continental drift + plate tectonics
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
key idea 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Where do convection currents exist?
What do these do?
Asthenosphere
Caused by vast amounts of heat generated in mantle.
Semi-molten asthenosphere flows carrying with it the solid lithosphere and crust.
properties of the continental crust?
Thickness: 30-70km
Density: 2.6-2.7
Mineral composition: mainly granitic, silicon, aluminium
properties of the oceanic crust?
Thickness: 5-10km
Density: 3.0
Mineral composition: mainly basaltic, silicon and magnesium
properties of the mantle?
Thickness: To a depth of 2900km
Density: 5.6 at core
Mineral composition: rich in magnesium and iron
role of convecion currents?
heat from core creates currents in the mantle
hot magma rises, cools + sinks → drive plate movement
slab pull: subducting plate pulls rest of the plate
ridge push: new crust at mid ocean ridges pushes plates apart
Alfred Wegener's idea?
continental drift: continents used to fit together (Pangea) and moved apart overtime
plate tectonics: movement of plates on semi-fluid aesthenosphere
What is paleomagnetism?
magnetic minerals in basalt align with earth’s magnetic field
earth’s magnetic field flips
symmetrical magnetic stripes of either ridges
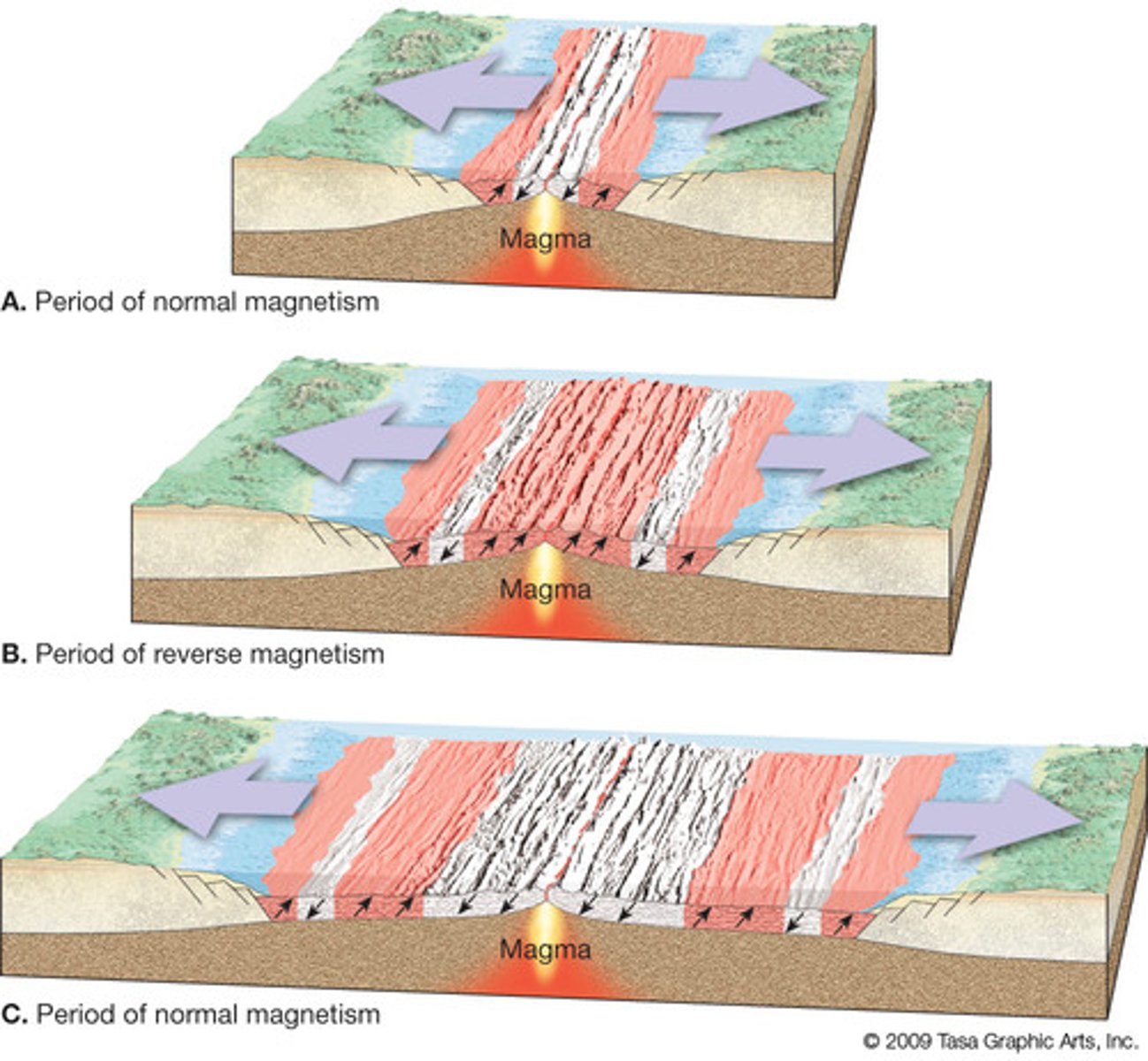
What is sea-floor spreading?
harry hess proposed it
occurs at mid ocean ridges → new oceanic crust is formed, pushes old crust away
what is age of sea floor rocks?
rocks are youngest near mid-ocean ridges, older further away
confirmed by radiometric dating techniques
what is evidence from ancient glaciations?
