Mouth & Throat (Exam 2)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Basic Tooth Anatomy
-Enamel
-Crown
-Dentin
-Pulp
-Root
-Periodontium
-Gingiva
Most common childhood disease and cause
-Dental Caries
-S. Mutans
Gingivitis
-Reversible inflammation of gingiva due to plaque & can progress
Periodontitis
-Caused by chronic inflammation of gingiva & support tissue by Gram (-) bacteria
-If present in pediatrics, consider systemic disease such as DM, Down syndrome, leukemia, histocytosis
-Presents as interdental papillae edema, erythema and bleeding; tartar build up
-Education on prevention is key!
Treatment of Periodontitis
-Chlorhexidine mouthwash
-Professional dental care
-Periodontal surgery
Oral Pain
-Majority is related to inflamed or injured tooth pulp or periodontal disease
Non-dental oral pain
-Myofascial pain
-Bruxism (grinding of teeth)
-Temperomandibular joint disorder
-Osteoarthritis
-RA
-Trigeminal neuralgia
-Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
-Bell's palsy
-Herpes Zoster
-Maxillary sinusitis
Treatment of Dental/Oral Pain
-NSAIDs
-Consider Narcotics sparingly
When are ABX indicated for an Oral infection?
-When fever, lymphadenopathy, progressing disease, or IC
What ABX are indicated for Oral pain?
Amoxicillin, Augmentin, Clindamycin, doxycyline
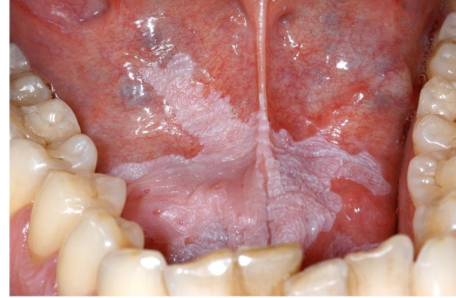
Leukoplakia
-Caused by Hyperkeratosis related to chronic irritation
-Small % are dysplastic or early SCC
-MC in middle aged & older men
-CX: White lesion on mucosa; can NOT be rubbed off; can be small
-DX: Punch biopsy
-TX: excision
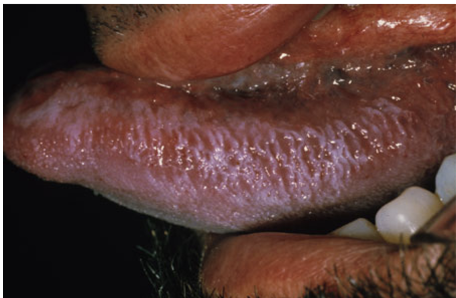
Hairy Leukoplakia
-Most prevalent in HIV pts; ALSO s/p organ transplant
-Associated with EBV & long term corticosteroid use
-Slightly raised areas develop rapidly on lateral border of tongue with "Hairy" surface
-Waxes and wanes, moderately irritative
