6.2 The blood system
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Cardiovascular system
A closed circulatory system in vertebrates
3 types of blood vessels
Arteries, veins and capillaries
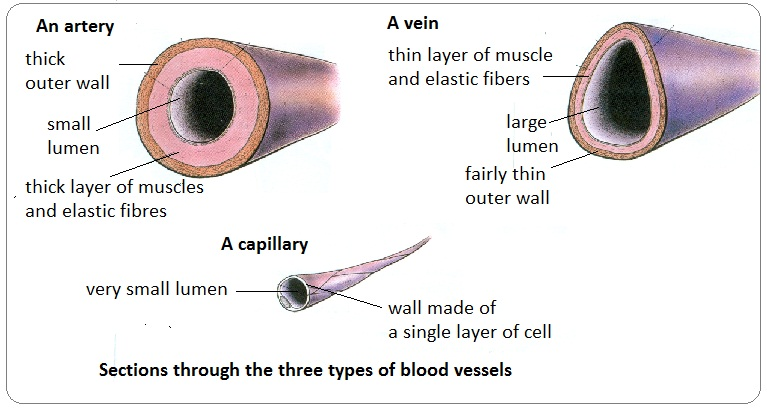
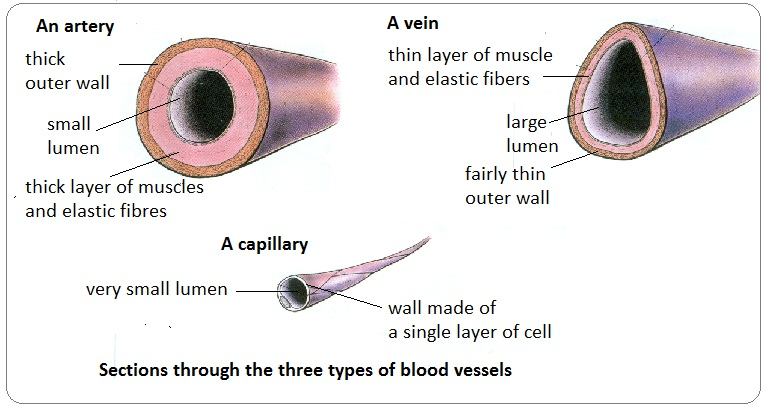
Arteries
A type of blood vessel which branches into arterioles and carries blood away from the heart into capillaries.
Thick wall and narrow lumen to deal with high blood pressure as the heart pumps the blood.
