1.2.1-1.2.2 Causes of Contraction & Makeup of a Muscle
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
striated muscle
muscle that has a striped appearance
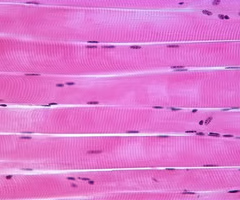
skeletal muscle
striated muscle that is throughout the body and attached to bones via tendons which aids in movement, posture, and heat protection
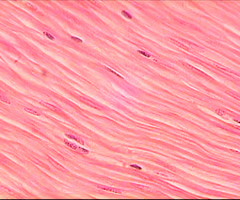
smooth muscle
muscle in the walls of several organs that helps organ function and maintaining homeostasis
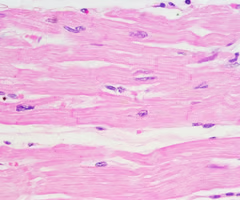
cardiac muscle
striated muscle in the heart used to pump blood
phosphate groups
group where the energy of ATP is located
ADP
low energy molecule because it doesn't have a 3rd phosphate group
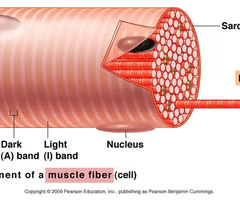
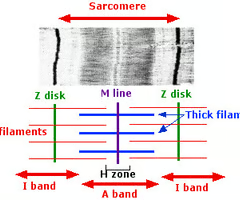
sarcomere
fundamental unit of a muscle fiber
actin
thin/light filaments of globular proteins
myosin
thick/dark fibrous protein filaments, "motor proteins"
M-line
the middle of the sarcomere
A-band
contains entire length of the myosin filaments
H-zone
region where myosin is located without actin overlapping
Z-line
anchors the actin at the ends of the sarcomere
tropomyosin/troponin
filament that wraps around actin
I-band
extends from the Z-line to the edge of the A-band, where actin and myosin filaments overlap
sliding filament theory
explains muscle contraction, where muscle cells shorten as thin actin filaments slide past thick myosin filaments within the sarcomere, the muscle's basic unit
muscle contraction (1)
as a nerve impulse reaches the ends of the axon terminal, ACh is released from synaptic vesicles & attaches to receptors
action potential (2)
muscle fibers become more positively charged which generates this to happen along the sarcolemma to the T-tubules
calcium (3)
ion released from the SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum)
troponin binding (4)
calcium binds to this on the actin filaments of muscle fibers to signal tropomyosin to leave myosin
powerstroke (5)
energized myosin heads, ADP+Pi, bind to the open myosin binding site, forming the actin-myosin cross bridge and the myosin heads rotate and release ADP+Pi, thin actin slides past thick filament
actin-myosin detachment (6)
cross-bridge stays intact until ATP binds to myosin head and myosin detaches from actin
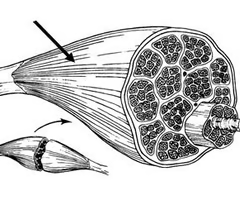
fasicle
bundles of myocytes (muscle cells)
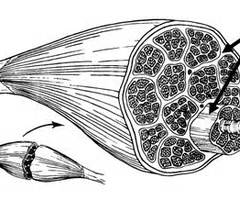
perimysium
sheath that surrounds each fasicle
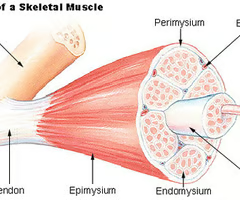
endomysium
sheath that surrounds each myocyte
tendon
connects muscle to bone
epimysium
ensheathes entire muscle and protects against friction
t-tubules
extensions of sarcolemma that penetrate into myocyte and bring the SR closer to calcium
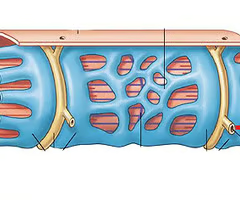
sarcolemma
under endomysium, semi-permeable membrane
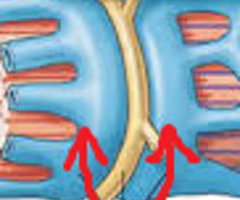
sarcoplasmic reticulum
stores, releases, and reabsorbs Ca+2
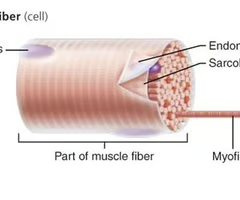
myofibril
"rod-like" organelles made of sarcomeres end-to-end