Chapter 9: Key Concepts of DNA Replication
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Main purpose of DNA replication
To make an identical copy of DNA before cell division
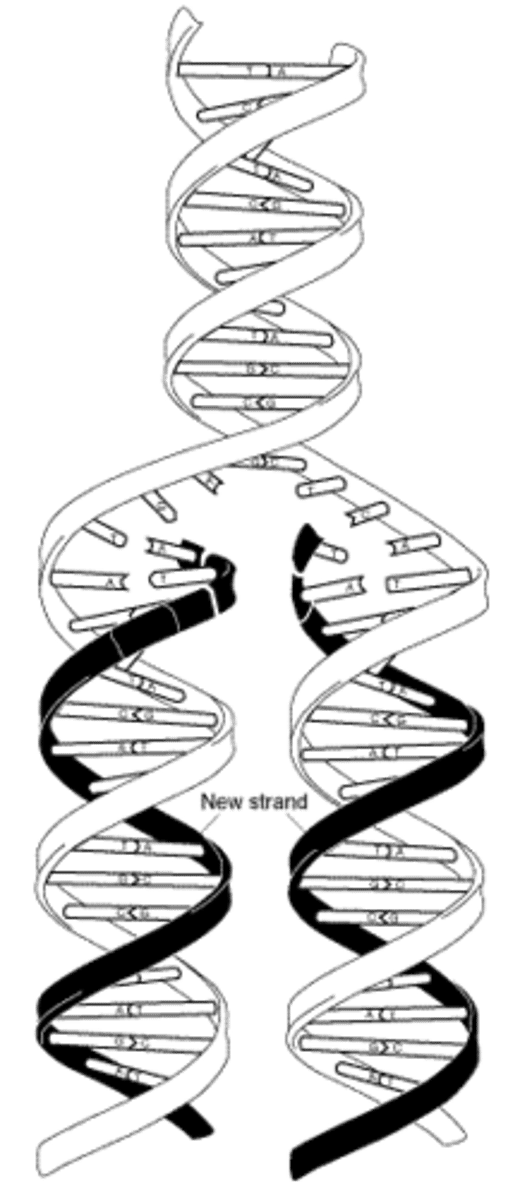

Semi-conservative in DNA replication
Each new DNA molecule consists of one original and one new strand
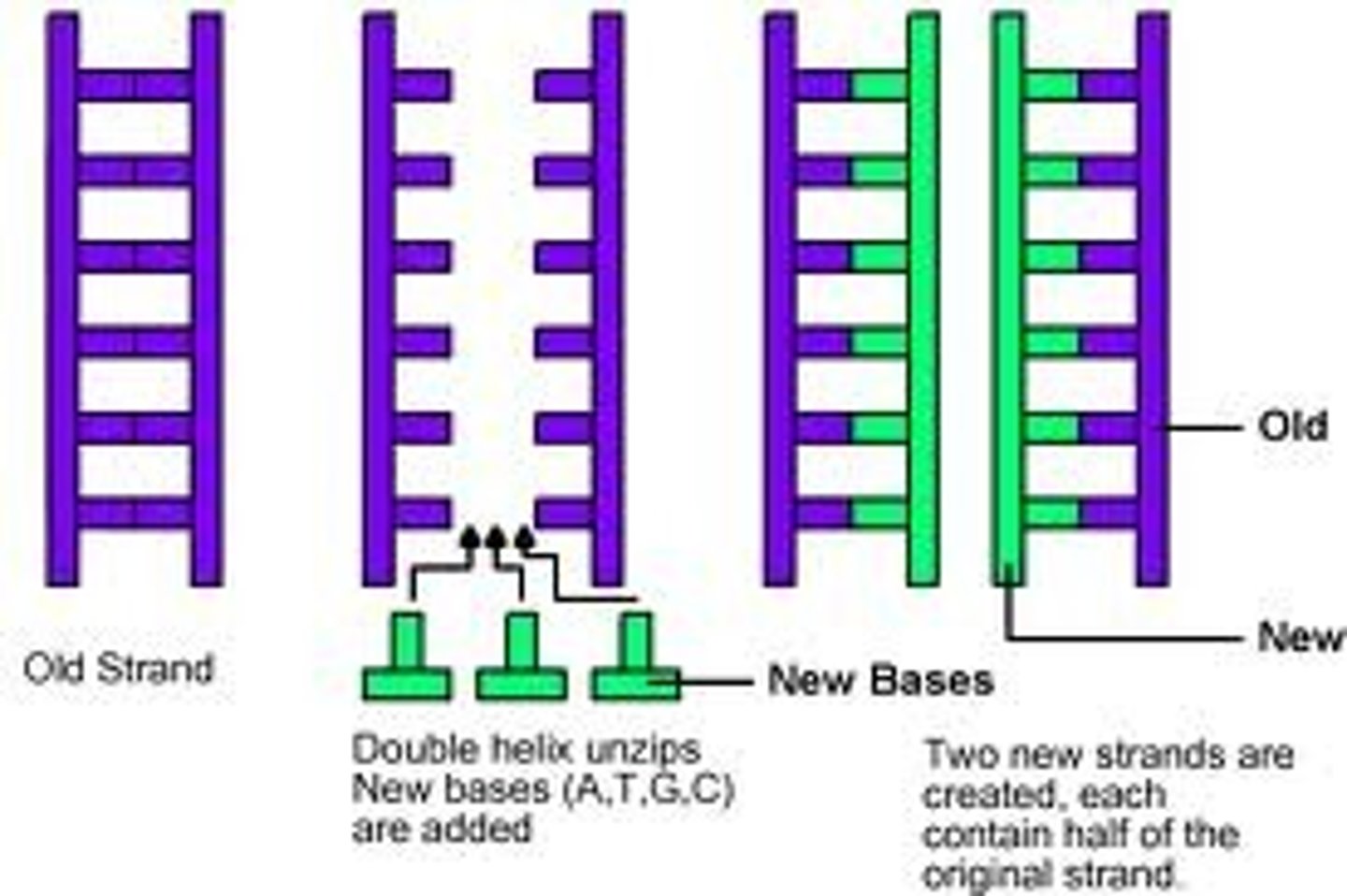
First step in DNA replication
DNA helicase unwinds the DNA molecule
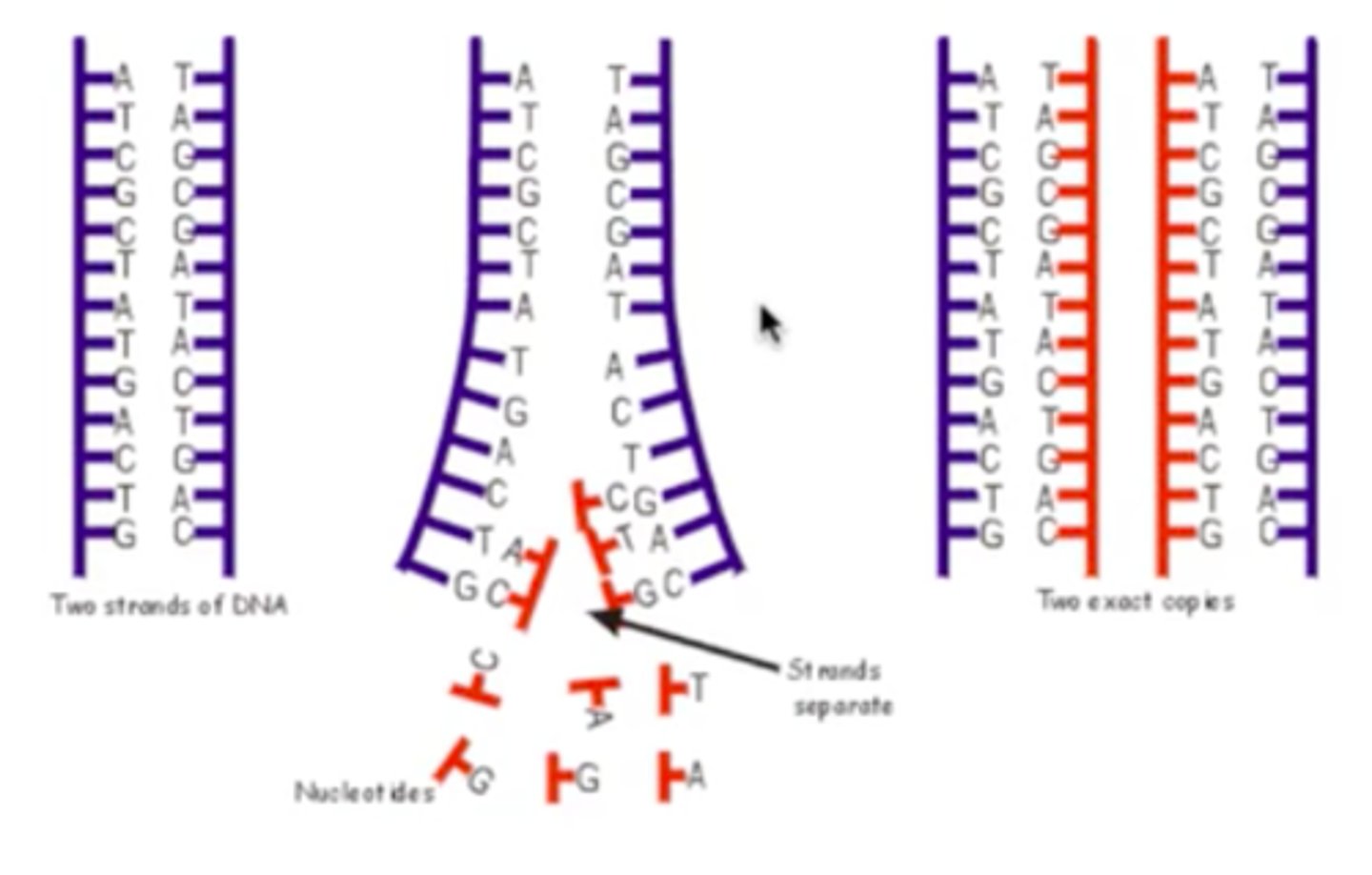
Original DNA strands as templates
They serve as a model for assembling complementary strands
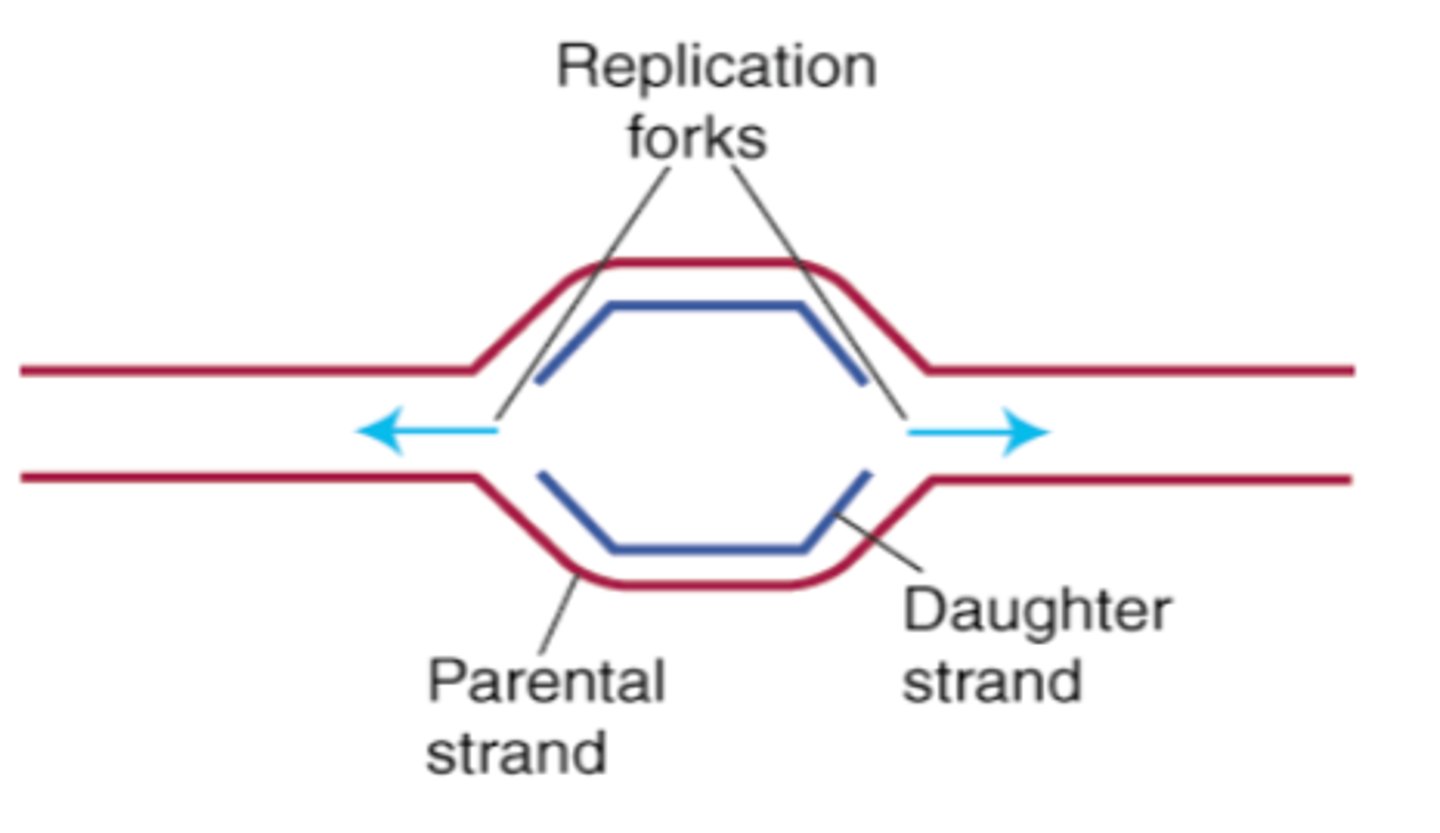
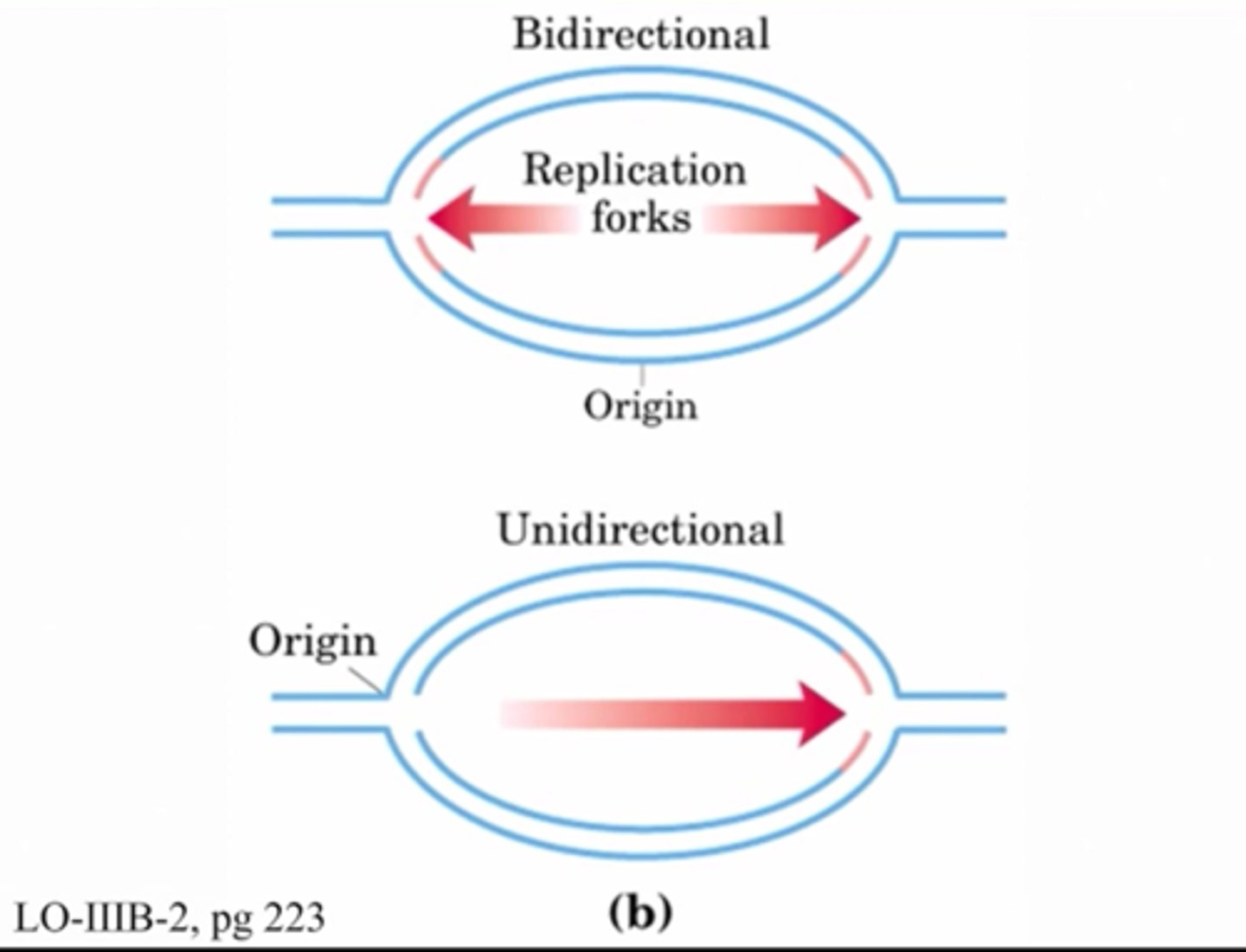
Bidirectional DNA replication is