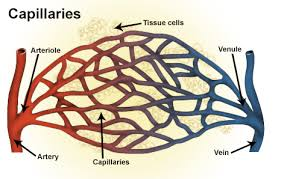
Capillary beds
Networks of capillaries where chemical exchange occurs between the cells and the blood.
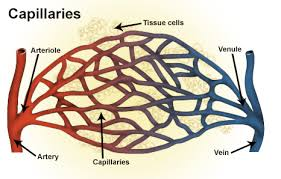
Venules
What the capillaries converge to which then converge back into veins.
Veins
Blood vessels which carry blood towards the heart
Wide lumen as blood flowing through there has low pressure so also thin walls.
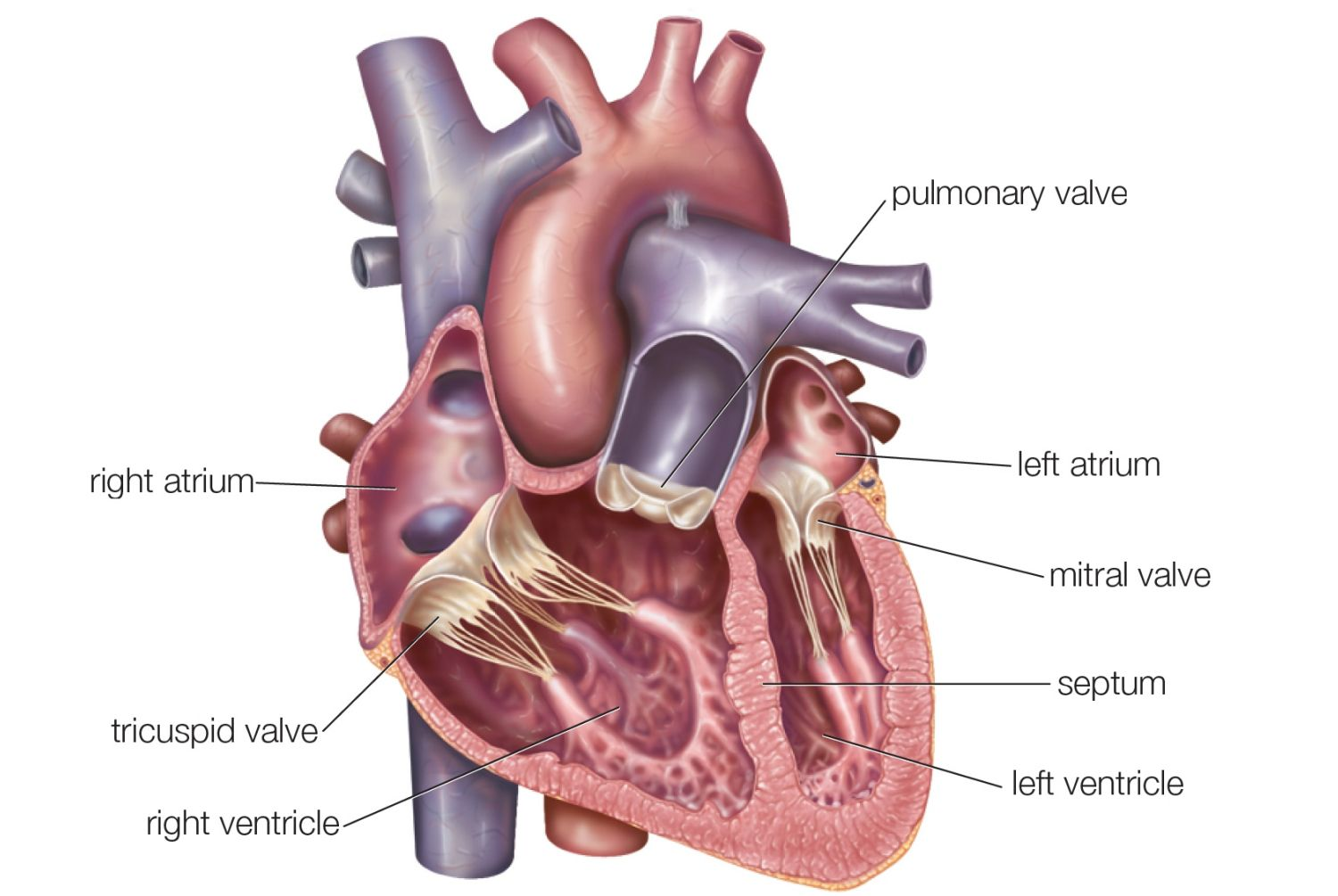
