BU111 - Exam
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Canadian Population
40 Million
Life expectancy
83 Years
Median age
40.8 years
People per household
2.5 years
Median household income
$61,400
Smartphone penetration
86%
Online shopping
28.1million people
Urban area
81%
Big 6 Cities
Toronto Montreal Calgary Ottawa Edmonton Vancouver
Market Segmentation
15-20% low end
60-65% average
15-20% high end
Under age 15
cohort size 16%
15-19 age
cohort size 6%
20-25 age
cohort size 7%
25-40 age
cohort size 21%
40-65 age
cohort size 33%
Over 65 age
cohort size 17%
What is population? What drives it (insights)? How is it applicable?
# of people in an area
Answer driven by population in area ie stores
Market size/share, revenue, profitability, supply needed, saturation, competition
What is when you break a probably down on an individual level? What drives it (insights)? How is it applicable?
Anything consumed at an individual level
Calculate individual consumables/demand ie phone
Market size/share, revenue, profitability
What is it when you break a problem down on an household level? What drives it (insights)? How is it applicable?
Things used as a group
Calculate group consumables/demand ie refrigerator, hose, roof
Market size/share, revenue, profitability
What is when you break a probably using a proxy? What drives it (insights)? How is it applicable?
*Biggest driver of estimate or easiest variable to observe
Number of stores in an area; population/store
Ie. stores, gas pumps
Company revenue/profitability, market size, supply, saturation of market
TAM
TAM - Total Addressable Market
Entire market for your product
100% share
Restaurants
SAM
SAM - Serviceable Available Market
Size of your segment (target)
Italian Restaurants
SOM
SOM - Serviceable obtainable Market
Your share: how much of segment you can win
Waterloo area
How do you break a problem down into market frequency approach (the equation)
Population (household or individual)
Defining characteristics of the population = % of pop
X purchase frequency
X Purchase quantity
X Unit cost
Social Factors break down into 4 main elements and why is it important?
Customs
Habits
Values/attitudes
Demographic characteristics
These are all important as they affect customer preferences and worker attitudes and behavior, standards of business conduct and corporate social responsibility
Demographics
the study of human population, cohorts = homogeneous groups within the larger population
Powerful predictor of behaviors/trends
Certainty and simplicity of age data
Predicts supply and demand and informs environment analysis and human resource decisions
What are the advantages of a smaller cohort group?
Less people, less variation
Less competition (compete to get a job. Fill the millennials)
What are advantages and disadvantages of large cohort groups?
Disadvantage of large cohorts
More competition
Advantage of large cohorts
Large market will be targeted more often
Influence on business/government/media
Will make choice in favour of majority group
Currently millennials are the largest cohort
Canadian Population Distribution
1) Labour force
2) Economy
3) Market
4) Implications
5) Immigrants?
6) Implications of immigrants
1) → fewer incoming than outgoing
2) → fewer supporting pensions
3) → children of boomers = relatively large group
4) Eco has greater market impact, Vulnerable seniors - demand for care, Increasing strain on pension and healthcare, Potential labour shortages
5) Increase number of immigrants - younger and more likely to live in city than average Canadian
6) Many consumers having difficulty interacting with marketplace, Immigrants may not have the same skil lset,Creates opportunities, Diverse workforce able to serve multiple different consumers, More likely to live in more civil/rural areas, More opportunities, More well known
What is a Cohort
Number of people in each age group
Impacted by fertility rate, birth rate
What are the aging boomers and their implications
Baby boomers 1946-64 - larger cohort
Now the aging population creates opportunity → increased need for retirement homes, care, etc.
Implications/Challenges include increased elder care, sandwiched generation (people have to take care of their parents and kids), increased vulnerable seniors
As Boomers age, shortage of employees to fill their jobs → impacting the economy
Immigration will be necessary to sustain the economy
How are Canadian households changing? and what are the implications?
One-person households greater than one-family households
Decreasing over time
One-person households are increasing over time
Lower birth rates, higher costs associated with having a family, divorce rates are increasing, aging population, women live longer than men
Implications
Lost economies of scale in living, shopping
Families face time constraints
They are busy - focusing on convenience
Must focus on needs - less shopping on non essentials
One-person homes are less likely to use things such as Costco
Only one person contribute to costs of household
Population Living in Rural Areas of Canada
Shrinking rural communities
Rural living predominates in Atlantic Canada, Saskatchewan, Territories
Most provinces less and less are living in rural communities
More people are living in bigger cities and areas around them
Now we are starting to see the donut effect
The hole is the city
Most people can't afford to live in the city, but vast majority live in the suburbs surrounding the city
who is moving and why?
