BIOL 103 Quizzes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
1
New cards
LESSON 1 QUIZ
2
New cards
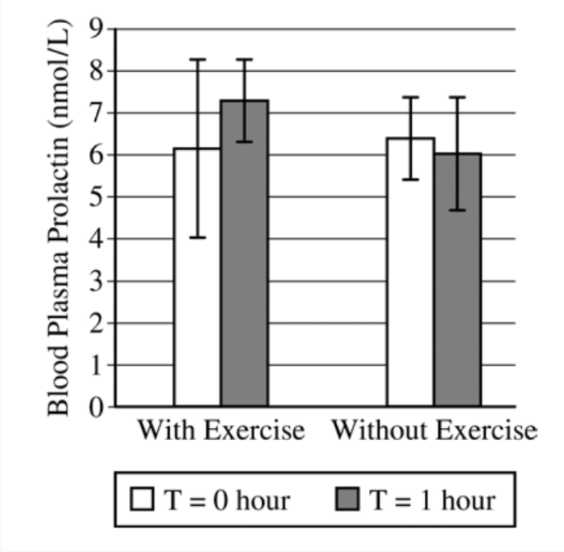
The experimental group is:
1. Choice 1 of 5:Blood plasma prolactin (nmol/L)
2. Choice 2 of 5:0 hour
3. Choice 3 of 5:Without Exercise
4. Choice 4 of 5:1 hour
5. Choice 5 of 5:With Exercise
1. Choice 1 of 5:Blood plasma prolactin (nmol/L)
2. Choice 2 of 5:0 hour
3. Choice 3 of 5:Without Exercise
4. Choice 4 of 5:1 hour
5. Choice 5 of 5:With Exercise
Choice 5 of 5:With Exercise
3
New cards
The dependent variable is:
1. Choice 1 of 5:0 hour
2. Choice 2 of 5:Without exercise
3. Choice 3 of 5:With Exercise
4. Choice 4 of 5:Blood plasma prolactin (nmol/L)
5. Choice 5 of 5:1 hour
1. Choice 1 of 5:0 hour
2. Choice 2 of 5:Without exercise
3. Choice 3 of 5:With Exercise
4. Choice 4 of 5:Blood plasma prolactin (nmol/L)
5. Choice 5 of 5:1 hour
Choice 4 of 5:Blood plasma prolactin (nmol/L)
4
New cards
Which of the following is the more likely hypothesis the scientists began this study with?
1. Choice 1 of 2:Exercising can cause prolactin levels to decrease.
2. Choice 2 of 2:People with high levels of prolactin can exercise longer than people without elevated prolactin levels.
1. Choice 1 of 2:Exercising can cause prolactin levels to decrease.
2. Choice 2 of 2:People with high levels of prolactin can exercise longer than people without elevated prolactin levels.
Choice 1 of 2:Exercising can cause prolactin levels to decrease.
5
New cards
How many mutant alleles of p53 are needed to have a mutant phenotype?
1. Choice 1 of 2:one
2. Choice 2 of 2:two
1. Choice 1 of 2:one
2. Choice 2 of 2:two
Choice 2 of 2:two
6
New cards
A scatterplot is a good tool for being able to see:
1. Choice 1 of 3:individual quantitative outliers
2. Choice 2 of 3:a large amount of categorical data
3. Choice 3 of 3:averages of many individual points
1. Choice 1 of 3:individual quantitative outliers
2. Choice 2 of 3:a large amount of categorical data
3. Choice 3 of 3:averages of many individual points
CHECK
7
New cards
LESSON 2 QUIZ
8
New cards
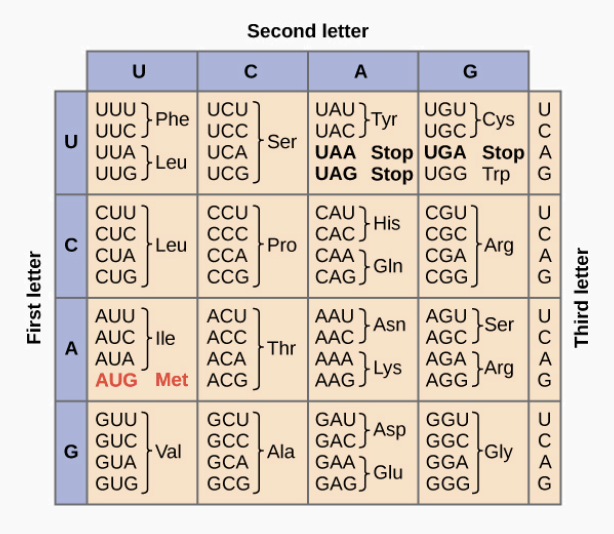
Below is a DNA template strand:
3’ TAC CGA TGT GCC CCA ATT 5’
What is the amino acid sequence that would be produced in the protein?
3’ TAC CGA TGT GCC CCA ATT 5’
What is the amino acid sequence that would be produced in the protein?
Met - Ala - Thr - Arg - Gly
9
New cards
If a newly synthesized protein is found in the golgi apparatus, where might it normally be found later?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Mitochondrion
2. Choice 2 of 4:Nucleus
3. Choice 3 of 4:Cytosol (liquid of cytoplasm)
4. Choice 4 of 4:On the outside of cell attached to plasma membrane
1. Choice 1 of 4:Mitochondrion
2. Choice 2 of 4:Nucleus
3. Choice 3 of 4:Cytosol (liquid of cytoplasm)
4. Choice 4 of 4:On the outside of cell attached to plasma membrane
Choice 4 of 4:On the outside of cell attached to plasma membrane
10
New cards
The genetic therapy called CRISPR would affect which molecule directly?
1. Choice 1 of 3:mRNA
2. Choice 2 of 3:protein
3. Choice 3 of 3:DNA
1. Choice 1 of 3:mRNA
2. Choice 2 of 3:protein
3. Choice 3 of 3:DNA
Choice 3 of 3:DNA
11
New cards
A gene coding for a nuclear protein has a mutation. Specifically, the DNA sequence for the nuclear localization signal is missing. Choose the best answer below about the most likely consequence of this change.
1. Choice 1 of 4:There will be no consequence since this signal is spliced out of the mRNA in the nucleus.
2. Choice 2 of 4:The ribosome will not be able to translate the mRNA, so no protein will be made.
3. Choice 3 of 4:The mRNA will not leave the nucleus for translation and no protein will be made.
4. Choice 4 of 4:The synthesized protein will remain in the cytoplasm until the cell recycles it.
1. Choice 1 of 4:There will be no consequence since this signal is spliced out of the mRNA in the nucleus.
2. Choice 2 of 4:The ribosome will not be able to translate the mRNA, so no protein will be made.
3. Choice 3 of 4:The mRNA will not leave the nucleus for translation and no protein will be made.
4. Choice 4 of 4:The synthesized protein will remain in the cytoplasm until the cell recycles it.
Choice 4 of 4:The synthesized protein will remain in the cytoplasm until the cell recycles it.
12
New cards
Which would be a way to “turn on” expression of the gamma (fetal) hemoglobin in adults to treat sickle cell disease?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Add a “gene switch” to increase expression from the beta hemoglobin gene
2. Choice 2 of 4:Increase expression of BCL11A mRNA
3. Choice 3 of 4:Destroy BCL11A mRNA
4. Choice 4 of 4:Correct a mutation in the beta hemoglobin gene
1. Choice 1 of 4:Add a “gene switch” to increase expression from the beta hemoglobin gene
2. Choice 2 of 4:Increase expression of BCL11A mRNA
3. Choice 3 of 4:Destroy BCL11A mRNA
4. Choice 4 of 4:Correct a mutation in the beta hemoglobin gene
Choice 3 of 4:Destroy BCL11A mRNA
13
New cards
LESSON 3 QUIZ
14
New cards
Select all the characteristics that describe Werner’s syndrome. You must mark all correct answers and no incorrect answers - no partial credit.
1. Choice 1 of 6:X-linked recessive
2. Choice 2 of 6:Autosomal recessive
3. Choice 3 of 6:Main phenotype is premature aging affecting many tissues and organs
4. Choice 4 of 6:Autosomal dominant
5. Choice 5 of 6:Main phenotype is muscle weakness and wasting in all muscle types
6. Choice 6 of 6:Pleiotropic
1. Choice 1 of 6:X-linked recessive
2. Choice 2 of 6:Autosomal recessive
3. Choice 3 of 6:Main phenotype is premature aging affecting many tissues and organs
4. Choice 4 of 6:Autosomal dominant
5. Choice 5 of 6:Main phenotype is muscle weakness and wasting in all muscle types
6. Choice 6 of 6:Pleiotropic
choice 2, 3, 6
15
New cards
To detect where WRN protein is located in a tissue, which would you need to use in your molecular technique?
1. Choice 1 of 3:Primary and secondary antibodies
2. Choice 2 of 3:Both of the above
3. Choice 3 of 3:A specific DNA primer
1. Choice 1 of 3:Primary and secondary antibodies
2. Choice 2 of 3:Both of the above
3. Choice 3 of 3:A specific DNA primer
Choice 1 of 3:Primary and secondary antibodies
16
New cards
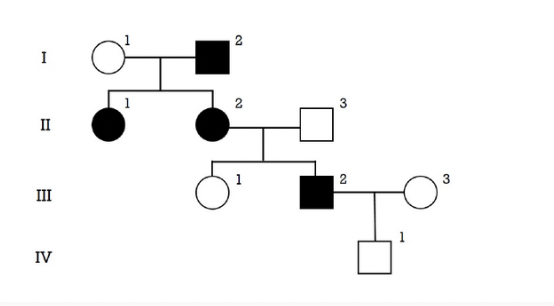
Considering the disease allele is very rare in the population (assume people "marrying in" are not carriers), this trait is most likely:
1. Choice 1 of 2:recessive
2. Choice 2 of 2:dominant
1. Choice 1 of 2:recessive
2. Choice 2 of 2:dominant
Choice 2 of 2:dominant
17
New cards
A male with an X-linked recessive disorder has many children with a female that does not have this disorder in her family (so she is not a carrier). The expected outcome would be:
1. Choice 1 of 5:Half the daughters will have the disorder
2. Choice 2 of 5:None of their children will have the disorder
3. Choice 3 of 5:All the sons will have the disorder and none of the daughters
4. Choice 4 of 5:All the daughters will have the disorder
5. Choice 5 of 5:Unable to predict given only this information
1. Choice 1 of 5:Half the daughters will have the disorder
2. Choice 2 of 5:None of their children will have the disorder
3. Choice 3 of 5:All the sons will have the disorder and none of the daughters
4. Choice 4 of 5:All the daughters will have the disorder
5. Choice 5 of 5:Unable to predict given only this information
Choice 2 of 5:None of their children will have the disorder
18
New cards
A wildtype allele and a mutant allele differ by a few nucleotides in the gene sequence for an important protein in neuron metabolism. In an individual who is a heterozygote, both the mutant and the wildtype proteins are synthesized in neurons. At the organismal level, the mutant allele is:
1. Choice 1 of 3:dominant
2. Choice 2 of 3:recessive
3. Choice 3 of 3:we cannot know from this information
1. Choice 1 of 3:dominant
2. Choice 2 of 3:recessive
3. Choice 3 of 3:we cannot know from this information
Choice 3 of 3:we cannot know from this information
19
New cards
LESSON 4 QUIZ
20
New cards
Gene *abc* is expressed ("on") in a heart cell. Gene *abc* is not expressed ("off") in a liver cell. This is because
1. Choice 1 of 4:Gene *abc* is present in heart cells but not in liver cells
2. Choice 2 of 4:The activators for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
3. Choice 3 of 4:Both the enhancers and the activators for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
4. Choice 4 of 4:The enhancers for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
1. Choice 1 of 4:Gene *abc* is present in heart cells but not in liver cells
2. Choice 2 of 4:The activators for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
3. Choice 3 of 4:Both the enhancers and the activators for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
4. Choice 4 of 4:The enhancers for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
Choice 2 of 4:The activators for gene *abc* are present in heart cells but not liver cells
21
New cards
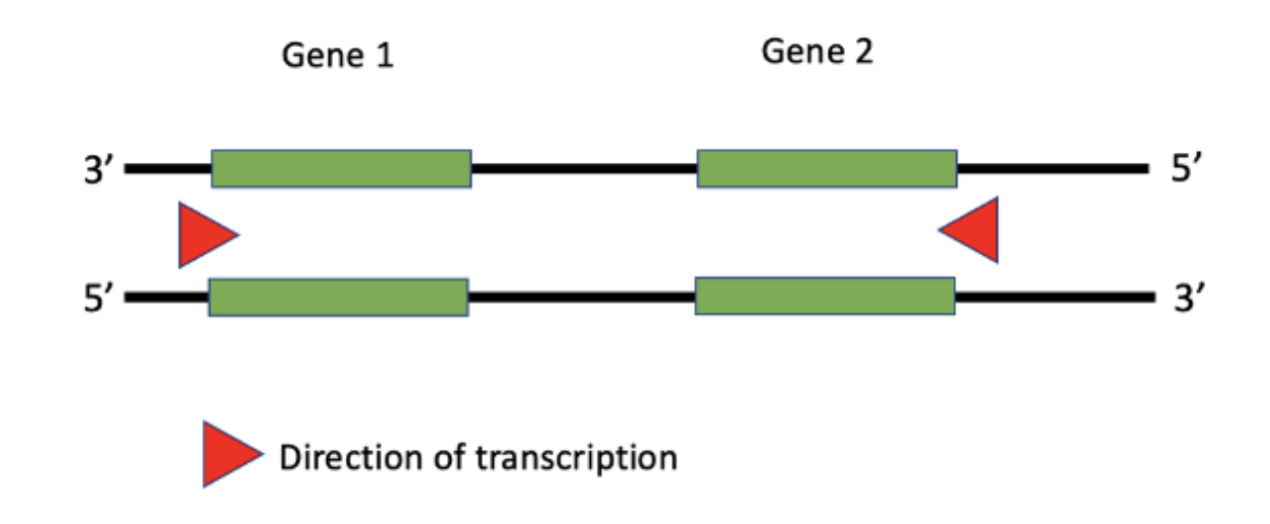
Fill in the blanks about transcription. For Gene 1, the **___** strand is the template strand and for Gene 2, the **____** strand is the non-template strand.