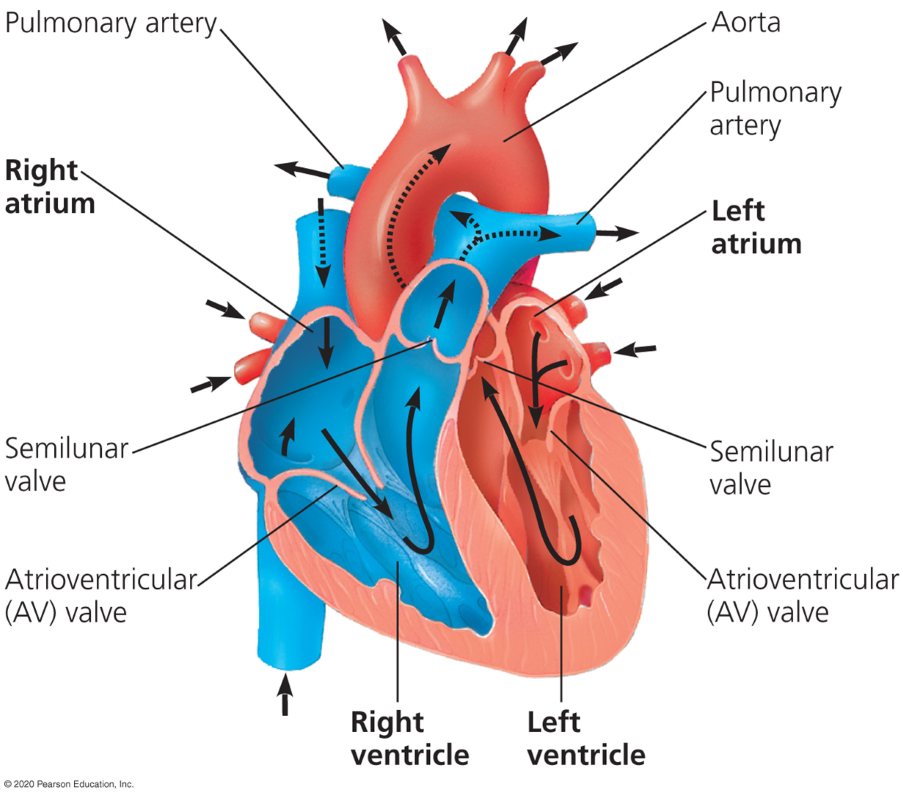
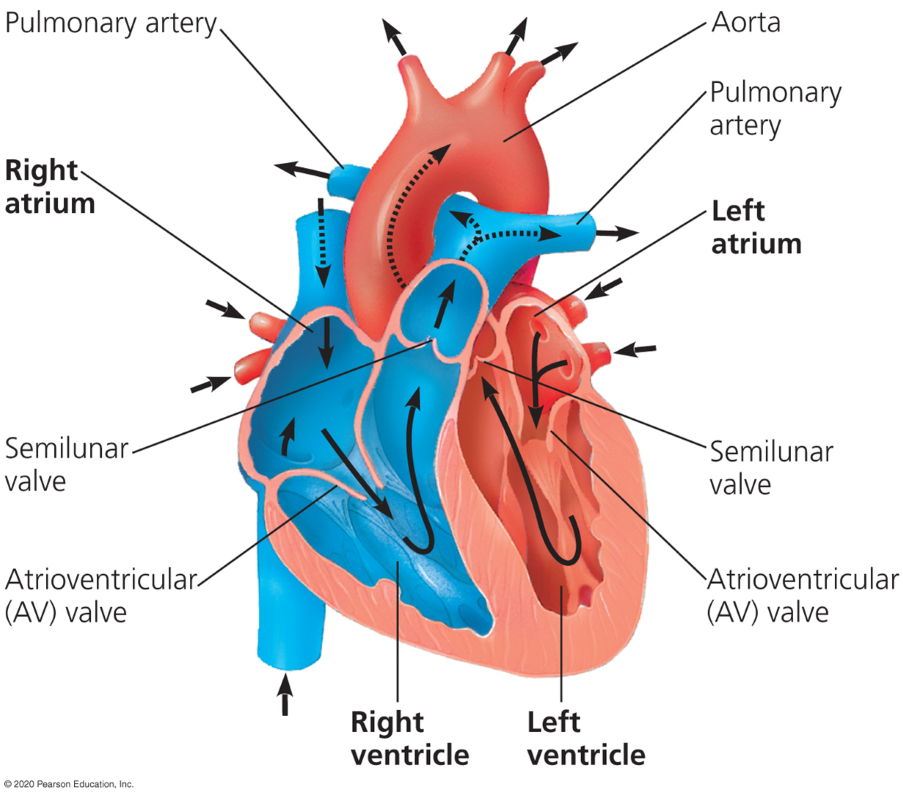
Atria
Where blood enters the heart
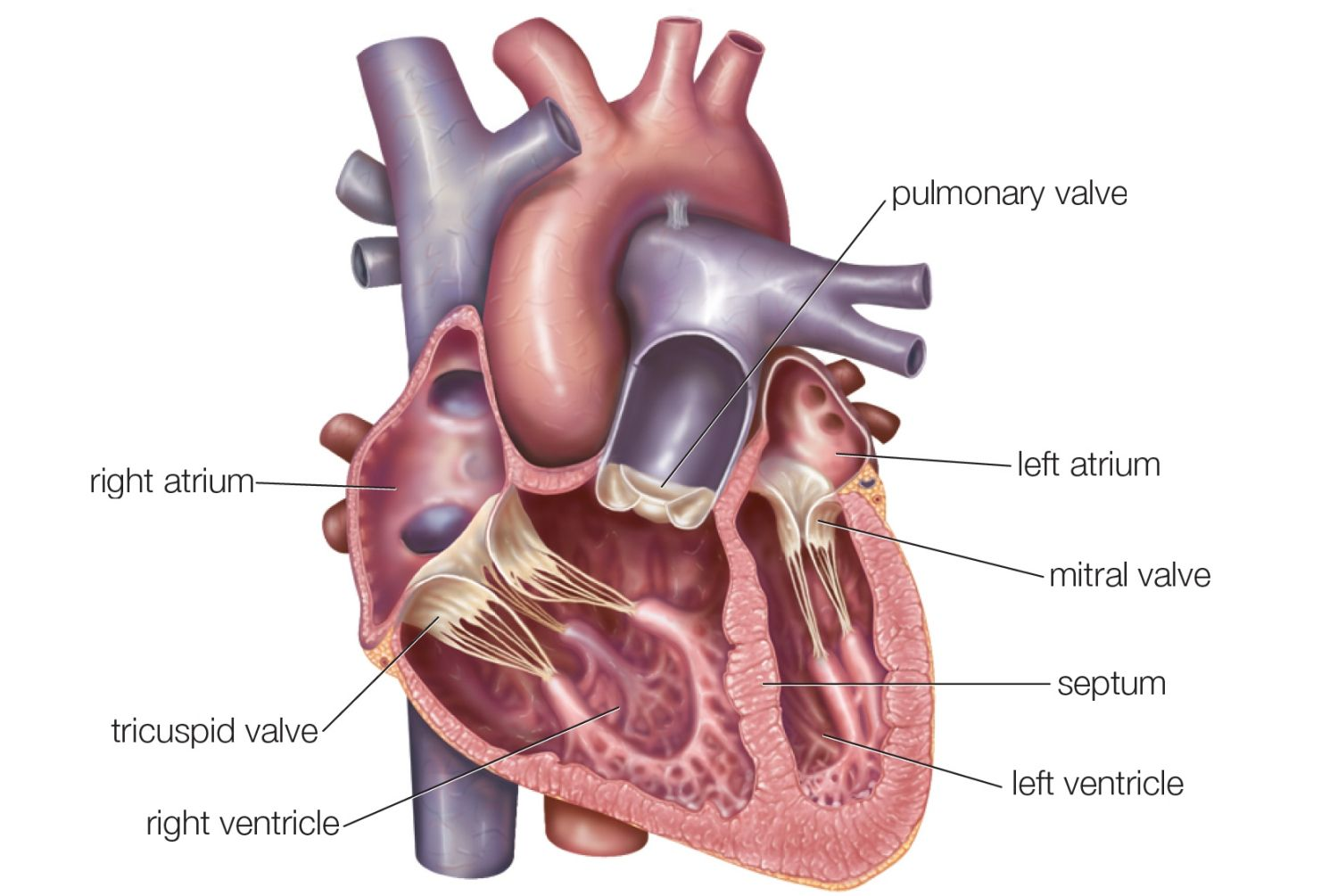
Ventricles
Where blood exits the heart
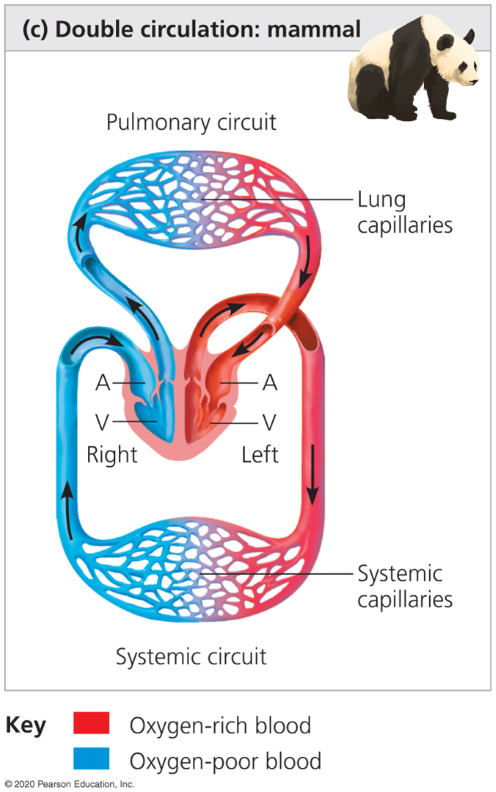
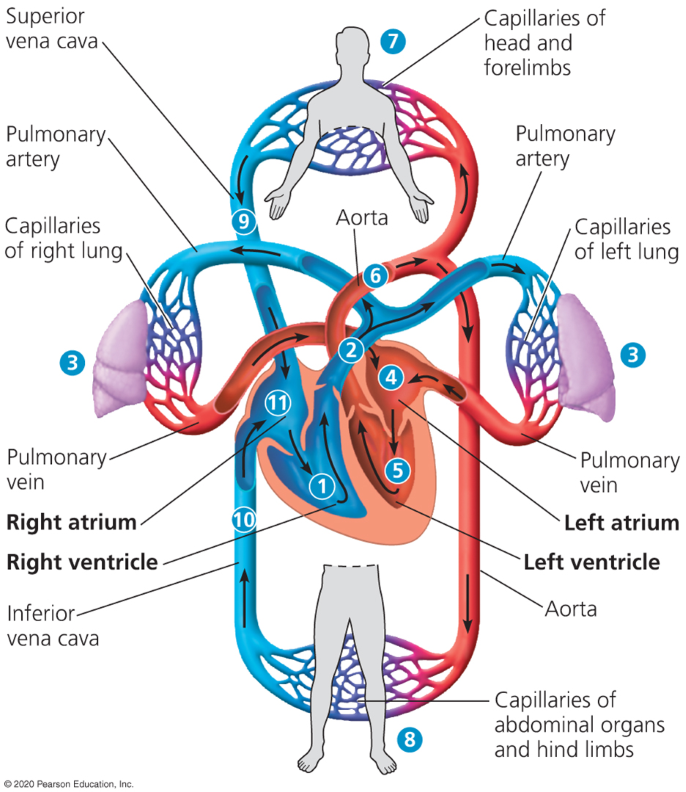
Double circulation
2 pumps in heart where oxygen poor and oxygen rich blood is pumped separately in the left and right sides of the heart.
Oxygen-poor blood is moved to the capillaries from the right side of the heart to get oxygen.