DNA synthesis starts at one origin and continues outward in both directions
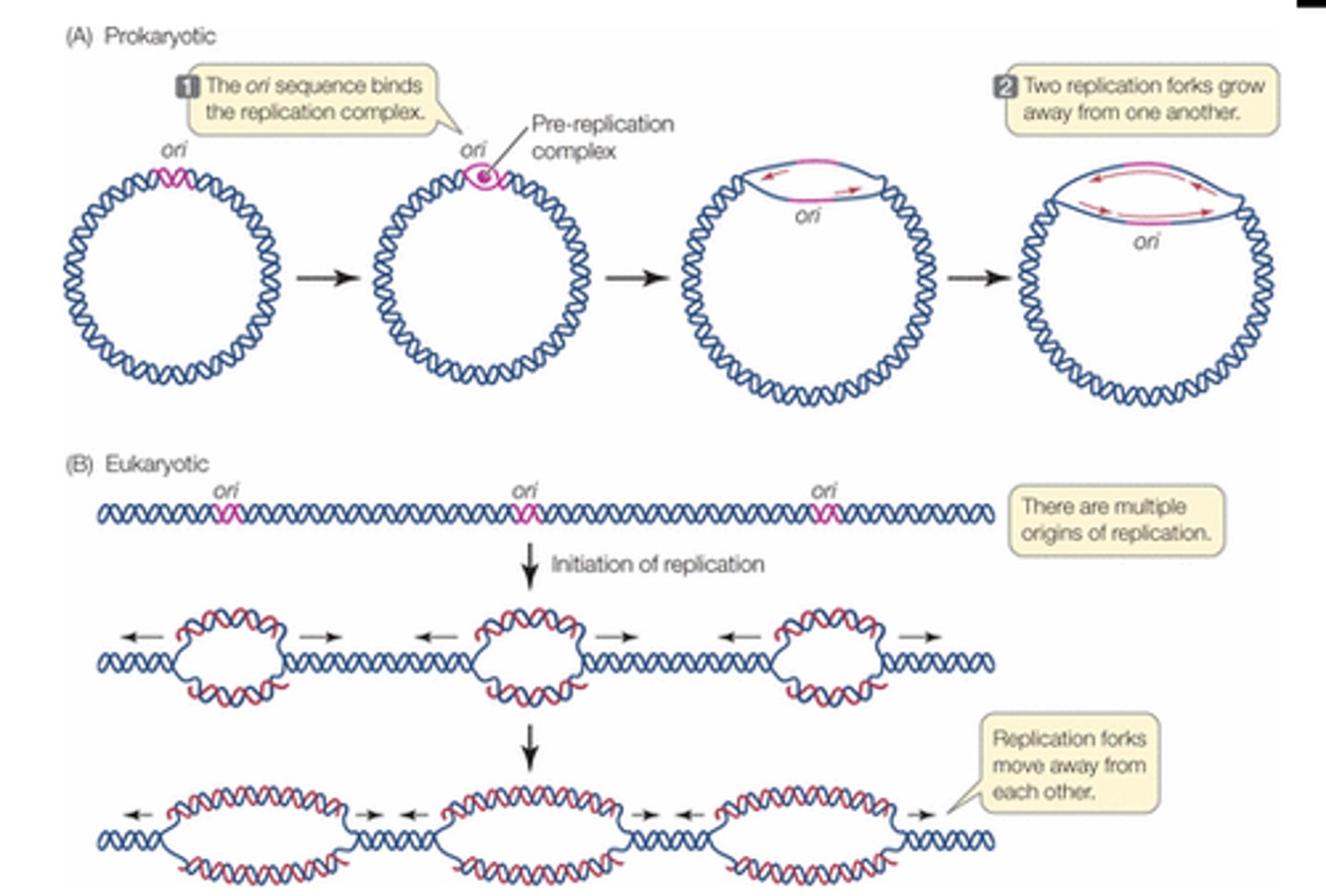
What is the 'Origin of replication'
The specific site where replication begins
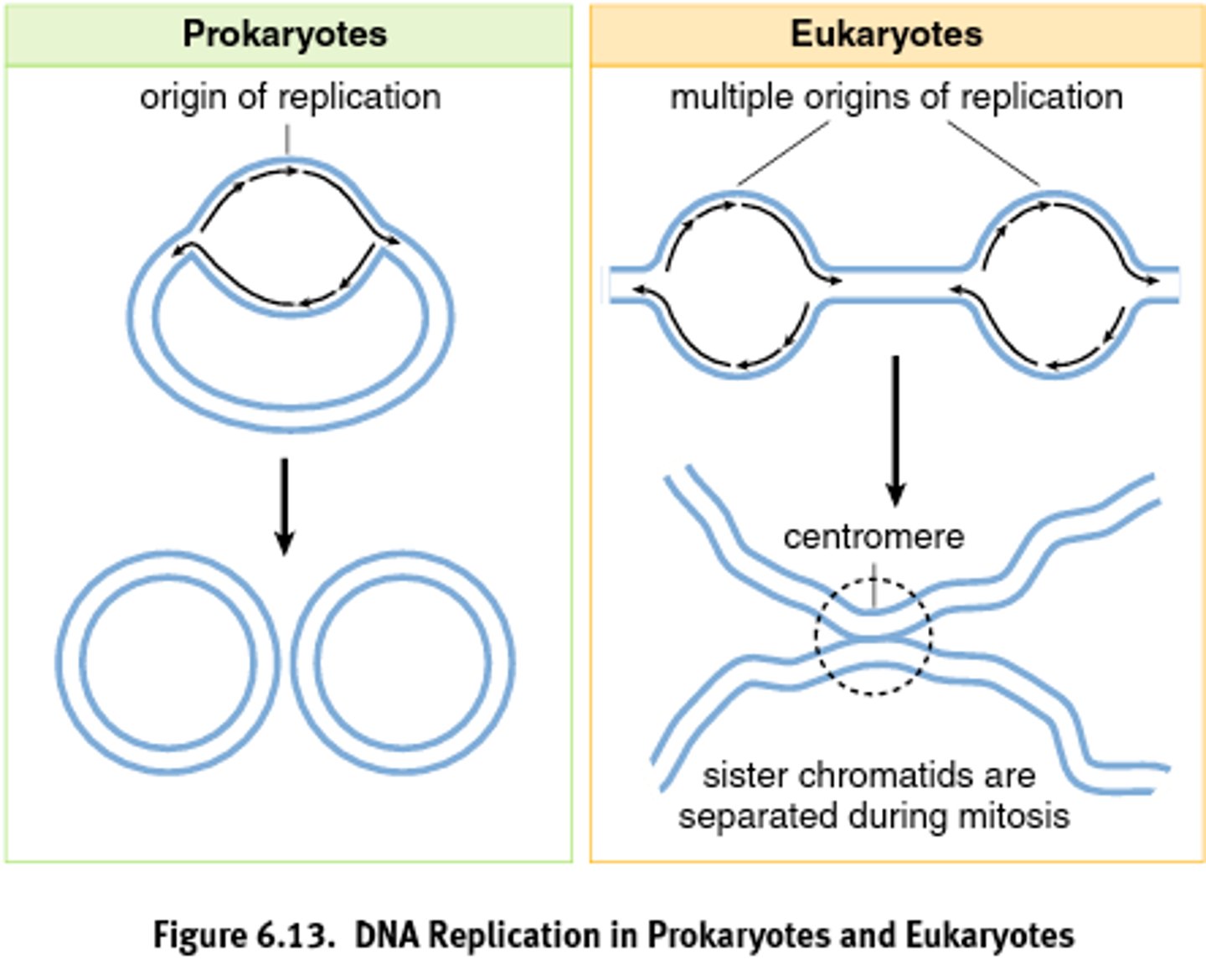
How many origins of replication in prokaryotic chromosomes?
One
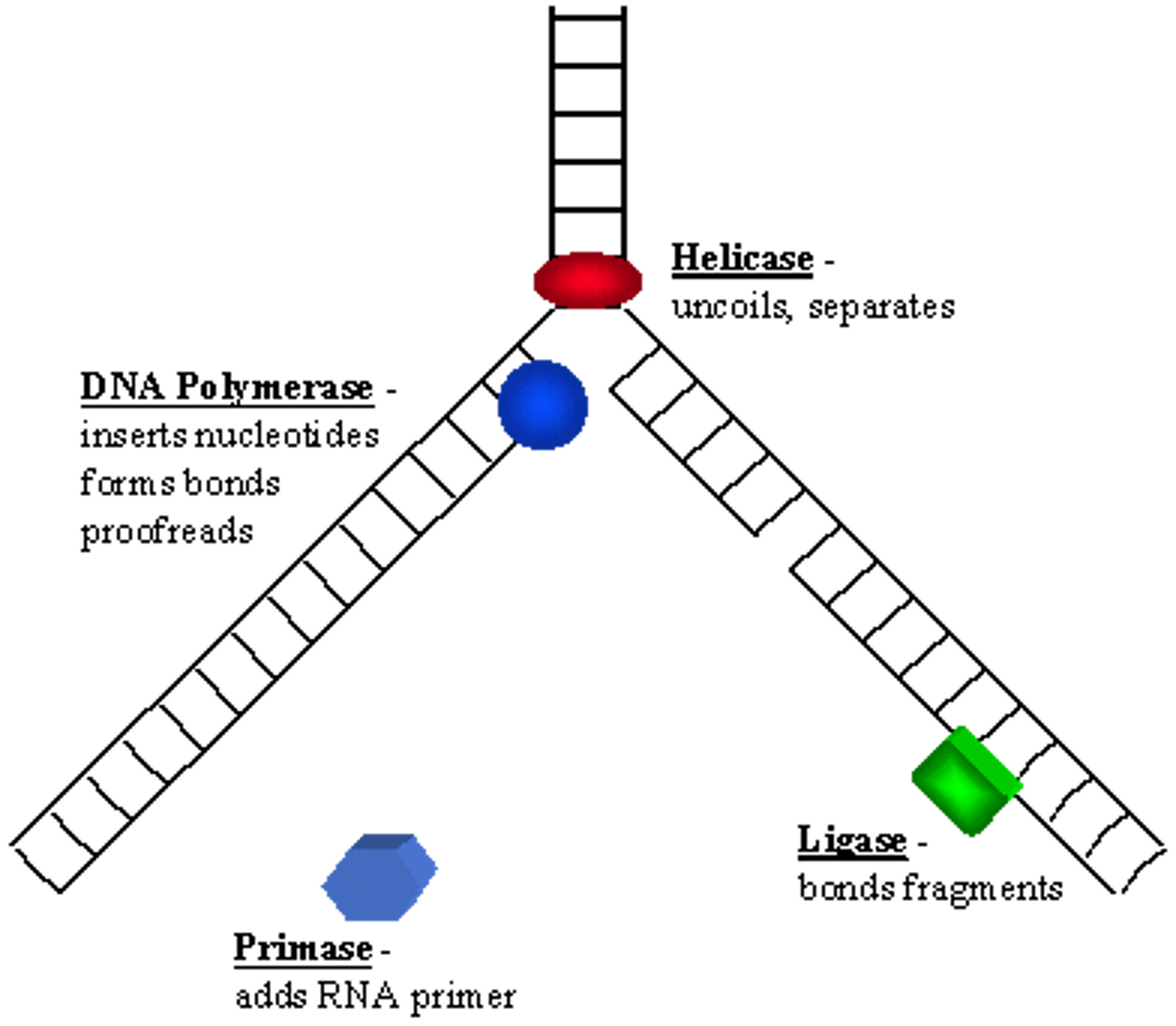
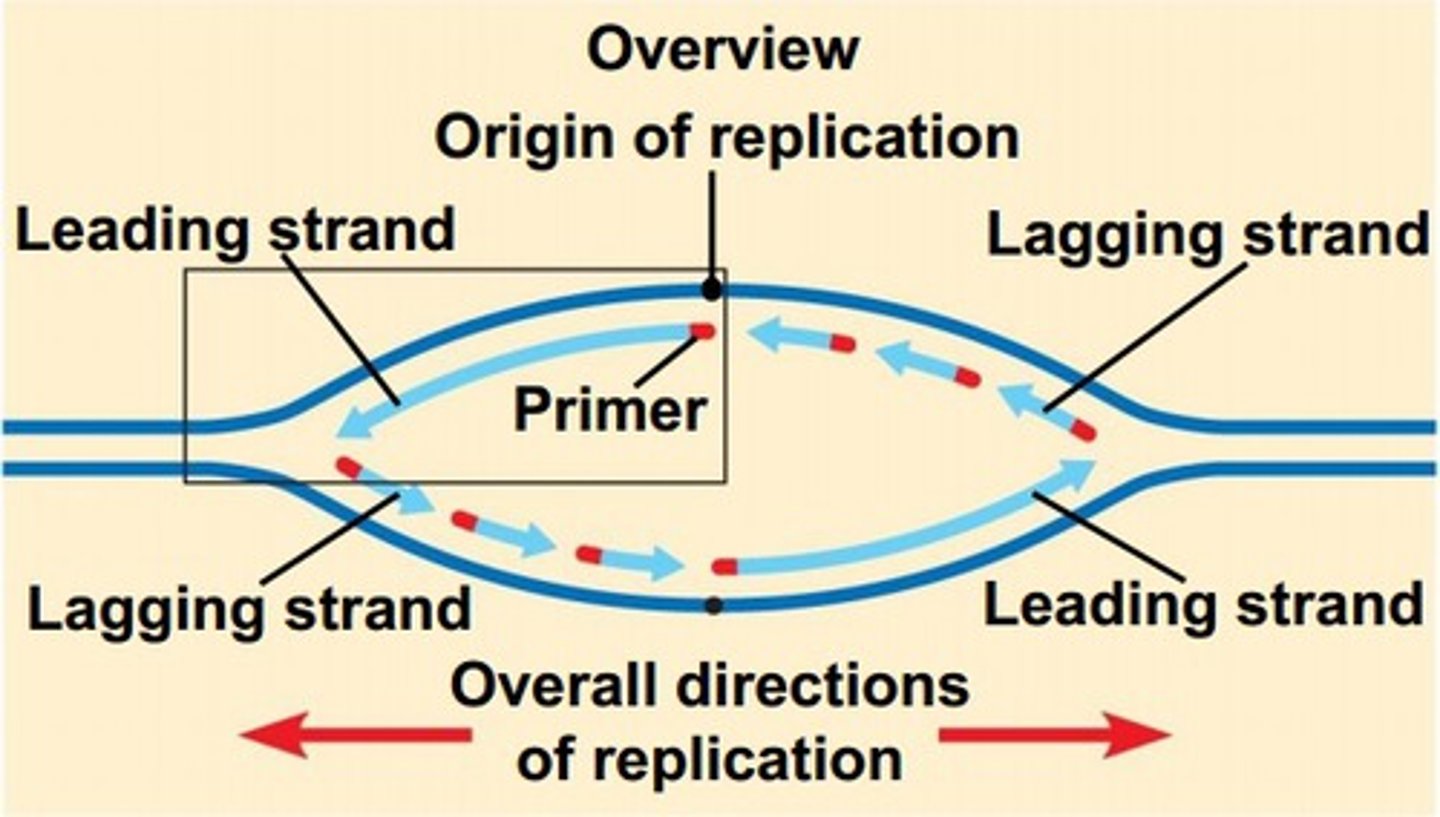
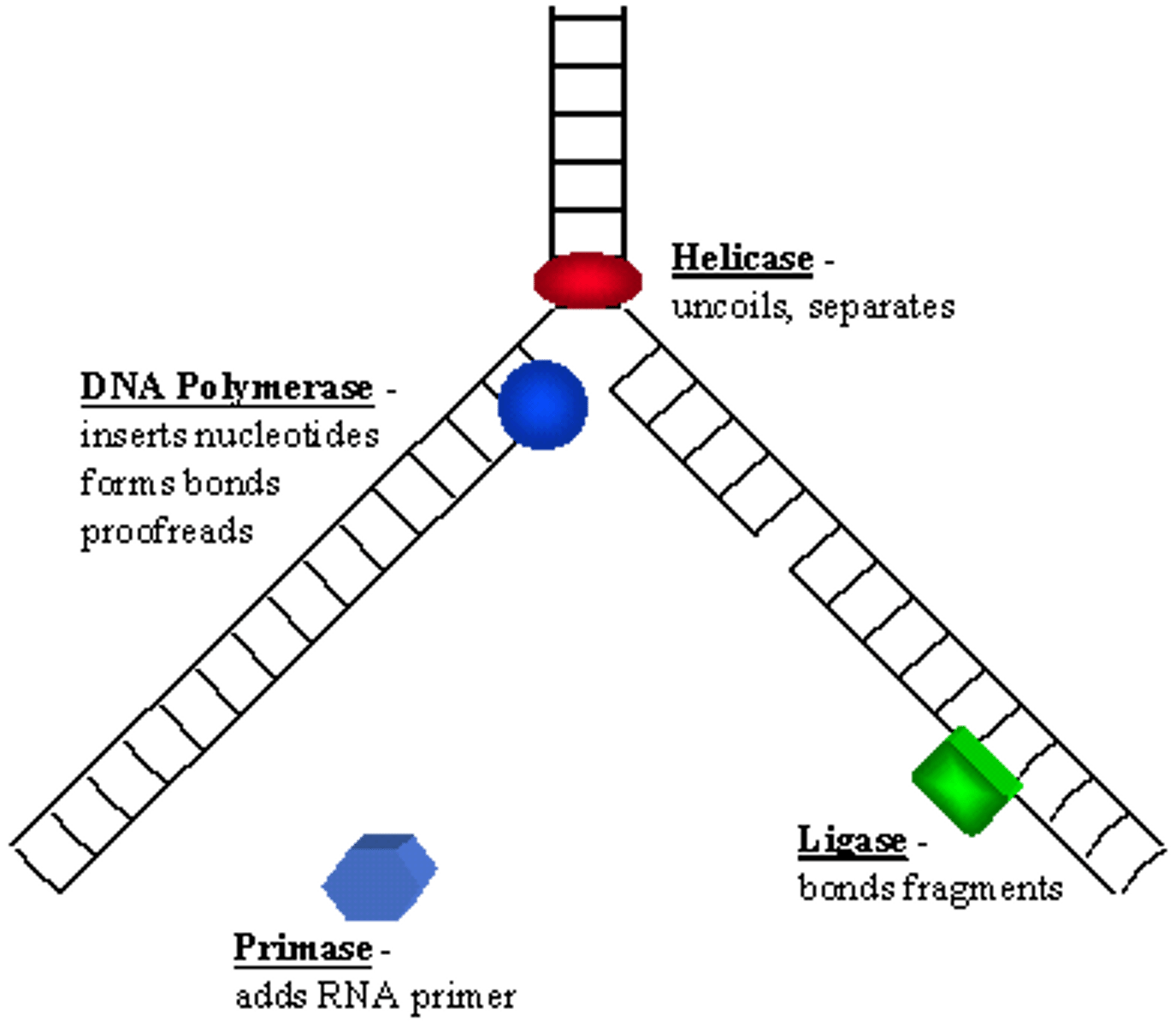
Enzyme adding DNA nucleotides to daughter strand
DNA polymerase
Role of DNA ligase in replication
"molecular glue" - the enzyme that binds DNA fragments
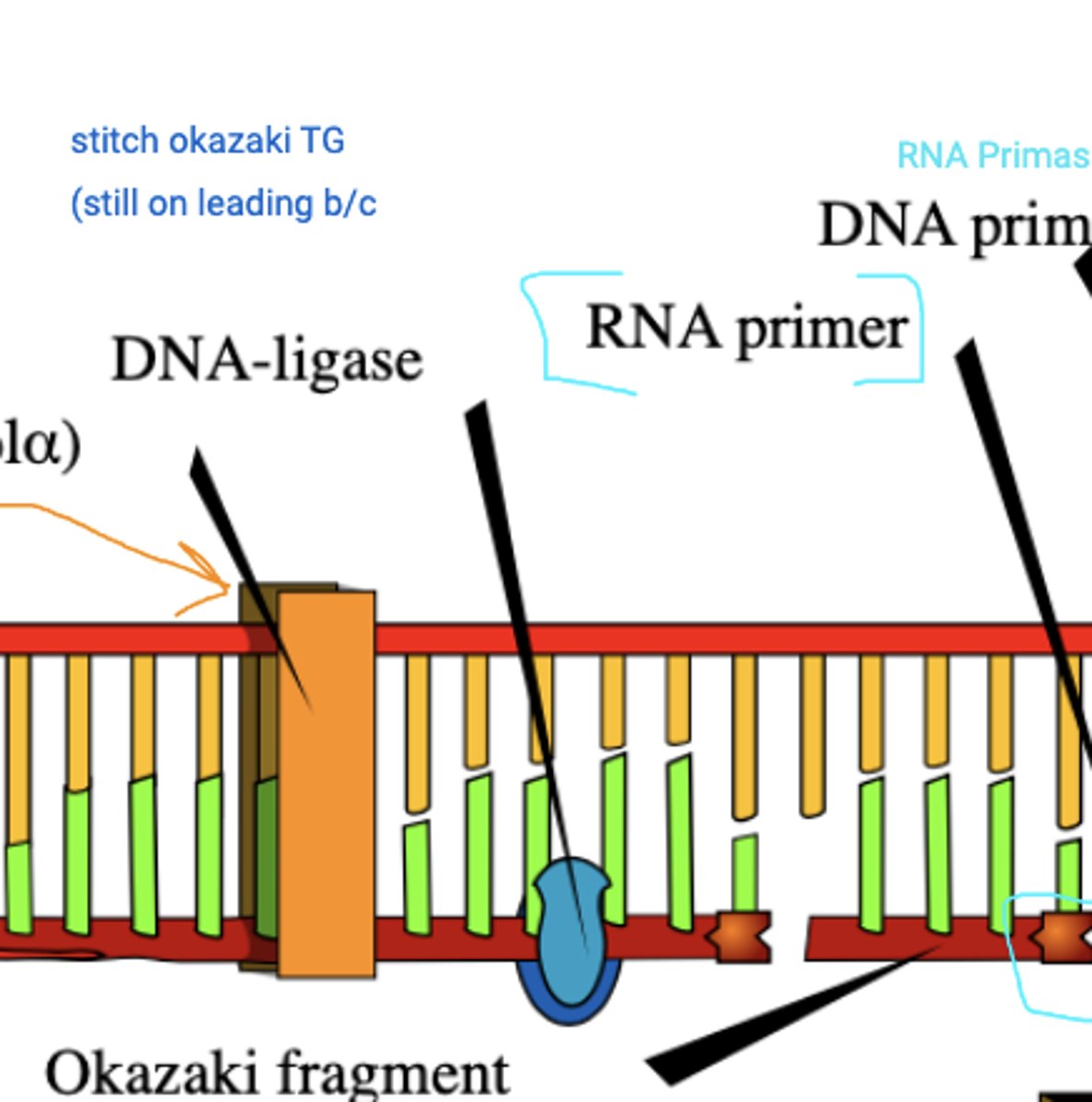
Okazaki fragment