1. Choice 1 of 4:bottom, bottom
2. Choice 2 of 4:top, top
3. Choice 3 of 4:bottom, top
4. Choice 4 of 4:top, bottom
1. Choice 1 of 4:bottom, bottom
2. Choice 2 of 4:top, top
3. Choice 3 of 4:bottom, top
4. Choice 4 of 4:top, bottom
Choice 2 of 4:top, top
22
New cards
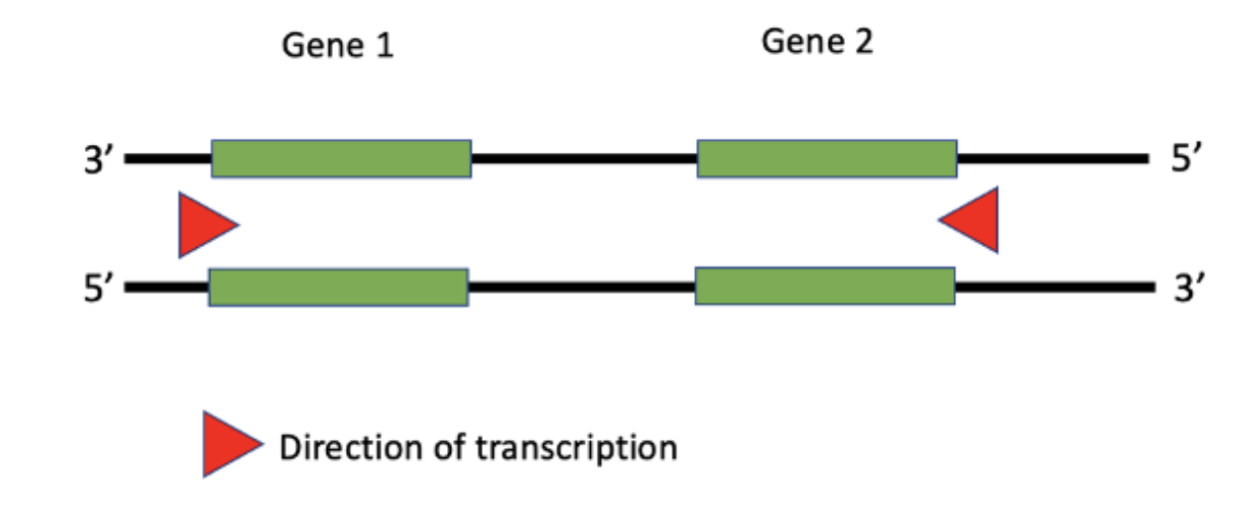
Would the promoter for Gene 2 be on the left or right of the green coding region?
1. Choice 1 of 3:Left
2. Choice 2 of 3:Right
3. Choice 3 of 3:Unable to determine using the information given
1. Choice 1 of 3:Left
2. Choice 2 of 3:Right
3. Choice 3 of 3:Unable to determine using the information given
Choice 2 of 3:Right
23
New cards
Which of these is most likely to lead to a longer protein compared to the wild type protein?
1. Choice 1 of 4:A mutation in the transcription termination sequence
2. Choice 2 of 4:A silent mutation in exon 4
3. Choice 3 of 4:None of the options would result in a longer protein.
4. Choice 4 of 4:A nonsense mutation in the first exon
1. Choice 1 of 4:A mutation in the transcription termination sequence
2. Choice 2 of 4:A silent mutation in exon 4
3. Choice 3 of 4:None of the options would result in a longer protein.
4. Choice 4 of 4:A nonsense mutation in the first exon
Choice 3 of 4:None of the options would result in a longer protein.
24
New cards
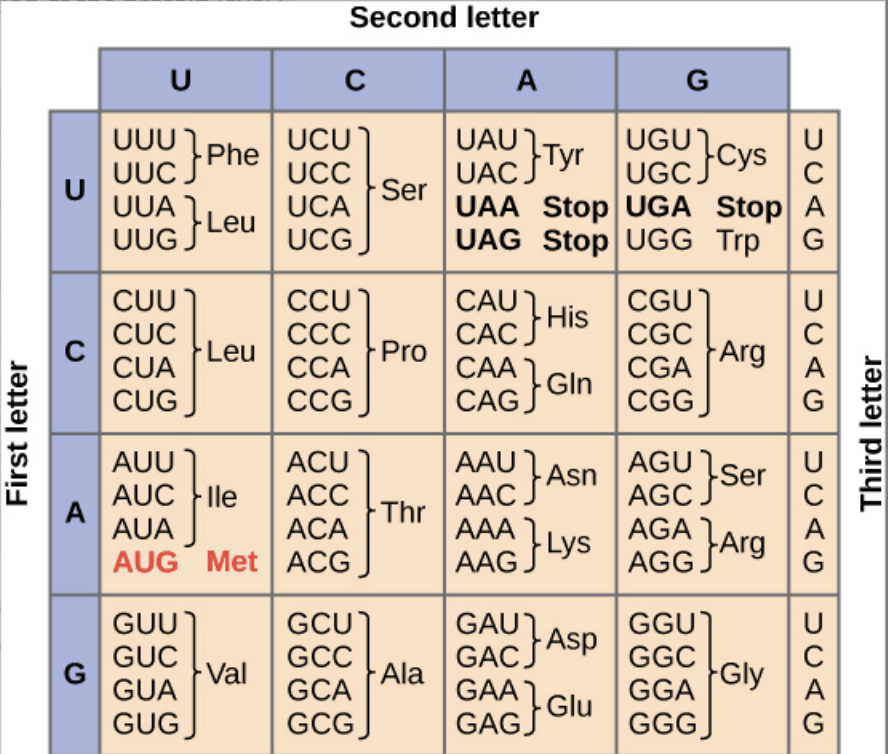
The top sequence is a wildtype template sequence. The single nucleotide mutation depicted in the bottom sequence will be what kind of mutation at the protein level?
\
WT: 3’ TAC TTT TCG CTC GGG 5’
MUTANT: 3’ TAC TTT TCG ATC GGG 5’
\
1. Choice 1 of 3:nonsense
2. Choice 2 of 3:missense
3. Choice 3 of 3:silent
\
WT: 3’ TAC TTT TCG CTC GGG 5’
MUTANT: 3’ TAC TTT TCG ATC GGG 5’
\
1. Choice 1 of 3:nonsense
2. Choice 2 of 3:missense
3. Choice 3 of 3:silent
Choice 1 of 3:nonsense
25
New cards
LESSON 5 QUIZ
26
New cards
Select all that would be true if I had a missense mutation in an gene:
1. Choice 1 of 4:The missense mutant allele would be the same size as wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
2. Choice 2 of 4:The missense mutant allele would be a different size compared to wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
3. Choice 3 of 4:The missense mutant protein would be a different size by Western compared to the wildtype protein
4. Choice 4 of 4:The missense mutant protein would be the same size by Western as the wildtype protein
1. Choice 1 of 4:The missense mutant allele would be the same size as wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
2. Choice 2 of 4:The missense mutant allele would be a different size compared to wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
3. Choice 3 of 4:The missense mutant protein would be a different size by Western compared to the wildtype protein
4. Choice 4 of 4:The missense mutant protein would be the same size by Western as the wildtype protein
choice 1, 4
27
New cards
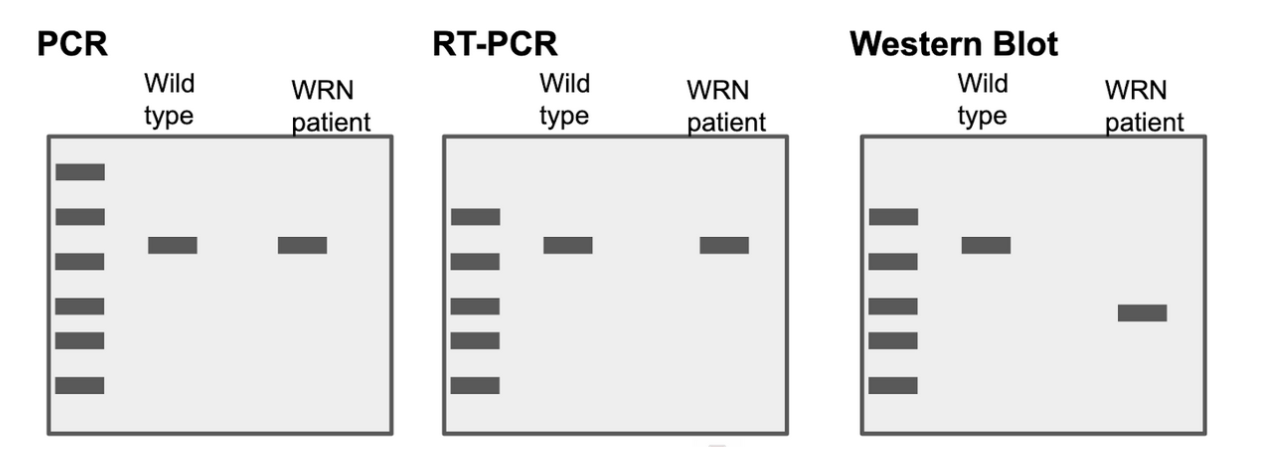
Which of the following techniques shown examines RNA?
