PRECIPITATION - BOOK
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Convectional Precipitation (Thermal Convection)
type of precipiation is in the form of local whirling thunder storms and is typical of the tropics
Frontal Precipitation (Conflict between two air masses)
two air masses due to contrasting temperatures and densities clash with each other, condensation and precipita tion occur at the surface of contact
Orographic Precipitation (Orographic lifting)
mechanical lifting of moist air over mountain barriers, causes heavy precipitation on the windward side
Cyclonic Precipitation (Cyclonic)
due to lifting of moist air converging into a low pressure belt, i.e., due to pressure differences created by the unequal heating of the earth’s surface
non-recording or recording type
Rainfall may be measured by a network of rain gauges which may either be of ____.
Recording Rain Gauge
also called self-recording, automatic or integrating rain gauge
Recording Rain Gauge
has an automatic mechanical arrangement consisting of a clockwork, a drum with a graph paper fixed around it and a pencil point, which draws the mass curve of rainfall
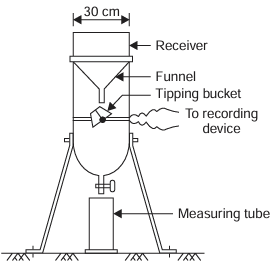
Tipping bucket rain gauge
consists of a cylindrical receiver 30 cm diameter with a funnel inside
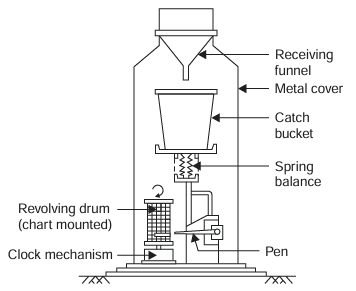
Weighing type rain gauge
type of rain-gauge, when a certain weight of rain fall is collected in a tank, which rests on a spring-lever balance, it makes a pen to move on a chart wrapped round a clock driven drum
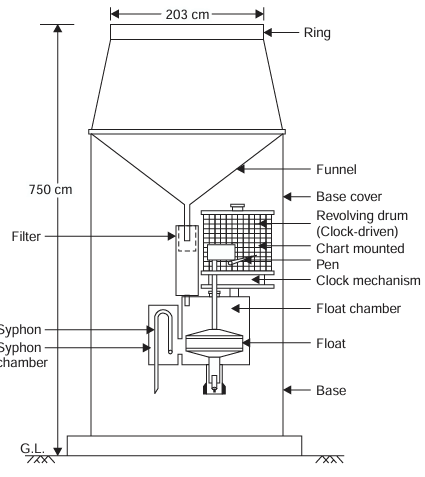
Float type rain gauge
the rain is collected in a float chamber, the float moves up which makes a pen to move on a chart wrapped round a clock driven drum
Automatic-radio-reporting rain-gauge
used in mountainous areas, which are not easily accessible to collect the rainfall data manually
Radars or radar signals
Determining the magnitude of storm precipitation and its areal distribution. This method is usually used to supplement data obtained from a network of rain gauges.
rain-gauge density
number of rain-gauges to be erected in a given area
Station-year method
In this method, the records of two or more stations are com bined into one long record provided station records are independent and the areas in which the stations are located are climatologically the same.
Double-mass analysis
trend of the rainfall records at a station may slightly change after some years due to a change in the environment (or exposure) of a station either due to coming of a new building, fence, planting of trees or cutting of forest nearby, which affect the catch of the gauge due to change in the wind pattern or exposure
Point rainfall
It is the rainfall at a single station. For small areas less than 50 km2, point rainfall may be taken as the average depth over the area. In large areas, there will be a net work of rain-gauge stations.
Arithmetic average method
It is obtained by simply averaging arithmetically the amounts of rainfall at the individual rain-gauge stations in the area
Thiessen polygon method
This method attempts to allow for non-uniform distribution of gauges by providing a weighting factor for each gauge.
isohyetal method
In this method, the point rainfalls are plotted on a suitable base map and the lines of equal rainfall are drawn giving consideration to orographic effects and storm morphology.
Drizzle
a light steady rain in fine drops (0.5 mm) and intensity <1 mm/hr
Rain
the condensed water vapour of the atmosphere falling in drops (>0.5 mm, maximum size—6 mm) from the clouds.
Glaze
freezing of drizzle or rain when they come in contact with cold objects
Sleet
frozen rain drops while falling through air at subfreezing temperature.
Snow
ice crystals resulting from sublimation (i.e., water vapour condenses to ice)
Snow flakes
ice crystals fused together.
Hail
small lumps of ice (>5 mm in diameter) formed by alternate freezing and melting, when they are carried up and down in highly turbulent air currents.
Dew
moisture condensed from the atmosphere in small drops upon cool surfaces.
Frost
a feathery deposit of ice formed on the ground or on the surface of exposed objects by dew or water vapour that has frozen
Fog
a thin cloud of varying size formed at the surface of the earth by condensation of atmospheric vapour (interfering with visibility)
Mist
a very thin fog
Tipping bucket rain gauge
Weighing type rain gauge
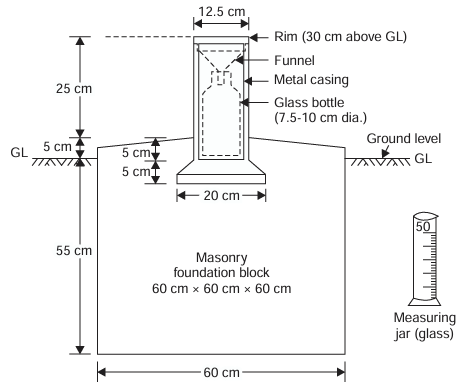
Symon’s rain gauge
non-recording rain gauge used by the meteorological department of India; rainwater is collected in a cylindrical bottle which is measured manually on daily basis.
Symon’s rain gauge
Float type rain gauge