-Acylovir/Valacyclovir for temp relief
Treatment of Hairy Leukoplakia
-Acyclovir or Valcyclovir
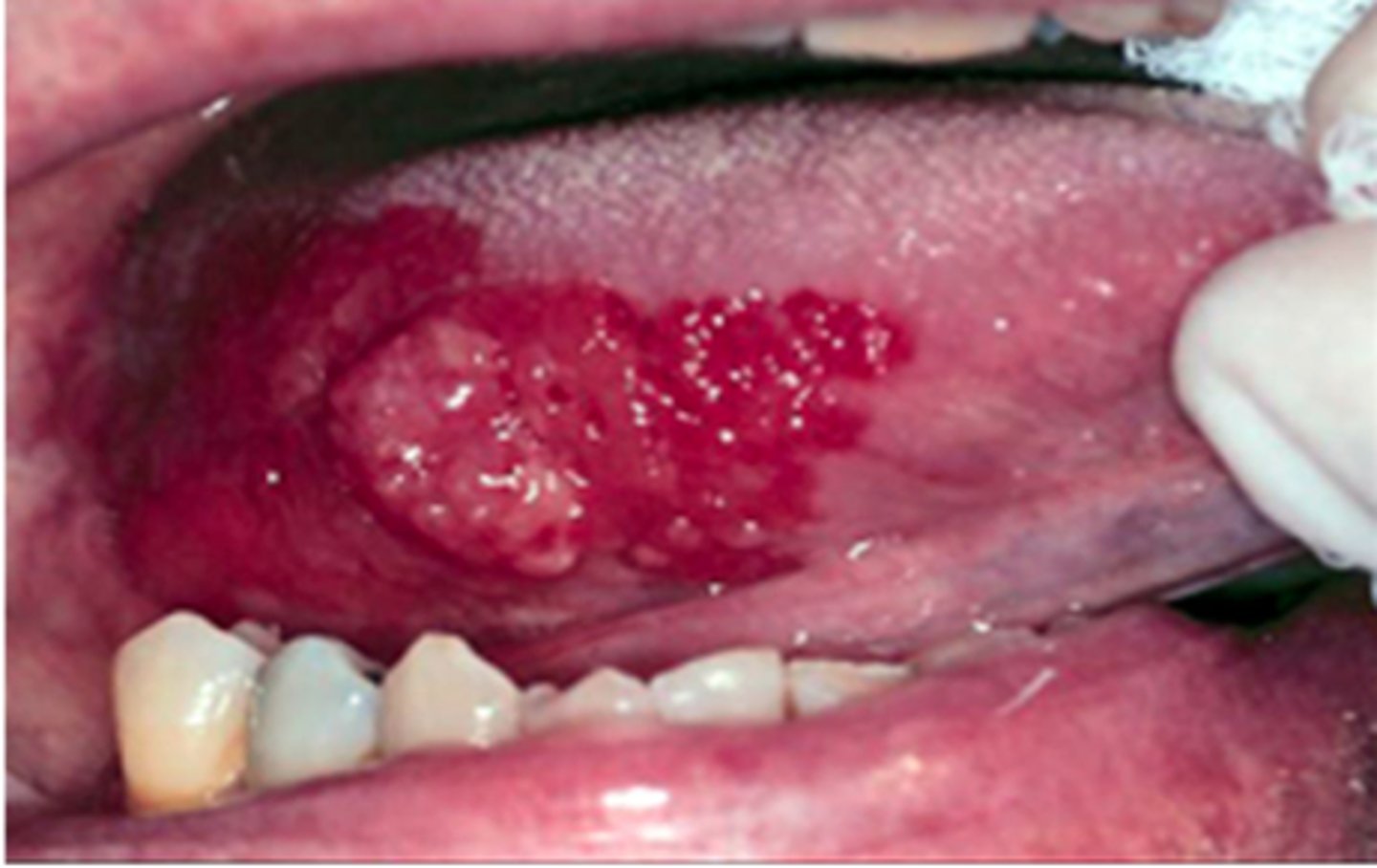
Erythroplakia
-Related to hyperkeratosis related to chronic irritation
-Most often associated with tobacco & alcohol use
-90% transform into malignancy
-MC in older pts
-CX: "Fiery" red, well demarcated lesions of mucosa; may be flat/depressed; smooth or granular
-DX: Biopsy
-TX: excision with clear margins
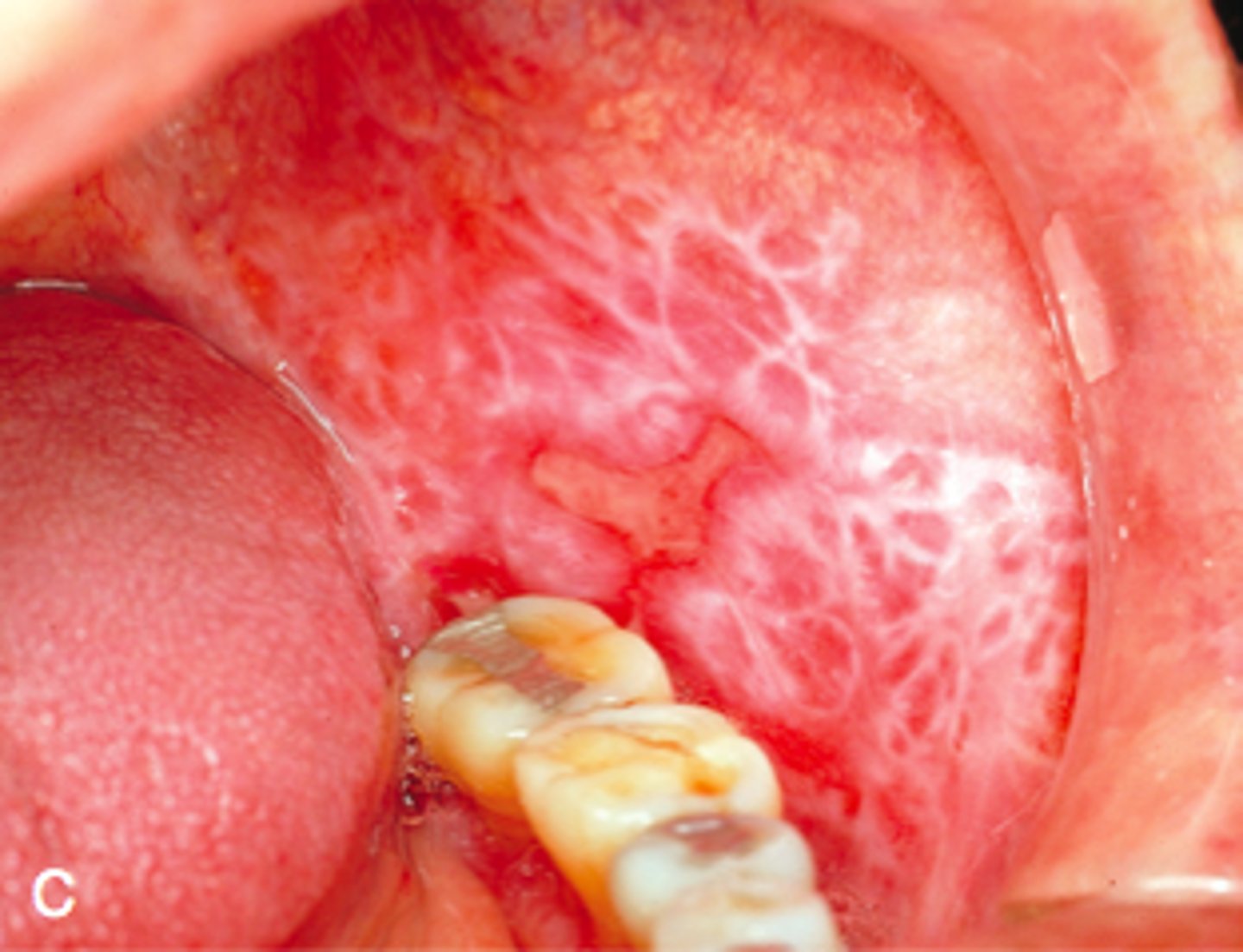
Oral Lichen Planus
-Uncommon autoimmune condition related to chronic inflammation
-Occurs in middle-aged and elderly women
-Associated with Hep C
-CX: Reticular, atrophic, bullous; MC on buccal mucosa, tongue, and gingiva, occurs bilaterally; Whickam striae, painful/burning; associated with dermal form
-Dx: punch biopsy, direct immunoflouresence
-Tx: clobetasol daily (or cyclosporines, retinoids, or tacromilus)
Diagnosis of Oral Lichen Planus
-Punch biopsy or direct immunofluorescence
Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus
-Topical mid/high potency corticosteroids (Clobetsol); Cyclosporins; Retinoids; Tacrolimus
Oral Cancer
-Epidemiology: 2-3% of all cancers in US
-Etiology: SCC; HPV accounts for 26-70% of cases; tobacco and ETOH use. MC in younger white men.
-CX: MC on tongue, lips, floor of mouth; most are advanced as diagnosis
-DX: biopsy non-healing white or red lesions. CT/MRI to see extent of disease
-TX: chemo, surgery, radiation
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
-Biopsy any non-healing white or red lesions present >2weeks
-CT or MRI for extent
Treatment of Oral Cancer
-Chemotherapy, surgery
-Radiation based on severity/extent
Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-High suspicion for raised, firm, white lesions with ulceration
-Lesions <4mm are unlikely to metastasize