deposits found in tropical regions suggest past glaciations
e.g glacial till in S. America, Africa, India + Australia = connected near south pole
what is fossil records?
identical fossils found on different continents
mesosaurus: freshwater reptile - s. america + africa
glossopteris: plant found in s.america, africa, antarctica + india
most reliable evidence?
paleomagnetism: symmetrical stripes, reversed magnetic polarity match earth’s magnetic reversal timeline
age of oceanic rocks supports this
least reliable evidence?
fit of the continents: subjective observation → can be influenced by erosion, sea level change.
What are the 3 types of plate boundary?
Divergent (constructive)
Convergent (destructive)
Conservative/tranform
what is a divergent boundary?
2 plates move apart
mid-ocean ridges + rift valleys
processes: sea floor spreading, volcanicsm, shallow earthquakes
what is a convergent plate boundary?
2 plate move towards each other which leads to:
oceanic-continental
oceanic-oceanic
continental-continental
what is a conservative boundary?
2 plates slide past each other
transform faults + linear valleys
oceanic-continental (destructive)
oceanic subducts under continental due to its higher density
features: deep ocean trenches, fold mountains
oceanic-oceanic (destructive)
1 oceanic plate subducts under the other
features: deep ocean trenches, island arcs
continental-continental (collision)
2 plates collide → no subduction due to low density → compressed + uplifted crust
features: fold mountains, plateaus
What is a mid-ocean ridge?
Very long chains of mountains on the sea floor.
At intervals, ridges are broken by transform faults.
