BIO 168 Module 2 Quiz Review
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
The result of __________ is the division of a cell's chromosomes into two new nuclei, each of which has the same amount and type of DNA as the original nucleus. The division of the cells cytoplasm is called __________and occurs with the production of two new cells.
mitosis; cytokinesis
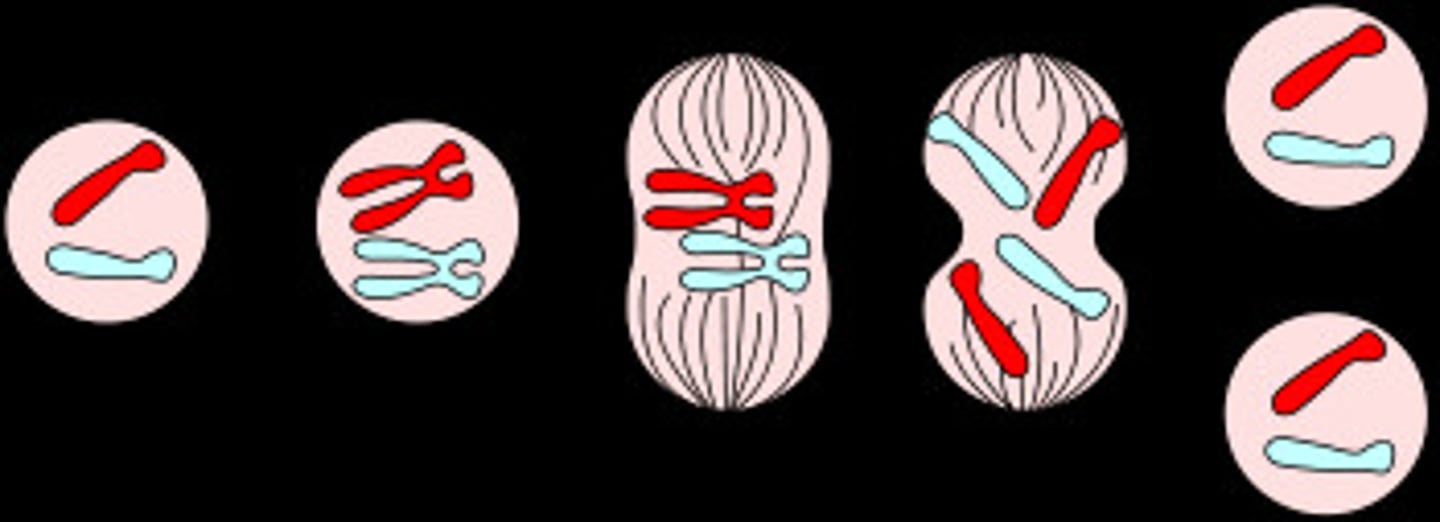
Place the following images into the correct order to represent mitosis.
refer to screenshot
Support, attachment of tissues, cushioning and protection are examples of functions for ______ tissue.
connective tissue
What attaches epithelial cells to the basement membrane?
hemidesmosomes
The type of connective tissue that contains chondrocytes, a rigid matrix of collagen fibers and proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid aggregates and few, if any, blood vessels is
cartilage.
Which of the following types of connective tissue is mismatched with its matrix?
cartilage - highly vascular matrix
Which of the following is correctly matched?
axons - conduct action potentials away from the cell body
A general characteristic of connective tissue is that it
consists of cells with much intercellular material (matrix) between them.
Match the function or location to the correct connective tissue.
Allows the growth of long bones
Hyaline cartilage
Intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis
Fibrocartilage
External ear, epiglottis, and auditory tubes
Elastic cartilage
Outer portion of all bones
Compact bone
Inside skull bones, vertebrae, and sternum
Spongy bone
Transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other substances
Blood
Produces new blood cells and stores lipids
Bone marrow
Capable of strength with stretching and recoil in several directions
Dense irregular elastic connective tissue
Tensile strength capable of withstanding stretch in all directions
Dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
Vocal folds and ligaments between vertebrae
Dense regular elastic connective tissue
Tendons and ligaments
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue
Provides superstructure for lymphatic tissues
Reticular tissue
Energy storage
Adipose tissue
Epithelial basement membrane sits on this
Areolar connective tissue
Precursor to adult connective tissues
Mesenchyme
Umbilical cord of the newborn
Mucous connective tissue
Fill-in the blanks with the appropriate tissue type being described. Each tissue type can be used more than once.