-TX: Lesions <2cm in Diameter tx with local resection; large= resection, neck dissection, and external beam radiation; radiation indicated for (+) margins or metastatic disease
Oropharyngeal SCC
-Presents later, lesions are deep in lymphoid tissue or tonsils
-Associated with tobacco, alcohol, and HPV
-Worse prognosis if tobacco/alcohol related
-Unilateral odynophagia, weight loss
-PE: may reveal ipsilateral lymphadenopathy
Necrotizing Ulcerating Gingivitis
-"Trench Mouth"
-Destruction of periodontium
-Associated with poor dental hygiene, emotional stress, tobacco use, IC state
-Caused by Fusobacterium & Spirochetes
-Pt presentation: Fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy; foul breath; metallic taste
-CX: Painful, edematous papillae; Ulcers with overlying pseudomembrane; gingiva is inflamed, friable, and necrotic
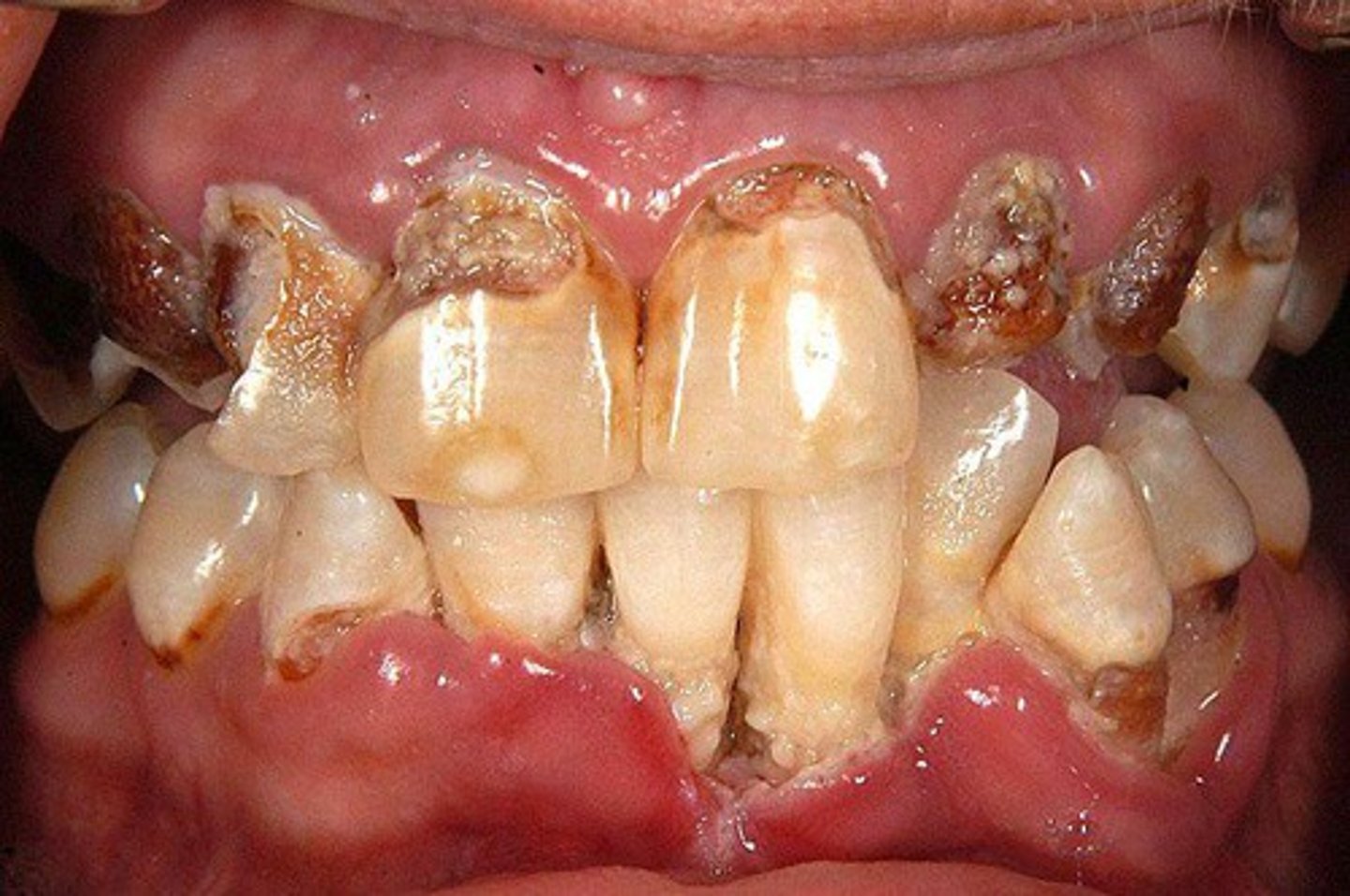
Treatment of Ulcerating Gingivitis
-Warm peroxide or chlorhexidine rinses
-Topical & oral analgesia
-PCN TID x 10 days
Aphthous Ulcer
-HHV6; associated with stress
-Occur on buccal mucosa
-Can be single or multiple, recurrent
-CX: Small, round ulceration with yellow/gray fibrous center; surrounded by red halo; Painful
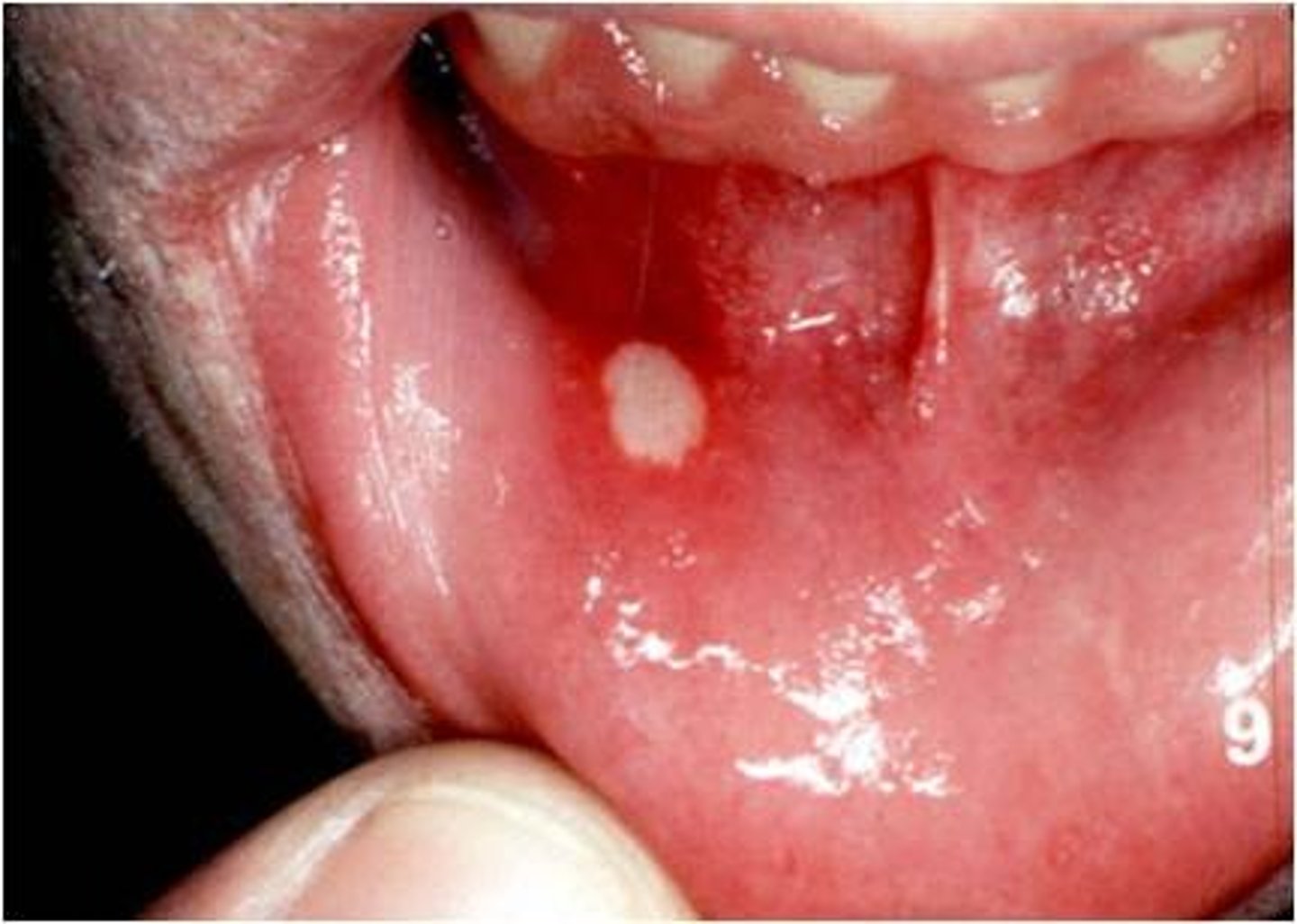
Treatment of Aphthous Ulcers
-Diclofenac 3%
-Cimetidine for recurrent
-Prednisone taper x 1week
Herpes Stomatitis
-Common and mild in IC; NO TX needed
-Burning, small vesicles that rupture and scab
-Found on lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, soft palate
-Presentation: Painful ulceration, fever, lymphadenopathy
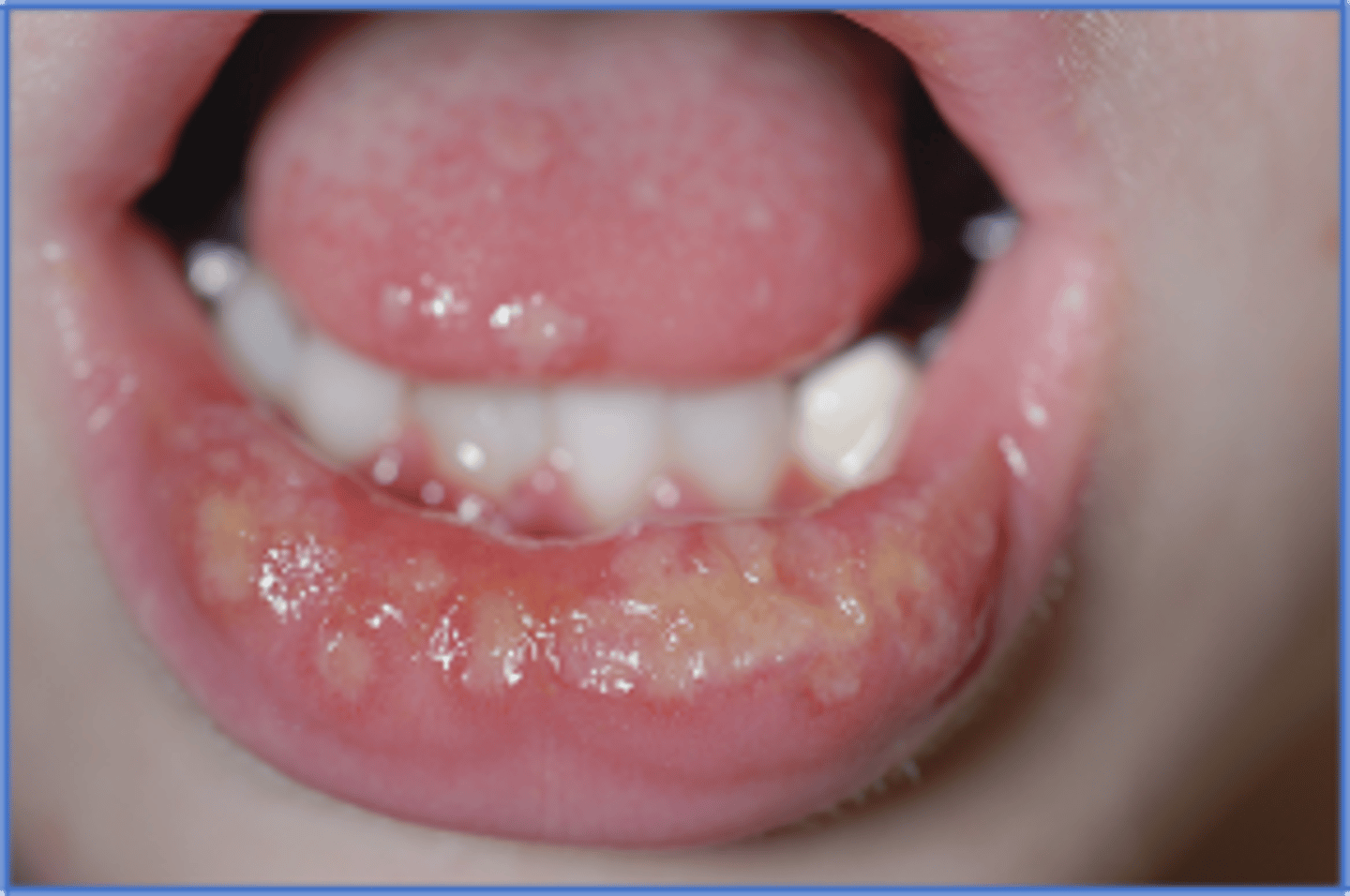
Treatment of Herpes Stomatitis
-Acyclovir 5x daily x 7-10 days
-Valcylovir BID x 7-10 days
Viral Pharyngitis
-MC is Rhinovirus; also coronavirus, adenovirus, HSV, Parainfluenza
-CX: Sore throat; Cough; Rhinorrhea
-CX findings: Vesicular or petechial patterns of soft palate; cervical lymphadenopathy