Family moving to urban areas - more space
More affordable housing is in the outskirts
Job opportunities
what are the challenges and implications of people moving to urban areas?
As people in rural areas move (the younger generation) this leaves majority of rural areas to be the aging population
Results in fewer people to fill jobs in these areas
Employees have to think how to get people to get jobs, but also have to think about how/why potential customers may be leaving
What they can do:
Any sort of incentive to keep people (something like healthcare benefits)
Expand market (move things online)
Allow people to work online
What are the four factors that influence demogrpahics?
Economics, technology, world events/news, parenting.
What is the characteristic, implication and an example of the demographic factor economics?
Values and priorities - how/time you were raised will impact your values on things such as money
How to attract, retain, motivate
People raised in the great depression are more frugal with their money
What is the characteristic, implication and an example of the demographic factor technology?
Lifestyle
What makes a product appealing
What is the characteristic, implication and an example of the demographic factor world events/news?
Habits (digital and other) - How do events impact people's
How to attract as consumers
9/11
What is the characteristic, implication and an example of the demographic factor parenting?
Mindset - How a person is raised impacts their mindset
How much they spend and what they spend on
Baby Boomers (1946-64) and their consumer/work implications
Prefer in person transactions
Long hours in office
1 carrer and company
Gen X (1965-79) and their consumer/work implications
Research online but buy in person
Brand loyal
Flexible work
Perfect career
Gen Y/Millennials (1980-94) and their consumer/work implications
Digitally savvy
Quality>brand
What authenticity
Customization and personalization, experiences vs assets
access>ownership
<socially minded
Meaningful, flexible, work-life balance
Will change jobs
Gen Z (1995-) and their consumer/work implications
Digitally savvy
<value uniqueness
+ want to “know” brand
Customization and personalization, experiences vs assets
Frugal/avoid debt
<socially minded
Meaningful, flexible, work-life balance
Several careers
How do the different cohorts work as employees?
Boomers willing to spend a large amount of time at a company/in the office
Gen-x may switch companies, but stay on the perfect career path
Millennials will switch job, industry, but around the same type of job
Gen-z expected to have multiple careers
What is market penetration
Sell more of existing product to existing target market
= greater market share and/or greater purchase frequency
Why would a company use a market penetration strategy?
build on what you have and know -no change, economies of scale in production and selling
Least risky → More of the same - want customers to buy more
Either buy more at once
Or buy more consistently
Pretty much a no brainer - always trying to sell more
Try new tactics to make this a reality
If producing more this will decrease costs, as you can buy in bigger bulks, will likely get discounts, economies of scale will come into play
What are the challenges with market penetration?
competitor reaction, winning customers
Competitive reaction
You can try, doesn't mean it will work
Comp may try to retaliate, eg. Under cut your price
Requires work to convince customers to buy more
What are tactics for market penetration?
Cut prices
Increase advertising, loyalty schemes -hopefully persuasive, Eg. buy 1 get 1 50% off from Starbucks for members
Increase distribution channels - Eg. McDonalds partner w uber eats
Easier for customers to access McDonalds
Leads to increase in volume/purchase frequency of the product
Volume incentives - 2 loafs of bread for $6
Buy a competitor
what questions should a company ask when taking on a market penetration strategy?
Return: If I decrease price will volume compensate for lower price? Will lower price affect brand image?
Can you sell enough in volume that sales will be equal to or more then if you kept the price the same - Move to try and drive volume transactions
Challenges - luxury brand items
No sales, Won't sacrifice the brand reputation
Diamond-E
Capabilities: Can I persuade customers to consume more of my product?
Resources: Do I have to use new distribution channels? Should I? Can I?
Resources: Do I have the production capacity to meet the increased demand?
Porter’s insights:
Buyers: Propensity to switch? Lock in/switching costs? Brand loyalty?
Are buyers already locked in? Are they brand loyal to us, willing to buy more?
Rivalry: Fragmented vs concentrated, growing vs declining, aggressive vs passive competitor
How will comp react? If market is concentrated and aggressive, it will be much more challenging to steal market share from them
How much share do I already have? Can it grow?
What is market development?