1. Choice 1 of 4:PCR and RT-PCR
2. Choice 2 of 4:RT-PCR
3. Choice 3 of 4:Western
4. Choice 4 of 4:PCR
1. Choice 1 of 4:PCR and RT-PCR
2. Choice 2 of 4:RT-PCR
3. Choice 3 of 4:Western
4. Choice 4 of 4:PCR
Choice 2 of 4:RT-PCR
28
New cards
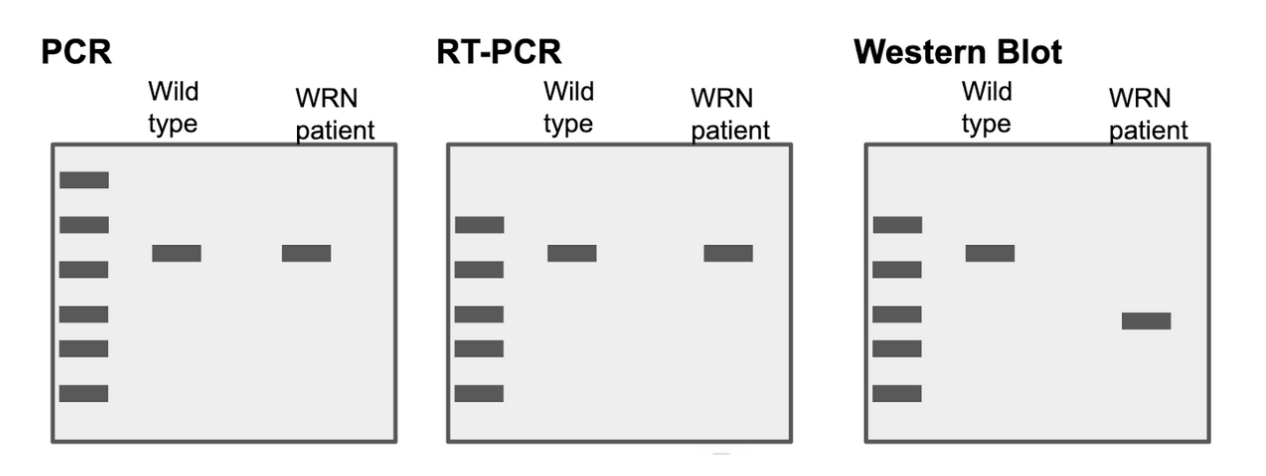
The image above shows that the individual with Werner syndrome (WRN) is:
1. Choice 1 of 2:Homozygous
2. Choice 2 of 2:Heterozygous
1. Choice 1 of 2:Homozygous
2. Choice 2 of 2:Heterozygous
Choice 1 of 2:Homozygous
29
New cards
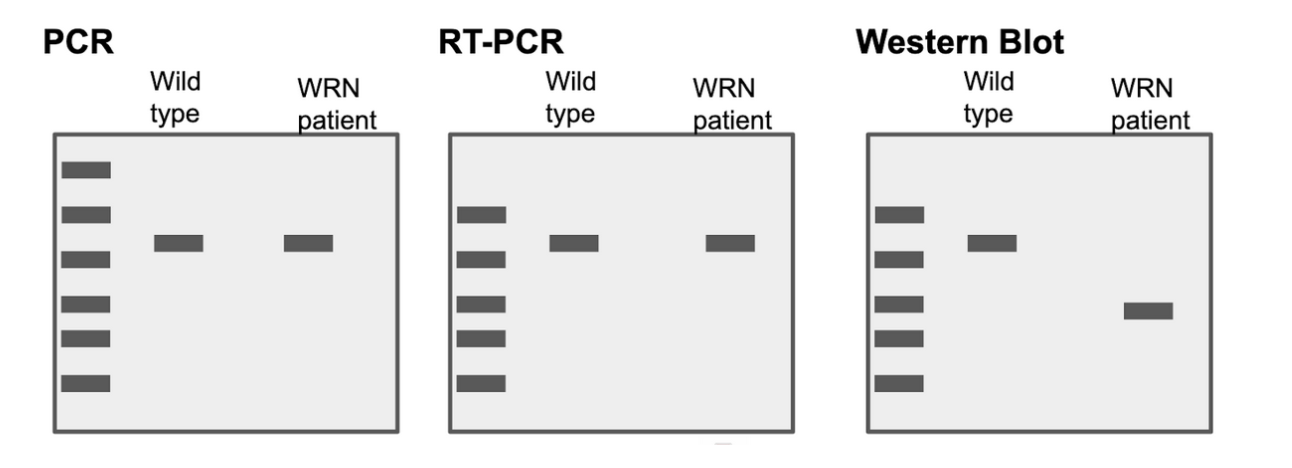
The individual with Werner syndrome:
1. Choice 1 of 3:Makes a protein that is longer than wildtype
2. Choice 2 of 3:Doesn’t make a protein
3. Choice 3 of 3:Makes a protein that is shorter than wildtype
1. Choice 1 of 3:Makes a protein that is longer than wildtype
2. Choice 2 of 3:Doesn’t make a protein
3. Choice 3 of 3:Makes a protein that is shorter than wildtype
Choice 3 of 3:Makes a protein that is shorter than wildtype
30
New cards
Select all that would be true if I had a nonsense mutation in an exon of a gene:
1. Choice 1 of 4:The nonsense mutant protein would be a different size by Western compared to the wildtype protein
2. Choice 2 of 4:The nonsense mutant allele would be the same size as wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
3. Choice 3 of 4:The nonsense mutant protein would be the same size by Western as the wildtype protein
4. Choice 4 of 4:The nonsense mutant allele would be a different size compared to wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
1. Choice 1 of 4:The nonsense mutant protein would be a different size by Western compared to the wildtype protein
2. Choice 2 of 4:The nonsense mutant allele would be the same size as wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
3. Choice 3 of 4:The nonsense mutant protein would be the same size by Western as the wildtype protein
4. Choice 4 of 4:The nonsense mutant allele would be a different size compared to wildtype by PCR-electrophoresis
choice 1, 2
31
New cards
LESSON 7 QUIZ
32
New cards
Heat disrupts hydrogen bonds. What would be the consequence of heating DNA?
1. Choice 1 of 3:the double stranded DNA would become single stranded
2. Choice 2 of 3:The nucleotides would separate from each other leading to a pool of free nucleotides
3. Choice 3 of 3:the nitrogenous bases would separate from the DNA backbone leaving free nitrogenous bases in solution
1. Choice 1 of 3:the double stranded DNA would become single stranded
2. Choice 2 of 3:The nucleotides would separate from each other leading to a pool of free nucleotides
3. Choice 3 of 3:the nitrogenous bases would separate from the DNA backbone leaving free nitrogenous bases in solution
Choice 1 of 3:the double stranded DNA would become single stranded
33
New cards
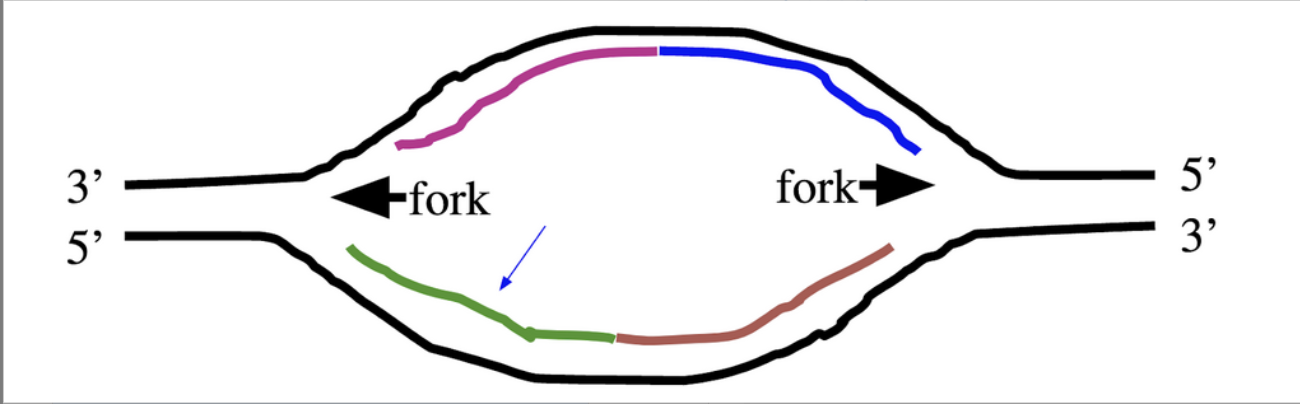
Which of the following newly-synthesized DNA strands would at some point contain RNA? Choose all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 4:the green strand on the bottom left
2. Choice 2 of 4:the blue strand on the top right
3. Choice 3 of 4:the purple strand on the top left
4. Choice 4 of 4:the brown strand on the bottom right
1. Choice 1 of 4:the green strand on the bottom left
2. Choice 2 of 4:the blue strand on the top right
3. Choice 3 of 4:the purple strand on the top left
4. Choice 4 of 4:the brown strand on the bottom right
all of the above
34
New cards
Which statement is true about the nitrogenous base composition of double stranded DNA?
1. Choice 1 of 3:the percentage of A+T = the percentage of G+C
2. Choice 2 of 3:the percentage of A+G = the percentage of T+C
3. Choice 3 of 3:both of the above statements are true
1. Choice 1 of 3:the percentage of A+T = the percentage of G+C
2. Choice 2 of 3:the percentage of A+G = the percentage of T+C
3. Choice 3 of 3:both of the above statements are true
Choice 2 of 3:the percentage of A+G = the percentage of T+C
35
New cards
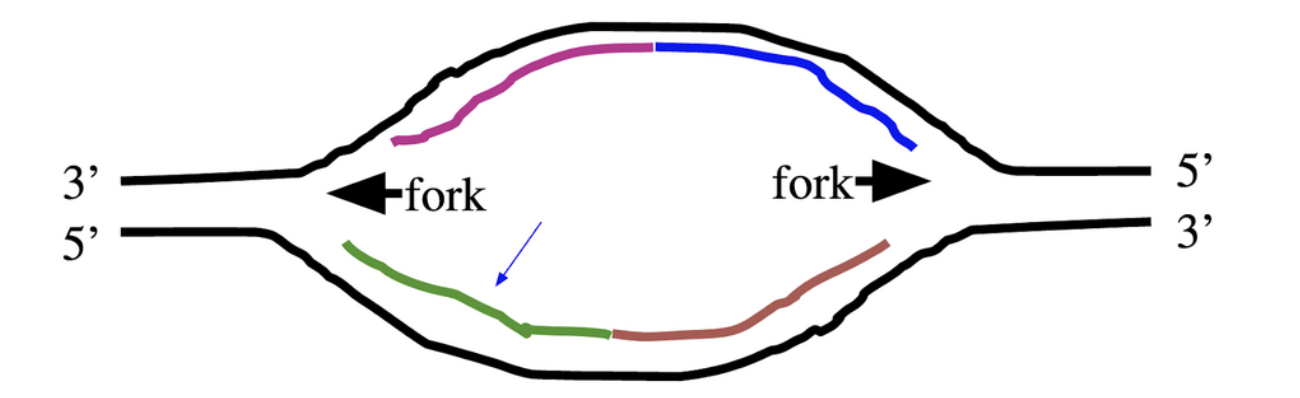
The arrow on the bottom left is pointing to a region of DNA that is being replicated:
1. Choice 1 of 2:discontinuously
2. Choice 2 of 2:continuously
1. Choice 1 of 2:discontinuously
2. Choice 2 of 2:continuously
Choice 2 of 2:continuously
36
New cards
You are designing a drug to block DNA polymerization (the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase). You want to design a synthetic nucleotide that acts as a “blocker” of the growing chain. Based on what we learned in class, you should focus on altering what is attached to which carbon?
1. Choice 1 of 5:1’
2. Choice 2 of 5:3’
3. Choice 3 of 5:4’
4. Choice 4 of 5:5’
5. Choice 5 of 5:2’
1. Choice 1 of 5:1’
2. Choice 2 of 5:3’
3. Choice 3 of 5:4’
4. Choice 4 of 5:5’
5. Choice 5 of 5:2’
Choice 2 of 5:3’
37
New cards
LESSON 8 QUIZ
38
New cards
Below is a sequence of one strand of DNA. The bold portion is a region you want to amplify.
5' TTGGCC**GTCGGCTGCCTTCTCCT**AGGAG 3'
Which could you use as one of the primers to amplify this region? Be sure to pay attention to 5' and 3' directionality.
1. Choice 1 of 4:5’ GAGGA 3'
2. Choice 2 of 4:none of these
3. Choice 3 of 4:5’ GGCCAA 3'
4. Choice 4 of 4:5’ AACCGG 3'
5' TTGGCC**GTCGGCTGCCTTCTCCT**AGGAG 3'
Which could you use as one of the primers to amplify this region? Be sure to pay attention to 5' and 3' directionality.
1. Choice 1 of 4:5’ GAGGA 3'
2. Choice 2 of 4:none of these
3. Choice 3 of 4:5’ GGCCAA 3'
4. Choice 4 of 4:5’ AACCGG 3'
Choice 2 of 4:none of these
39
New cards
In which cells would you NOT expect to find telomerase activity?