A short segment of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand
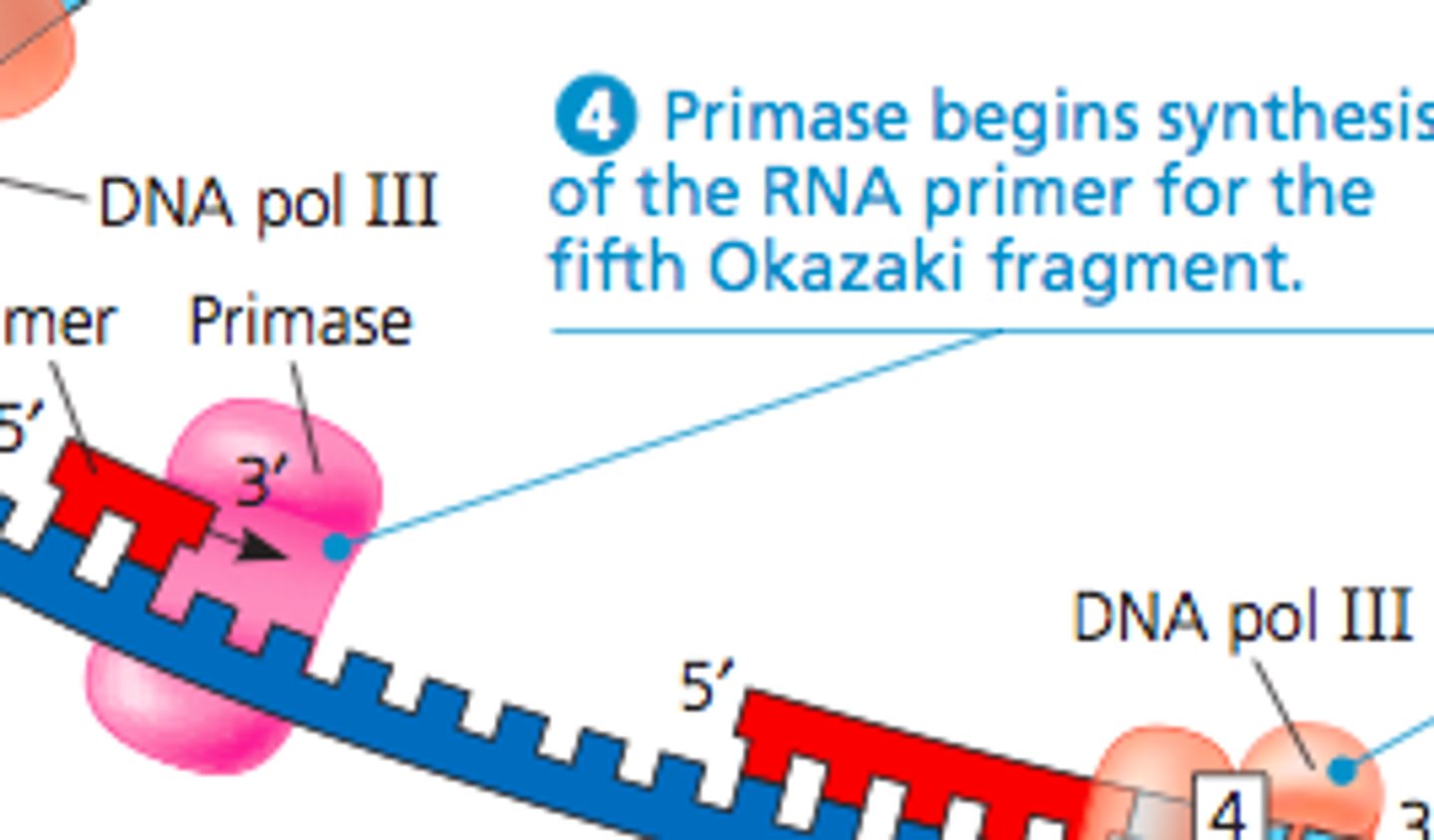
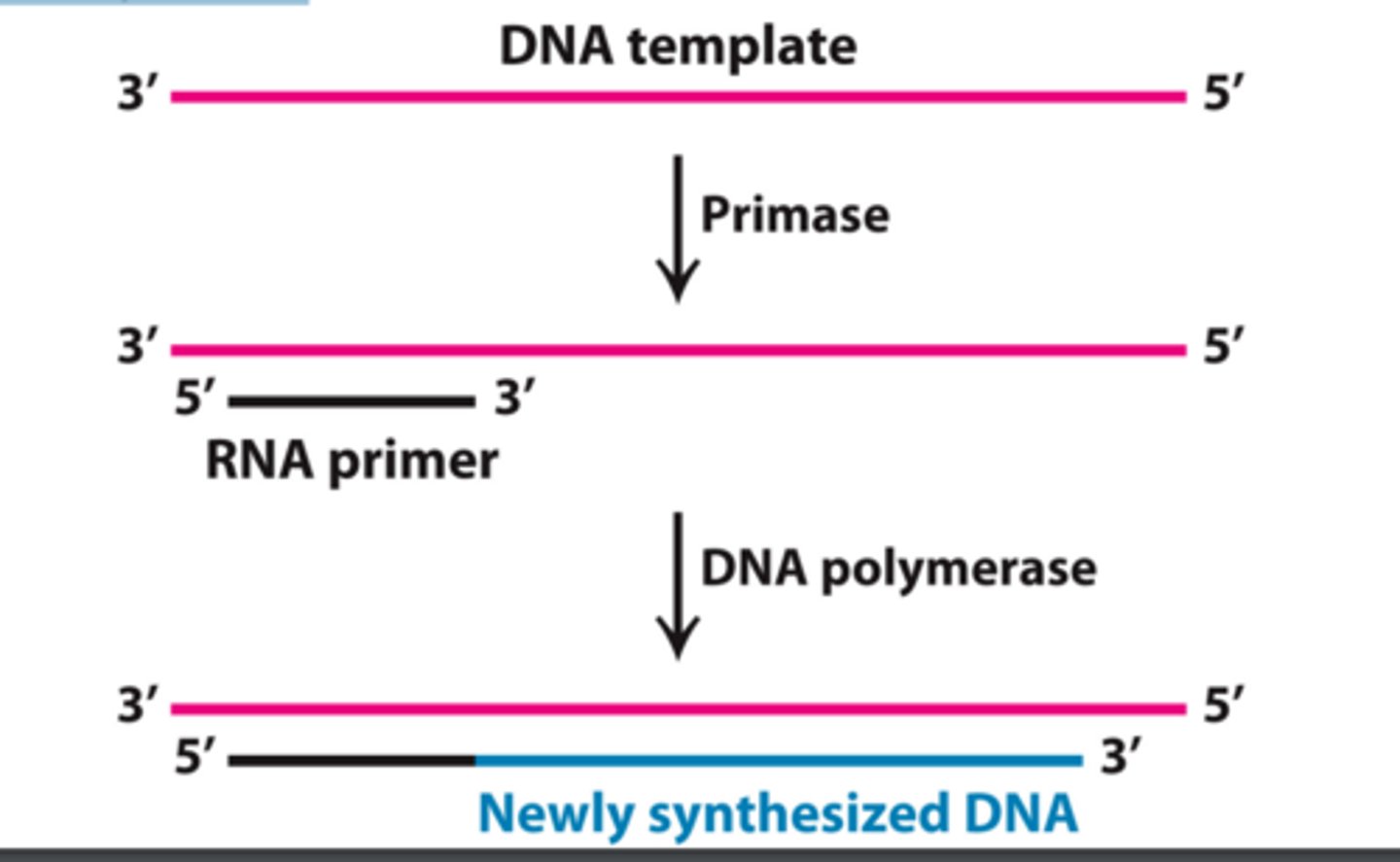
Enzyme synthesizing the RNA primer
Primase
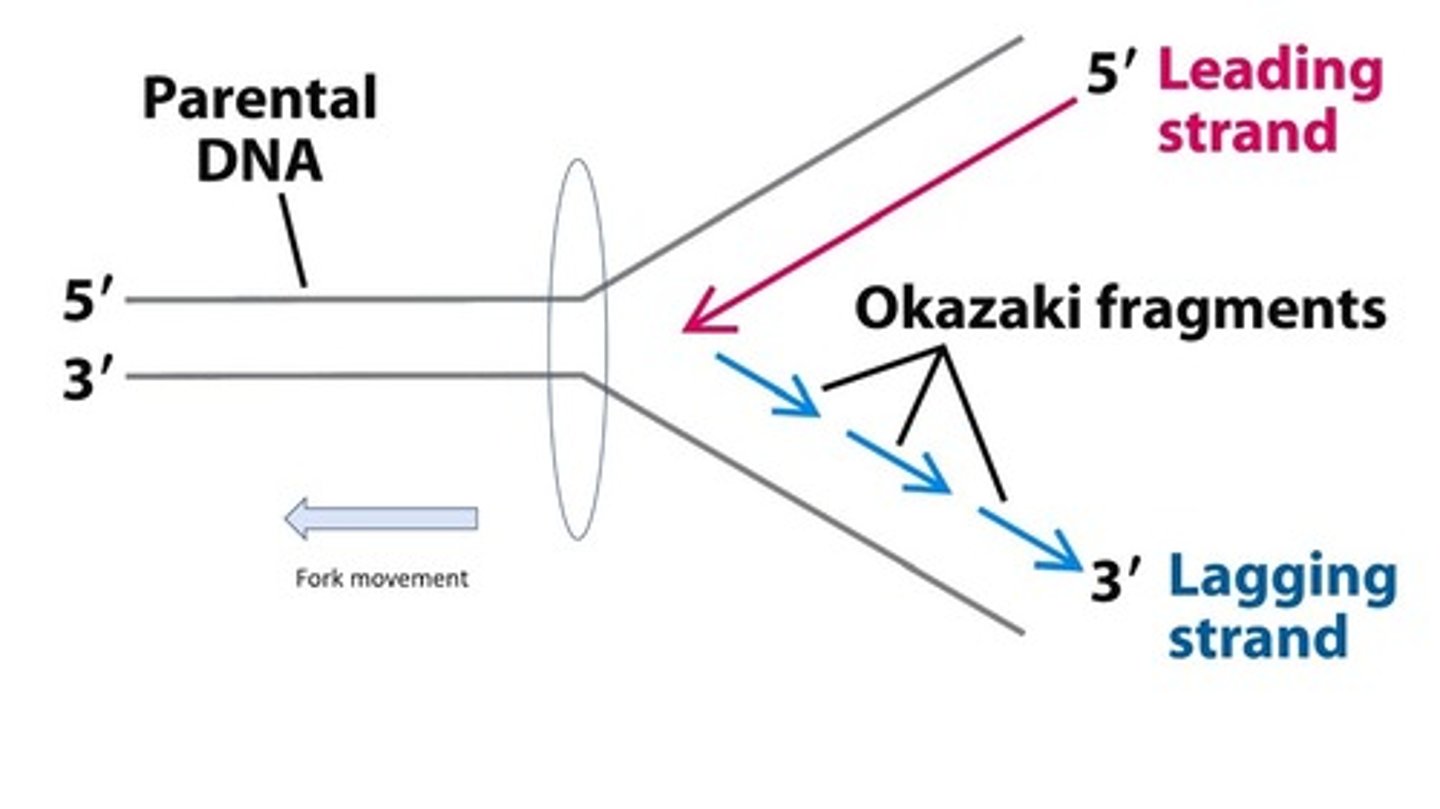
Difference between leading and lagging strands
The leading strand is synthesized continuously; the lagging strand is synthesized in fragments
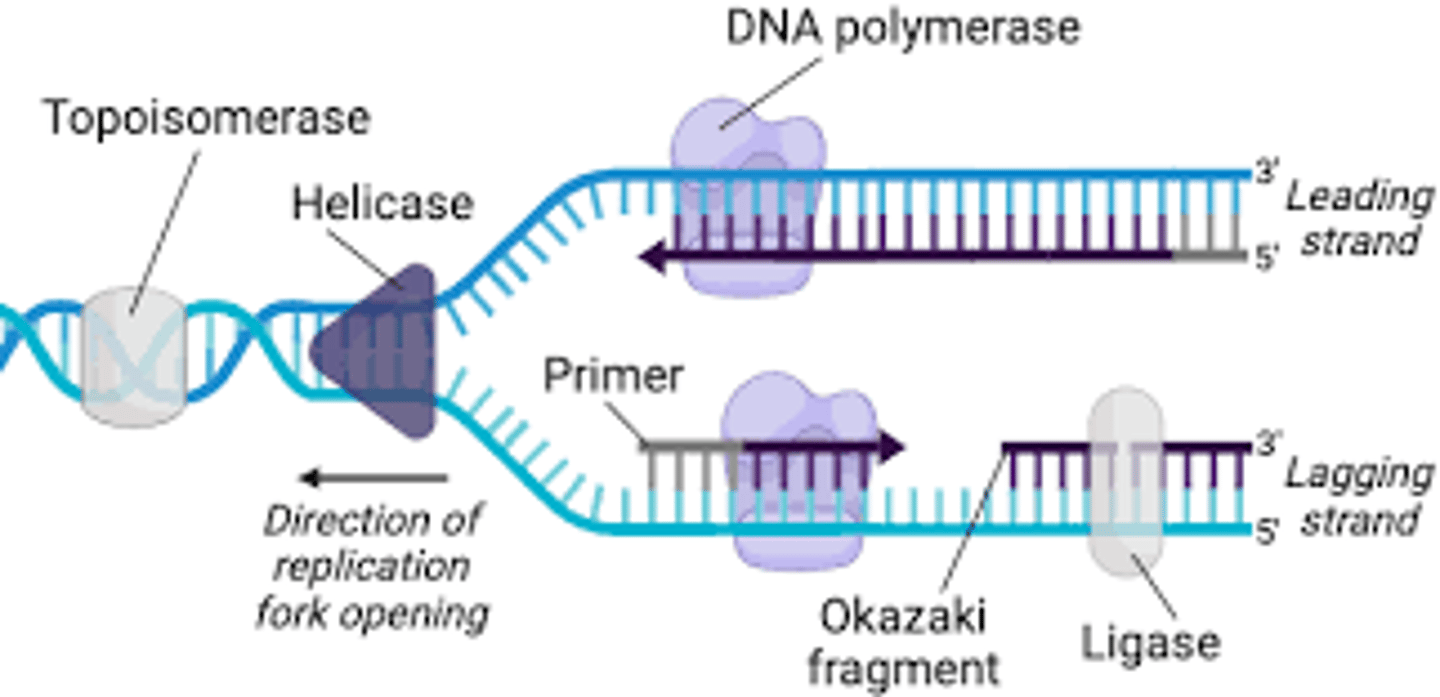
Enzyme unwinding the DNA double helix
Helicase
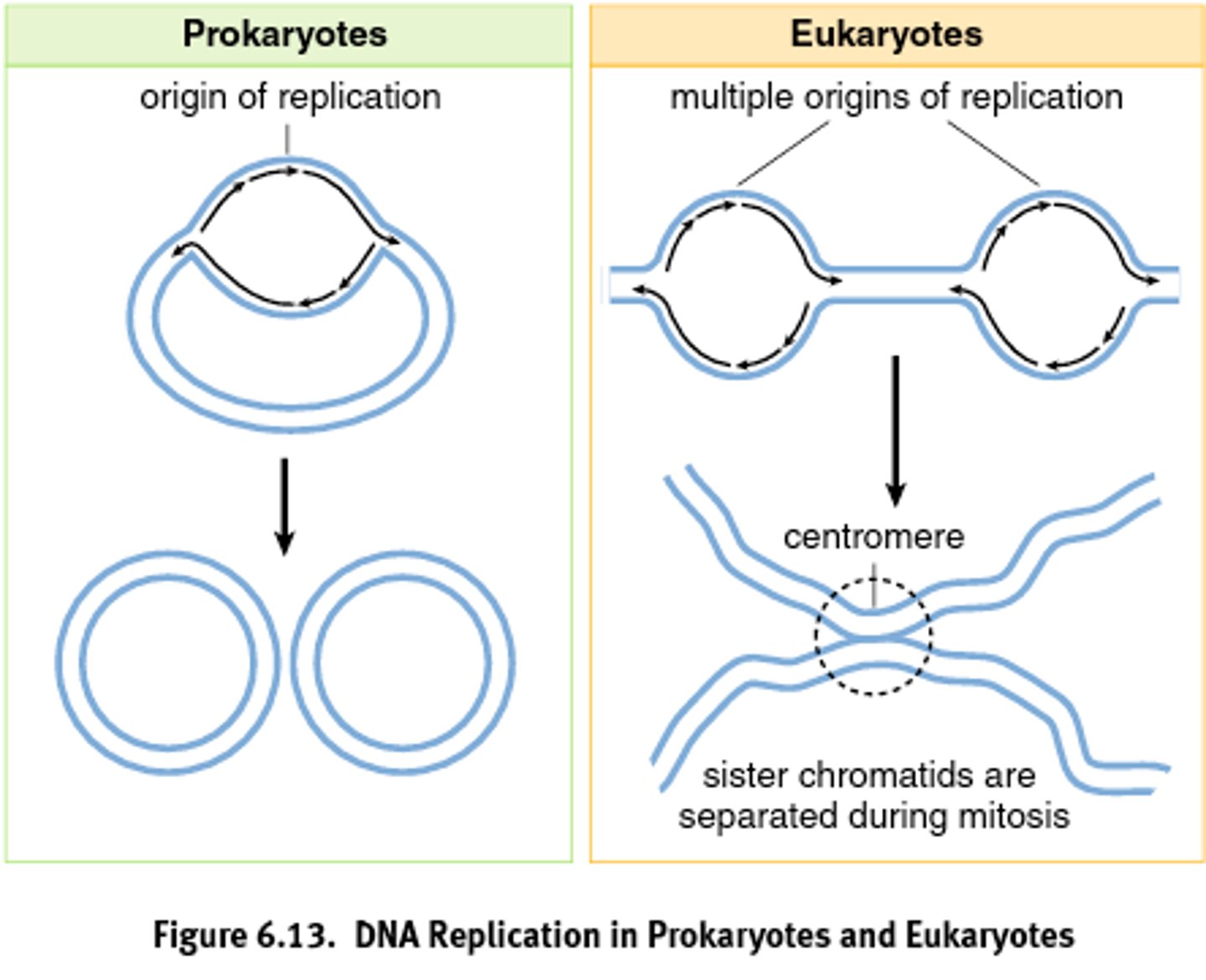
Formation at the origin of replication in eukaryotic chromosomes
A replication bubble with two replication forks
Fate of the RNA primer after DNA replication
It is removed and replaced by DNA nucleotides