Same product, new customer
Selling what you already produce to new target markets (market segments) or new geographic markets
Thinking about the questions of expansion
why would you choose a market development strategy?
Capitalize on production capabilities, economies of scale, pursue less contested or larger market; diversification of customer base
Economies of scale - ramping up volume → By increasing customer base
Diversification strategy → Diversify customer base
What is the challenge of market development?
customer access and awareness → Understand the new market
What are tactics for market development?
Create awareness in new market – pitch benefits to new customers
Ads - awareness
Expand geographically (use international expansion knowledge!)
Determine how you will expand internationally → Will you get an agent? Etc.
what questions should you ask when thinking about using a market development strategy?
Diamond-E:
Resources: Will this affect brand image? Should I use a different brand name?
Eg. When you expand to another country the people hate it and start posting about it on tik tok
Big companies will use different names so that they can adapt to local market and also protect themselves of brand impact if one market doesn't end up liking the product
Eg. Procter and gamble - Gain VS Tyde
Capabilities: Will the product need any adjustments? Can I make them?
Eg. McDonalds adapting menu to the location
Do I have the resources ($, brand equity, distribution network, knowledge of new customer) and capabilities (marketing, product redesign, international operations) to go international?
Depends on how you choose to execute the strategy
Can be super high or lower depending
Porter’s:
Can I access the distribution channels to reach this new market?
Are the customers accessible? Will they switch?
Rivalry: fragmentation, aggression, growth? Differentiation – are there market segments that are under-served?
Barriers to entry?
What is product development?
New product, Same Customer
Develop related or unrelated products your customers value; product line extension
Similar risk factor as market development
What is the benefit of product development?
build on customer knowledge & brand equity; possible distribution synergies & product complementarity/bundling
Already know about customers and can see a gap that can be filled
Can use the loyalty they have for one product and leverage this so they are loyal to a new product
what are the challenges of product development?
cannibalization
If you are coke and make coke 0, Will people just buy coke 0 only and sales plumet for coke. Leading to no overall growth
Be mindful they don't switch from your one product to the next
give up production efficiencies; must know what and how to develop new product
Not just focused on one product
what tactics should you use for product development?
Extend product
Repackage existing products
Create bundles of complementary products that add value to each other
What questions should you as when looking at using a product development strategy?
Diamond-E:
Can I leverage existing brand and/or distribution?
Can my facilities manage or do I have to build new ones?
Can I produce & sell at a profitable scale? Will you still be able to?
How much new product expertise will I need?
Porter’s:
Will customers be willing to switch to my new product?
Rivalry: aggression?
Barriers to entry?
What is a diversification strategy?
New products and markets
Chasing new customers with new products; creating new businesses
Concentric/horizontal → Less risk
Expanding into a product or market that is related to your existing
If you sell lawn mowers but then start making snow blowers
Similar items, but customers may not be the same
Vertical → Less risk
Talking about the supply chain.
Porters - backward and forward integration
Eg. Toyota makes cars, does backward integration and makes tires
Go backwards in the supply chain
Runs car and tire manufacturing companies
Eg. Virgin Records producing CDs and Records
Sold them to stores
Forward integration and made their own store
Became their own distributer
Conglomerate → Risker
Completely unrelated business lines
Eg. General electric
Makes lightbulbs but also has a bank
Bought companies that were underperforming and fixed it
Eg. Samsung sells computers but also sells washers and dryers and refrigerators
What are the benefits of a diversification strategy?
diversify business portfolio by building new business
If the economy starts to tank and doesn't want to buy new TVs but still need a washer/dryer
capitalize on existing capabilities in higher growth areas
May have support amongst different business lines
Eg. President of Samsung phones, president of Samsung washers
If there is efficiency in the phones they can use these learnings and scale across the difference business
what are the challenges of a diversification strategy?
many activities and capabilities must be created or changed = high risk of failure
Spreading recourses thin - easy to loose focus on one line when spending focus on another
what are the tactics of a diversification strategy?
Acquire other business → Buy and rebrand already existing businesses
Use joint ventures and alliances
If expanding internationally - joint venture
Can help reduce risk
Not just your capital on the line
What questions should you ask when thinking about a diversification strategy?
Will this affect brand image?
If you don't make you next product as good, your brand reputation may be tarnished
Diamond-E:
What new capabilities and resources will I need? Can I build or buy them?
Need a lot to have a lot of financial recourses
How much will I have to change operations? HR? Structure?