1. Choice 1 of 4:stem cells from an early mouse embryo
2. Choice 2 of 4:breast cancer cells in culture at UNC hospitals
3. Choice 3 of 4:skin cells from a 75 year old woman
4. Choice 4 of 4:germ cells in the testes of a blue whale
1. Choice 1 of 4:stem cells from an early mouse embryo
2. Choice 2 of 4:breast cancer cells in culture at UNC hospitals
3. Choice 3 of 4:skin cells from a 75 year old woman
4. Choice 4 of 4:germ cells in the testes of a blue whale
Choice 3 of 4:skin cells from a 75 year old woman
40
New cards
You are a geneticist working at SpaceX and you are asked to engineer mice that have a human beta hemoglobin gene. To test which mice have incorporated the gene, you design primers specific to the human beta hemoglobin gene. In addition to the mouse samples of DNA you test, you have a sample of only water and a sample of DNA from a mouse that you did not genetically alter in any way. What, if anything, is a problem with this design?
1. Choice 1 of 3:You are missing a negative control to be able to see contamination and false positives
2. Choice 2 of 3:You are missing a positive control to detect if the PCR reaction is working.
3. Choice 3 of 3:Nothing, the design looks great and you should have a set of mice to your boss in no time.
1. Choice 1 of 3:You are missing a negative control to be able to see contamination and false positives
2. Choice 2 of 3:You are missing a positive control to detect if the PCR reaction is working.
3. Choice 3 of 3:Nothing, the design looks great and you should have a set of mice to your boss in no time.
Choice 2 of 3:You are missing a positive control to detect if the PCR reaction is working.
41
New cards
In both PCR and in vivo replication:
1. Choice 1 of 6:more than one of the above is true
2. Choice 2 of 6:polymerase adds to the 3’ end of a growing strand of DNA
3. Choice 3 of 6:helicases are necessary
4. Choice 4 of 6:heat is used to separate the two strands
5. Choice 5 of 6:both a leading and lagging strand exist
6. Choice 6 of 6:none of the above are true
1. Choice 1 of 6:more than one of the above is true
2. Choice 2 of 6:polymerase adds to the 3’ end of a growing strand of DNA
3. Choice 3 of 6:helicases are necessary
4. Choice 4 of 6:heat is used to separate the two strands
5. Choice 5 of 6:both a leading and lagging strand exist
6. Choice 6 of 6:none of the above are true
Choice 2 of 6:polymerase adds to the 3’ end of a growing strand of DNA
42
New cards
One major difference between in vitro replication and in vivo replication is that in vitro replication only involves the transcription of a short fragment of DNA, whereas in vivo replication involves transcription of the entire genome.
1. Choice 1 of 2:False
2. Choice 2 of 2:True
1. Choice 1 of 2:False
2. Choice 2 of 2:True
Choice 1 of 2:False
43
New cards
LESSON 9 QUIZ
44
New cards
If a cell in G1 has 2X content, what would it have at G2? At anaphase?
1. Choice 1 of 3:4x; 1X
2. Choice 2 of 3:2X; 2X
3. Choice 3 of 3:4X; 4X
1. Choice 1 of 3:4x; 1X
2. Choice 2 of 3:2X; 2X
3. Choice 3 of 3:4X; 4X
Choice 3 of 3:4X; 4X
45
New cards
With regards to an inhibitory pathway, you would predict that a cell would divide when:
1. Choice 1 of 2:a signal is present
2. Choice 2 of 2:a signal is removed
1. Choice 1 of 2:a signal is present
2. Choice 2 of 2:a signal is removed
Choice 2 of 2:a signal is removed
46
New cards
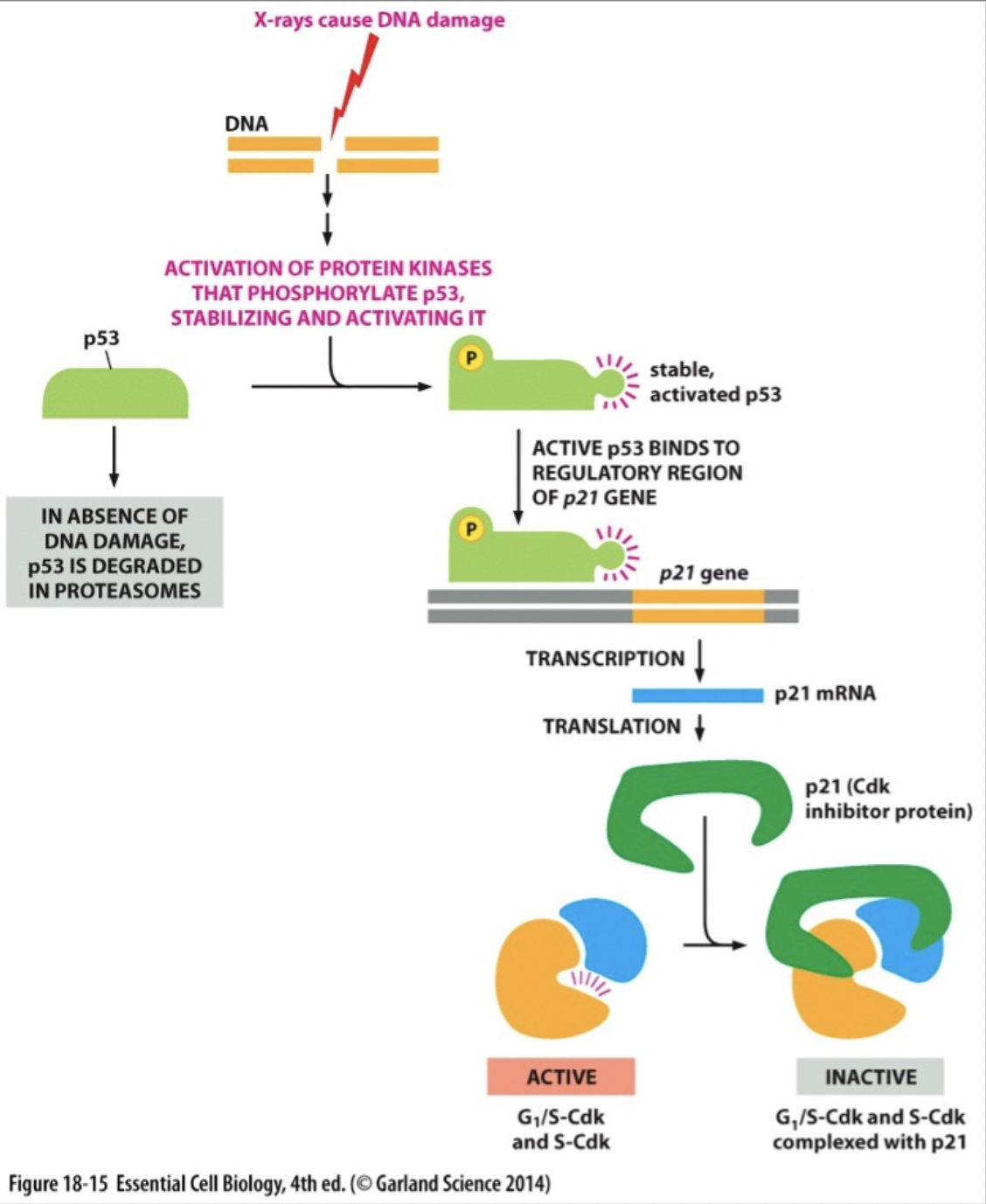
What would be the consequence of a homozygous loss of function of p21 in a cell?
1. Choice 1 of 2:cells progress through cell cycle when they should not
2. Choice 2 of 2:cells are permanently inhibited from moving through the cell cycle
1. Choice 1 of 2:cells progress through cell cycle when they should not
2. Choice 2 of 2:cells are permanently inhibited from moving through the cell cycle
Choice 1 of 2:cells progress through cell cycle when they should not
47
New cards
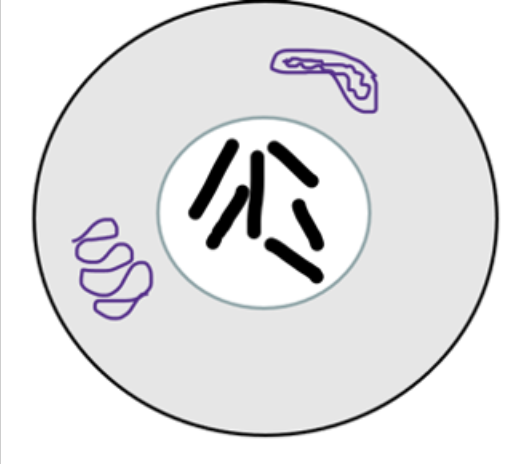
See the parent cell above. One daughter cell ends up with 6 chromosomes but the other daughter cell ends up with 5 chromosomes. What was probably not functioning probably based on these results?
1. Choice 1 of 3:The M checkpoint was faulty
2. Choice 2 of 3:Cytokinesis did not occur correctly
3. Choice 3 of 3:The cell did not go through S phase
1. Choice 1 of 3:The M checkpoint was faulty
2. Choice 2 of 3:Cytokinesis did not occur correctly
3. Choice 3 of 3:The cell did not go through S phase
Choice 1 of 3:The M checkpoint was faulty
48
New cards
By using flow cytometry and propidium iodide, we can distinguish cells in different stages of the cell cycle based on
1. Choice 1 of 5:the density/amount of DNA
2. Choice 2 of 5:how big a cell is
3. Choice 3 of 5:the rise and fall of certain of cyclins being expressed on the cell surface
4. Choice 4 of 5:the presence of CDKs on the plasma membrane
5. Choice 5 of 5:whether a spindle fiber is formed or not
1. Choice 1 of 5:the density/amount of DNA
2. Choice 2 of 5:how big a cell is
3. Choice 3 of 5:the rise and fall of certain of cyclins being expressed on the cell surface
4. Choice 4 of 5:the presence of CDKs on the plasma membrane
5. Choice 5 of 5:whether a spindle fiber is formed or not
Choice 1 of 5:the density/amount of DNA
49
New cards
LESSON 10 QUIZ
50
New cards
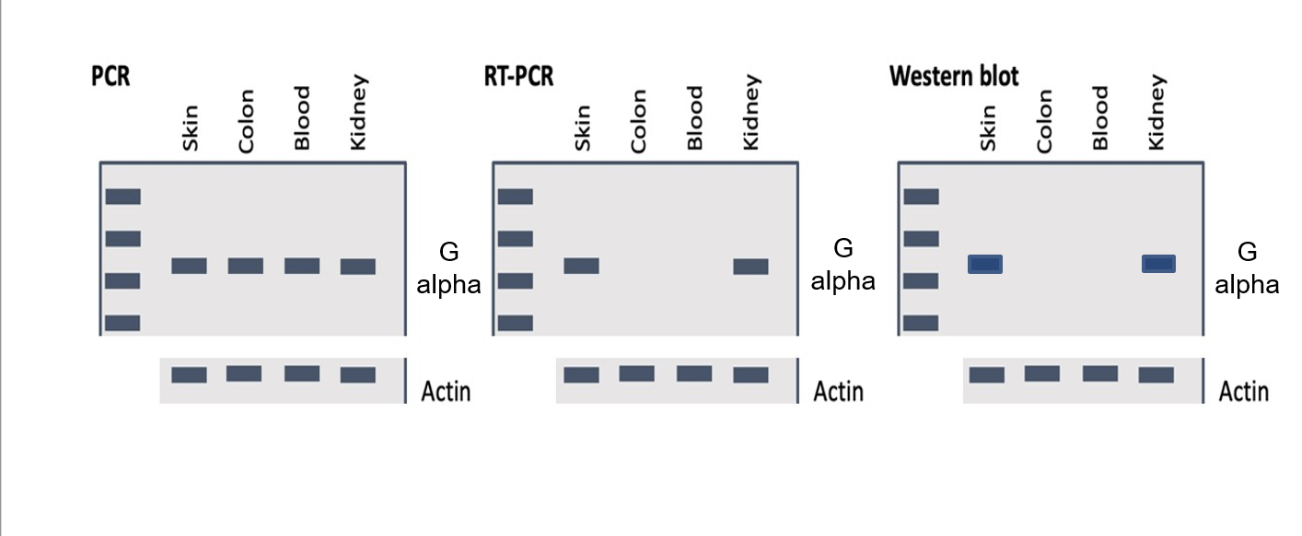
You are interested in studying a heterotrimeric G protein. You decide to focus on the alpha subunit of this G protein (written as G alpha in the diagram), since you know that activation of the alpha subunit of this G protein enhances the rate of cell division. Which of the following conclusions you can make based on the data shown? One or more answers may be correct, so choose all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 5:The skin and kidney cells are dividing faster than the colon and blood cells are dividing
2. Choice 2 of 5:The G protein alpha subunit gene is being (or has been) transcribed in skin cells
3. Choice 3 of 5:There is an early nonsense mutation in the G protein alpha subunit gene in colon and blood cells.
4. Choice 4 of 5:The promoter sequence for the G protein alpha subunit gene is different in the colon and blood cells than it is in the skin and kidney cells
5. Choice 5 of 5:Skin and kidney cells are actively proliferating
1. Choice 1 of 5:The skin and kidney cells are dividing faster than the colon and blood cells are dividing
2. Choice 2 of 5:The G protein alpha subunit gene is being (or has been) transcribed in skin cells
3. Choice 3 of 5:There is an early nonsense mutation in the G protein alpha subunit gene in colon and blood cells.
4. Choice 4 of 5:The promoter sequence for the G protein alpha subunit gene is different in the colon and blood cells than it is in the skin and kidney cells
5. Choice 5 of 5:Skin and kidney cells are actively proliferating
Choice 2 of 5:The G protein alpha subunit gene is being (or has been) transcribed in skin cells
51
New cards
The data shown above prove that the blood and colon cells will be unable to proliferate at all.