Vary in shape depending on rate of spreading
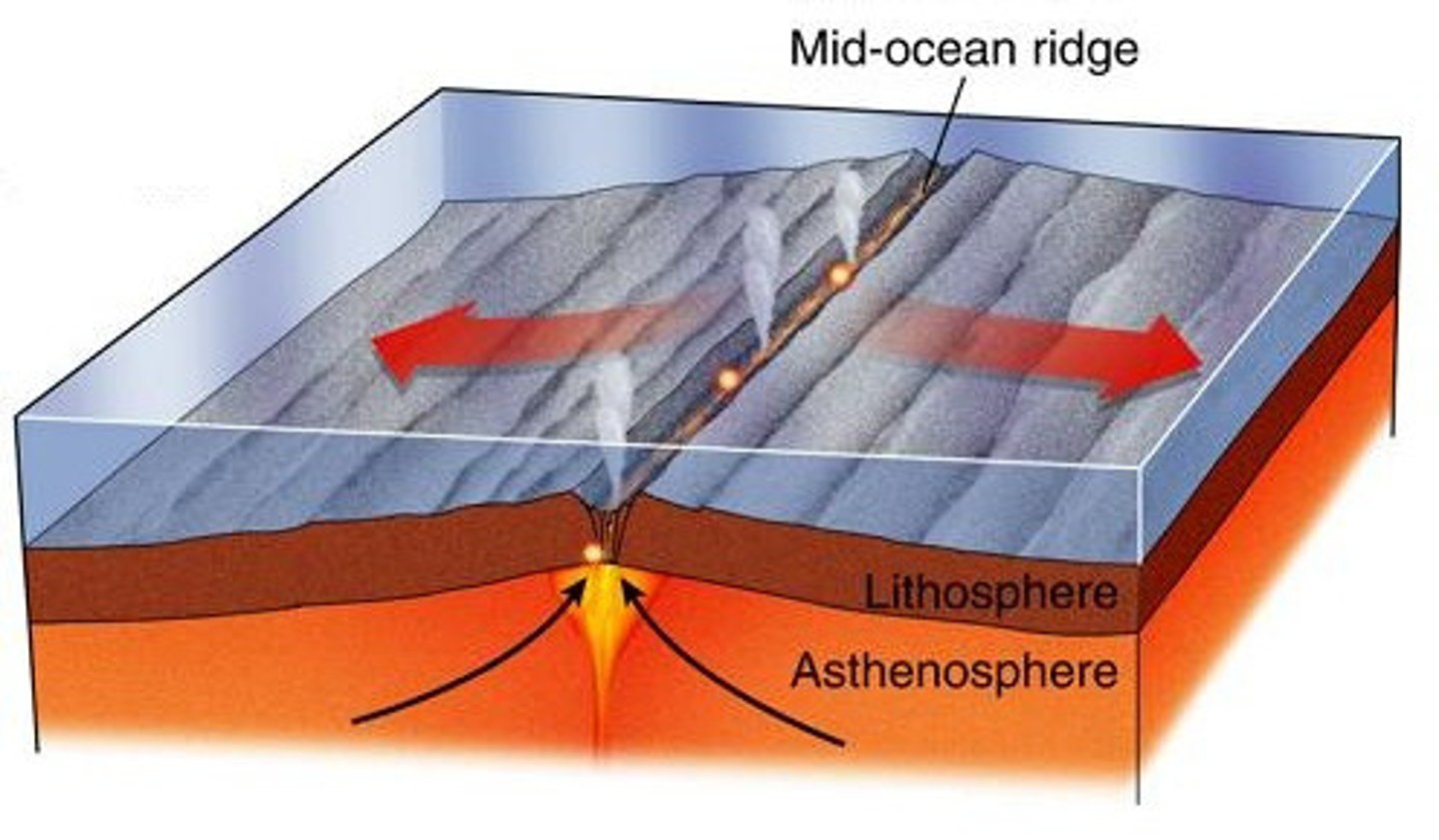
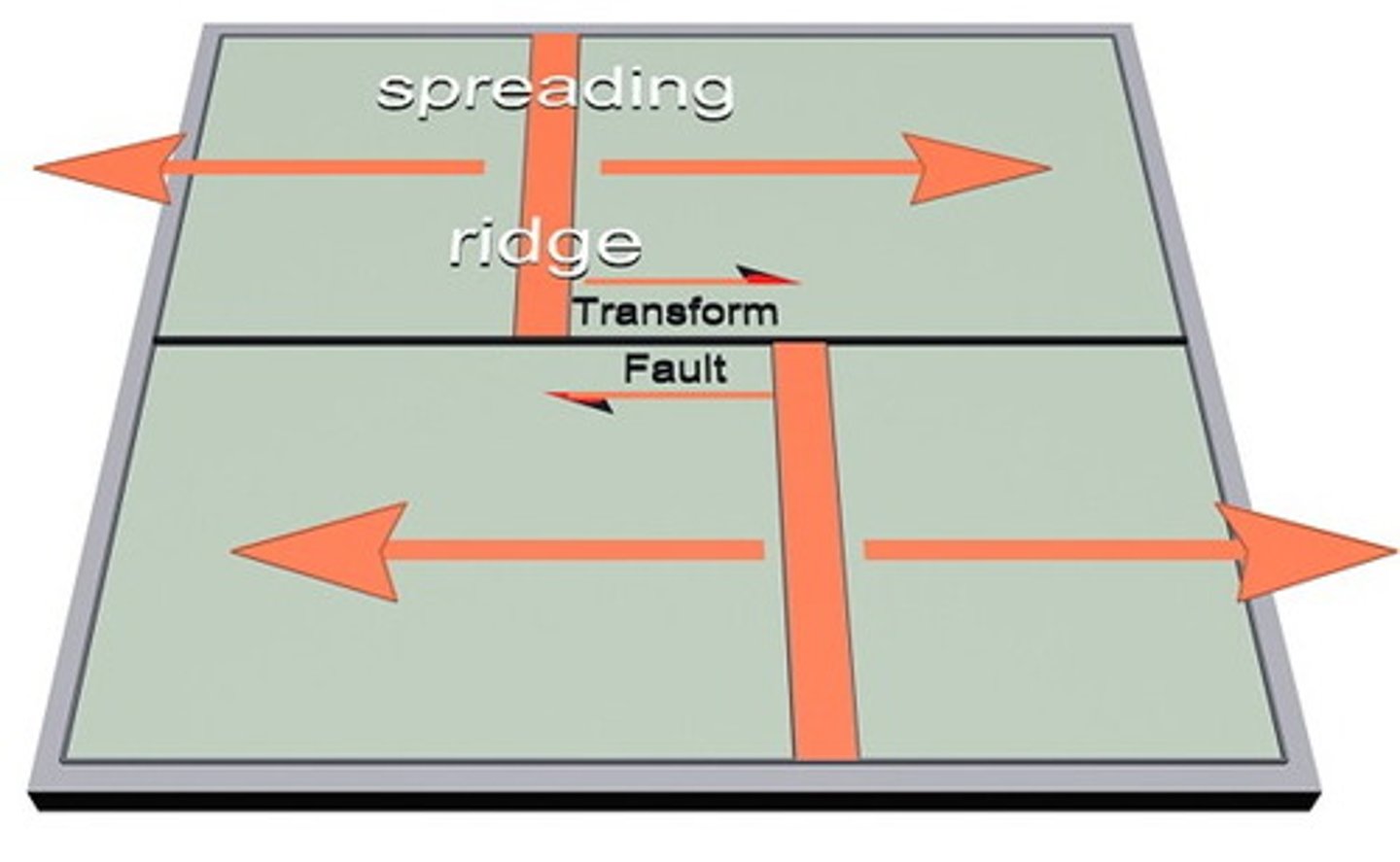
How does the spreading of plates cause earthquakes?
Transform faults
Small, shallow-focus earthquakes occur along their lengths as they slip.
What are transform faults?
Large-scale faults in the crust at right angles to a mid-ocean ridge, which range from tens to hundreds of km.
Describe the sequence of formation of a rift valley
(Underwater) Rising magma creates dome/bulge.
Plates continue to spread.
Brittle rocks fracture and fault.
Dome subsides (sinks) forming a steep-sided valley.
E.g. African rift valley (African plate splitting apart).