How do you ensure communication structure
Will have to adapt as you bring in new lines
Porter’s:
Can I access the distribution channels to reach this new market?
Are the customers accessible? Will they switch?
Rivalry: fragmentation, aggression, industry growth?
Barriers to entry?
What are the 3C’s and 1P you should think about in each quadrant of the anstrofx matrix?
Understand your company
Capacity, market understanding, production flexibility, brand equity, market share
Understand the customer
Segments-size, growth, profile, channel preference, value definition
Understand the competition
Position (target markets and market gaps), pricing, distribution, barriers, size, share, offerings
Understand the product
Differentiation, substitutes, ”job”, need for adjustments
What are the four foreign entry tactical strategies?
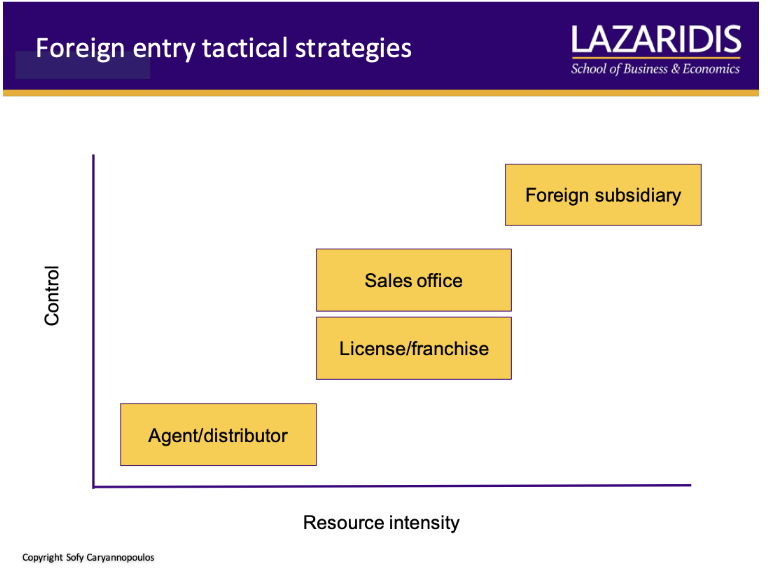
What should you ask when looking at sale volume criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
Large sales expected abroad? Extra capacity at home?
What should you ask when looking at customer knowledge criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
Understand what they want and how to sell to them?
What should you ask when looking at trade barriers criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
Know, can and have time to navigate the bureaucracy? Will tariffs make you uncompetitive?
What should you ask when looking at Financial, hr, IP resources criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
What capacity and knowledge does your hr have? Do you have the money to commit to a more expensive strategy? Are you concerned about IP? Do you have valuable IP?
What should you ask when looking at Market knowledge & network criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
How well do you understand the foreign market (customer and doing business)? Do you have existing or easily accessible distribution and/or supplier relationships?
What should you ask when looking at Mgmt capability criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
Do you have the capacity to manage a foreign operation? Do you have the knowledge to manage a foreign operation?
What should you ask when looking at risk tolerance criteria for any of the foreign entry strategy?
Do you prefer to enter carefully, test, learn and expand or do you want to enter assertively to capture market quickly and significantly?
What are the elements of political factors ?
Laws, regulations - How does this impact a business
Taxes
Trade agreements or conditions
Important
To help facilitate ease into expanding to other countries
Is there already trade agreements
Are the countries on good terms
Could lead to more competitors entering the market
What are is the significance of the elements of political factors?
Protection of consumers; ethical business; financial and physical safety
So businesses can't take a ton of shortcuts to employees and customers that would put them in a dangerous position
Support/ protection and regulation of domestic businesses; fair competition; entrepreneurship
Opportunity creation in foreign markets
Government wants to make jurisdiction competitive to have lots of companies want to set up
How does Business influence government?
Lobbying
A way to get government to enact/change a legislation
Lobbying Act - Lobbyers must be registered and follow specific rules
There to plead their case
Hired to represent company’s/group interes
Many times there is opposing sides of lobbyers
Trade associations - pool together a big group of people - representing members and their interests to government (example Ontario university lobbyers)
Collaberationg/Input
CRTC consoults with industry members
Advertising - Corporations influence voters
In Ontario and Canada
More and more restrictions on political advertising
Previously companies (third party organizations) would spend a ton of money on advertising that was negative political advertising
Would help all the other political parties
Trying to influence public votes
Companies would do this so they could get the policies they want for their company
Created grey area
Now more tighter regulations that businesses can have when it comes to advertising
How does government impact business, state the role, approach and impact.