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
52
New cards
Which type of mutation would lead to excess cell proliferation?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Neither options are correct
2. Choice 2 of 4:A loss of function mutation of Ras
3. Choice 3 of 4:A gain of function mutation of p53
4. Choice 4 of 4:Both options are correct
1. Choice 1 of 4:Neither options are correct
2. Choice 2 of 4:A loss of function mutation of Ras
3. Choice 3 of 4:A gain of function mutation of p53
4. Choice 4 of 4:Both options are correct
Choice 1 of 4:Neither options are correct
53
New cards
Which of the following hormones would have a cell surface, plasma membrane-associated receptor?
1. Choice 1 of 3:Insulin, a peptide (protein) hormone that is soluble in blood
2. Choice 2 of 3:Estrogen, a non-polar hormone derived from cholesterol
3. Choice 3 of 3:Sodium ions that are polar and soluble in water
1. Choice 1 of 3:Insulin, a peptide (protein) hormone that is soluble in blood
2. Choice 2 of 3:Estrogen, a non-polar hormone derived from cholesterol
3. Choice 3 of 3:Sodium ions that are polar and soluble in water
choice 1, 3
\
Edit: This should have said which of the following, not which of the following hormones. Question dropped - credit for all.
\
Edit: This should have said which of the following, not which of the following hormones. Question dropped - credit for all.
54
New cards
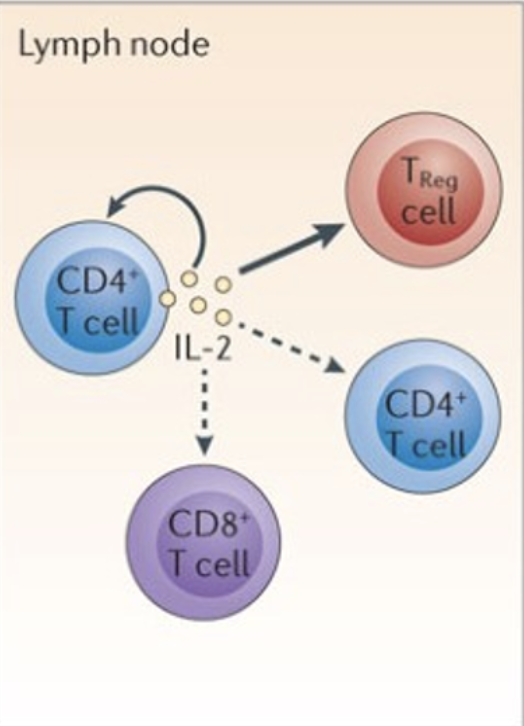
Based on what you see in this image and what we've learned in the course, which of the following are true? One or more may be correct, so choose all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 6:An example of contact-dependent signaling is depicted here
2. Choice 2 of 6:All three of these cell types contain the gene for the IL-2 receptor
3. Choice 3 of 6:An example of autocrine signaling is depicted here
4. Choice 4 of 6:An example of endocrine signaling is depicted here
5. Choice 5 of 6:All three of these cells types contain the gene for IL-2
6. Choice 6 of 6:An example of paracrine signaling is depicted here
1. Choice 1 of 6:An example of contact-dependent signaling is depicted here
2. Choice 2 of 6:All three of these cell types contain the gene for the IL-2 receptor
3. Choice 3 of 6:An example of autocrine signaling is depicted here
4. Choice 4 of 6:An example of endocrine signaling is depicted here
5. Choice 5 of 6:All three of these cells types contain the gene for IL-2
6. Choice 6 of 6:An example of paracrine signaling is depicted here
choice 2, 3, 6
55
New cards
LESSON 11 QUIZ
56
New cards
You inhibit the activity of MEK1/2, a MAPKK, in a cell that is exposed to a growth factor. What other signaling molecule(s) will be inhibited/not activated? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:RSK
2. Choice 2 of 4:Ras
3. Choice 3 of 4:Raf
4. Choice 4 of 4:ERK1/2 (MAPK)
1. Choice 1 of 4:RSK
2. Choice 2 of 4:Ras
3. Choice 3 of 4:Raf
4. Choice 4 of 4:ERK1/2 (MAPK)
choice 1, 4
57
New cards
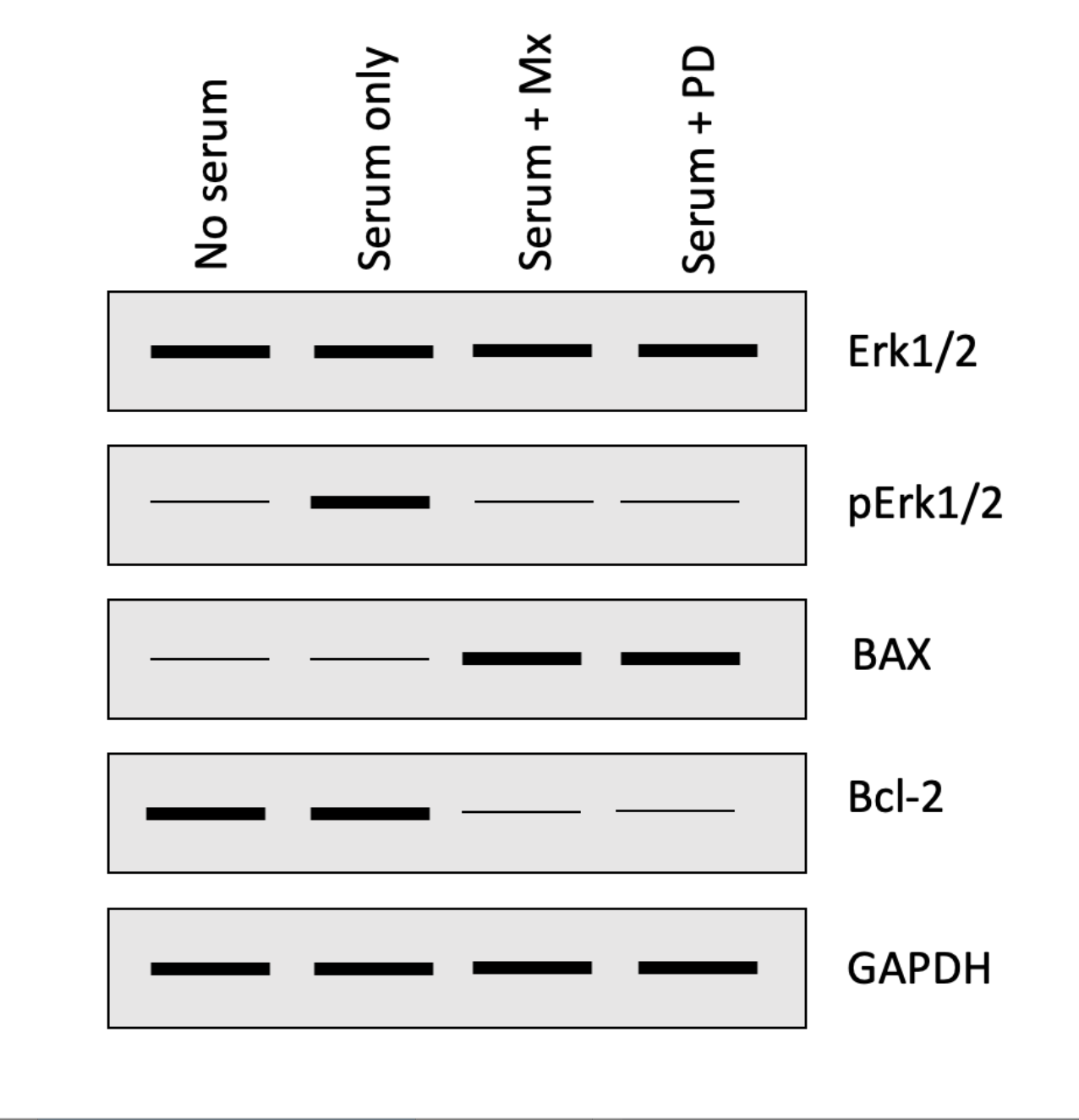
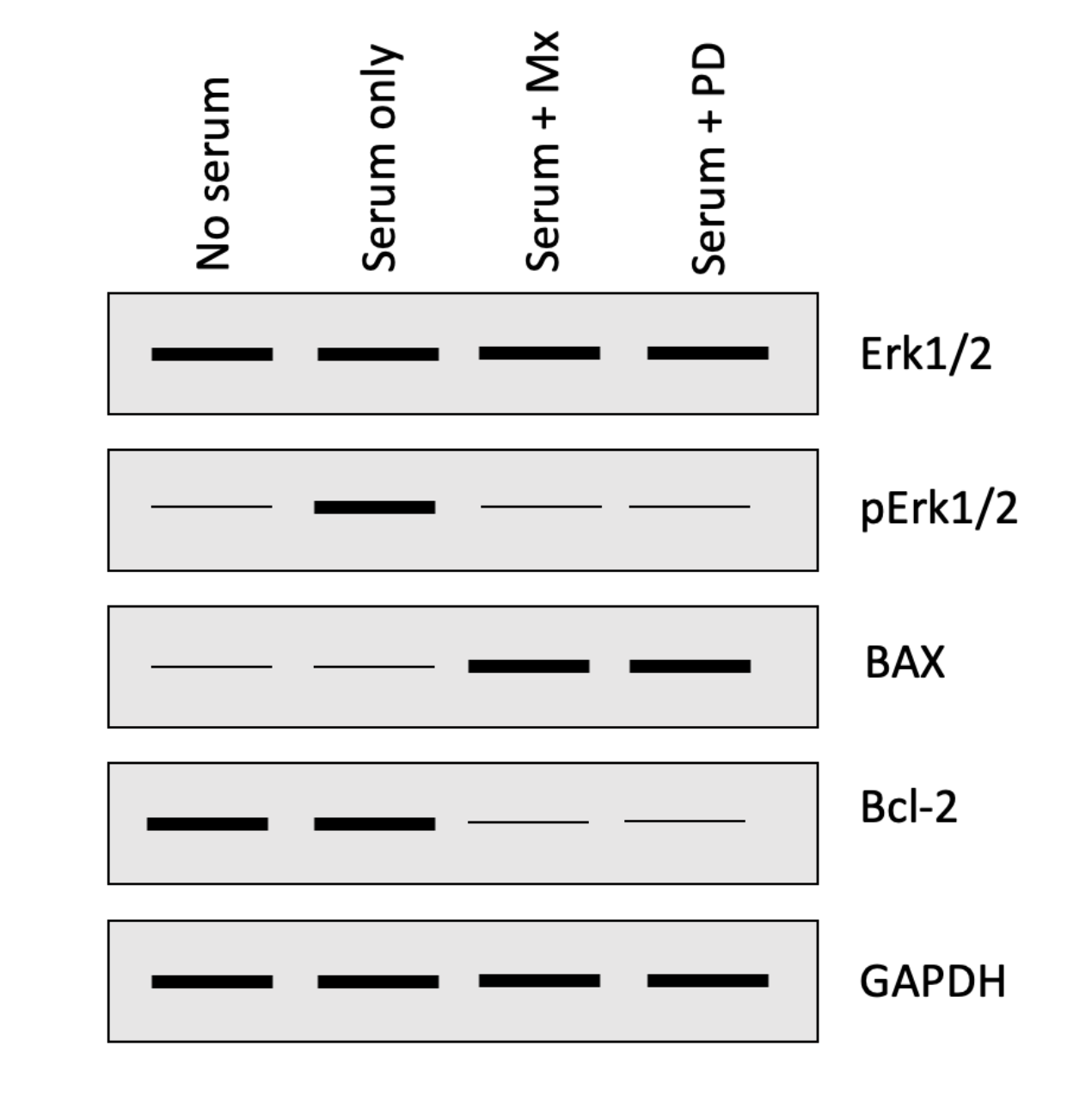
The following four questions refer to the Western blot below that investigated how a chemotherapeutic drug methotrexate (Mx) impacts the activation of the ERK1/2 and apoptosis pathways in HeLa cells (malignant cervical cancer cells). Cells were either serum starved (no serum) or grown in serum containing media with or without PD184352 (PD; ERK1/2 inhibitor) or Mx.