The left side of the heart moves oxygen rich blood to capillary beds in tissues and organs. Then the blood returns to the heart (systemic circuit)
Pulmonary arteries
Where the right ventricle begins pumping blood to the lungs
Loads O2 into blood and unloads Co2 in capillary beds of lungs
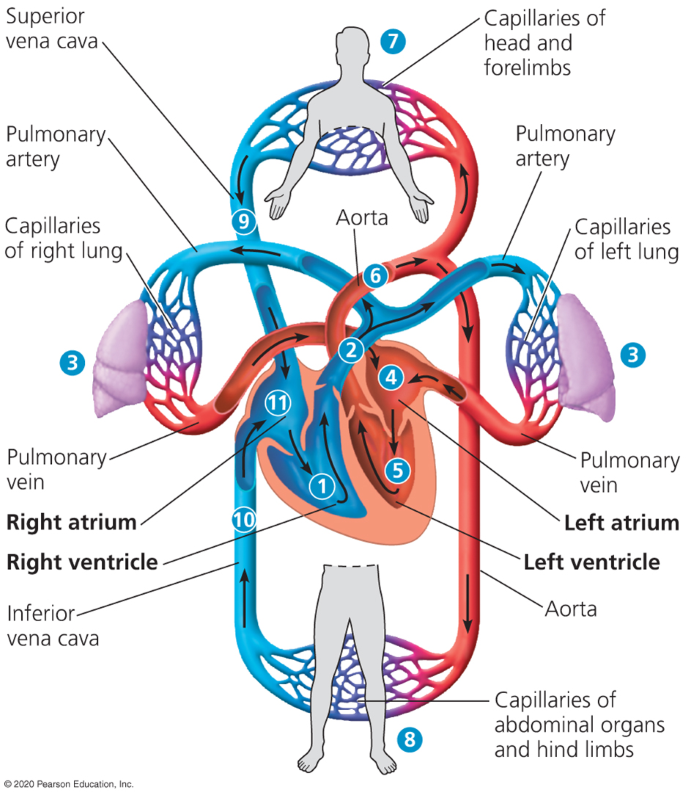
Pulmonary veins
Veins which allows oxygen rich blood to reenter the heart thorugh the left atrium.