Role | Approach | Impact |
Service Provider | Delivery, teaching | Competition, social goals |
Business Supports | Subsidies, trade agreements | Opportunity, protection |
Laws, Regulations | Competition, consumer, pollution laws, IP rights | Competion, consumer, protection, innovation, social goals, barriers |
Taxation | Income (Business and personal), Sales, Property Restrictive | Customer spending, incentives, barriers |
What are examples of service providers and what do they do?
Class rooms
Meet societal goals
Educated workforce
Roads
Mail delivery - seen as a service and competition (to UPS, Fed Ex, etc.)
Government act as a competitor to other businesses in society
In order to be a service provider the government must act as…
a customer to businesses
Buy the desks, and other supplies for schools
Buy the Vans for the mailman
Buy the equipment to make the roads
How does the government support business through subsidies?
Subsidies - Incentives
Example: give money to company's investing in green energy
Example: during the pandemic, government would pay up to 75% of their employees wages up to a certain number
Huge support to businesses
How does the government support businesses through trade agreements?
Trade agreements - importance of having relations with other countries to allow for expansion opportunities
Joe Biden seen as protectionism
Inflation reduction act passed in the USA
Gave huge subsidies to American base companies - gave money to customers money for buying electric cars that were American made
Canadian companies competing in the USA would have large challenges to compete
How does the government help businesses through laws and regulations?
One of the biggest approaches - competition act
In Canada we try to encourage the markets to drive the cost
As many competitors
The more the choice, the better the quality, and price
Forces businesses to compete
There to protect the consumer
Laws to protect the environment
Intellectual property rights
Patents, trade marks, copyrights
A way to protect innovation - and allow for establishment in the market
As well help inspire to build upon innovation and expand on the idea as the patent will expire
How does the government use taxation?
Income tax - taxed on income
Sales tax - GHT
Property tax - paid to the region
Funds policing, transit, sewers, garbage
Restrictive tax
Example cigarettes, alcohol, cannabis
Impacts consumer spending
Create incentives - climate action incentive, taxed on carbon tax
Connect the role governments play to porters five forces.
Customers
Large customer - high bargaining power
Able to demand a lower price
Competitor
Compete as a rival in your industry
Role on government - Regulator ( Laws)
Potential entrants can be high if low regulation
Potential entrants can be low if lots of regulation
Taxation
Industry where customers are taxed higher can impact the quantity
Provider of essential services
Substitutions - public transportation
Provider of incentives and assistance
Threat of new entry - supports start-ups
Compare sole proprietorship and partnership
Characteristic | Sole Proprietorship (1) | Partnership (2 + owners) |
Ease of formation | ||
Regulations |
| |
Control over profits and decisions | ||
Resources & capabilities | ||
Taxation* | ||
Liability | ||
Characteristic | Sole Proprietorship (1) | Partnership (2 + owners) |
Ease of formation | Simple; inexpensive | Simple; inexpensive; optional partner agreement |
Regulations | Few
| |
Control over profits and decisions | Complete | Shared |
Resources & capabilities | Whatever owner brings | Slightly more; more partners = more resources |
Taxation* | Taxed as personal income (advantage if business has losses) | Same but shared amounts |
Liability | Unlimited | Unlimited except if limited partner* |
What is an advantage if you have a sole proprietorship while having another job?
If the business losses money - you can deduct it from the salary currently being made
Allows for a reduction in what you have to pay for the government
As you are taxed less
Example:
Brandon can deduct his loss of $15000 in his bakery from his $60 000 salary as a prof and only be taxed on the $45 000
Only beneficial if you have a second income or else you just loose $15 000
What are the types of partnerships?
