Carnivore Social Systems
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Describe the African Wild Dog
23kg for both genders
home range of 1500-2000sqkm
group size avg 9.8 (2-50)
both sex hunt
alpha female and male reproduce
gestation 70 days
parental care seen in both genders.
African Wild Dog Social Structure for males?
There is one alpha male within the pack. If it dies, the next oldest male is chosen in the dominance hierarchy to become the reproductive male. Sometimes, growing males leave the pack and join other packs.
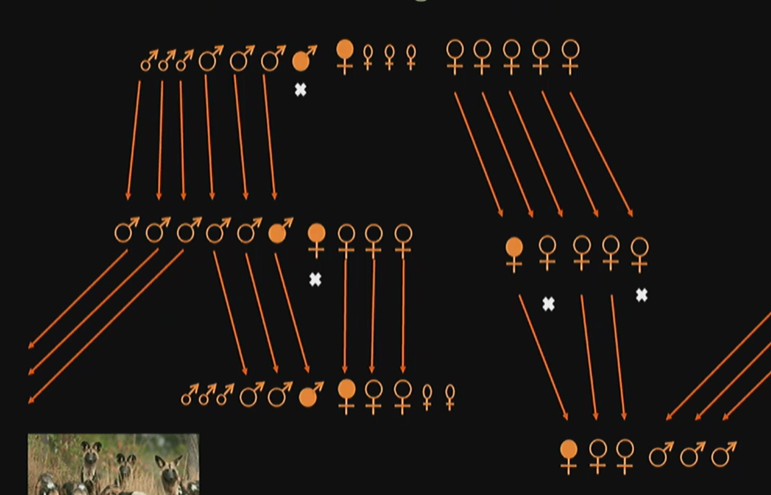
African Wild Dog Social Structure for females?
Similar to the male packs, one is chosen. The departing males join with female packs to reproduce with.
Describe the African Lion
230kg male, 140kg female
homerange 70sq
average group size 15
most hunting females
both gender reproduce
gestation 110 days
cub raised in open
parental care only for mothers and other females
male imigrate.
male form coalitions to defend to take over prides.
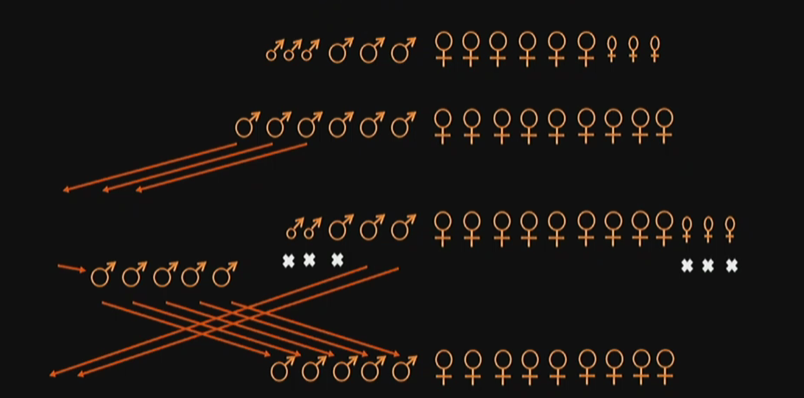
Lion Social Structure?
Some males leave the pride, and whenever a pride is taken over from another, all the cubs of both genders are killed and one male. The other males within that pride are driven away, and the invading pride (mostly male) take over the pride of females.
Describe the Spotted Hyaena
80kg male 86kg femae
30-1000 sqkm
avg 10-90 group size
both gender hunt, reproduce and scavenge
strict social heirarchy in reproduction
pups raised in den
parental care seen in mothers.
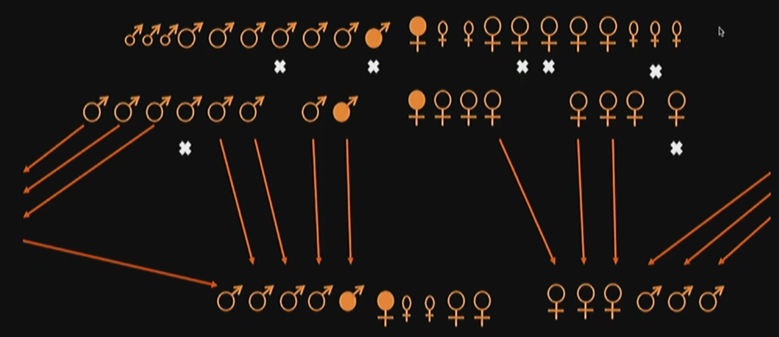
Spotted Hyenas social structure?
Large number of males and females within a group. One alpha female and male. Very aggressive animals (fighting amongst themselves), and many dispersals of both genders. Alpha title can be fought, and whoever wins becomes the new alpha. A very complex structure. Lots of emigration and dispersal.
Benefits of groups in carnivores?
Increase social hunting.
territorial clashes are won by larger prides.
Larger number of females in pride reduce risk of infanticide (death of young) by neighbouring males. Females defend.
In defense, what are the probability in response and number of defenders when intruders come?
When there is more intruders, there is more defenders but lesser probability of response if there are no other lions to help out. Vice versa with less intruders.
Relationship between Lions and Hyaenas?
Both these animals scavenge food from each other. In Mara, food lost by Hyaenas, and in Amboseli, the opposite.
What is Altruistic behaviour and when does it occur?
Behaviour that benefits another individual at the cost of one self.
Hamilton’s rule suggest that it persists when the fitness costs for the helper must be less than the fitness benefits to the receiver multiplied by the genetic relatedness of the two.