Name three or more ways DNA analysis is used in science and medicine
crime solving, paternity
testing, human identification, genetic
testing & diagnostics, genealogy,
identifying pathogens, vaccine
development and cancer therap
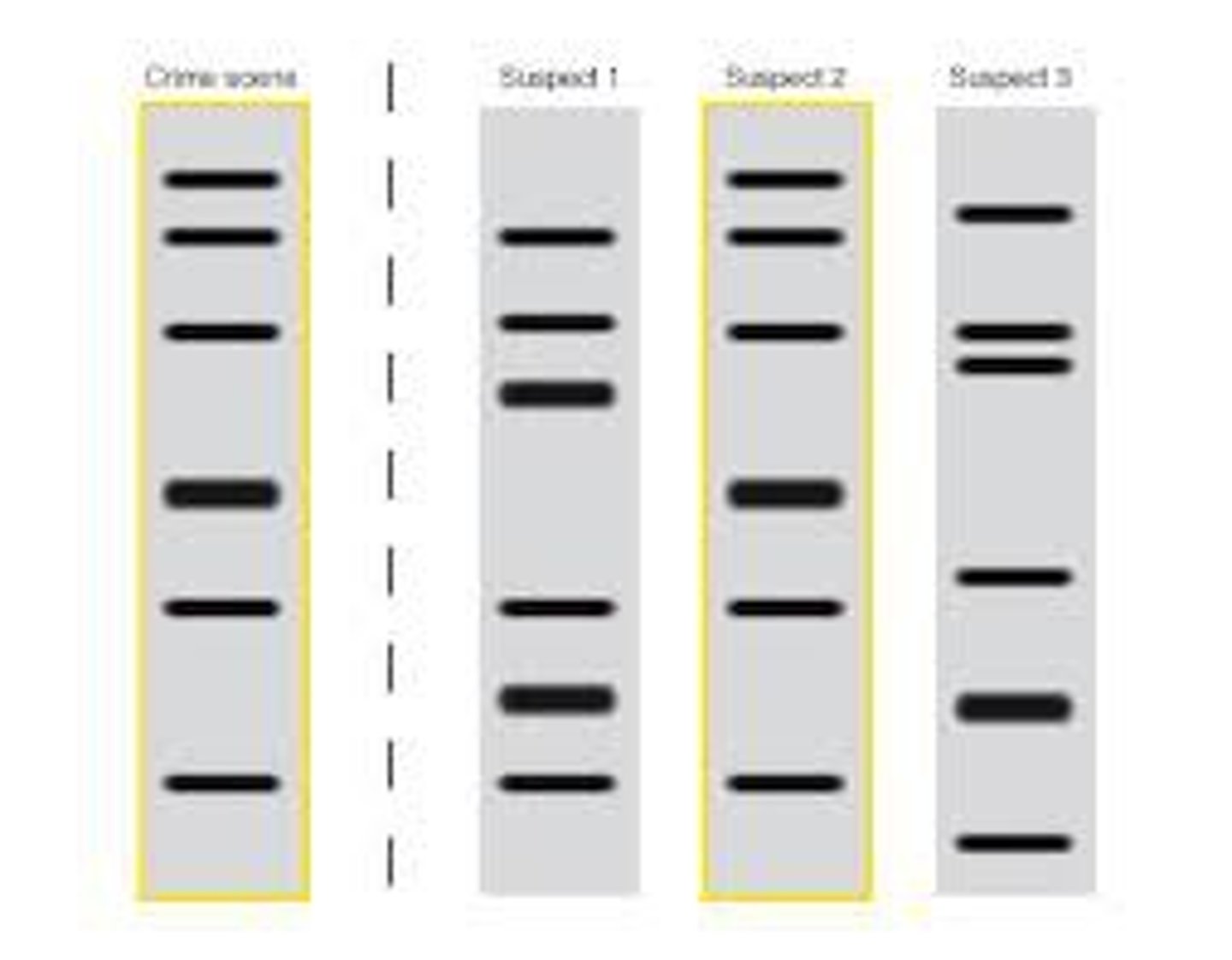
What are some sources of DNA (e.g., from a crime scene)
hair, blood, or
saliva
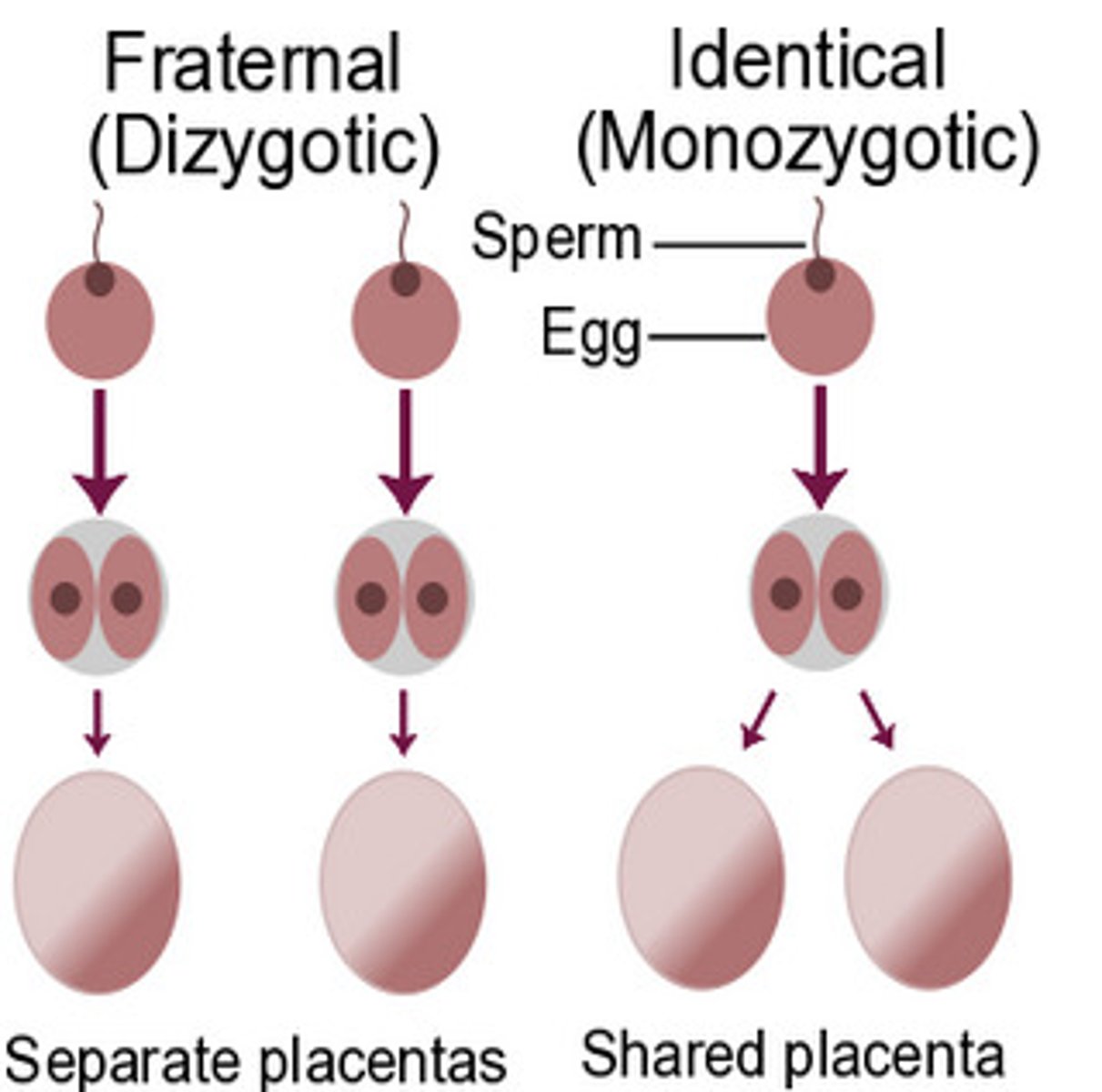
With the exception of ______________ _________, each
person's DNA is unique and it is possible
to detect differences between human
beings on the basis of their unique DNA
identical twins
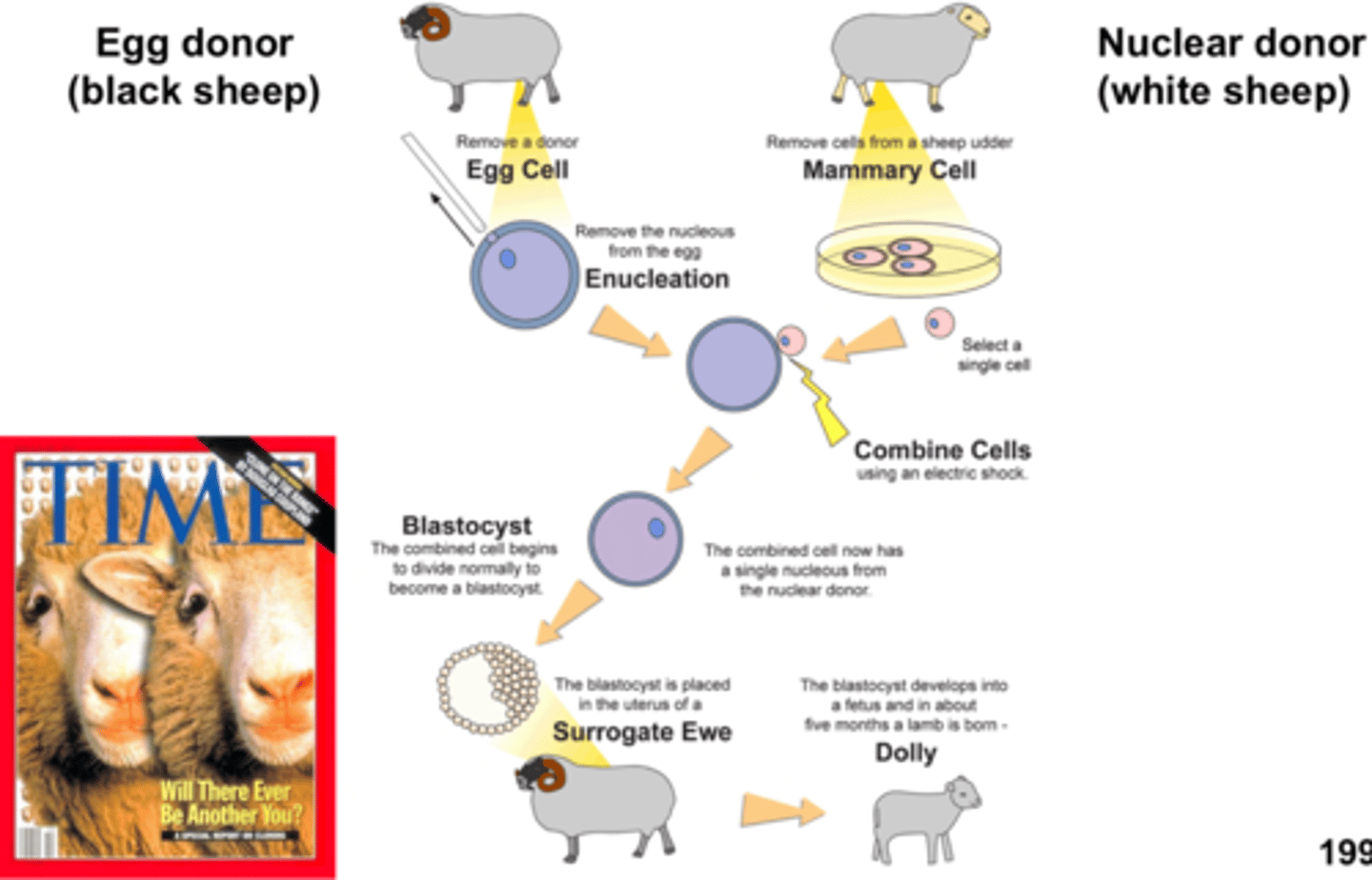
What is special about Dolly the Sheep (1996)?