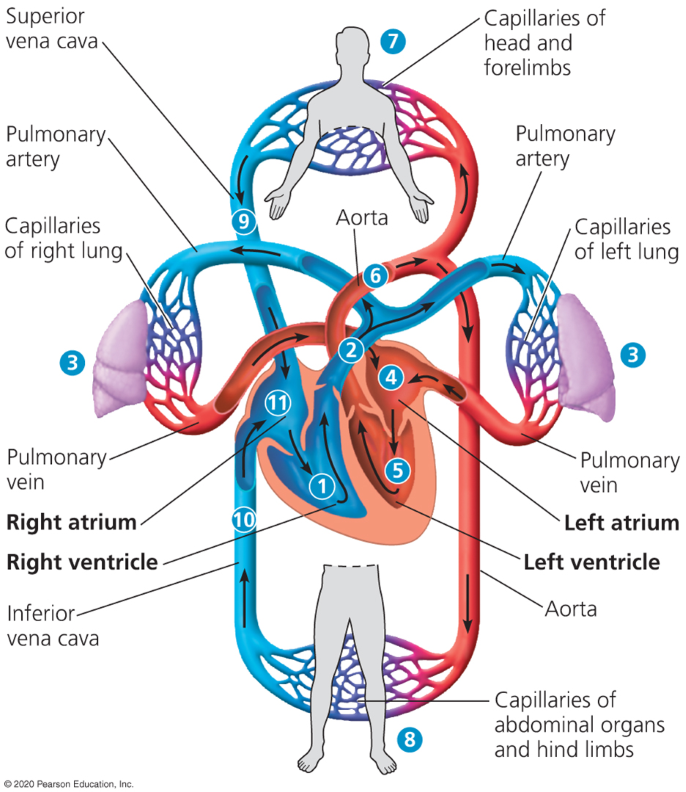
Aorta
Pumps blood that just entered the left atrium into the body
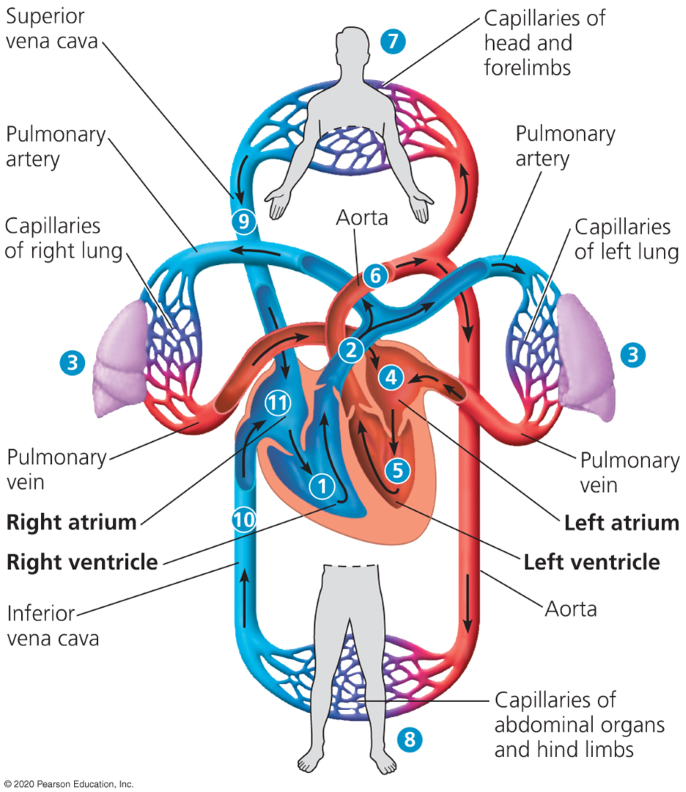
Superior vena cava
Large vein which moves deoxygenated blood back into the right atrium
Inferior vena cava
Another vein which moves deoxygenated blood back into the right atrium.
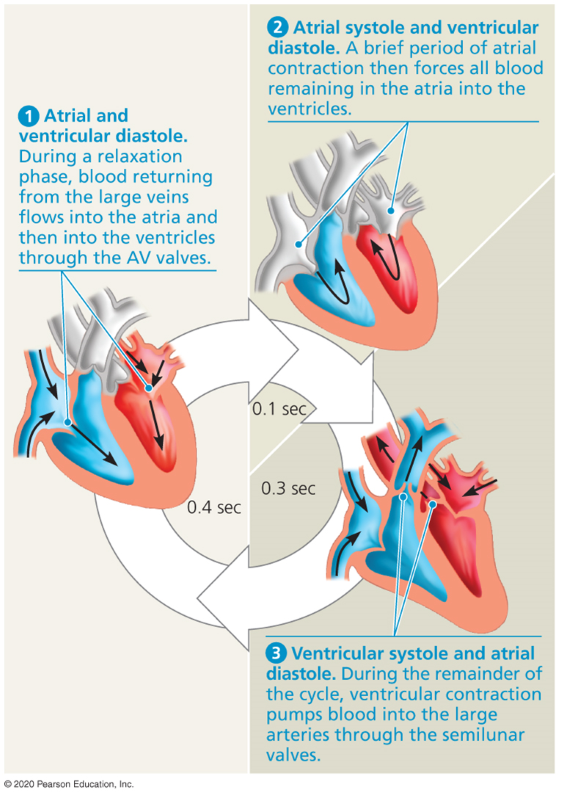
Cardiac cycle
A sequence of pumping and filling blood
Systole
The contraction of the cardiac cycle.