Diagnosis of Viral Pharyngitis
-No testing required except in Influenza, mono, or acute retrovrial syndrome are suspected
Treatment of Viral Pharyngitis
-Symptomatic
-NSAIDs, rest
-IV fluids if too dehydrated
Bacterial Pharyngitis
-Associated with Group-A Beta Hemolytic Strep (GAHBS), Neisseira Gonorrhea, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia Trachomatis
-Presentation: CENTOR criteria; Cervical adenopathy, Exudates, NO cough, Temperature, Age
-DX: Rapid Antigen; Throat culture
Streptococcal Bacterial Pharyngitis Tx
-TX: 1st line is PenVK 500 mg BID x 10 days
-Cephalexin; Azithromycin
-Supportive: Analgesics; Fluids
Scarlet Fever
-Complication of strep pharyngitis
-Caused by pyogenic streptococcal exotoxins
-Scarletina erythematous rash with fine red papules "Sandpaper" rash
-Starts on trunk, spreads to extremities; Spares palms and soles
-Most severe in groin
-Blanches with pressure
-Circumoral pallor
-Fades in 2-5 days
-"Strawberry tongue"
-TX: Supportive, PCN
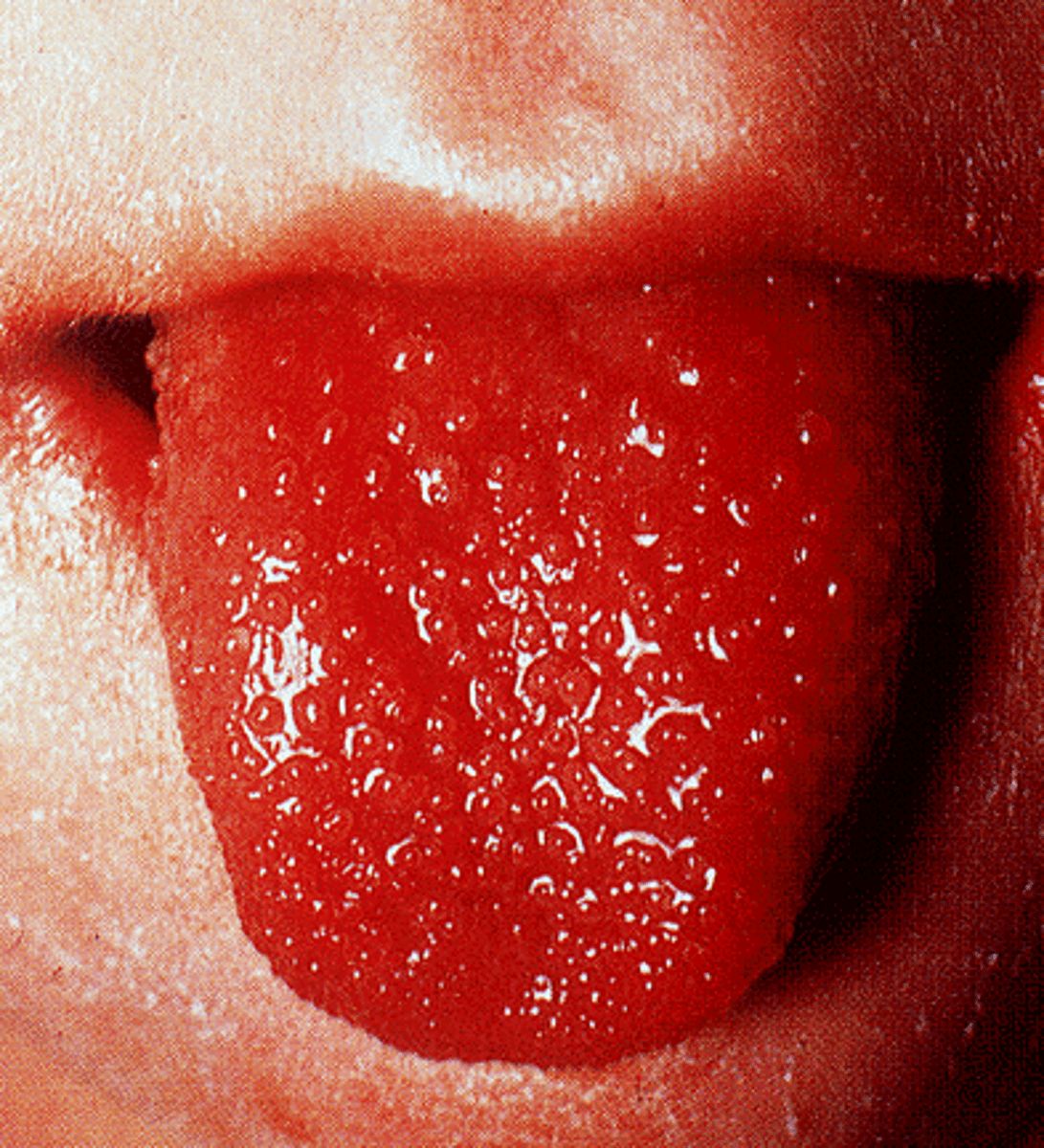
Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
-Complication of Strep Pharyngitis
-Caused by nephritogenic strains of GABHS, immune-mediated process
-Onset 1-3 weeks after pharyngitis
-More common in children/elderly
-Presentation: Hematuria, Dysuria, Edema, HTN, Renal failure, HA, Malaise, Anorexia, Flank pain
-DX: ASO titers; Anti-DNAse; Anti-hyaluronidase Ab; Biopsy
-TX: Supportive; Control HTN, edema; Hemodialysis prn; ABX (PCN)
Rheumatic Fever
-Complication of Strep Pharyngitis
-Systemic immune response to beta-hemolytic strep
-Possibly due to similar surface antigens between strep and human proteins
-Onset: 2-3 weeks after pharyngitis
-MC in children 5-15 yrs old
-Most often affects Mitral Valve (75-80%), less often aortic valve (25%)
-CX: Carditis, Arthritis, Chorea, Subcutaneous modules, Erythema marginatum