NERVOUS TISSUE is a network of specialized cells that monitors the internal and external environment and initiates commands through which the body reacts.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE can be classified using the number of cell layers, and the shape of the cell at the apical surface.
There are three types of MUSCLE TISSUE: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
MUSCLE TISSUE is widely distributed throughout the body to allow for movement of the skeleton or other tissues of the body.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE is diverse, abundant, and widely distributed through the body.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE forms the surface layer of the body, lines body cavities, hollow organs and structures, and constitutes most gland tissue.
NERVOUS TISSUE is composed of two types of cells: neurons and glial cells.
Identify the specific tissue type shown in each picture.
refer to screenshot
Identify the types of muscle tissue by dragging the muscle type labels to the matching image.
refer to screenshot
1 - skeletal muscle
2 - cardiac muscle
3 - smooth muscle
Describe the movement of melanin in the skin.
Melanin is transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes.
Keratinocytes
are responsible for the reduction of water loss from the skin.
The integumentary system has many functions, one of which is
detection of heat and touch.
Which type of skin cancer is the most common?
basal cell carcinoma
Which of the following statements concerning vitamin D is false?
Vitamin D causes the kidney to excrete calcium.
Complete each sentence by dragging the proper word or phrase into the correct position. Then place the sentences in order from superficial to deep.
The STRATUM CORNEUM is made up of multiple layers of dead keratinocytes that regularly exfoliate.
The next layer is the STRATUM LUCIDUM, which is present only on the soles of the feet, hands, fingers, and toes.
The STRATUM GRANULOSUM is named for the presence of dark-staining granules; keratinization begins in this layer.
Toward the apical surface, in the STRATUM SPINOSUM the keratinocytes cease cell division. Epidermal dendritic cells are in this layer.
Composed of cuboidal and colulmnar cells, the STRATUM BASALE contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, and tactile cells.
Drag each label to the appropriate layer (A, B, or C) for each term or phrase.
A: (EPIDERMIS)
-composed primarily of epithelial tissues
-creates a water barrier with the environment
-epidermis
-includes the 4-5 strata of the skin
-epidermis
-avascular
B: (DERMIS)
-the layer that is made into leather products after removal of more superficial and deeper tissues
-principally comprised of dense irregular connective tissue
-includes hair follicles, glads, and blood vessels
C: (HYPODERMIS)
-not actually considered a part of the skin
-contains tissues associated with energy storage, thermal insulation, and mechanical padding
-hypodermis
-deepest layer
Drag each label to the appropriate anatomical structure.
refer to screenshot
Place the appropriate words and descriptions with the correct low magnification picture of integumentary glands highlighted below.
MEROCRINE GLAND:
-secretes sweat
-ducts open directly on the surface of skin
-functions in temperature regulation
APOCRINE GLAND:
-ducts open into hair follicles
-secretes sweat
-secretion is influenced by hormones
SEBACOUS GLAND:
-secretes sebum
-ducts open into hair follicles
-secretion is influenced by hormones
refer to screenshot
Which of the following is correctly matched?
short bone - carpal bone
An X-ray determines that Peter fractured the shaft of his humerus. The break is in the _____________ of the bone.
diaphysis
Which type of bone cells combine hydroxyapatite and collagen to form extracellular bone matrix?
osteoblasts
Some marrow of long bones is termed "red" marrow. The function of red marrow is to
manufacture blood cells.
The type of lamellae found between osteons (Haversian systems) is
interstitial.
Each of the following steps are necessary in preparing and observing a wet mount. Place the steps in the correct order.
1. Obtain a clean slide and cover slip.
2. Using a transfer pipette, obtain a drop of specimen and place onto the center of the slide.
3. Carefully place the cover slip over the drop of specimen.
4. Observe preparation under the 10X objective lens.
5. Observe preparation under the 40X objective lens.
Complete the calculations for total magnification produced by various combinations of the eyepiece and objective lenses. Remember, to calculate the total magnification achieved when using a particular objective, multiply the power of the eyepiece by the power of the objective used.
When the scanning (4x) objective is used the total magnification will be 40x.