General
Must have at least one general partner in your partnership
This person has unlimited liability, actively manages day to day operations, makes these decisions as they have the greatest impact on them
All partners have joint and several liability
joint liability – together share liability → Bank can go after both of you
several liability – 1 may be liable for all → Bank can go after whoever is the easiest and has the money
Example if your partner flees the country you pay it all
Limited
limited partners liability = investment
limited partners cannot be active in management
at least one general partner
They can only go after your business assets, not personal assets
Less liable
Do not participate in day to day operations → Provide initial capital investment, Strategic decisions
Tell me about corperations
Seperate entity from the owners (bank cannot come after personal assets)
Crown corporation → owend by the crown (government of Canada) i.e. Canada Post
Public corporation → starts with IPO
Private corporation
Compare Private Corporation VS Sole Propritership
Characteristic | Sole Proprietorship (1) | Private corporation (1-49) |
Ease of formation | ||
Regulations | ||
Control over profits and decisions | ||
Resources & capabilities | ||
Taxation | ||
Liability |
Characteristic | Sole Proprietorship (1) | Private corporation (1-49) |
Ease of formation | Simple; inexpensive | Slightly more; still straightforward |
Regulations | Few | Slightly more but still simple |
Control over profits and decisions | Complete | Shared with other shareholders |
Resources & capabilities | Whatever owner brings | Whatever owners bring |
Taxation | Taxed as personal income (advantage if business has losses) | Taxed separately from shareholders; lower than personal income tax rates Once you are taxed if you choose to take the after tax profits and issue them back to shareholders as a form of a dividend - the shareholders dividend can be taxed (however there is a tax credit on a portion of the dividends)
|
Liability | Unlimited | Limited to investment except personal assets brought into business |
Compare private vs public corporation
Characteristic | Private corporation (1-49) | Public corporation (unlimited) |
Ease of formation | ||
Regulations | ||
Control over profits and decisions | ||
Resources & capabilities | ||
Taxation | ||
Liability |
Characteristic | Private corporation (1-49) | Public corporation (unlimited) |
Ease of formation | Straightforward; relatively inexpensive | Expensive; complicated |
Regulations | Relatively few; simple | Many Examples:
|
Control over profits and decisions | Shared with other shareholders | Board of Directors; less control The more shares you sell, the more money you can raise |
Resources & capabilities | Whatever owners bring | Can afford to buy them |
Taxation | Private corporate rates | Taxed separately from shareholders;
|
Liability | Limited to investment except personal assets brought into business | Limited to investment |
What is a social enterprise?
Hybrid between traditional for-profit businesses and non for profit
What are the key facets of a social enterprise
Help overcome market inequities/failures
Inefficient allocation of resources; markets don’t address all societal needs
Often in areas of education, health, environment, food insecurity, poverty
Looking to solve some of the worlds wicked problems
Usually focus in on trying to address the UN sustainable development goals
Social value is the primary objective BUT financial sustainability imperative
Donor and government funding not reliable
Look to create a sustainable business model that allows their profit to fund their social goal, but their end goal is finically motivated
Implications:
Economic value not required priority
Dual stakeholders – those served & those supporting; one or both pay
Example of a social enterprise
Grameen Bank – providing (micro-credit) loans to women in impoverished areas of rural Bangladesh
Wicked problem: poverty, no access to reasonable small loans
Social Value: women start business; able to invest in children’s education, building their own homes etc.
Self-sustaining: loans are repaid, capital given to others
Form: not-for profit
Constraint: no collateral
For-profit + Social Enterprise Partnership
what are the similarities and differences of a social enterprise and traditional entrepreneurship
Traditonal Entreprentuer | Socail Entrepenurship | |
Value definition and financial priority | Generate revenue, Financial ROI; finance is primary | Not about maximizing the profits, about making enough to sustain itself; social ROI |
Social Benefit Focus | Secondary | Primary |
Who they serve/stake holders | Paying customers Share holders/investors | Community/whoever is receiving the social benefit (beneficiary) |
Organizational form | For profit focused | Various forms - eg. Non for profit works with profit |
What do the differences mean for how you run the two businesses (social and traditional enterprise)?
Managerial preference, how and what you run your business will be impacted by the way you choose to run it
The world has become a …. system
interdependent
What are the driving forces of globalization
Cost and market benefit
tech makes it easier, faster, cheaper
If looking to grow and expand - international markets may have bigger opportunities
The ability to offshore manufacturing can create lower cost
Competitive pressure
If all of the competition is growing or doing something
Have to adapt to compete
Be aware of their doing and take advantage of what they aren't
Example: if they are only focused on international, you may focus on the local market
What are considerations of globalization
Should we do it
Barriers might encounter
Strategies to overcome these barriers
What are the internal factors you should identify when expanding internationally?
Internal Factors: Knowledge/ capabilities, Production, Preference, Finances
Look at if you have the recourses and capabilities to make it happen
Do you have the recourses and capacity- human and financial?