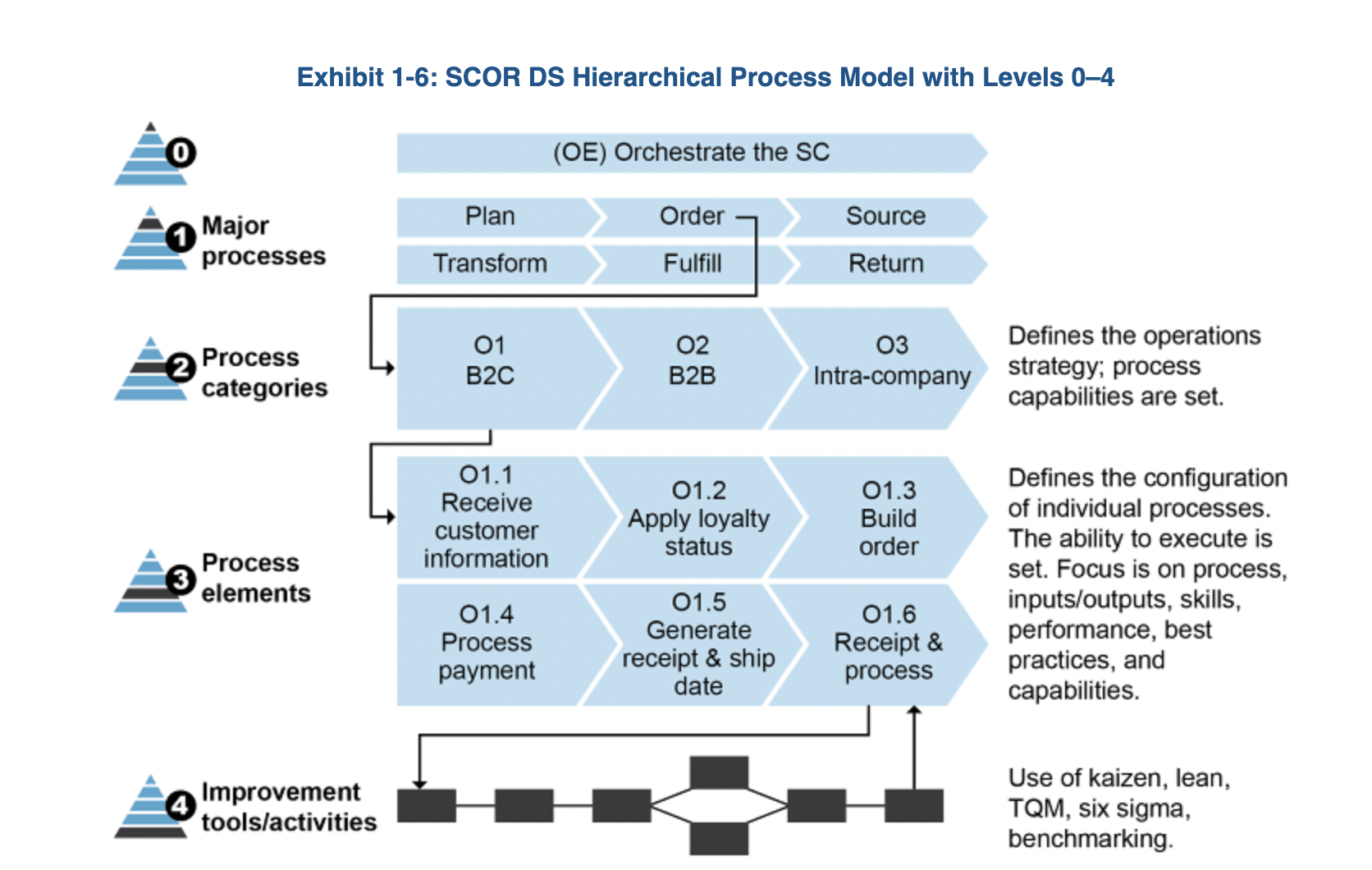
SCOR DS Processes
Orchestrate:
Demand vs Supply
Synchronise vs Regenerate
SCOR DS Model - Demand
Order: managing customer purchase attributes including location, payment methods, fulfilment status, or visibility.