When the low power (10x) objective is used the total magnification will be 100x.
When the high power (40x) objective is used the total magnification will be 400x.
When the oil immersion (100x) objective is used the total magnification will be 1000x.
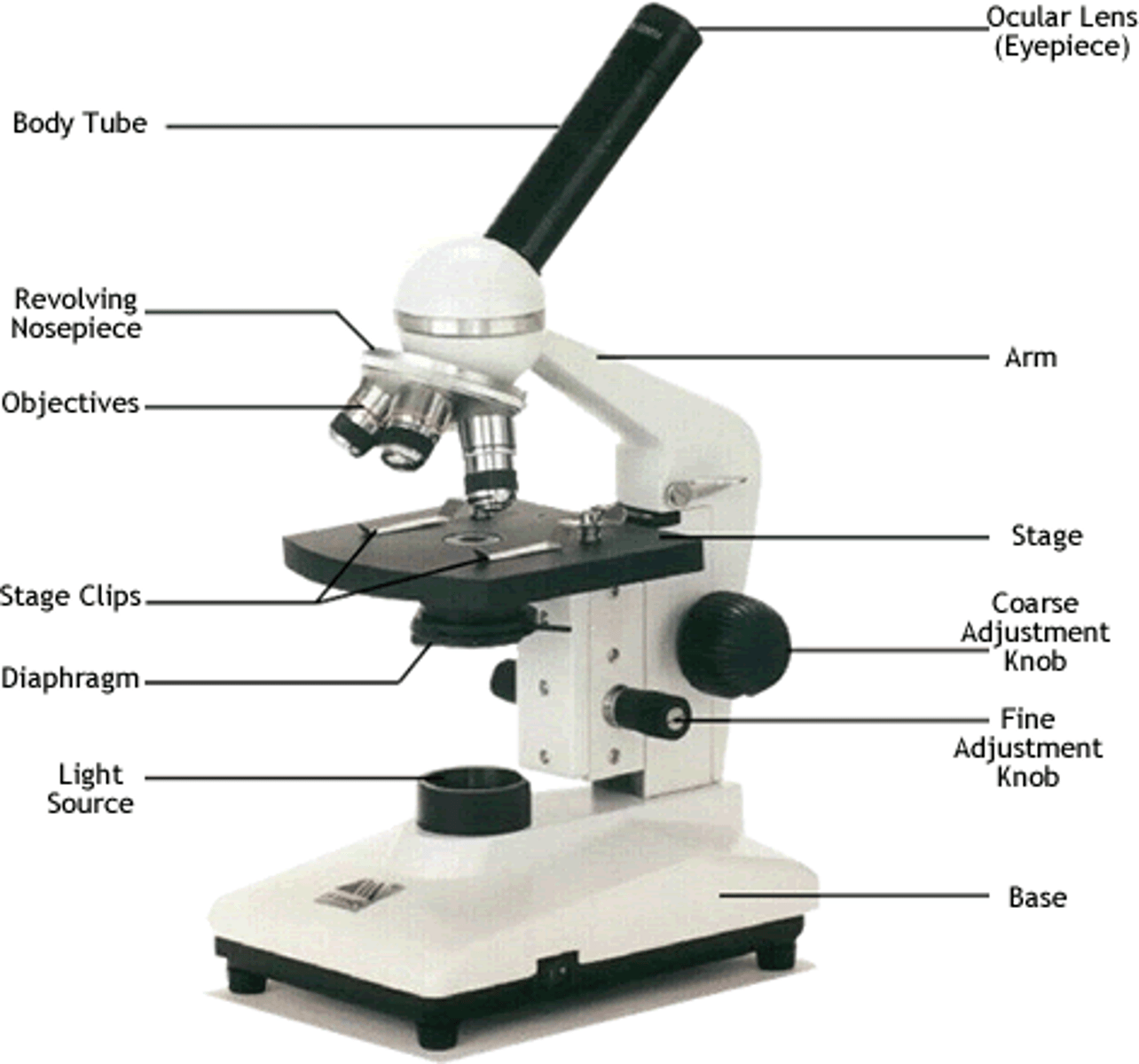
Label the image of a compound light microscope using the terms provided.
refer to screenshot
Indicate the correct order of steps as you bring an object into focus under high power.
