4: Solid-supported synthesis of peptides
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is solid support peptide synthesis (SPPS)
the construction of peptides on insoluble functionalised polymer beads or ‘resin’
which side of the amino acid is attached to the resin
C-terminus, the polypeptide chain is built from the N-terminus
how does SPPS work
peptide is immobilised on resin
reagents are in solution
the tap is closed, the reaction happens, the tap is open and the reagents can be washed away after the reaction
product cleaved off after synthesis is complete
resin commonly consists of:
crosslinked polystyrene, an insoluble polymer
how is the first amino acid attached to the resin?
need a functionalised resin that can be covalently linked to carboxylate of amino acid
merrifield resin (chloromethyl polystyrene) is uses, and the amino acid is linked by substitution of the chloride leaving group
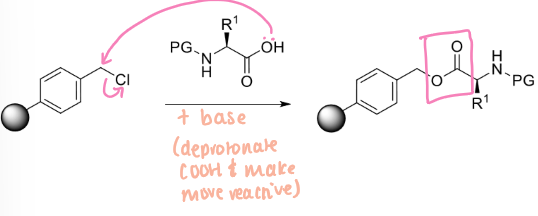
conditions for linking amino acid to merrifield resin
amino acid with PG on N-terminus and merrifield resin
base to deprotonate COOH
what is wang resin
resin-CH2-OH
wang resin coupling conditions and product
DIC as coupling reagent
makes ester bond

what is rink amide resin
resin-CH2-NH2
rink amide resin coupling conditions and product
DIC as coupling reagent
makes amide bond

how peptide synthesis on solid support works
deprotection, Fmoc or Boc removal
coupling, Y-Xaa-OH, coupling agent, base
peptide assembly (repeating 1 and 2)
cleavage from resin and side chain deprotection
purification
additional considerations for SPPS
protecting group for N-terminus cannot be boc to avoid releasing peptide during deprotection, so Fmoc
coupling reagent must be DIC m(HATU, PyBOP), not DCC for solid phase to avoid an insoluble urea byproduct and precipitates out of solution
side chain protecting groups, generally chosen so deprotection occurs with the release of the peptide, so side chain PGs are often not stable to acidic conditions (boc, tBu)
how are peptides released from resin
acidic conditions
cleavage from merrifield resin requires HF (corrosive and toxic acid)
what can be done to avoid using HF for releasing peptides
use other types of resin that contains linkers to allow cleavage under different conditions (usually solution of TFA in an organic solvent)
how is wang resin cleaved
TFA
has +M effect of O
how is sasrin resin cleaved (more acid labile)
dilute TFA = 1%
advantages of SPPS
no work-up or purification of intermediates
can be automated
limitations of SPPS
accumulation of impurities and by-products as no intermediate purification is possible while peptide is bound
purification of final product can be challenging, usually leads to mixtures of products
limited amount of peptide produced