Fulfil: fulfilling customer orders by scheduling order delivery, picking, packing, shipping, installing, commissioning, and invoicing processes
SCOR DS Model - Supply
Source: procuring, ordering, and scheduling the ordering, delivery, receipt, and transfer of products/services in a way that meets market demand and quality expectations.
Transform: creating products (including production, assembly or disassembly, or MRO - Maintenance, Repair, Operations) and services to meet customer demand.
SCOR DS Model - Synchronize
Plan: creating plans for order, source, transform, fulfil, and return to operate the supply chain; balancing requirements and resources; determining capability gaps; and identifying actions to correct gaps
SCOR DS Model - Regenerate
Return: diagnosing, evaluating entitlement of, and determining disposition of approved returned goods from suppliers, distributors or consumers.
SCOR DS - Hierarchical Model
mission
the overall goals set within the parameters of the business scope
mission statement
statement of purpose - why the company exists
vision
the shared perception on the company future - what the organization will achieve and a supporting philosophy
“where are we going?”
corporate culture
set of important assumptions that members of the company shares
STEEPLE analysis
tool to scan organisational external environment on 7 layers:
Sociocultural
Technological
Economic
Environmental
Political
Legal/Regulatory
Ethical
environmental scanning
process used to expose the organization’s potential SWOT. OT primarily external
competitive analysis
analysing the competitor on its strategies, capabilites, prices, and costs
macro environment
the environment external to a business including, technological, economic, natural, and regulatory forces that marketing efforts cannot control. Analyzed through STEEPLE
S - Sociocultural Factors
Demographics, Values and Preferences
T - Technological Factors
Identifying emerging and speculative technology
E - Economical Factors
economic conditions such as gross domestic product, employment level, family or disposable income, interest or currency exchange rates
E - Environmental Factors
natural events, trends, also includes reactions to those trends namely: changes in insurance rates, agricultural practices…
P - Political Factors
political, institutional, governmental practices
L - Legal and regulatory Factors
laws and regulations that are enacted as a result of political attitude.
E - Ethical Factors
business ethics, good governance, ethical sourcing, social responsibility, moral standards, accountability, and sustainability
5 Forces Framework
Competitive Rivalry
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Risk of Substitutes
Possibility of New Entrants
Internal Capabilities
resource
anything that adds value to a good or service in its creation, production or delivery.
tangible resources
physical
financial
technological
organizational
intangible resources
human assets and intellectual capital
brands and reputation
relationships
culture and the compensation system
VRIN
valuable resource or capability is directly related
VRIN stands for Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, Nonsubstitutable
VRIN - Valuable
directly related to the strategy being considered - relevant, will help to create a competitive advantage over competitors
VRIN - Rare
something that the competitors lack
VRIN - Inimitable
Something that is hard to copy for the competitors
VRIN - Nonsubstitable
an asset/resource that cannot be easily altered by the competitor
Value Chain
the functions within a company that add value to the goods or services that the organization sells to consumers and for which it receives payments
It is divided between primary and support activities.
Primary activities are those that create value, while support activities make the primary activities possible.
trading partner
any organization external to the company that play an integral role within the supply chain community and whose business fortune depends on the supply chain community
Value Chain Analysis
an examination of all links a company uses to produce and deliver its products and services, starting from the origination point and continuing through the delivery to the final consumer.
Product Life Cycle
1) The stages a new product goes through from beginning to end 2) the time from initial R&D to the time at which sales and support of the product to the customers are withdrawn 3) the period of time during which a product can be produced and marketed profitably.