first successful mammalian cloning
Describe 2 (or more) of Rosalind Franklin's contributions to science
Used X-ray diffraction to discover the double-helical structure of DNA (photo 51!); research on the structure of coal led to better gas masks for WWII; advancing knowledge of the structure of viruses

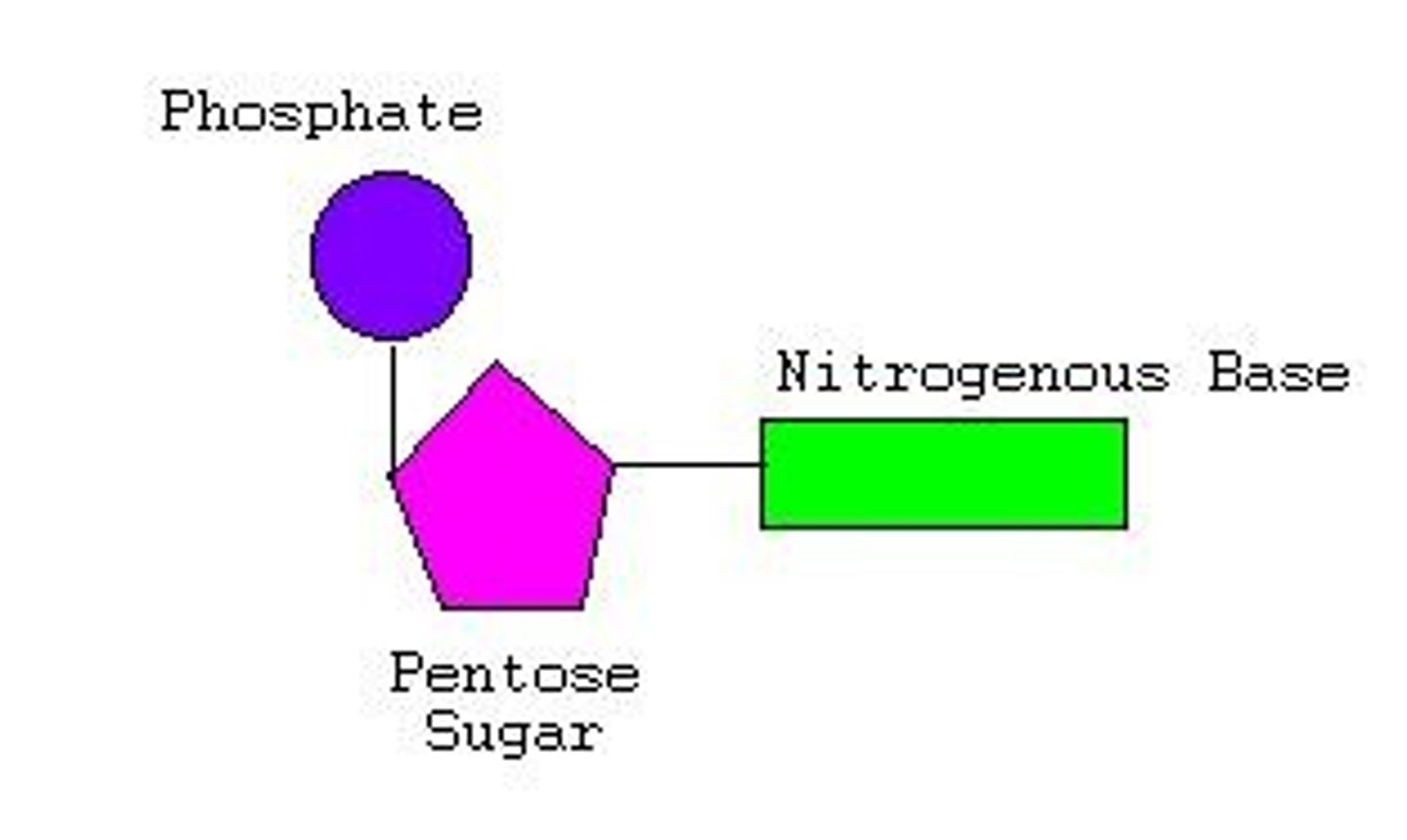
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Nucleotide
In its natural state, each DNA molecule is
actually composed of two single strands
held together along their length with
_________________ bonds between the bases
hydrogen bonds
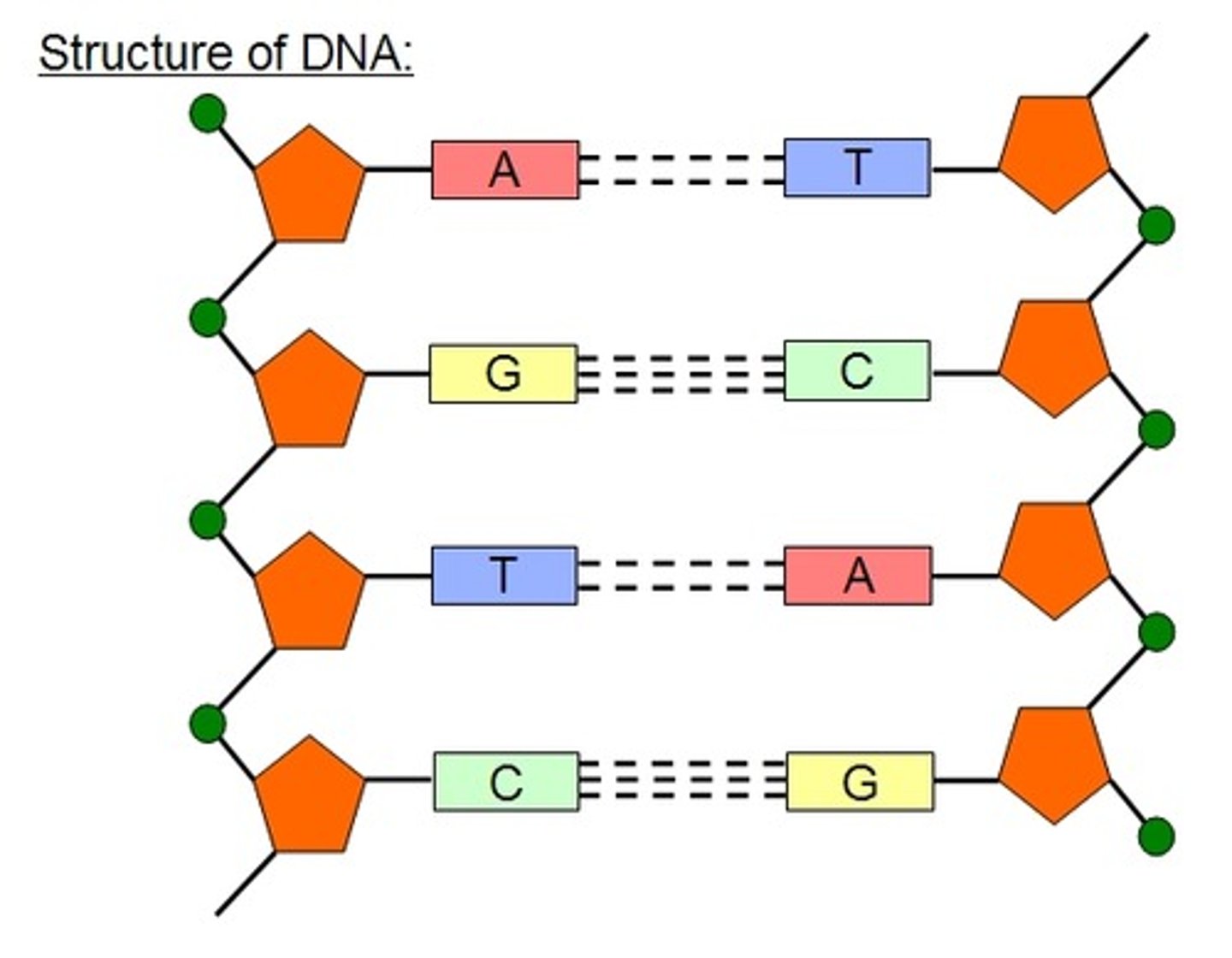
DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted
around each other to form a right-handed
helix, called a __________ __________.
double helix
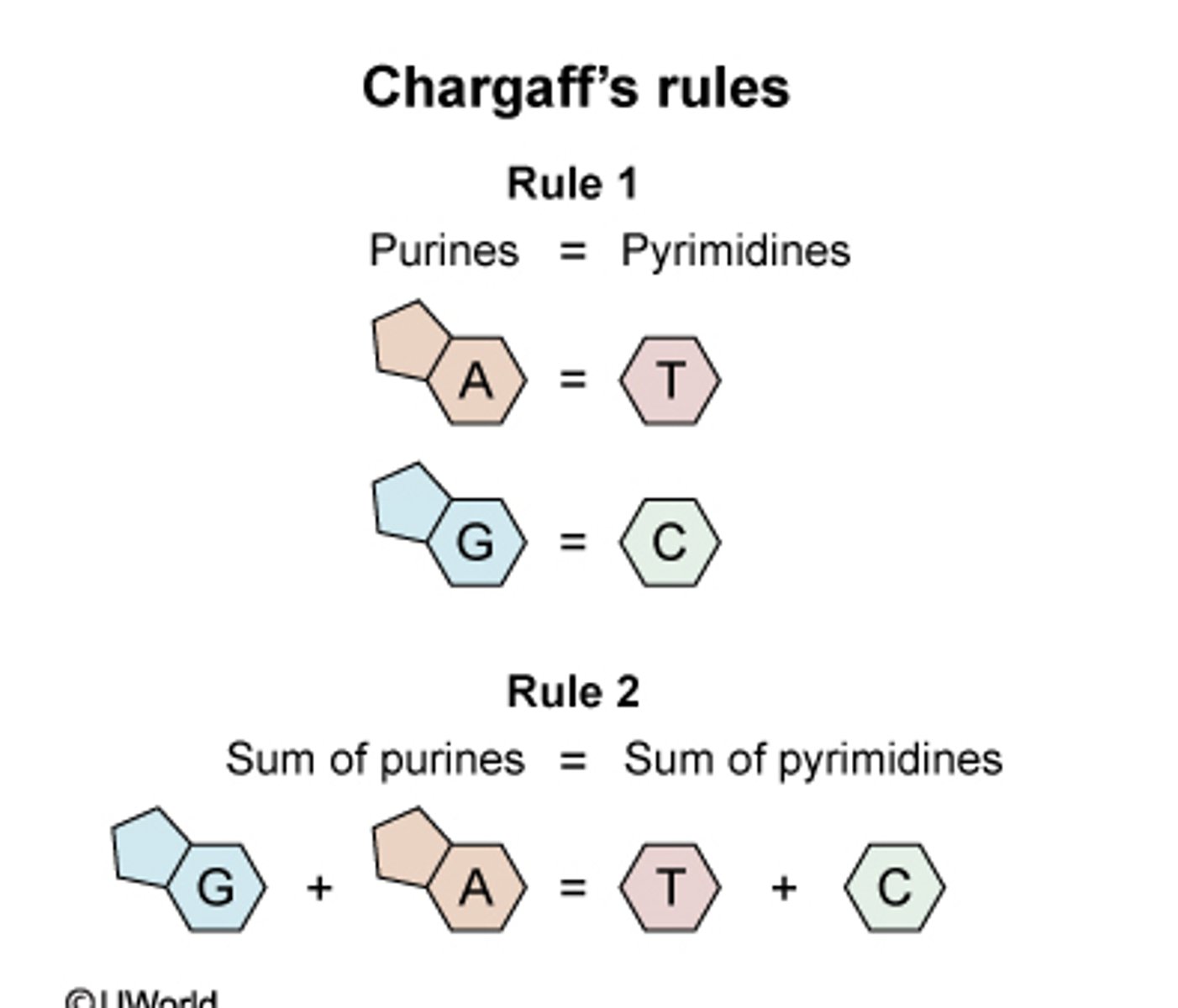
Describe Chargaff's rules
observations by Erwin Chargaff that concentrations of the four nucleotide bases differ among species; and that, within a species, the concentrations of adenine and thymine are always about the same and the concentrations of cytosine and guanine are always about the same
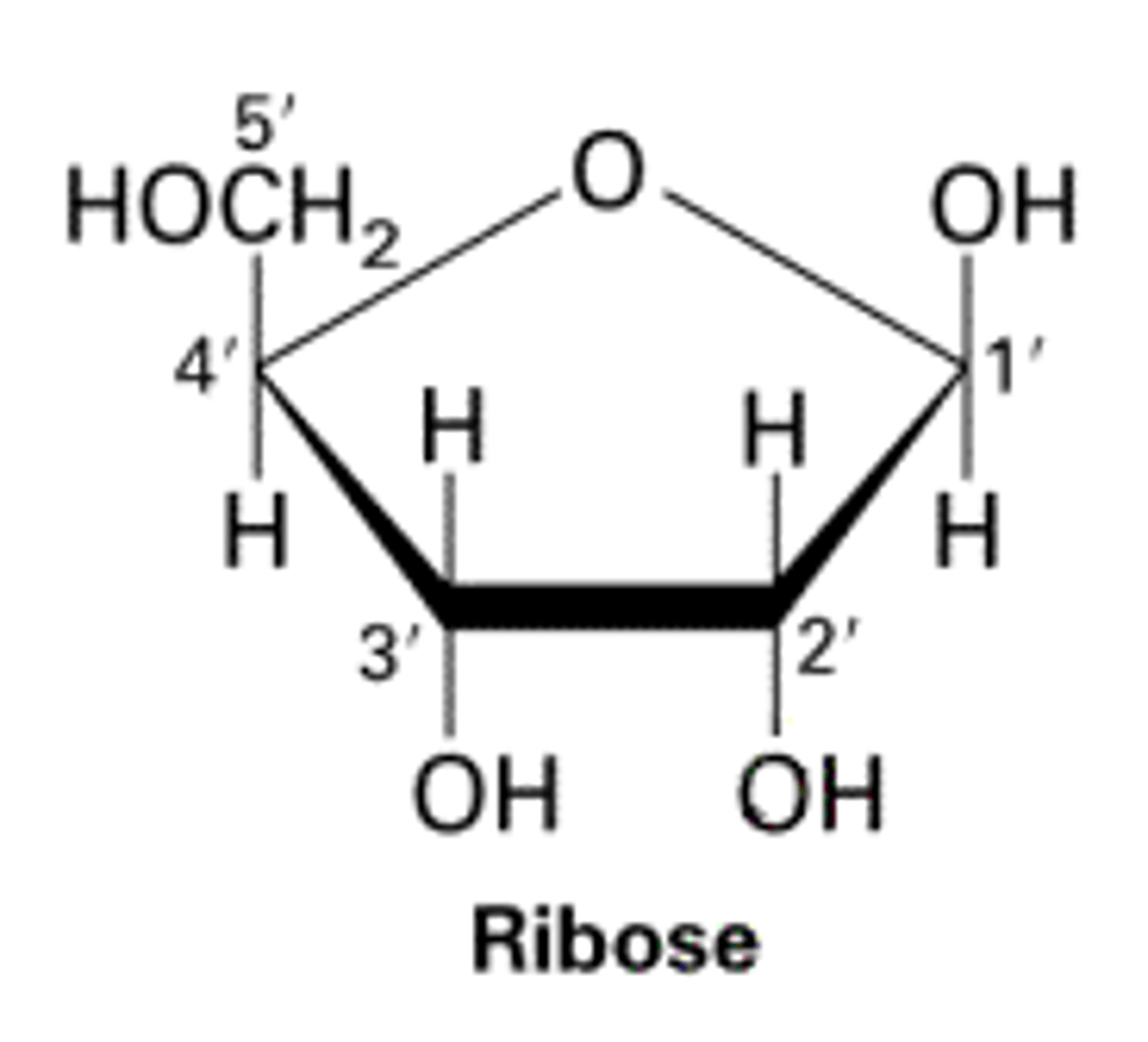
What is ribose?