-DX: Jones Criteria (2 major OR 1 major + 2 minor)
Treatment of Rheumatic Fever
1.2 million units of IM PCN once
-Bed rest, NSAIDs; PCN or Erythromycin if PCN allergic
-Corticosteroids for joint pain if not responsive to salicylates (prednisone)
-Prevention: Early tx of strep pharyngitis; prophylaxis is PCN G
Gonococcal Pharyngitis
-Neisseria gonorrhea infection transmitted via oral sex & occurs simultaneously with genital gonorrhea
-Asymptomatic or with sx: Sore throat, pharyngeal exudates, lymphadenopathy
-DX: Culture or NAAT
-TX: Single dose of Ceftriaxone 1g IM
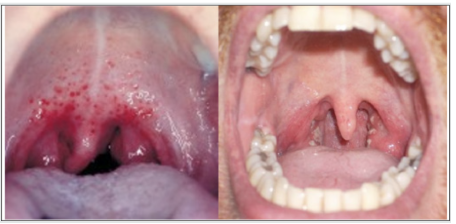
Glossdynia
-Benign; Burning painful tongue
-With glossitis: DM, drugs, tobacco, candidiasis
-If no cx findings: "Burning mouth syndrome" tx with Alpha-lipoic acid or Clonazepam; behavioral therpay
Glossitis
-Absence of filiform papillae
-Smooth, red tongue
-Rarely painful
-Nutritional deficiencies, drug rxs, dehydration, irritants, foods/liquids, autoimmune
-TX: ID underlying cause; empiric nutritional replacement therapy
Oral Candidiasis
-Colonization of mucosal epithelium
-Occurs s/p ABX use, corticosteroid, head/neck radiation
-Common in very young, and IC, chronic irritation also
-CX: Erythematous mucosa; creamy white curd-like plaques; may have pain; easily rubbed off
-DX: Clinical
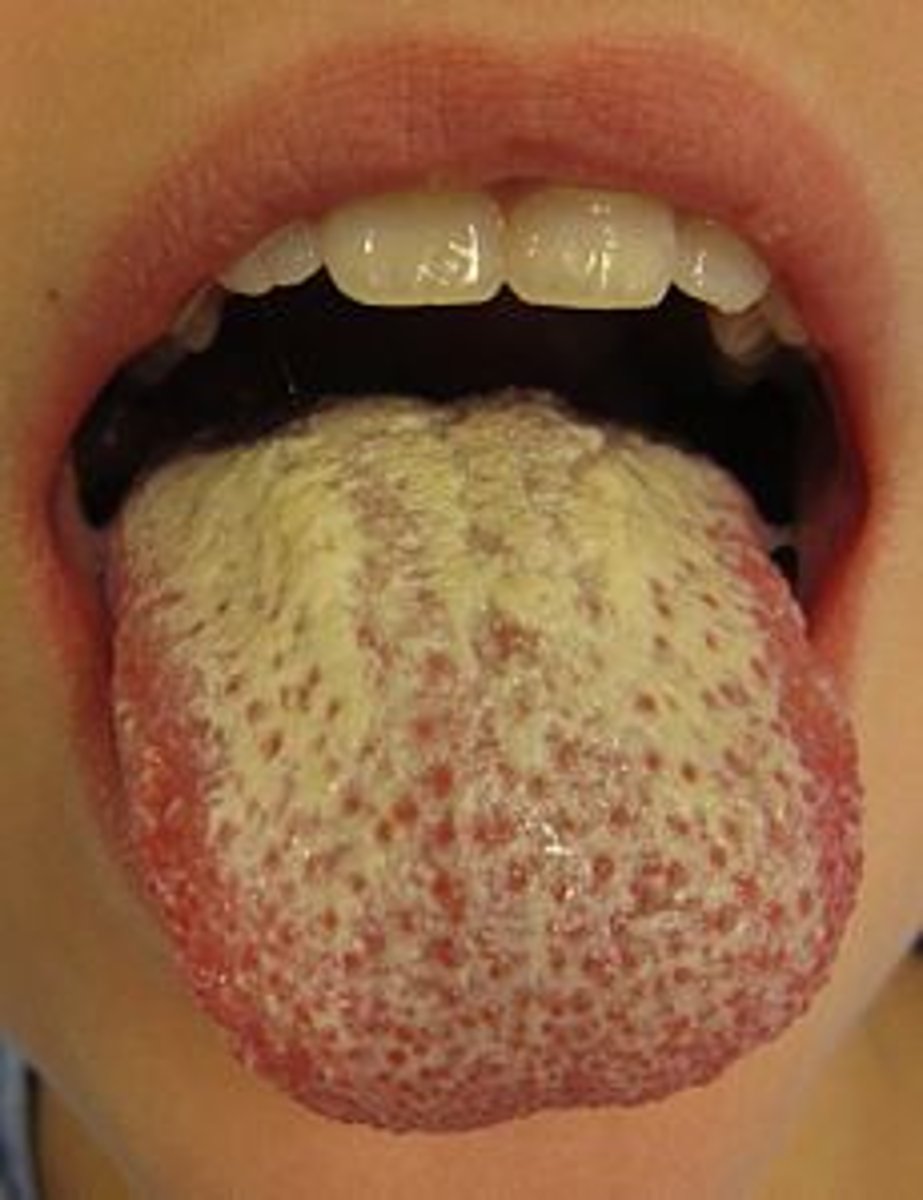
Treatment of Oral Candidiasis
-Oral: Fluconazole, clotrimazole, nystatin mouth rinse
-HIV pts- longer tx with variconazole
Peritonsillar abscess
-Spreading infection beyond tonsillar capsule
-Most often strep, may be multimicrobial w/anaerobes. can progress into quincy abcess.
-Presentation: Fever, Severe sore throat, Odynophagia, Trismus, Muffled "Hot potato" Voice
-CX: Erythema; medial deviation of soft palate; deviated uvula
-TX: Amoxicillin, augmentin, clindamycin. Supportive measures- Needle aspiration, I&D, tonsillectomy