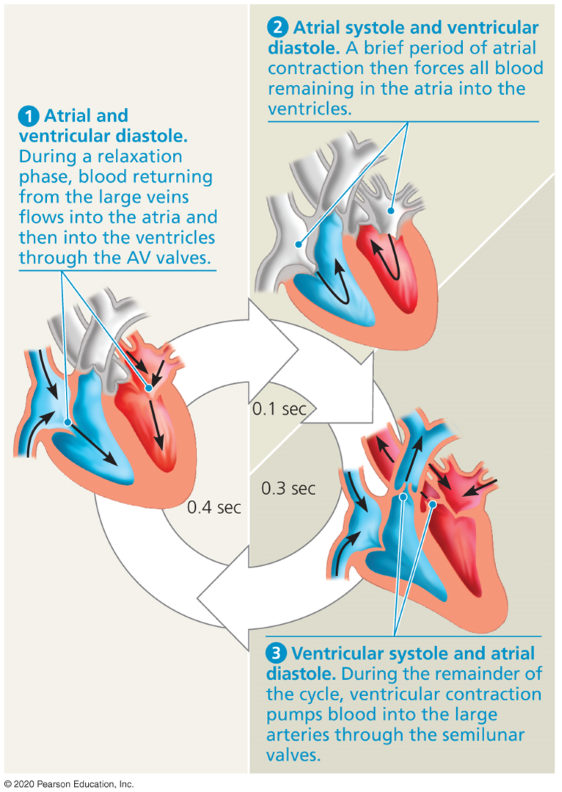
Diastole
The relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle
Atrioventricular valves (AV)
Valves which separate each atrium and ventricles
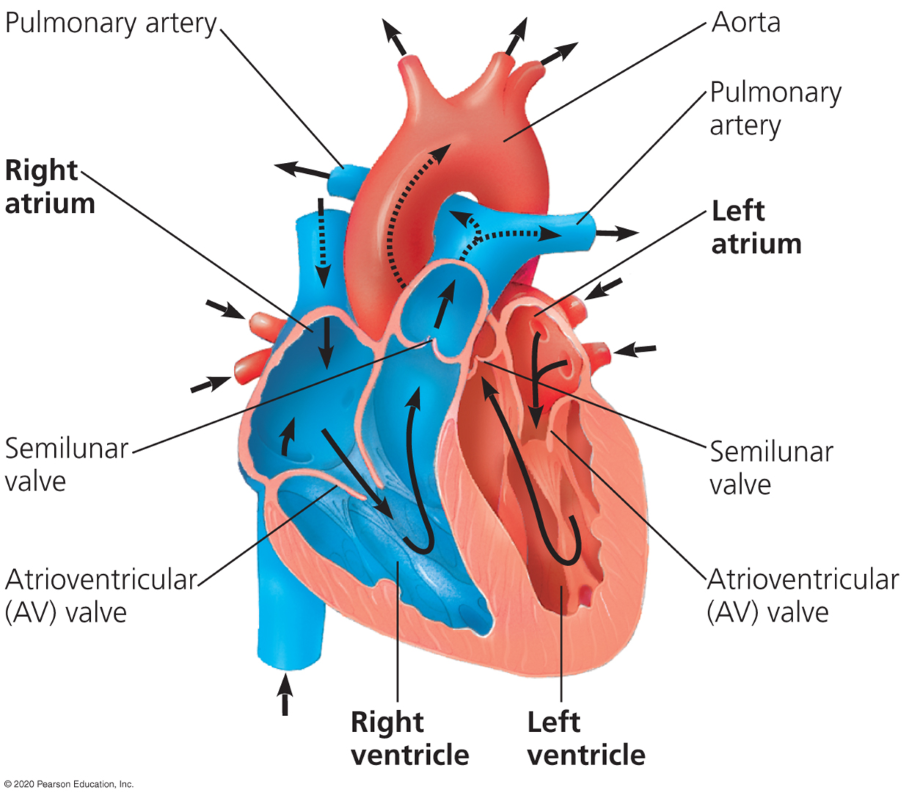
Semilunar valves
Valves which control blood flow to the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
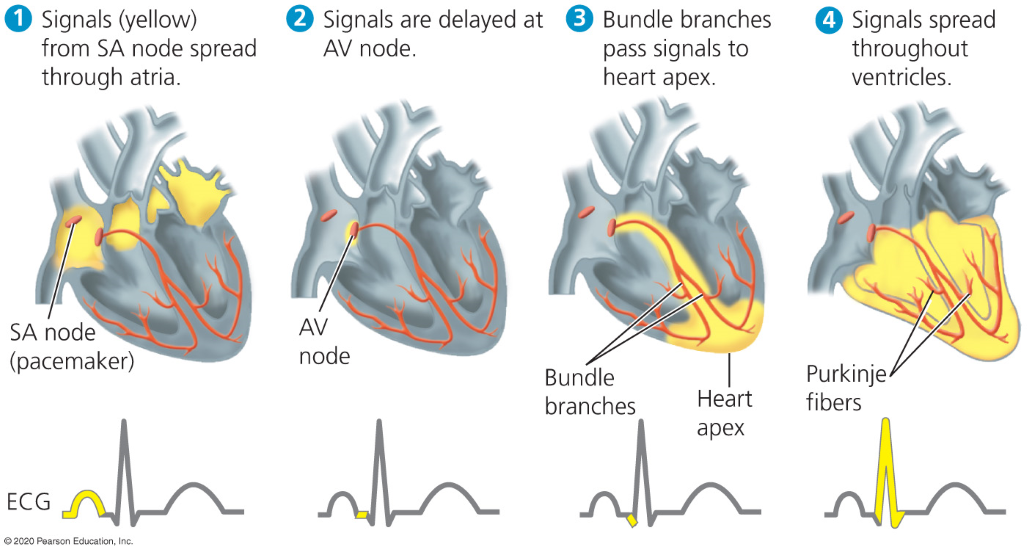
Sinoatrial (SA) nodes
Pacemaker which sets the rate and timing at which all other cardiac muscles cells contract.