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
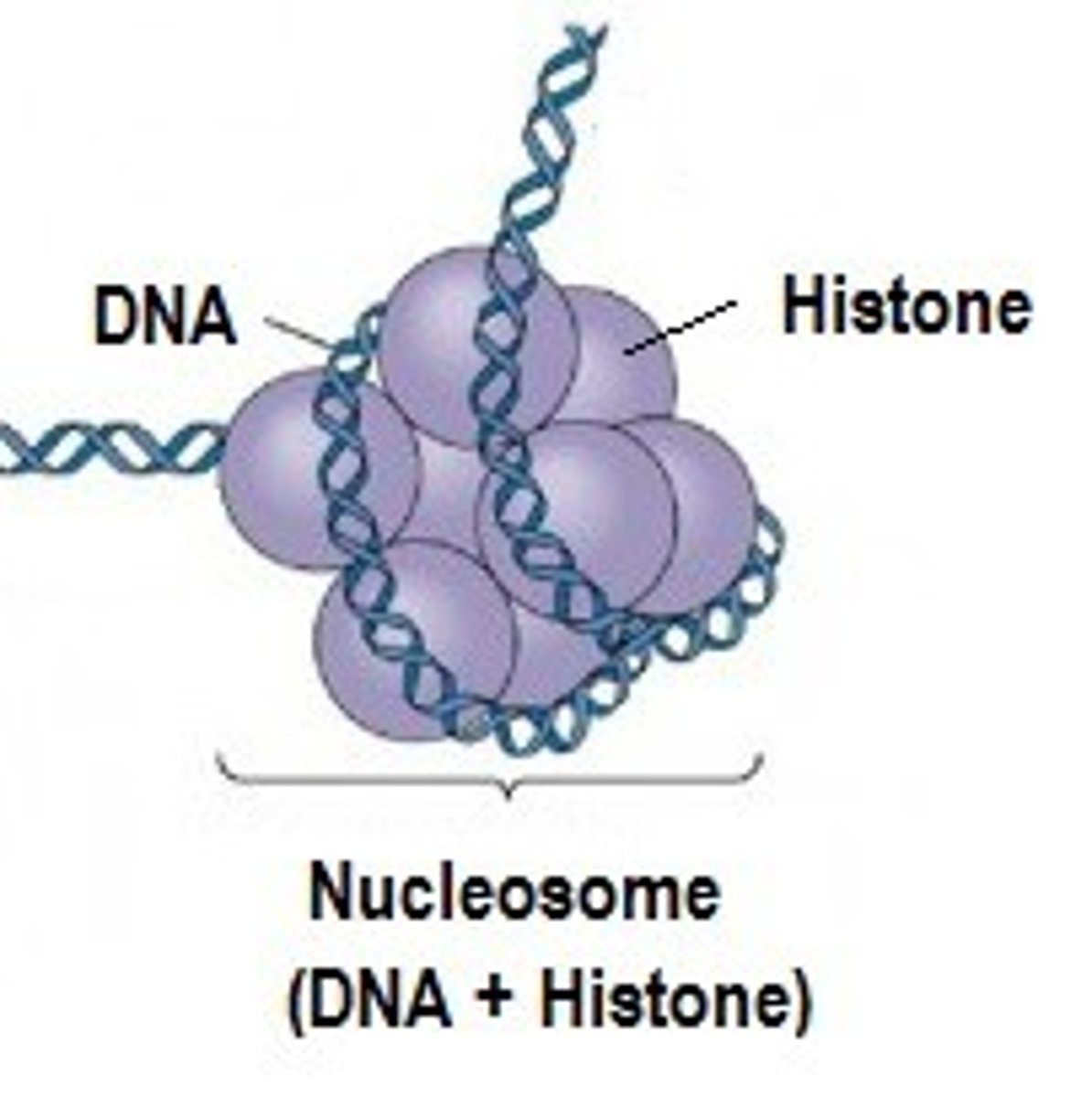
histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
A DNA strand has the following sequence:
5' - ATCGCAGTCACCAA - 3'
What is the sequence of the complementary strand
3' - TAGCGTCAGTGGTT - 5'

True of False: Eukaryotic chromosomes may have hundreds of origins
TRUE
What does it mean that DNA replication is bidirectional? How does this benefit a cell?
replication proceeds in two directions away from the origin of replication; allows DNA to be copied more efficiently and quickly
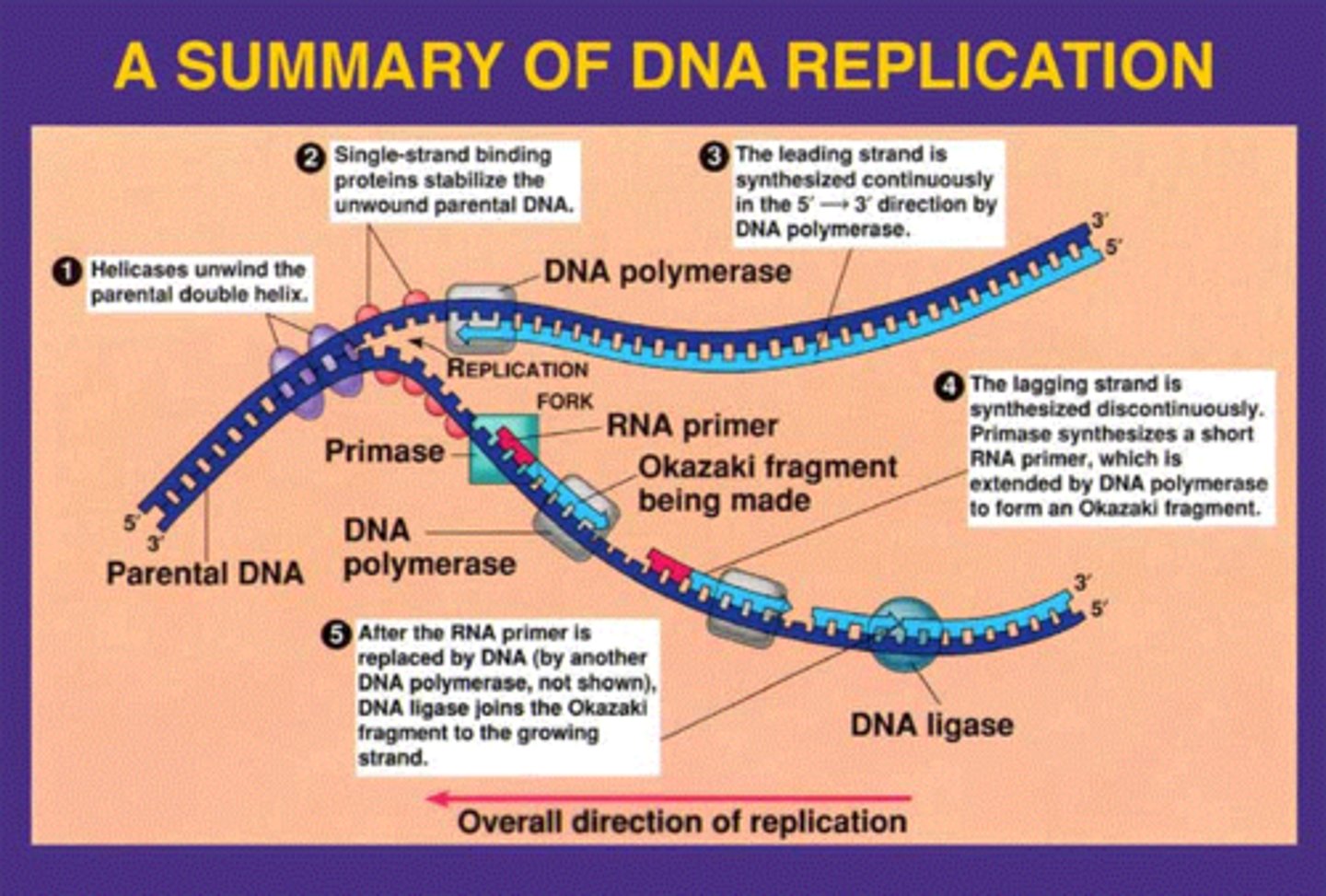
DNA replication general steps?
1. The DNA unzips at the origin of replication by the enzyme Helicase
2. The primase enzyme attaches RNA nucleotides to form a primer
(5’ 3’)
3. The DNA polymerase III attaches DNA nucleotides in the 5’ 3’
4. Because the DNA is antiparallel, one strand replicates
continuously (leading strand), while the other replicates
discontinuously (lagging strand).
5. The RNA primer is removed and the gap is filled by DNA
nucleotides.