\
In what cells is the ERK1/2 pathway activated? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:No serum
2. Choice 2 of 4:Serum + Mx
3. Choice 3 of 4:Serum only
4. Choice 4 of 4:Serum + PD
\
In what cells is the ERK1/2 pathway activated? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:No serum
2. Choice 2 of 4:Serum + Mx
3. Choice 3 of 4:Serum only
4. Choice 4 of 4:Serum + PD
Choice 3 of 4:Serum only
58
New cards
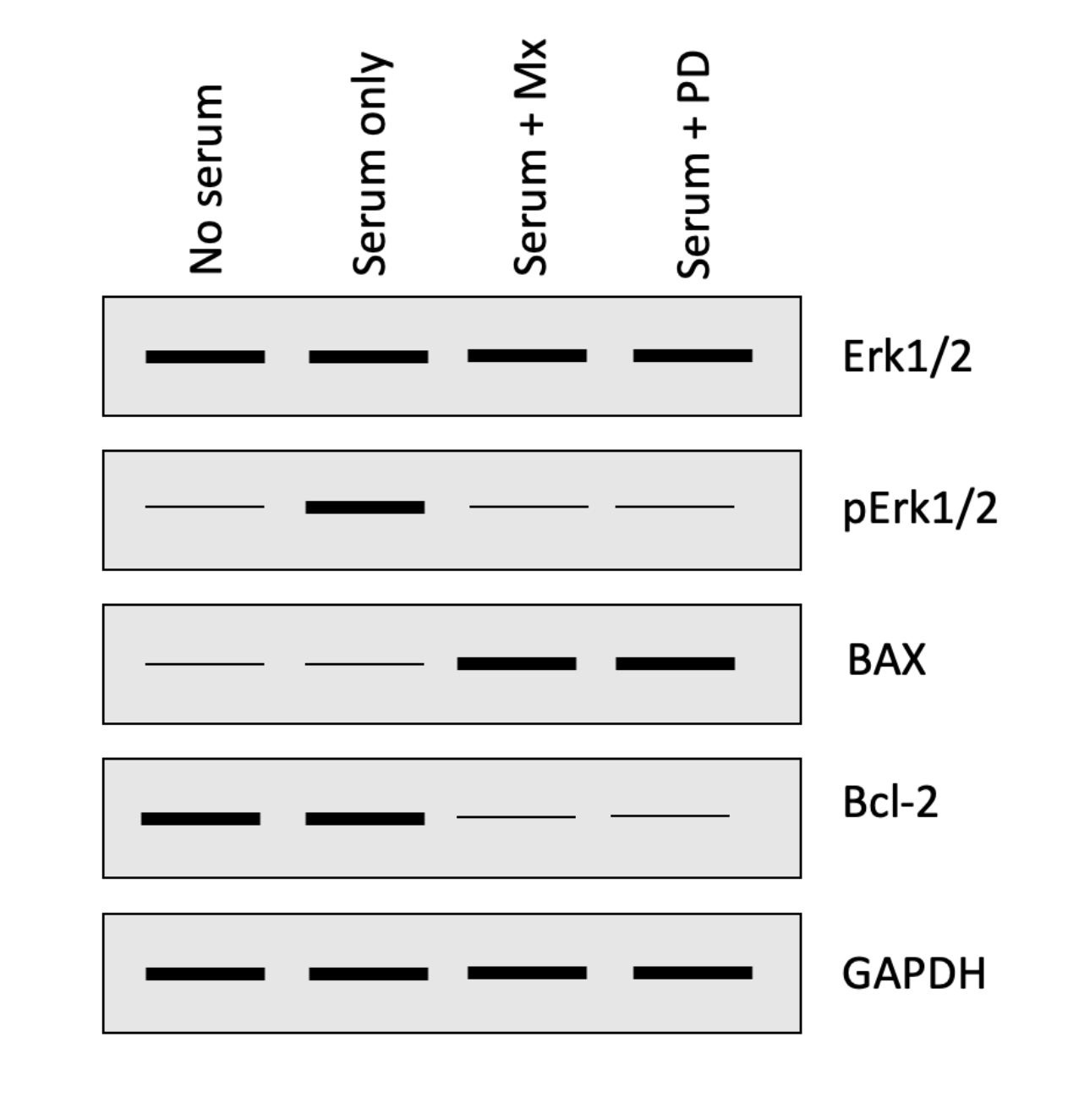
The following four questions refer to the Western blot below that investigated how a chemotherapeutic drug methotrexate (Mx) impacts the activation of the ERK1/2 and apoptosis pathways in HeLa cells (malignant cervical cancer cells). Cells were either serum starved (no serum) or grown in serum containing media with or without PD184352 (PD; ERK1/2 inhibitor) or Mx.
\
Based on what we saw in class, if you had run a western blot to detect **CREB**, in which of the lanes would you have expected to see a thick/intense band? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:Serum only
2. Choice 2 of 4:Serum + PD
3. Choice 3 of 4:Serum + Mx
4. Choice 4 of 4:No serum
\
Based on what we saw in class, if you had run a western blot to detect **CREB**, in which of the lanes would you have expected to see a thick/intense band? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:Serum only
2. Choice 2 of 4:Serum + PD
3. Choice 3 of 4:Serum + Mx
4. Choice 4 of 4:No serum
all of the above
59
New cards
The following four questions refer to the Western blot below that investigated how a chemotherapeutic drug methotrexate (Mx) impacts the activation of the ERK1/2 and apoptosis pathways in HeLa cells (malignant cervical cancer cells). Cells were either serum starved (no serum) or grown in serum containing media with or without PD184352 (PD; ERK1/2 inhibitor) or Mx.
\
Based on what we saw in class, if you had run a western blot to detect **Cyclin D1**, in which of the lanes would you have expected to see a thick/intense band? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:No serum
2. Choice 2 of 4:Serum + Mx
3. Choice 3 of 4:Serum + PD
4. Choice 4 of 4:Serum only
\
Based on what we saw in class, if you had run a western blot to detect **Cyclin D1**, in which of the lanes would you have expected to see a thick/intense band? One or more may be correct, so select all that apply:
1. Choice 1 of 4:No serum
2. Choice 2 of 4:Serum + Mx
3. Choice 3 of 4:Serum + PD
4. Choice 4 of 4:Serum only
Choice 4 of 4:Serum only
60
New cards
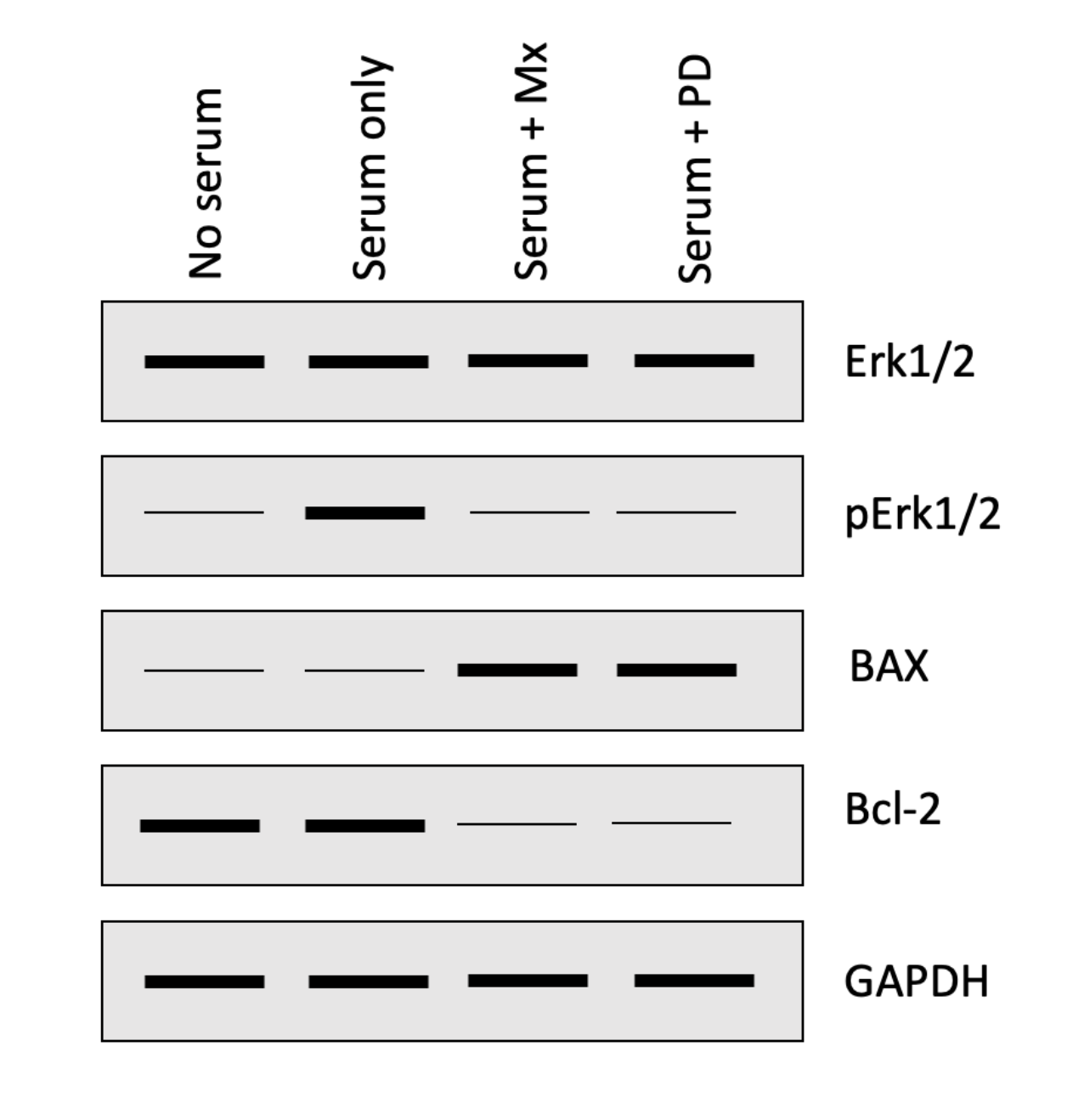
The following four questions refer to the Western blot below that investigated how a chemotherapeutic drug methotrexate (Mx) impacts the activation of the ERK1/2 and apoptosis pathways in HeLa cells (malignant cervical cancer cells). Cells were either serum starved (no serum) or grown in serum containing media with or without PD184352 (PD; ERK1/2 inhibitor) or Mx.
\
What was the purpose of GAPDH in this experiment?
1. Choice 1 of 4:GAPDH is phosphorylated by ERK1/2
2. Choice 2 of 4:Neither option is correct.
3. Choice 3 of 4:Both options are correct
4. Choice 4 of 4:GAPDH is degraded during apoptosis
\
What was the purpose of GAPDH in this experiment?
1. Choice 1 of 4:GAPDH is phosphorylated by ERK1/2
2. Choice 2 of 4:Neither option is correct.
3. Choice 3 of 4:Both options are correct
4. Choice 4 of 4:GAPDH is degraded during apoptosis
Choice 2 of 4:Neither option is correct.