Impulse from Sa node travesl to relay point at atrioventricular node
Impulses delayed at AV node which allows atria to empty before the ventricles contract
Also altered by hormones and temperature.
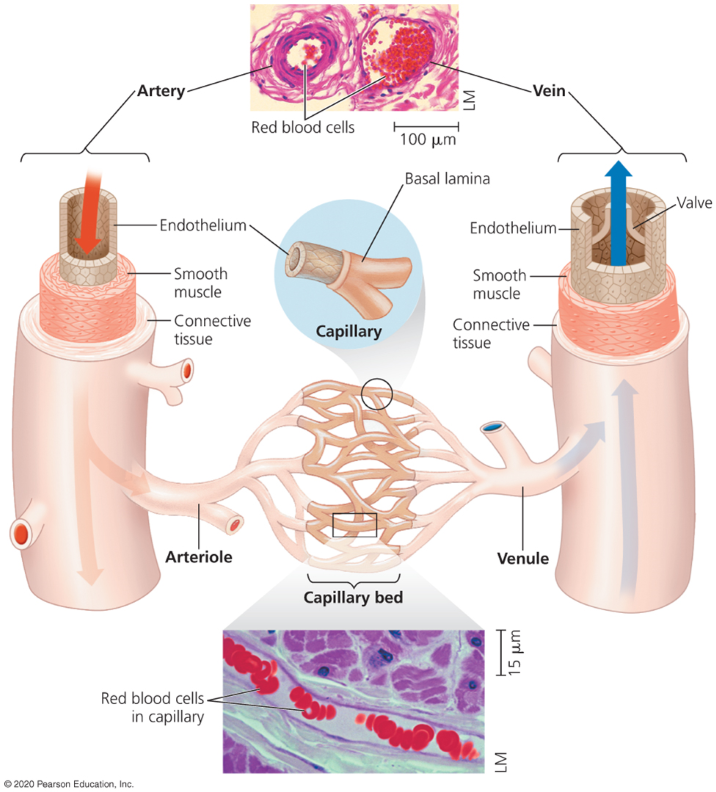
Endothelium
An epithelial layer that lines blood cells, allows minimal resistance to blood flow.
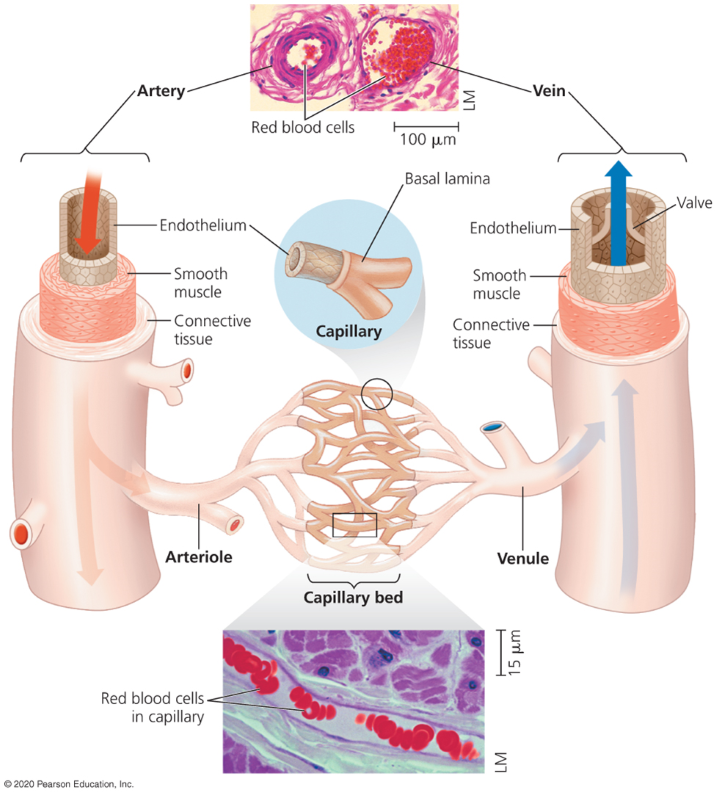
Endothelium and basal lamina (walls)
Thin walls that line capillaries.
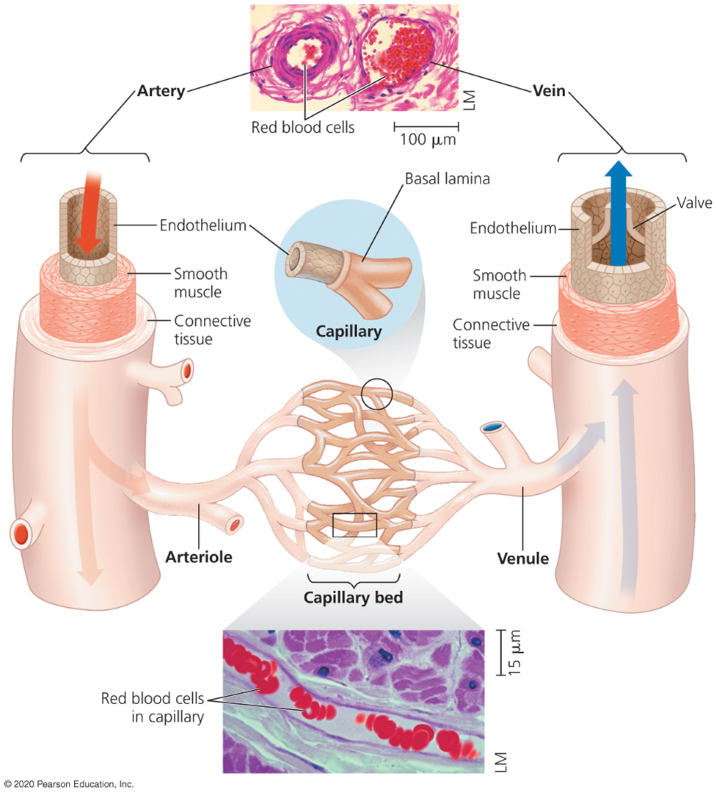
Walls of arteries and veins
Outer walls with collagen and elastic fibers
Inner layer with smooth muscle and more elastic fibers.