Retropharyngeal Abscess
-Complication of peritonsillar abscess
-Preceeded by URI, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis media, or wound
-Most common GAHBS, S. Aureus, MRSA, Hib, respiratory anaerobes
-CX: Fever, Sore throat, excessive drooling, voice change, neck stiffness
-CX findings: Midline edema of posterior pharynx; tender anterior cervical adenopathy; decreased cervical ROM
Diagnosis of Retropharyngeal Abscess
-Lateral neck x-ray will reveal edema
-CT with contrast is gold standard
Treatment of Retropharyngeal Abscess
-Assess airway!
-ASAP: Clindamycin or Ampicillin-sulbactam IV
-IV hydration
-Needle aspiration; ENT consult
Ludwig Angina
-Spreading cellulitis of submandibular and sublingual spaces from mandibular molars
-MC Strep, Staph, bacteroides
-MC in males, ages 20-60 yrs
-CX: Fever, odynophagia, dysphonia
-CX findings: Painful, brawny edema & induration of tissue Bilaterally; poor dental hygiene; trismus
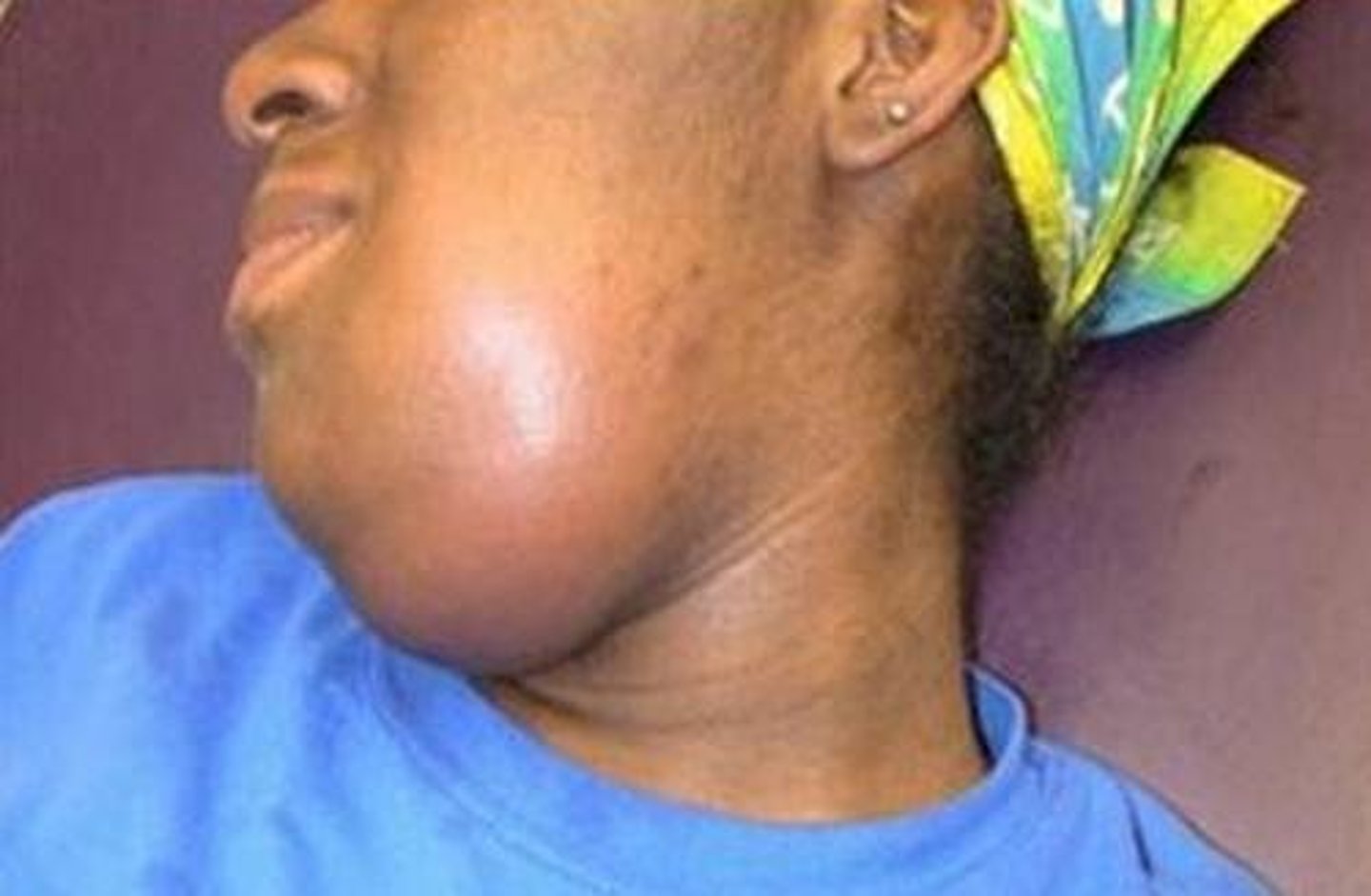
Diagnosis of Ludwig Angina
-CT or MRI
Treatment of Ludwig Angina
-Airway mangement
-IV ABX x 2-3 weeks: Ampicillin-sulbactam or ceftriaxone; clindamycin with levoflaxacin (PCN allergic); add vanco or linezolid for MRSA
-Analgesia
-IND; ICU admission for airway surveillance
-Complications: Acute laryngospasm & airway compromise
Complications of Ludwig Angina
-Acute laryngospasm & airway compromise
Sialadenitis
-Caused by obstructed duct
-MC pathogen is S. Aureus
-MC affects parotid gland
-Often occurs in dehydration & chronic illness
-CX: Acute swelling; pain with eating; tender & erythematous duct opening
-CX Findings: Erythema of skin; pain; trismus; induration
Diagnosis of Sialadenitis
-Clinical
-CT or US if unresponsive to ABX
Treatment of Sialadenitis
-IV Nafcillin q4-6h x 48 hrs then po PCN x 10 days