6. The end of the strands are “glued” by DNA ligase.
What does DNA polymerase III do?
adding bases (5' to 3') to the new DNA chain; proofreading the chain for mistakes
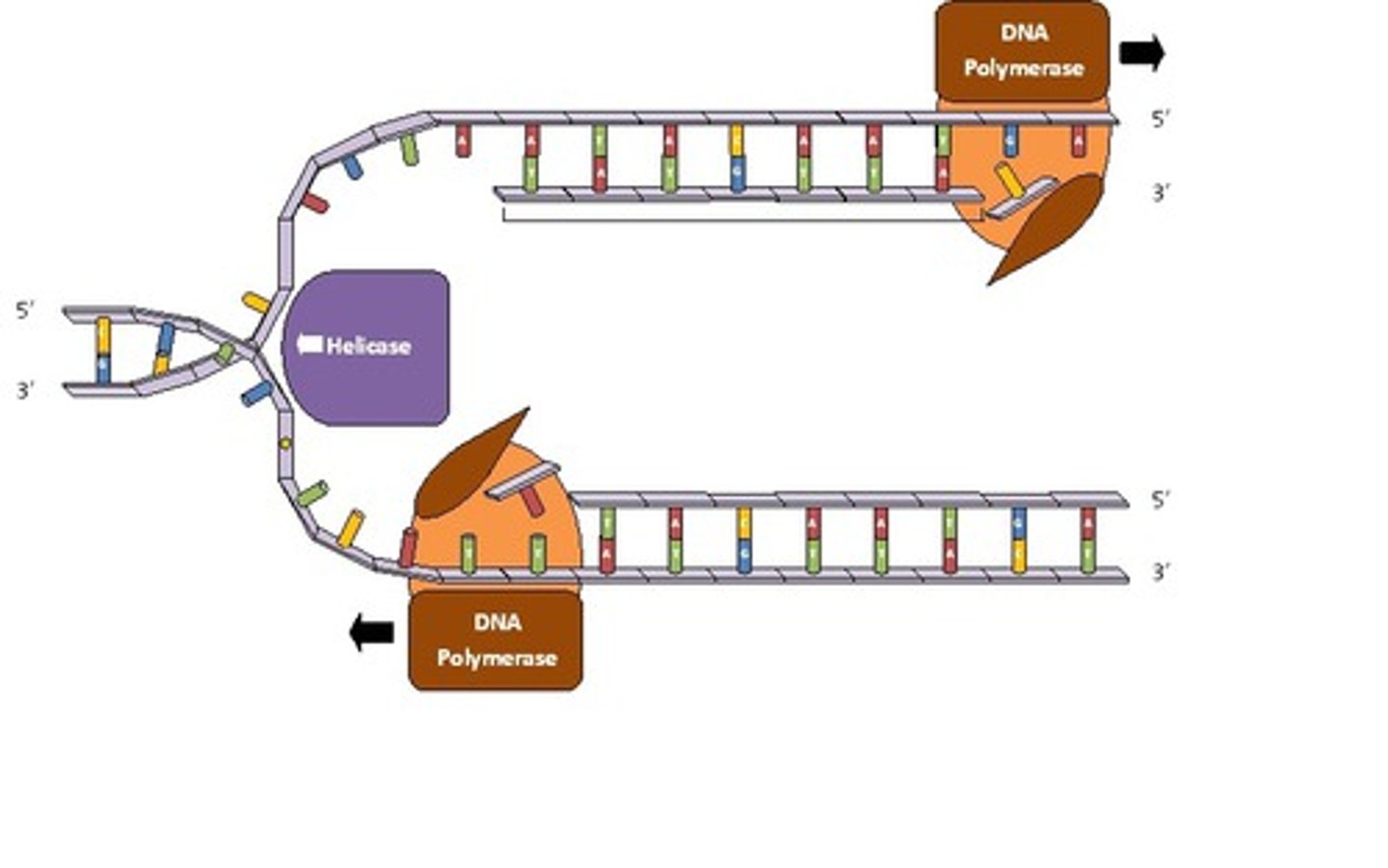
exonuclease
removes RNA primers
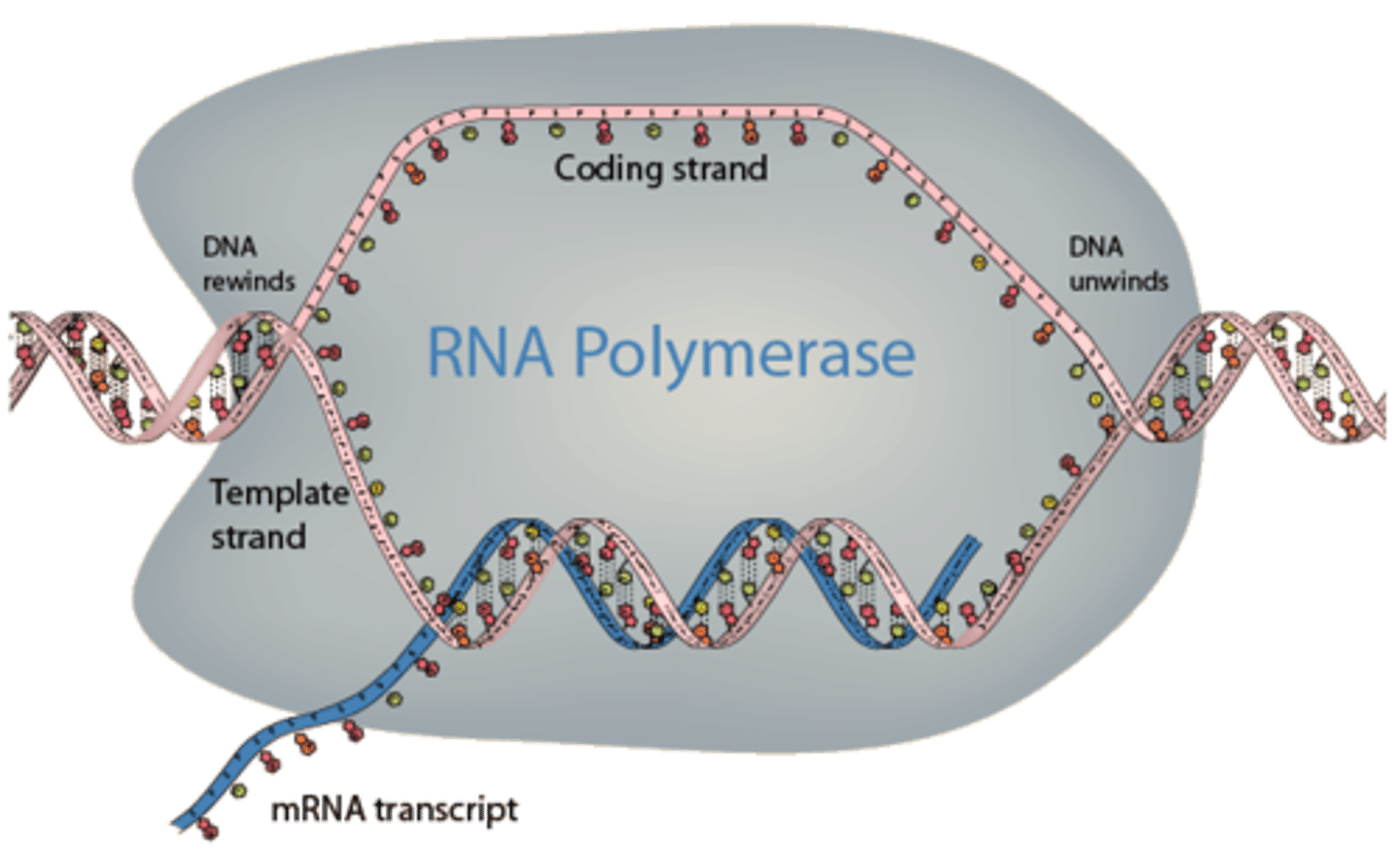
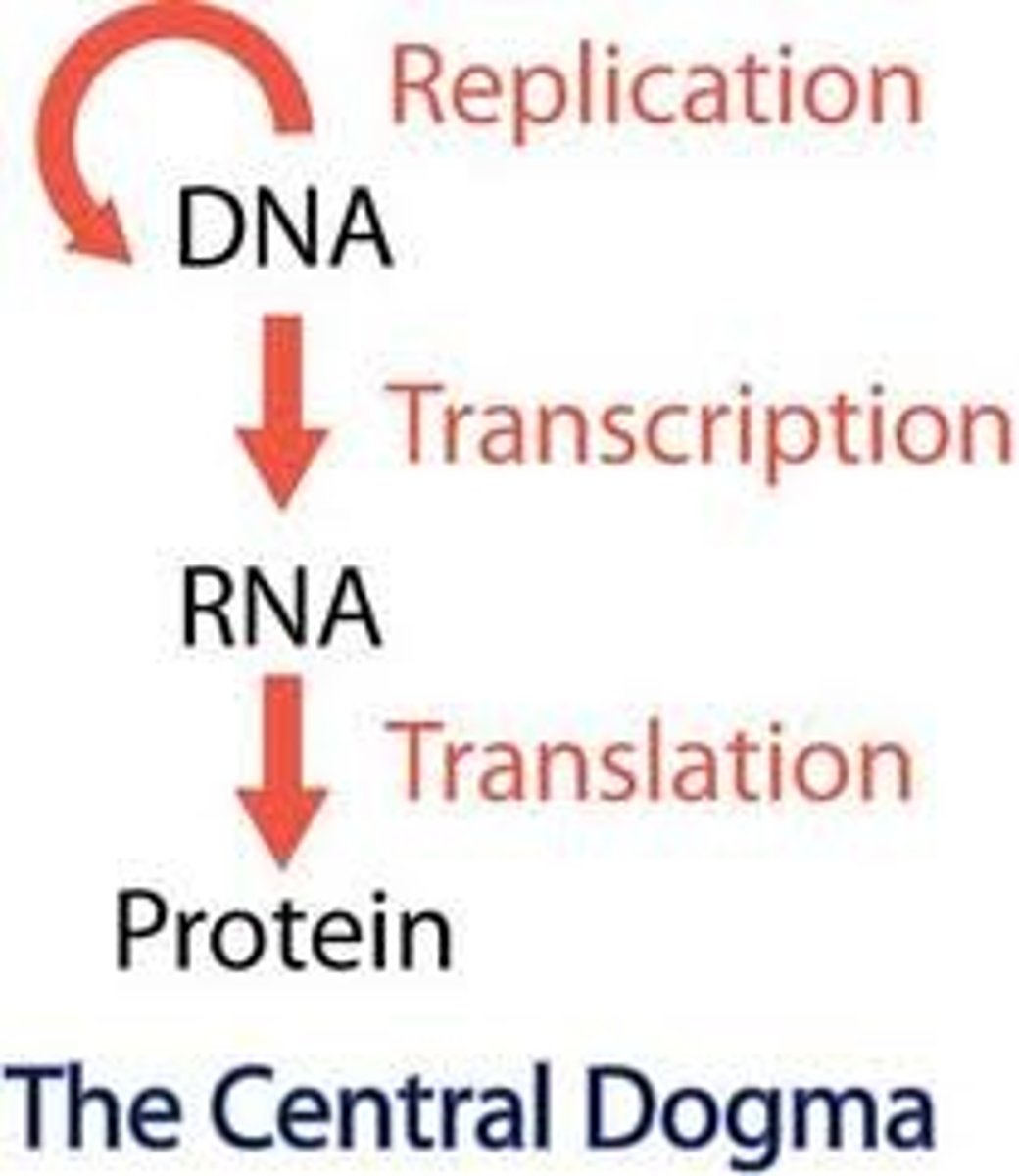
What is the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The gene expression process by which the instructions in DNA are converted into a functional product
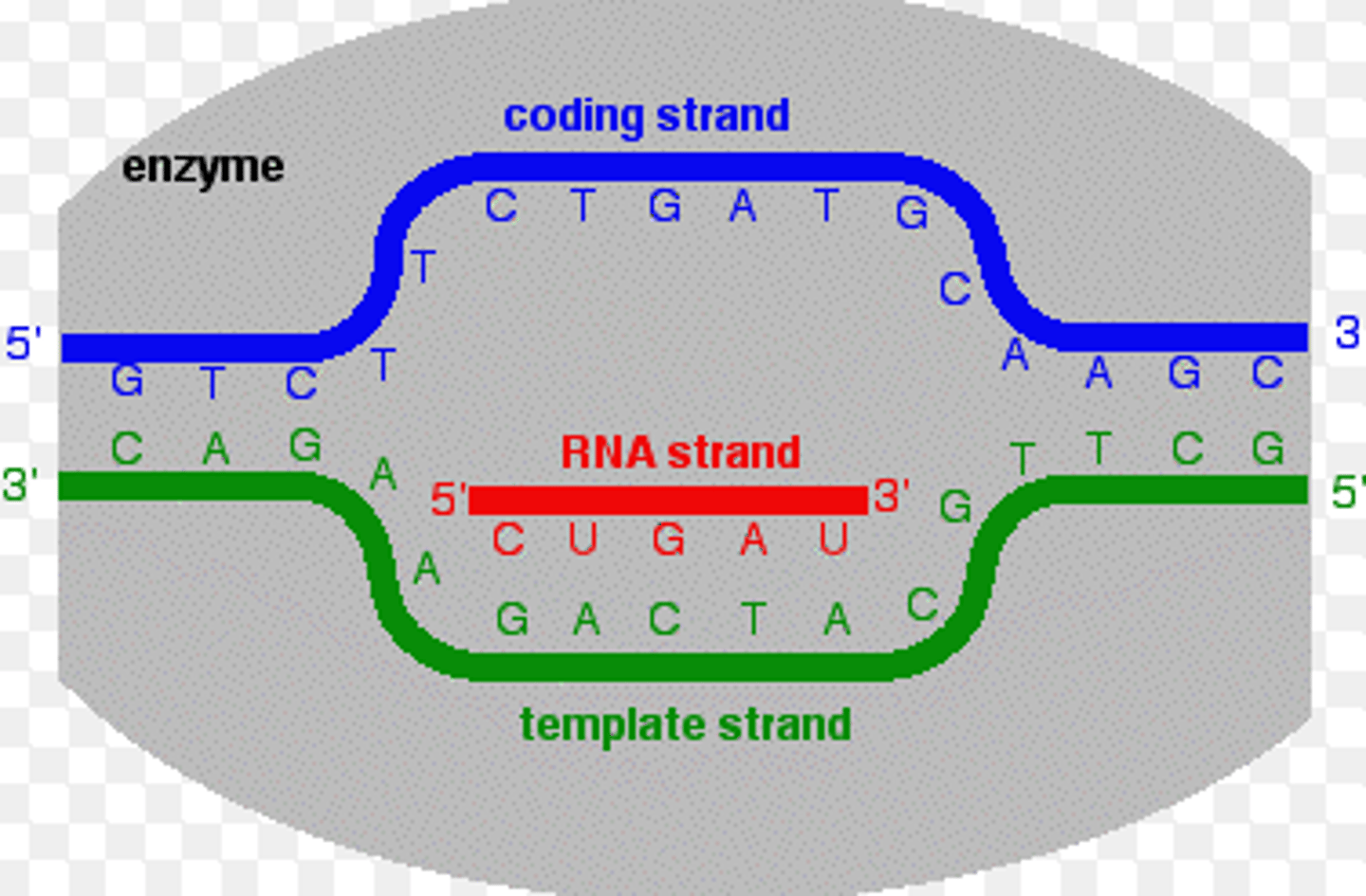
Is this DNA strand the Coding Strand (Sense Strand) or the Template (antisense) Strand?
5' - ATGCCTACGAAATGA - 3'
Coding
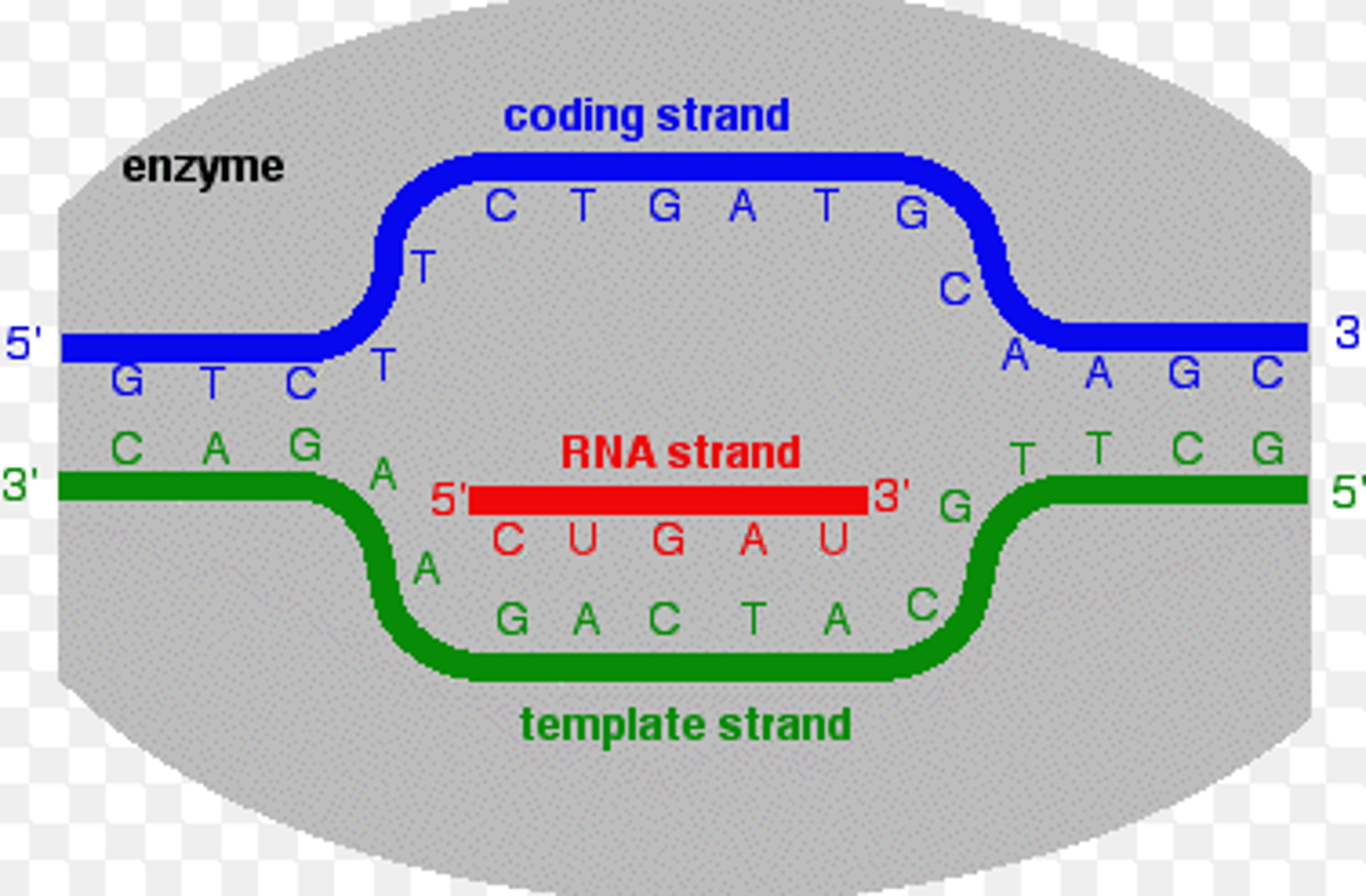
Write the template strand to this strand of DNA:
5' - ATGCCTACGAAATGA - 3'
3' - TACGGATGCTTTACT - 5'
Transcribe this DNA molecule:
3' - TACGGATGCTTTACT - 5'
5' - AUGCCUACGAAAUGA - 3'
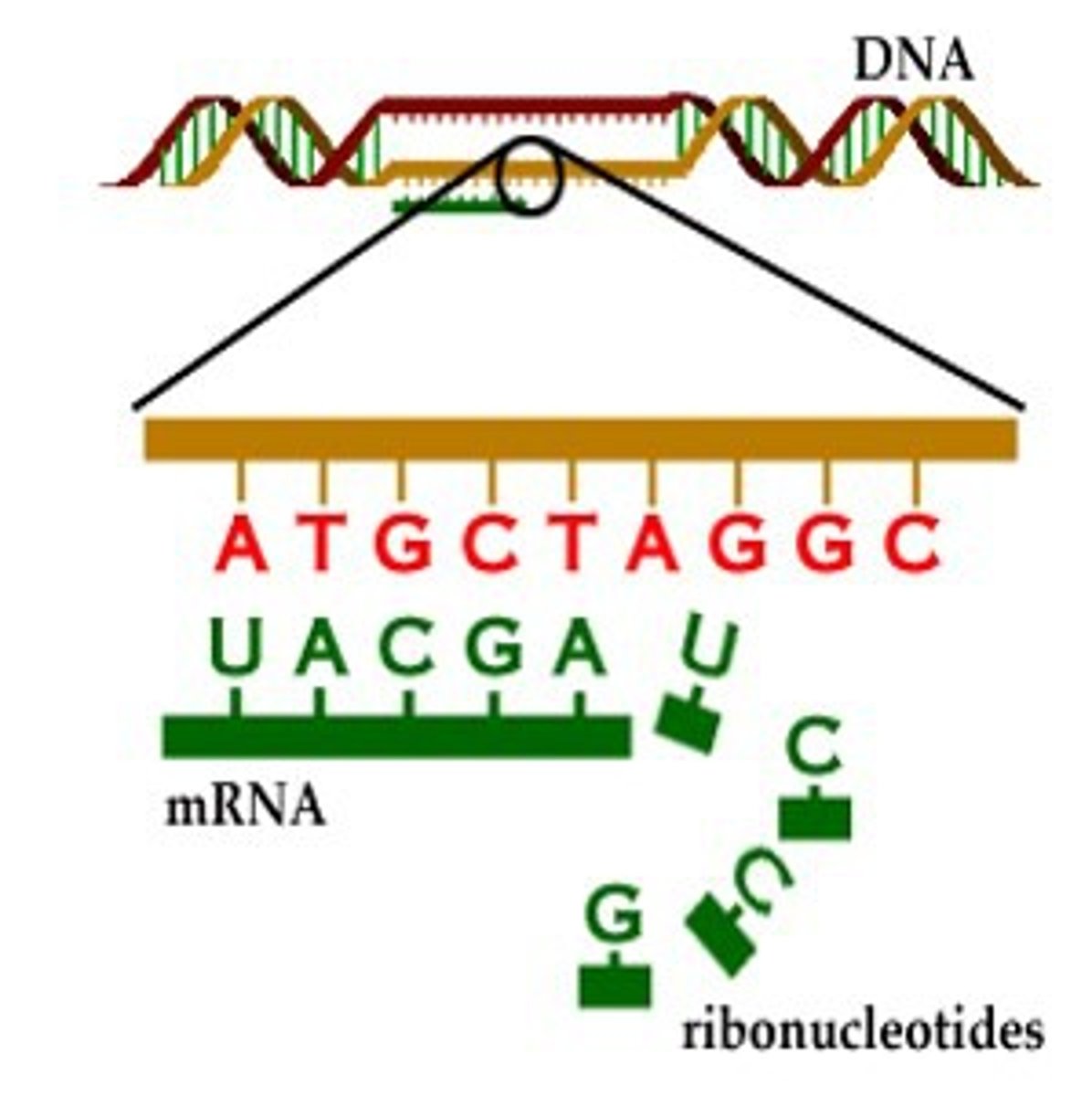
What are the codons in this mRNA molecule?
5' - AUGCCUACGAAAUGA - 3'
mRNA Codons (Triplets):
AUG | CCU | ACG | AAA | UGA
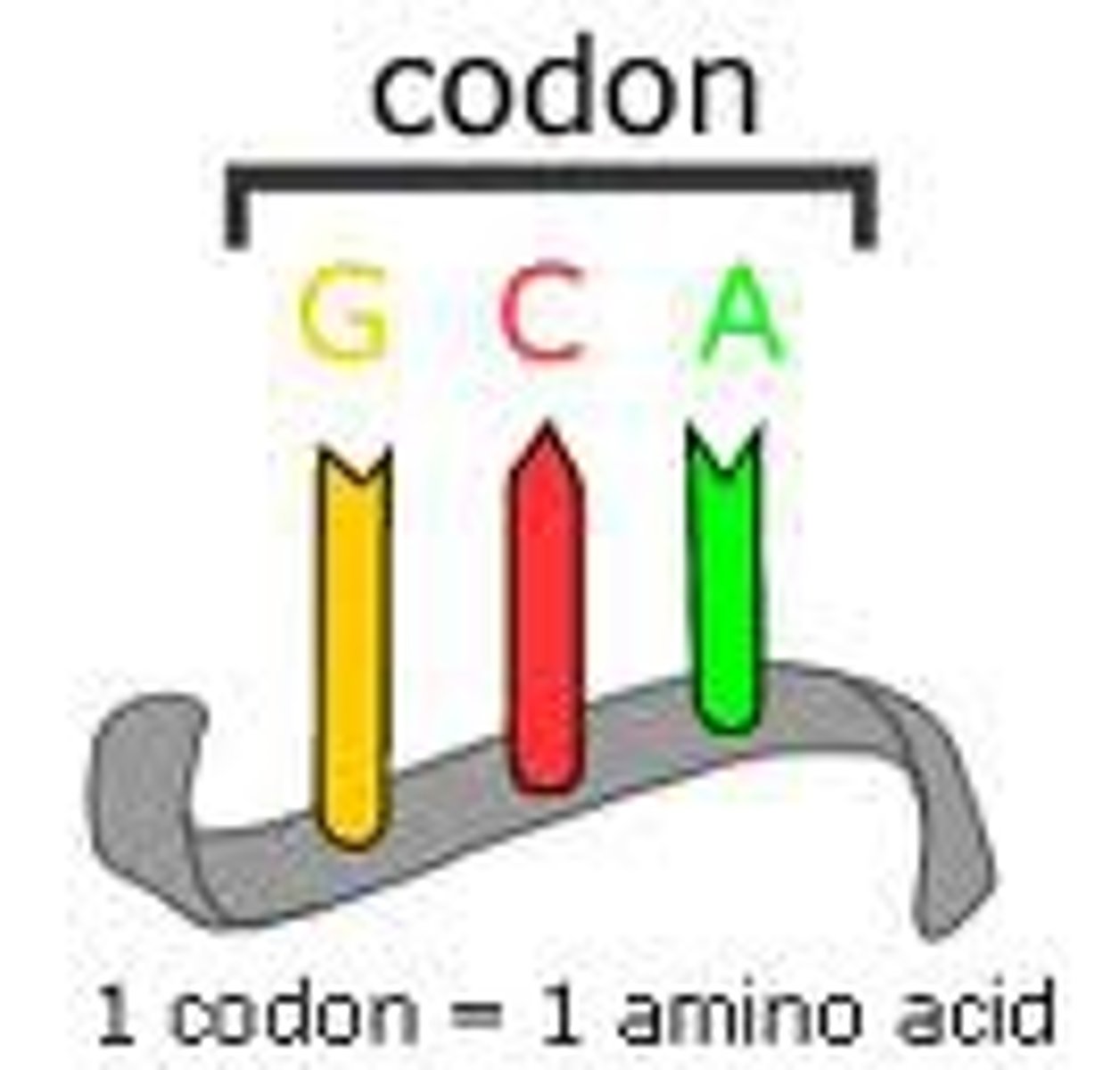
What is a codon chart?