61
New cards
LESSON 12 QUIZ
62
New cards
Which of the following are true of BOTH stem cells and cancer cells, according to what we learned in class? One or more answers may be correct, so select all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 4:Undergo mitosis
2. Choice 2 of 4:Immortality
3. Choice 3 of 4:Ability to migrate
4. Choice 4 of 4:Abnormal number of chromosomes
1. Choice 1 of 4:Undergo mitosis
2. Choice 2 of 4:Immortality
3. Choice 3 of 4:Ability to migrate
4. Choice 4 of 4:Abnormal number of chromosomes
choice 1, 2, 3
63
New cards
Consider a neutrophil and neuron (distinct cell types) from the same individual. What will be the exact same about these cells?
1. Choice 1 of 5:None of the options are correct
2. Choice 2 of 5:The promoter sequence for the insulin gene
3. Choice 3 of 5:The proteins they express
4. Choice 4 of 5:More than one of the options are correct
5. Choice 5 of 5:The transcription factors they express
1. Choice 1 of 5:None of the options are correct
2. Choice 2 of 5:The promoter sequence for the insulin gene
3. Choice 3 of 5:The proteins they express
4. Choice 4 of 5:More than one of the options are correct
5. Choice 5 of 5:The transcription factors they express
Choice 2 of 5:The promoter sequence for the insulin gene
64
New cards
Which of the following processes take place during the embryonic development of a multi-cellular organism, based on what we learned in class? One or more answers may be correct, so select all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 5:Activation of signal transduction cascades
2. Choice 2 of 5:Cell migration
3. Choice 3 of 5:Changes in gene expression of cells
4. Choice 4 of 5:Apoptosis
5. Choice 5 of 5:Mitosis
1. Choice 1 of 5:Activation of signal transduction cascades
2. Choice 2 of 5:Cell migration
3. Choice 3 of 5:Changes in gene expression of cells
4. Choice 4 of 5:Apoptosis
5. Choice 5 of 5:Mitosis
all of the above
65
New cards
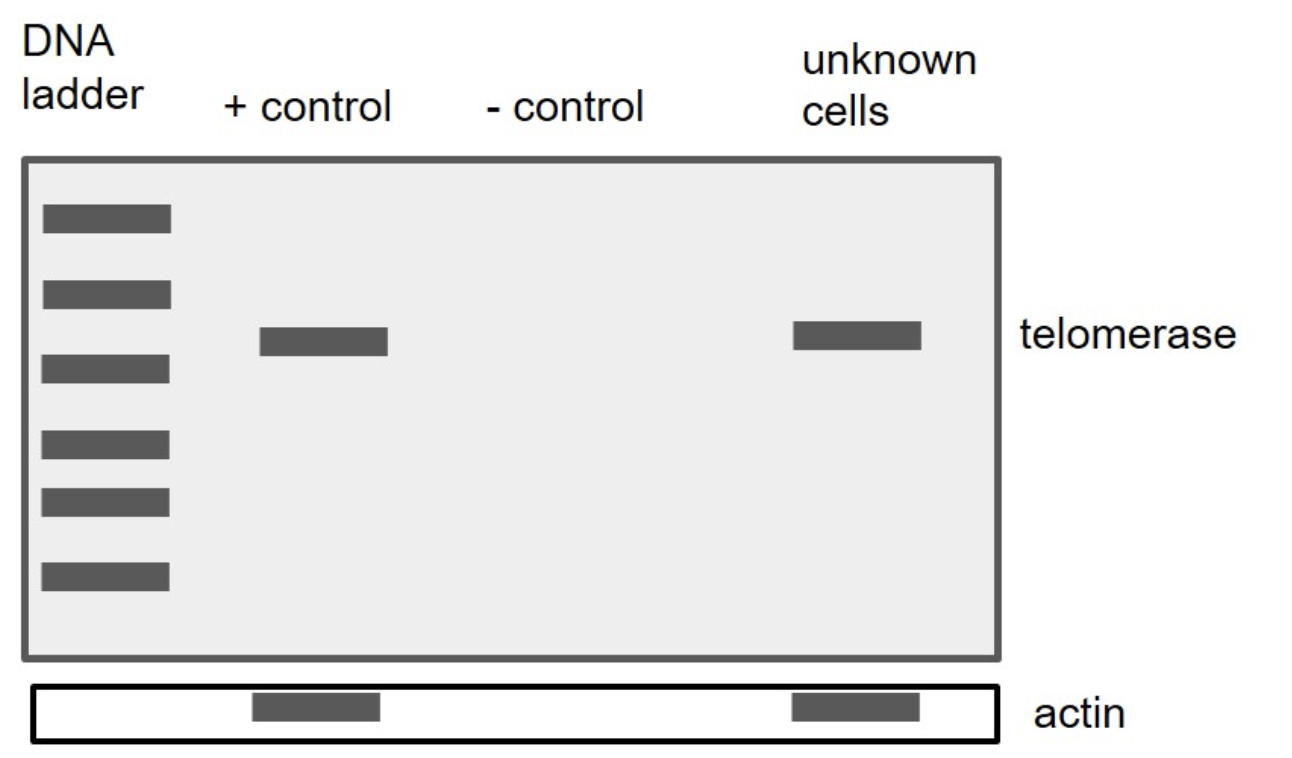
You are trying to figure out what type of cells are in a sample you've found. So, you decide to run a PCR with primers specific for the telomerase gene. You run correct/appropriate positive and negative controls (here, your negative control is water) for your PCR. You obtain these results after running your gel:
\
Based on these results, what could your unknown cells be? One or more may be correct, so choose all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 5:Hematopoietic (blood) stem cells
2. Choice 2 of 5:Embryonic stem cells
3. Choice 3 of 5:Heart muscle cells
4. Choice 4 of 5:Retina (eye) cells
5. Choice 5 of 5:Brain cancer cells
\
Based on these results, what could your unknown cells be? One or more may be correct, so choose all that apply.
1. Choice 1 of 5:Hematopoietic (blood) stem cells
2. Choice 2 of 5:Embryonic stem cells
3. Choice 3 of 5:Heart muscle cells
4. Choice 4 of 5:Retina (eye) cells
5. Choice 5 of 5:Brain cancer cells
all of the above
\
the DNA the same in all cells? YES! Remember that a PCR is telling you about the DNA, and we know that the DNA for the telomerase gene is present in ALL CELLS. That means that you should see a telomerase band in your PCR from ANY CELL TYPE. Challenge: What techniques would let you look at which cells **express** telomerase?
\
the DNA the same in all cells? YES! Remember that a PCR is telling you about the DNA, and we know that the DNA for the telomerase gene is present in ALL CELLS. That means that you should see a telomerase band in your PCR from ANY CELL TYPE. Challenge: What techniques would let you look at which cells **express** telomerase?
66
New cards
All the promoters for the genes found within a single eukaryotic cell are identical, since the DNA in all cells is the same.
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
This question asks about the promoters for genes found **within** a single cell, meaning all the different genes that one individual cell would contain. As we talked about last week (Lesson 12 Part 1 Slides 17-20), the promoter for the **same** gene in two **different** cells would be the same, but the promoters for **different** genes are different, and contain different regulatory elements which allow them to be differentially expressed in different cell types!
\
This question asks about the promoters for genes found **within** a single cell, meaning all the different genes that one individual cell would contain. As we talked about last week (Lesson 12 Part 1 Slides 17-20), the promoter for the **same** gene in two **different** cells would be the same, but the promoters for **different** genes are different, and contain different regulatory elements which allow them to be differentially expressed in different cell types!
67
New cards
LESSON 13 QUIZ
68
New cards
As shown in the movie, the exact same deletion on chromosome 15 can lead to two different syndromes, Angelman’s syndrome or Prader-Willi syndrome. What accounts for the difference?
1. Choice 1 of 3:whether the child is a biological male or female
2. Choice 2 of 3:whether the deletion happened before or after birth
3. Choice 3 of 3:Whether the deletion is inherited from mother or father
1. Choice 1 of 3:whether the child is a biological male or female
2. Choice 2 of 3:whether the deletion happened before or after birth
3. Choice 3 of 3:Whether the deletion is inherited from mother or father
Choice 3 of 3:Whether the deletion is inherited from mother or father
69
New cards
As shown in the movie, researchers study a brown thin mouse and an obese, yellowish mouse. These mice are identical twins but differ at the agouti gene. What specifically is different in the brown mice vs. the yellow, obese mice?
1. Choice 1 of 3:acetylation of histones at the agouti gene
2. Choice 2 of 3:methylation of DNA at the agouti gene
3. Choice 3 of 3:the sequence of DNA of the agouti gene
1. Choice 1 of 3:acetylation of histones at the agouti gene
2. Choice 2 of 3:methylation of DNA at the agouti gene
3. Choice 3 of 3:the sequence of DNA of the agouti gene
Choice 2 of 3:methylation of DNA at the agouti gene
70
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of histone acetylation and DNA methylation in gene regulation?
1. Choice 1 of 4:DNA methylation reduces transcription, and histone acetylation promotes transcription.
2. Choice 2 of 4:DNA methylation and histone acetylation both promote transcription.
3. Choice 3 of 4:DNA methylation promotes transcription, and histone acetylation reduces transcription.
4. Choice 4 of 4:DNA methylation and histone acetylation both reduce transcription.
1. Choice 1 of 4:DNA methylation reduces transcription, and histone acetylation promotes transcription.
2. Choice 2 of 4:DNA methylation and histone acetylation both promote transcription.
3. Choice 3 of 4:DNA methylation promotes transcription, and histone acetylation reduces transcription.
4. Choice 4 of 4:DNA methylation and histone acetylation both reduce transcription.
Choice 1 of 4:DNA methylation reduces transcription, and histone acetylation promotes transcription.
71
New cards
Methylation of a tumor suppressor gene such as p53 would lead to:
1. Choice 1 of 2:less cell proliferation
2. Choice 2 of 2:more cell proliferation
1. Choice 1 of 2:less cell proliferation
2. Choice 2 of 2:more cell proliferation
Choice 2 of 2:more cell proliferation
72
New cards
A researcher was studying the epigenome, specifically methylation patterns. She examined two sets of identical twins and immediately knew which set of twins was young and which was older. How?
1. Choice 1 of 2:The older twins had more differences in their methylation pattens compared to the younger twins
2. Choice 2 of 2:The younger twins had more differences in their methylation pattens compared to the older twinS
1. Choice 1 of 2:The older twins had more differences in their methylation pattens compared to the younger twins
2. Choice 2 of 2:The younger twins had more differences in their methylation pattens compared to the older twinS
Choice 1 of 2:The older twins had more differences in their methylation pattens compared to the younger twins
73
New cards
LESSON 14 QUIZ
74
New cards

For the DNA sequence below, find the open reading frame(s) and determine the number of amino acids for the longest polypeptide?
1. Choice 1 of 4:8
2. Choice 2 of 4:11
3. Choice 3 of 4:10
4. Choice 4 of 4:None of the options are correct
1. Choice 1 of 4:8
2. Choice 2 of 4:11
3. Choice 3 of 4:10
4. Choice 4 of 4:None of the options are correct
Choice 3 of 4:10
75
New cards
The SARS CoV-2 virus is a (+)ssRNA virus, meaning that its genome mimics mRNA in a cell. As a result, which of the following statements is TRUE about the genome and life cycle of SARS CoV-2?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Both statements are true
2. Choice 2 of 4:Neither of the statements are true
3. Choice 3 of 4:RNA polymerase is necessary in order to express viral proteins from the SARS CoV-2 genome
4. Choice 4 of 4:Viral genes can be translated in cells infected with SARS CoV-2
1. Choice 1 of 4:Both statements are true
2. Choice 2 of 4:Neither of the statements are true
3. Choice 3 of 4:RNA polymerase is necessary in order to express viral proteins from the SARS CoV-2 genome
4. Choice 4 of 4:Viral genes can be translated in cells infected with SARS CoV-2
Choice 4 of 4:Viral genes can be translated in cells infected with SARS CoV-2
76
New cards
When considering an open reading frame, what is the first amino acid of the polypeptide that is translated?