-Hydration, warm compress
Complications of Sialadenitis
-Suppurative
-Present with fever
-Often don't respond to hydration & IV ABX
-Require operative IND
Sialolithiasis
-Stone formation in Wharton (Larger) or Stenson duct (smaller)
-Occur in dehydration, chronic disease
-CX: Postprandial pain; swelling of gland; gritty FB in mouth
-CX Findings: Induration of floor of mouth; may palpate stones near orifice
Diagnosis of Sialolithiasis
-Sialography, CT, US; endoscopy
Treatment of Sialolithiasis
-Intraoral extraction
-Surgical Excision
-Endoscopy
Dysphonia/Hoarseness
-Abnormal vibration of vocal chords
-Breathy: Unilateral paralysis
-Harsh: Laryngitis, malignancy
-Rough: edema of chords
-High pitched: Narrow airway above chord
-MC cause is Viral laryngitis
Diagnosis Dysphonia/Hoarseness
-History is central!
-Sx present for >2 weeks must be evaluated
-Tobacco use is concerning or lung cancer
-Other HEENT sx
Treatment of Dysphonia/Hoarseness
-REFER to ENT!
-Treat underlying disorder
-Voice rest
-Medication: ABX, Glucocorticoids, anatacids, NSAIDS
-Surgery
Laryngitis
-Acute is MC
-Chronic is rare and bacterial (TB, Candida, Crypto)
-Most often is Viral (M. Catarrhalis & Hib)
-Presents with hoarseness & URI sx
-CX: Diffuse laryngeal edema, vascular engorgement of vocal cords
Treatment of Laryngitis
-Voice rest
-Humidification
-ABX NOT indicated
Epiglottitis
-Medical Emergency!
-Caused by Hib, now GAHBS, S. Pneumo, H Parainfluenza, S. Aureus
-CX: Rapid sore throat; Odynophagia; high fever; tachycardia; drooling; stridor; "tripoding"
-CX Findings: Respiratory distress; signs of systemic toxicity; normal pharyngeal exam
Diagnosis of Epiglottitis
-Clinical findings
-Laryngoscopy in OR: cherry red epiglottis
-Lateral neck x-ray: enlarged "Thumbprint sign"
-Blood cultures
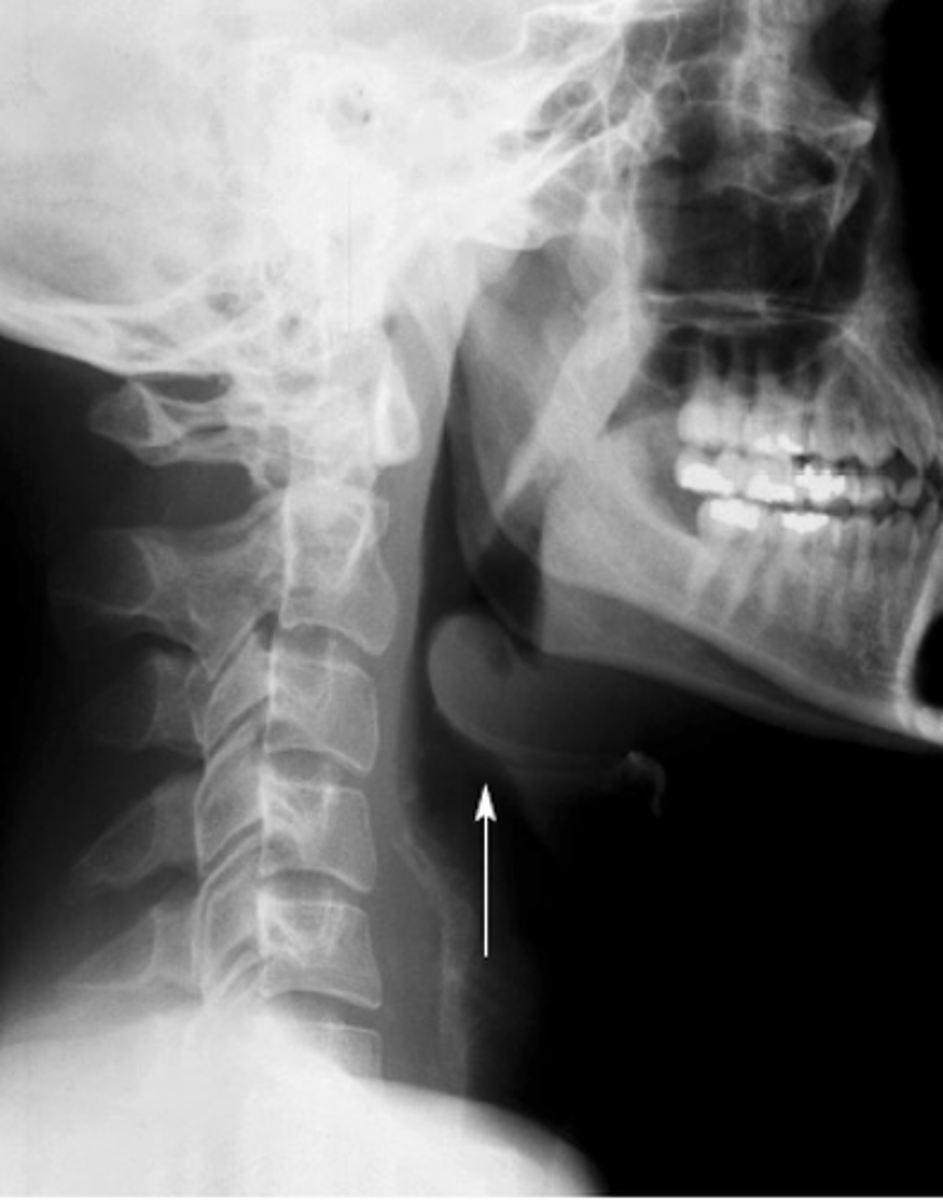
Treatment of Epiglottitis
-Secure Airway!