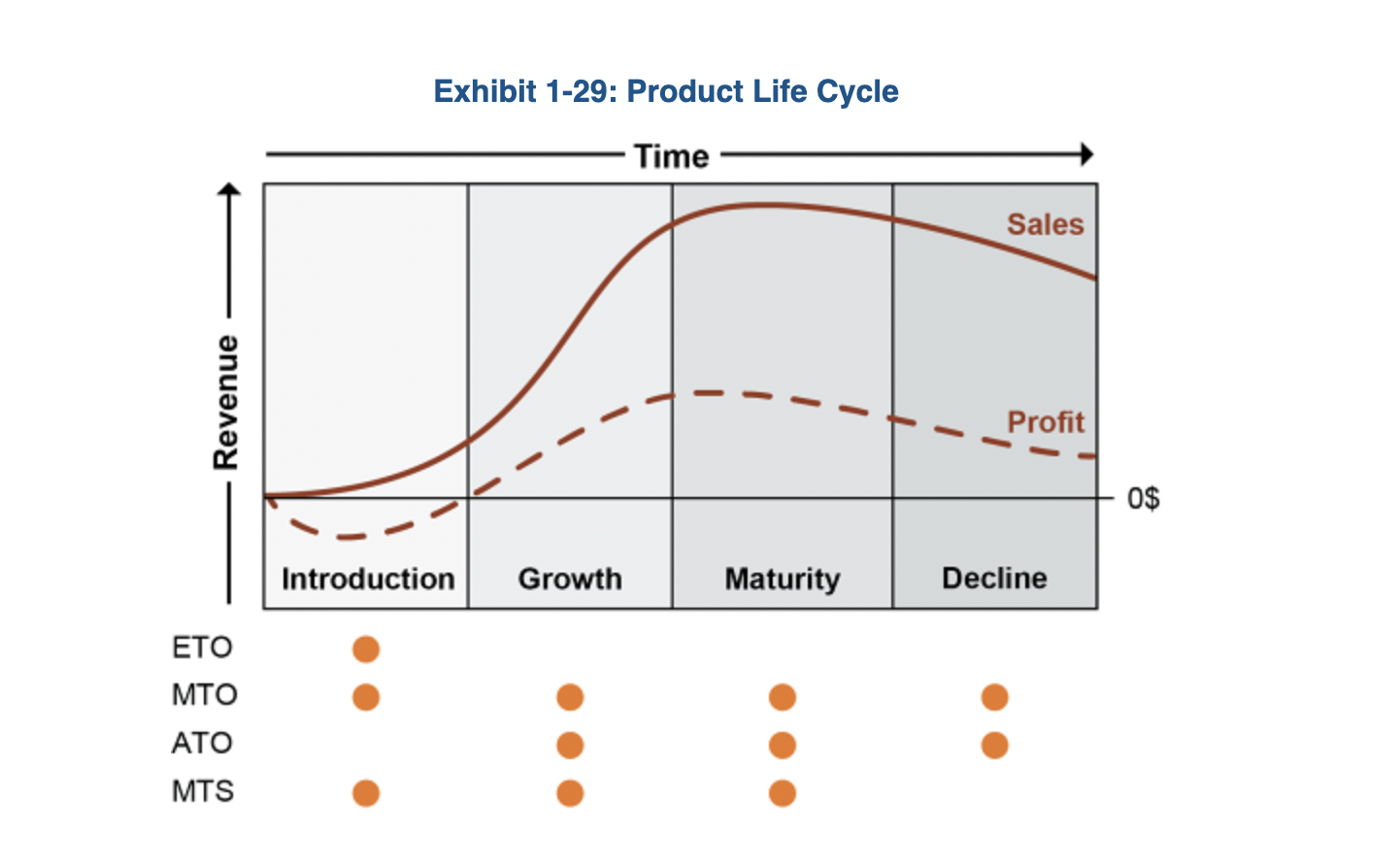
Phases of Product Life Cycle (PLC)
Introduction
Growth
Maturity
Decline
functional product
mature products that tend to have a low profit margin and a predictable demand