1. Choice 1 of 4:PRO
2. Choice 2 of 4:MET
3. Choice 3 of 4:Varies based on the nucleotide sequence
4. Choice 4 of 4:GLY
1. Choice 1 of 4:PRO
2. Choice 2 of 4:MET
3. Choice 3 of 4:Varies based on the nucleotide sequence
4. Choice 4 of 4:GLY
Choice 2 of 4:MET
77
New cards
A mutation arose in the Kozak consensus sequence of a gene (all other aspects of the gene are unaffected). As a result, you would expect abnormal:
1. Choice 1 of 5:Two of the above
2. Choice 2 of 5:Transcription of the gene product only
3. Choice 3 of 5:Three of the above
4. Choice 4 of 5:Translation of the gene product only
5. Choice 5 of 5:Replication of the gene product only
1. Choice 1 of 5:Two of the above
2. Choice 2 of 5:Transcription of the gene product only
3. Choice 3 of 5:Three of the above
4. Choice 4 of 5:Translation of the gene product only
5. Choice 5 of 5:Replication of the gene product only
Choice 4 of 5:Translation of the gene product only
78
New cards
You recently discovered a novel organic compound that prevents the function of ribosomes (all types). This could be used to treat which type of infection in plants?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Both bacterial and viral infections
2. Choice 2 of 4:Bacterial infection only
3. Choice 3 of 4:Viral infection only
4. Choice 4 of 4:Neither bacterial nor viral infections
1. Choice 1 of 4:Both bacterial and viral infections
2. Choice 2 of 4:Bacterial infection only
3. Choice 3 of 4:Viral infection only
4. Choice 4 of 4:Neither bacterial nor viral infections
Choice 4 of 4:Neither bacterial nor viral infections
79
New cards
LESSON 15 QUIZ
80
New cards
Glucose and O2 are both present at a higher concentration in the extracellular space outside of a cell. While we would expect both to passively diffuse across the membrane:
1. Choice 1 of 3:glucose will diffuse across the membrane more rapidly than oxygen
2. Choice 2 of 3:Both would diffuse across the membrane at the same rate
3. Choice 3 of 3:oxygen will diffuse across the membrane more rapidly than glucose
1. Choice 1 of 3:glucose will diffuse across the membrane more rapidly than oxygen
2. Choice 2 of 3:Both would diffuse across the membrane at the same rate
3. Choice 3 of 3:oxygen will diffuse across the membrane more rapidly than glucose
Choice 3 of 3:oxygen will diffuse across the membrane more rapidly than glucose
81
New cards
If you stimulated cells with a drug that increases the activity of myosin and exposed the cells to SARS CoV-2, what would you expect to occur? Assume the cells express physiologically normal levels of ACE-2 and actin.
1. Choice 1 of 2:Increased entry of SARS CoV-2 into the cell
2. Choice 2 of 2:Decreased entry of SARS CoV-2 into the cell
1. Choice 1 of 2:Increased entry of SARS CoV-2 into the cell
2. Choice 2 of 2:Decreased entry of SARS CoV-2 into the cell
Choice 1 of 2:Increased entry of SARS CoV-2 into the cell
82
New cards
For a neuron, the concentration of K+ is greater inside the cell than outside of the cell. Knowing that humans get K+ from their diet, how might K+ get into the cytoplasm of a neuron from its extracellular space? (Select all that apply)
1. Choice 1 of 4:Active transport
2. Choice 2 of 4:Pinocytosis
3. Choice 3 of 4:Phagocysosis
4. Choice 4 of 4:Facilitated diffusion
1. Choice 1 of 4:Active transport
2. Choice 2 of 4:Pinocytosis
3. Choice 3 of 4:Phagocysosis
4. Choice 4 of 4:Facilitated diffusion
choice 1, 2
83
New cards
Carrot slices placed in a 2 g/L salt solution for several hours become flaccid (limp). Carrot slices placed in fresh water for several hours become turgid (stiff). Why?
1. Choice 1 of 4:The fresh water is hypotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the carrot slices
2. Choice 2 of 4:The fresh water and salt solution are both hypertonic to the cells of the carrot slices
3. Choice 3 of 4:The fresh water is hypertonic and the salt solution is hypotonic to the cells of the carrot slices
4. Choice 4 of 4:The fresh water and salt solution are both hypotonic to the cells of the carrot slices
1. Choice 1 of 4:The fresh water is hypotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the carrot slices
2. Choice 2 of 4:The fresh water and salt solution are both hypertonic to the cells of the carrot slices
3. Choice 3 of 4:The fresh water is hypertonic and the salt solution is hypotonic to the cells of the carrot slices
4. Choice 4 of 4:The fresh water and salt solution are both hypotonic to the cells of the carrot slices
Choice 1 of 4:The fresh water is hypotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the carrot slices
84
New cards
For a neutrophil to phagocytose a bacterium, it must have:
I. functional actin filaments
II. functional myosin filaments
III. a receptor
1. Choice 1 of 4:I, II, and III
2. Choice 2 of 4:I and II
3. Choice 3 of 4:III only
4. Choice 4 of 4:I only
I. functional actin filaments
II. functional myosin filaments
III. a receptor
1. Choice 1 of 4:I, II, and III
2. Choice 2 of 4:I and II
3. Choice 3 of 4:III only
4. Choice 4 of 4:I only
Choice 1 of 4:I, II, and III
85
New cards
LESSON 16 QUIZ
86
New cards
SARS CoV-2 has a single-stranded RNA genome. A toll-like receptor that would recognize the SARS CoV-2 genome, and thus activate an inflammatory response, would be found:
1. Choice 1 of 3:In the cytosol
2. Choice 2 of 3:Within an endosome
3. Choice 3 of 3:On the plasma membrane
1. Choice 1 of 3:In the cytosol
2. Choice 2 of 3:Within an endosome
3. Choice 3 of 3:On the plasma membrane
Choice 2 of 3:Within an endosome
87
New cards
Which of the following events is generally shared by both a water-soluble and lipid (or hormone) steroid?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Production of second messengers
2. Choice 2 of 4:Activation of transcription factors
3. Choice 3 of 4:Entry of ligand into the cytoplasm
4. Choice 4 of 4:Activation of the p38 MAPK pathway
1. Choice 1 of 4:Production of second messengers
2. Choice 2 of 4:Activation of transcription factors
3. Choice 3 of 4:Entry of ligand into the cytoplasm
4. Choice 4 of 4:Activation of the p38 MAPK pathway
Choice 2 of 4:Activation of transcription factors
88
New cards
Inhibiting the activity of TAK1, a MAPKKK, would inhibit the activation of p38 MAPK.
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
89
New cards
Which of the following is NOT associated with signaling via a G-coupled protein receptor (GPCR)?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum
2. Choice 2 of 4:Transcription of gene products
3. Choice 3 of 4:Entry of the signaling ligand into the cytoplasm
4. Choice 4 of 4:Activation of phosphorylation cascades
1. Choice 1 of 4:Release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum
2. Choice 2 of 4:Transcription of gene products
3. Choice 3 of 4:Entry of the signaling ligand into the cytoplasm
4. Choice 4 of 4:Activation of phosphorylation cascades
Choice 3 of 4:Entry of the signaling ligand into the cytoplasm
90
New cards
You scraped your arm while mountain biking, causing a bacterial infection of your skin. How many of the following symptoms might be considered a hallmark of the inflammation that you’re experiencing?
* Separation of layers of skin near the wound, causing blisters.
* Swelling of the skin near the wound site.
* Pain near the site of the wound.
1. Choice 1 of 4:3 of the above
2. Choice 2 of 4:0 of the above
3. Choice 3 of 4:2 of the above
4. Choice 4 of 4:1 of the above
* Separation of layers of skin near the wound, causing blisters.
* Swelling of the skin near the wound site.
* Pain near the site of the wound.
1. Choice 1 of 4:3 of the above
2. Choice 2 of 4:0 of the above
3. Choice 3 of 4:2 of the above
4. Choice 4 of 4:1 of the above
Choice 3 of 4:2 of the above
91
New cards
LESSON 17 QUIZ
92
New cards
What feature(s) of a eukaryotic mature mRNA molecule allow for the transcript to be exported from the nucleus? (Select all that apply)
1. Choice 1 of 4:Signal sequence peptide
2. Choice 2 of 4:5’ cap
3. Choice 3 of 4:Kozak consensus sequence
4. Choice 4 of 4:poly(A) tail
1. Choice 1 of 4:Signal sequence peptide
2. Choice 2 of 4:5’ cap
3. Choice 3 of 4:Kozak consensus sequence
4. Choice 4 of 4:poly(A) tail
choice 2, 4
93
New cards
Which of the following approaches could be used to prevent the loading of viral epitopes/peptides on the MHC Class I molecules?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Both of the above would work
2. Choice 2 of 4:Treat cells with an inhibitor of lysosomes
3. Choice 3 of 4:Treat cells with an inhibitor of the proteasome
4. Choice 4 of 4:Neither of the above would work
1. Choice 1 of 4:Both of the above would work
2. Choice 2 of 4:Treat cells with an inhibitor of lysosomes
3. Choice 3 of 4:Treat cells with an inhibitor of the proteasome
4. Choice 4 of 4:Neither of the above would work
Choice 3 of 4:Treat cells with an inhibitor of the proteasome
94
New cards
Brefeldin A is a molecule produced by fungus that prevents the movement of vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. We would therefore expect that treatment of cells with Brefeldin A would:
1. Choice 1 of 3:have abnormally low levels of plasma membrane-associated proteins
2. Choice 2 of 3:have improperly folded proteins
3. Choice 3 of 3:have abnormal N-linked glycosylation
1. Choice 1 of 3:have abnormally low levels of plasma membrane-associated proteins
2. Choice 2 of 3:have improperly folded proteins
3. Choice 3 of 3:have abnormal N-linked glycosylation
Choice 1 of 3:have abnormally low levels of plasma membrane-associated proteins
95
New cards
NLRP1 is a multi-domain protein component of the inflammasome, a cytoplasmic structure that is involved in the production of proinflammatory mediators (cytokines). Where would you expect the tertiary structure of NLRP1 to be formed within a eukaryotic cell?
1. Choice 1 of 4:In the nucleus
2. Choice 2 of 4:In the endoplasmic reticulum
3. Choice 3 of 4:In the Golgi apparatus
4. Choice 4 of 4:In the cytoplasm
1. Choice 1 of 4:In the nucleus
2. Choice 2 of 4:In the endoplasmic reticulum
3. Choice 3 of 4:In the Golgi apparatus
4. Choice 4 of 4:In the cytoplasm
Choice 4 of 4:In the cytoplasm
96
New cards
You tag a protein with a fluorescent probe and use microscopy to evaluate where within the cell the protein travels at various time points. During your experiment, you notice that the protein is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Which best describes the final location of this protein?
1. Choice 1 of 4:Neither option is possible
2. Choice 2 of 4:The protein is associated with the plasma membrane
3. Choice 3 of 4:The protein is secreted from the cell
4. Choice 4 of 4:Both of the options are possible
1. Choice 1 of 4:Neither option is possible
2. Choice 2 of 4:The protein is associated with the plasma membrane
3. Choice 3 of 4:The protein is secreted from the cell
4. Choice 4 of 4:Both of the options are possible
Choice 4 of 4:Both of the options are possible
97
New cards
LESSON 18 QUIZ
98
New cards
The epitope that is loaded into the peptide groove of an MHC class I molecule:
1. Choice 1 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a B cell
2. Choice 2 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a CD8+ cytotoxic T cell
3. Choice 3 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a CD4+ helper T cell
1. Choice 1 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a B cell
2. Choice 2 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a CD8+ cytotoxic T cell
3. Choice 3 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a CD4+ helper T cell
Choice 2 of 3:Is the same epitope that is recognized by a CD8+ cytotoxic T cell
99
New cards
Antigen presenting cells present peptides from antigens they have phagocytosed on MHC class II molecules, and they can secrete different cytokines depending on the type of pathogen they have encountered.
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
1. Choice 1 of 2:True
2. Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
100
New cards
Because B cells are activated by CD4+ helper T cells, the humoral immune system is always activated before the cell-mediated immune system.
1. Choice 1 of 2:False
2. Choice 2 of 2:True
1. Choice 1 of 2:False
2. Choice 2 of 2:True
Choice 1 of 2:False