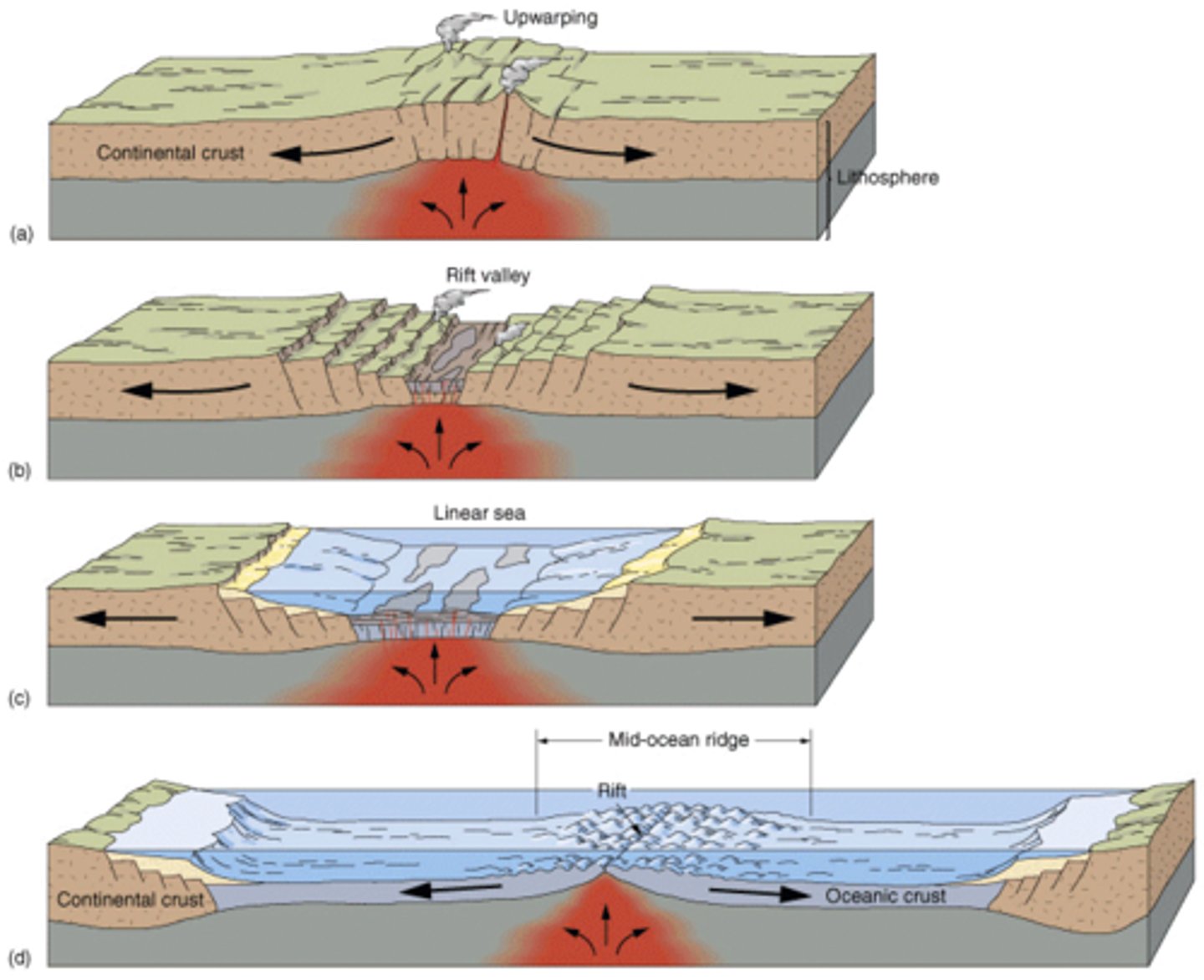
Rift zones on land
Continental crust must be thin for rifting to occur.
E.g. Red Sea northwards to Turkey.
Crust has been stretched, causing faulting and forming a sunken valley known as a graben.
As rift widened, magma erupted to surface.
Eventually rift valley sank below sea level, forming the present-day Red Sea.