Device used to determine the amino acid coded for by a codon
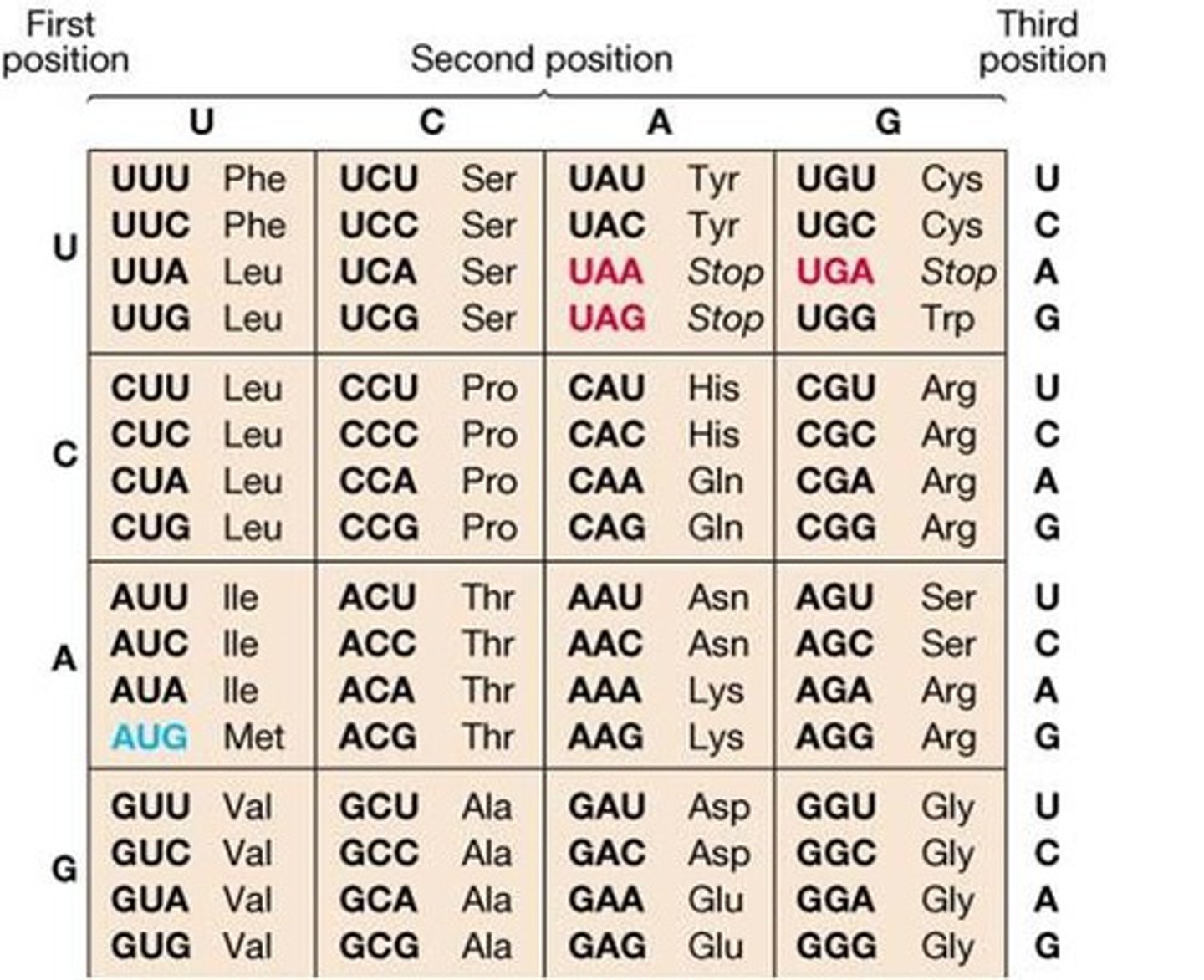
Translate this mRNA into a protein:
AUG | CCU | ACG | AAA | UGA
AUG → Methionine (Met) (Start)
CCU → Proline (Pro)
ACG → Threonine (Thr)
AAA → Lysine (Lys)
UGA → Stop (Translation ends)
Remove the Stop Codon: Met – Pro – Thr – Lys
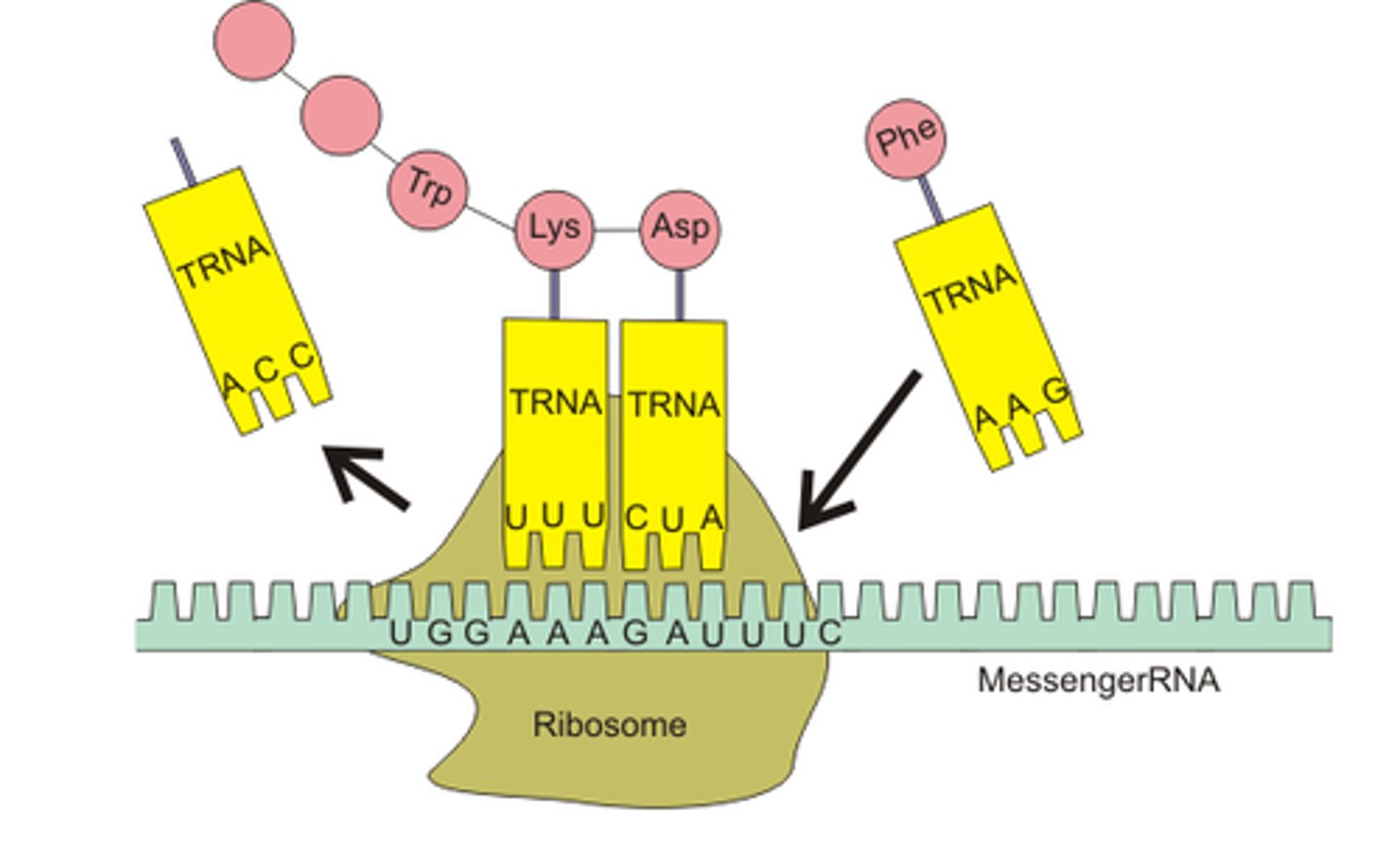
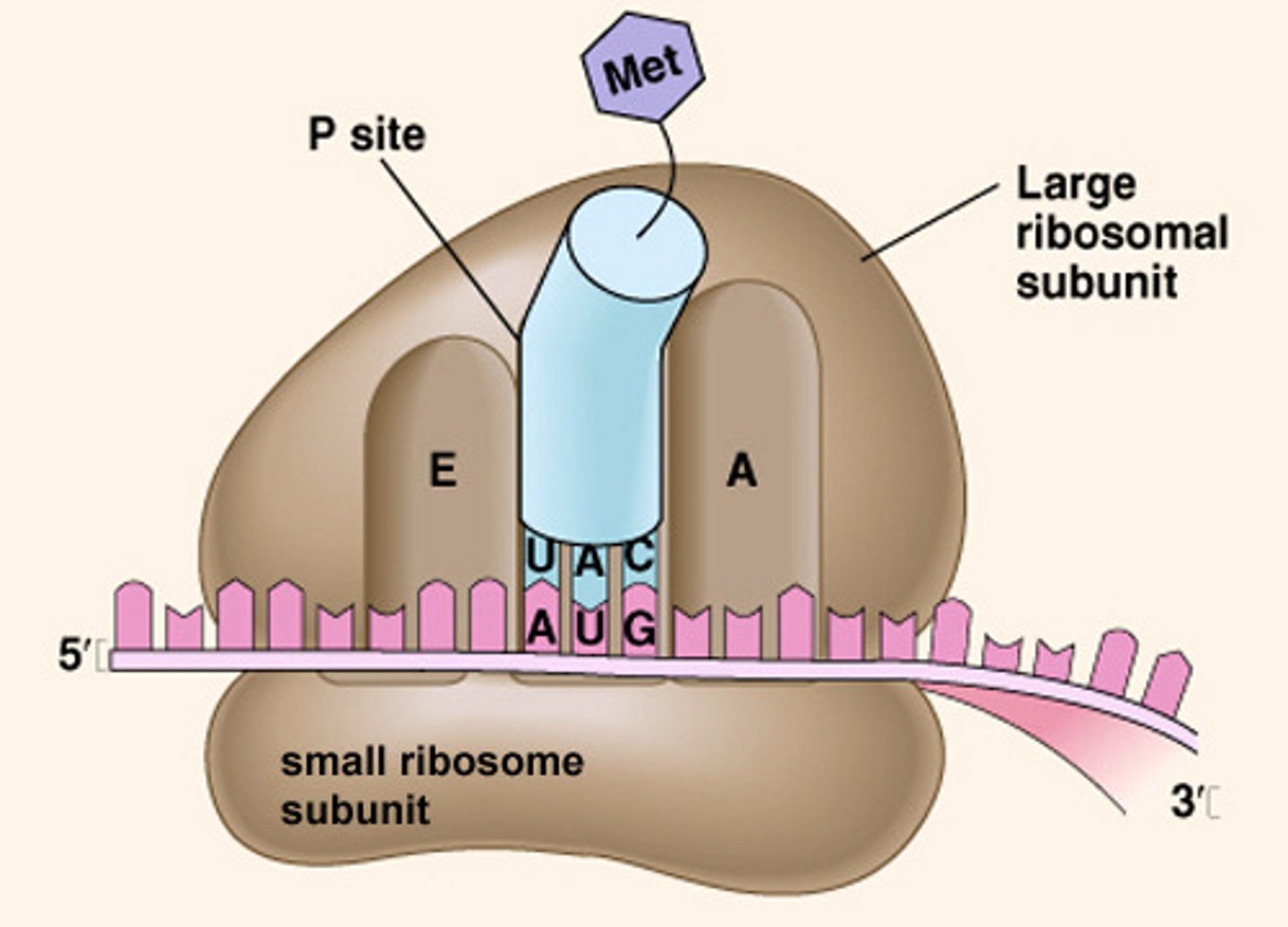
During translation, mRNA is read by _______________. This process results into the synthesis of a protein.
ribosome
There will be one (general) question from your BLAST homework
Make sure you understood what you were "doing" in this assignment.
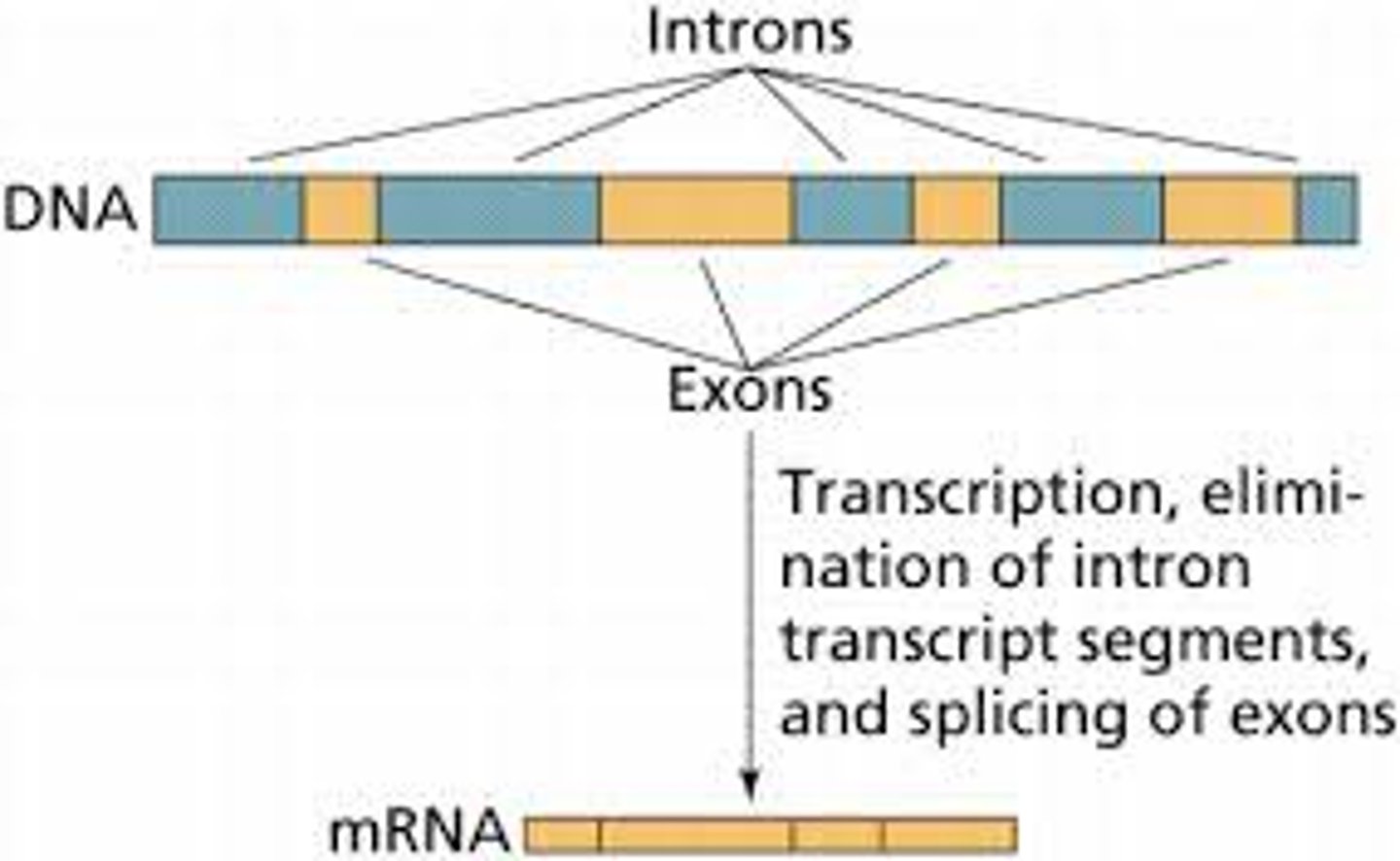
Introns vs. exons
Exons contain the actual genetic information coding for protein. Introns are intervening noncoding segments of DNA. ("IN trons stay IN the nucleus, whereas EX ons EX it and are EX pressed")