-IV ABX: Ampicillin-sulbactam, cefotaxime or ceftriaxone; vancomycin if MRSA; Clindamycin or bactrim for PCN allergy
-Admit to ICU
SCC of Larynx
-Epidemiology: MC malignancy of larynx; exclusive to tobacco users; common in men 50-70 yrs old
-CX: Hoarseness is MC; throat or ear pain; hemopytsis; dysphagia; weight loss; stridor
Diagnosis of SCC of Larynx
-Imaging: CT or MRI
-Biopsy via laryngoscopy
Treatment of SCC of Larynx
Radiation is standard
-Partial laryngectomy may be considered
-Chemotherapy with cisplastin and radiation for advanced stage
Neck masses
-DX depends on location; age; & associated disease
-CX: Tender with rapid growth; firm, painless, slow growth, malignant process
-If pts uses tobacco or alcohol, consider metastasis from oral/oropharyngeal/laryngeal CA
-Suspect lymphoma if <30 or >70
-Types: Congenital, inflammatory, tumor associated
Branchial Cleft Cyst
-Congenital neck mass
-Soft cyst along anterior border of SCM
-Common in 2nd-3rd decades
-May have abrupt edema and infection
-Tx: Excision
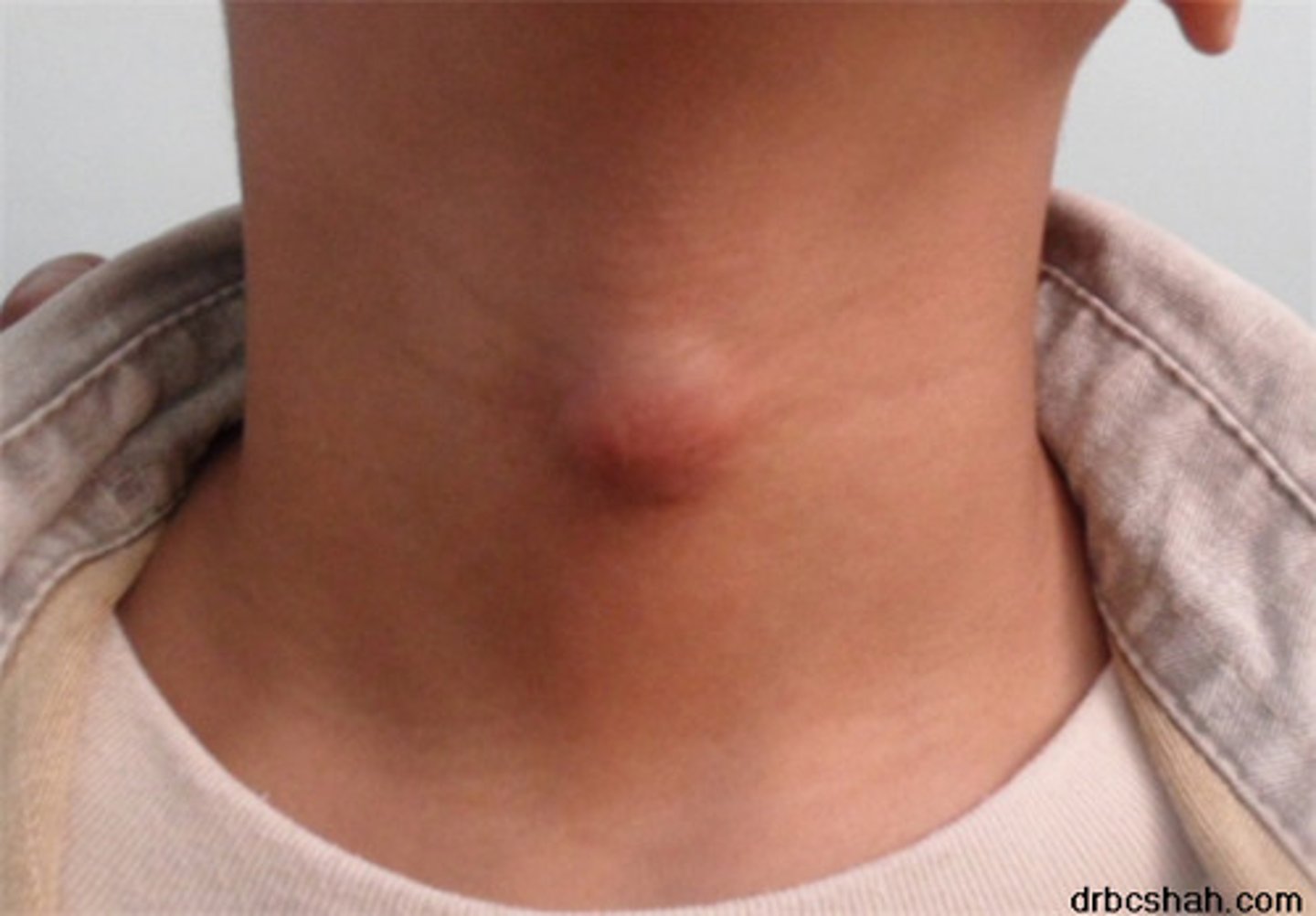
Thyroglossal duct cyst
-Midline mass, below hyoid bone, mobile with swallowing
-Common <20
-TX: excision
Reactive Cervical Lymphadenopathy
-Infectious/Inflammatory neck masses
-Persistent enlargement of LN s/p infection
-LN>1.5 cm (increased suspicion with tobacco/etoh use)
Granulomatous Mass
-Infectious & inflammatory mass
-Mycobacterium, sarcoides, cat-scratch disease
-Single or matted LN
-FNA bx with PCR or excisional Bx
Lyme Disease Mass
-Infectious & Inflammatory neck mass
-Often presents with cervical lymphadenopathy, HA, pain, facial paralysis
Malignancy Causing Neck masses
-Majority of fixed, firm, persistent, enlarging masses are metastatic in older patients
-Most often malignant SCC of head/neck that metastasize to cervical lymph nodes
-Lung, GI, and breast tumors metastasize to supraclavicular nodes
-DX: laryngoscopy, esophagoscopy, bronchoscopy, cytology if scopy fails
-10% present in neck: Rubbery nodes, MC in young or AIDS pts; bx required
Snoring
-Occurs in 60% people
-narrowing or upper airway
-Varies from simple without obstruction to severe obstructive apnea
-CX: Palate may be enlarged with excess mucosa hanging below soft palate
-DX: Recommend polysomnography to eval for OSA
-TX: Diet & Exercise; modification of position; CPAP; surgical correction