Unit 1: Biochemistry - #1 Water Reactions, Properties of Water
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
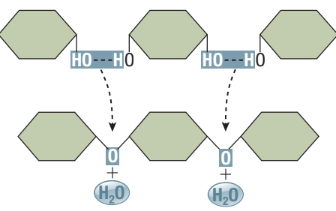
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction (Condensation)
Assembly of macromolecules
Removal of an -OH from one reactant and -H from another reactant
The -OH and -H form H2O, while the two reactants join together forming a covalent bond
Type of Anabolic Reaction: Used to assemble small molecules together into larger ones
Hydrolysis Reaction
Reverse of dehydration reactions
Disassembly of macromolecules
Water is a reactant to split a large molecule into smaller subunits
A covalent bond in the reactant molecule is broken and the -H and -OH from the water are attached, forming two products
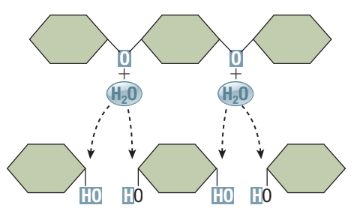
Catabolic Reaction
Macromolecules broken down into subunits (eg. digestion)
Properties of Water
Universal solvent
Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules, forming a water lattice.
This gives water the ability to float
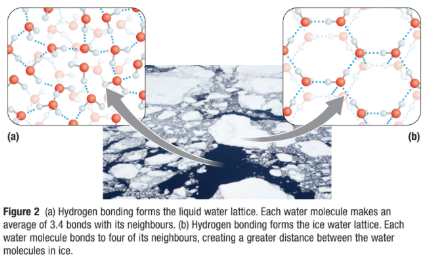
Liquid Water
Hydrogen bonds that hold the lattice together, constantly breaking and reforming in new configurations.
This gives liquid water its ability to float.
Ice
Water lattice is a rigid crystalline structure
Each water molecule in ice forms four hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules
This spaces water molecules farther apart that in liquid, so ice is less dense
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat: Amount of thermal energy required to increase the temperature of a given quantity of water by a degree.
As heat is added to water, most is absorbed by the process of breaking the H-bonds in the water lattice, which increases water temperature slowly
Water stays liquid until 100 degree C
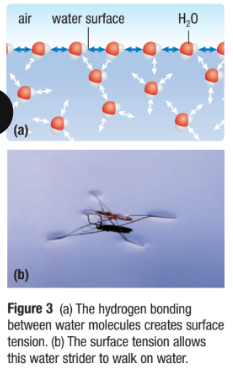
Cohesion (Water Sticks to Water)
A property of water where H-bond lattice results in water molecules staying close together
This creates surface tension: how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
This allows small insects to walk on water
Adhesion (Water Sticks to Other Stuff)
Property where water molecules can form H-bonds with other polar molecules
Eg. Water sticking to your skin when you get out of the shower
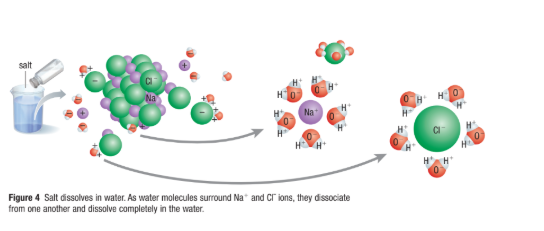
Aqueous Solutions
Water molecules are small and very polar
They surround other polar and charged molecules and ions
This hydration shell, reduces attraction between these other molecules and promote their separation (breaks the ion apart)
This separation allow the substance to dissolve in the solution
Hydrophilic Molecules
Polar molecules or ions that are strongly attracted to and very soluble in water
Hydrophobic Molecules
Non-polar molecules that are not strongly attracted to and soluble in water