Blood flow velocity
Depends on the diameter of the vessels.
Capillarie blood flow slow for exchange of material
Veins have faster blood flow.
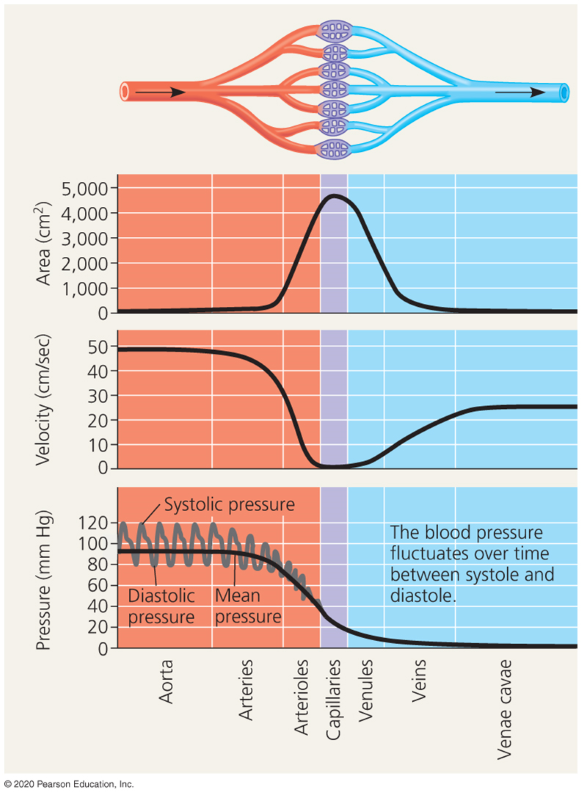
Blood pressure
Highest during systole (when heart contracts)
Lowest during diastole (when heart expands)
Pulse
Rhythmic bulging of artery walls with each heartbeat
Vasoconstriction
The contract of smooth muscle in arteriole walls, increasing blood pressure.
Vasodilation
The relaxation of smooth muscles in the arterioles which decreases blood pressure.
Capillary function
Blood flows through 5-10% of capillaries at a time.
Supplies tissues with blood
Exchanges substances along its walls
Drives fluid out of capillaries due to blood pressure.
Lymphatic system
Leaks fluid called lymph which leaks out of the capillary beds, draining into veins in the neck.
Swells when fighting infection due to the white blood cells multiplying.
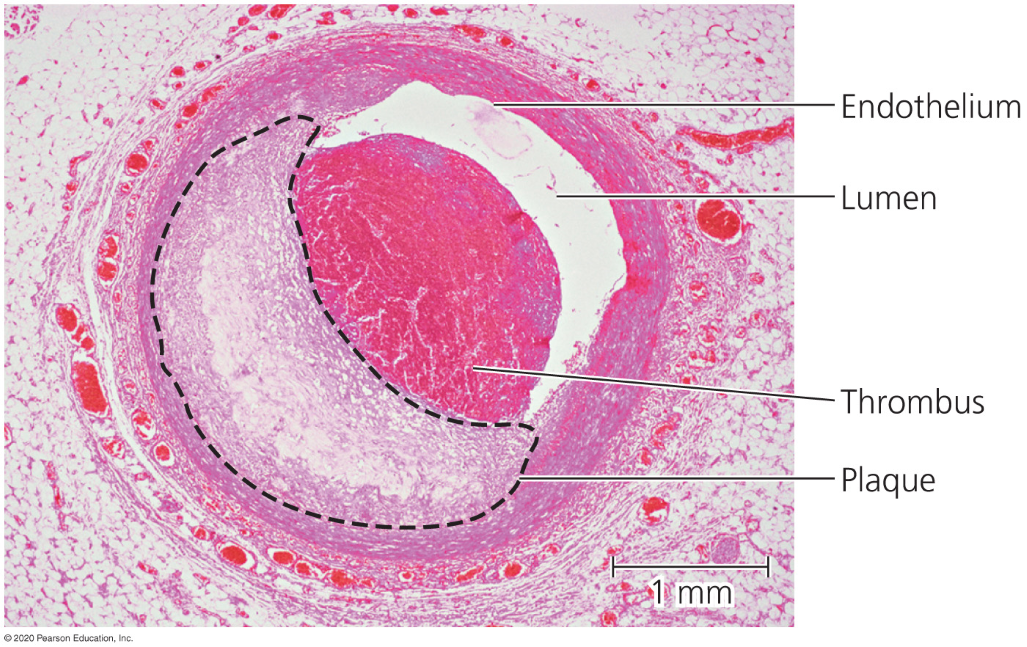
Atherosclerosis
The hardening of arteries due to the accumulation of fatty deposits.
Sometimes occurs due to fatty deposits.
Can also create thrombus which triggers stroke or heart attack.
Hypertension
High blood pressure