1. Place slide on stage and secures with stage clips.
2. Turn on the light and center the specimen over the light source.
3. Focus specimen on low power using coarse focus adjustment.
4. Use fine focus to sharpen the image under low power.
5. Rotate high power lens into position.
6. Readjust fine focus under high power to produce the sharpest image.
An exaggerated curvature of the lumbar region is
lordosis
Which of the following bones contains a sinus?
maxilla
The hyoid bone is part of the
axial skeleton.
In a herniated ("ruptured" or "slipped") disc, the ring of fibrocartilage called the ___________ cracks and the _____________ oozes out.
anulus fibrosus; nucleus pulposus
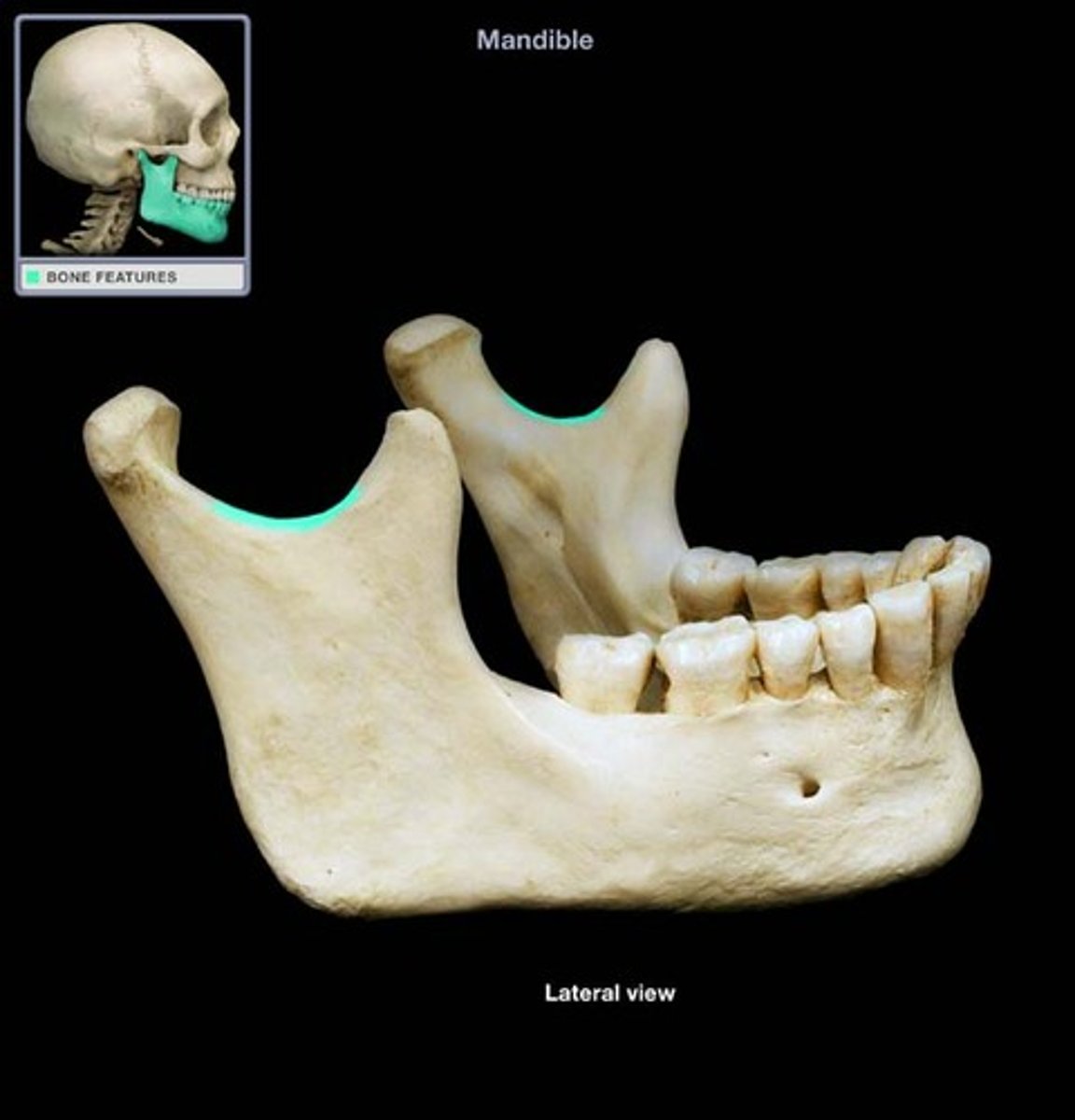
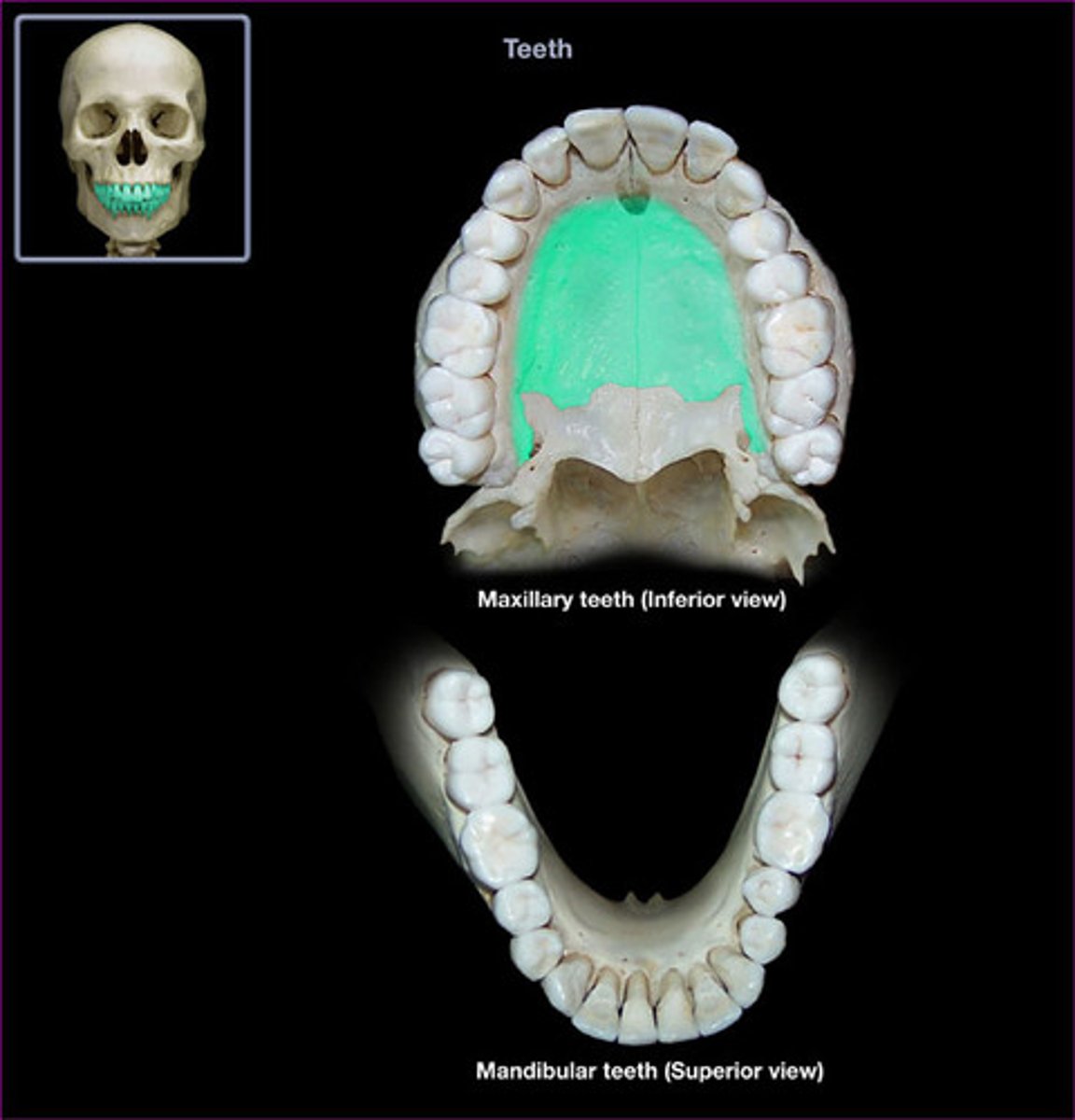
Which structure is highlighted?
palatine process of maxilla
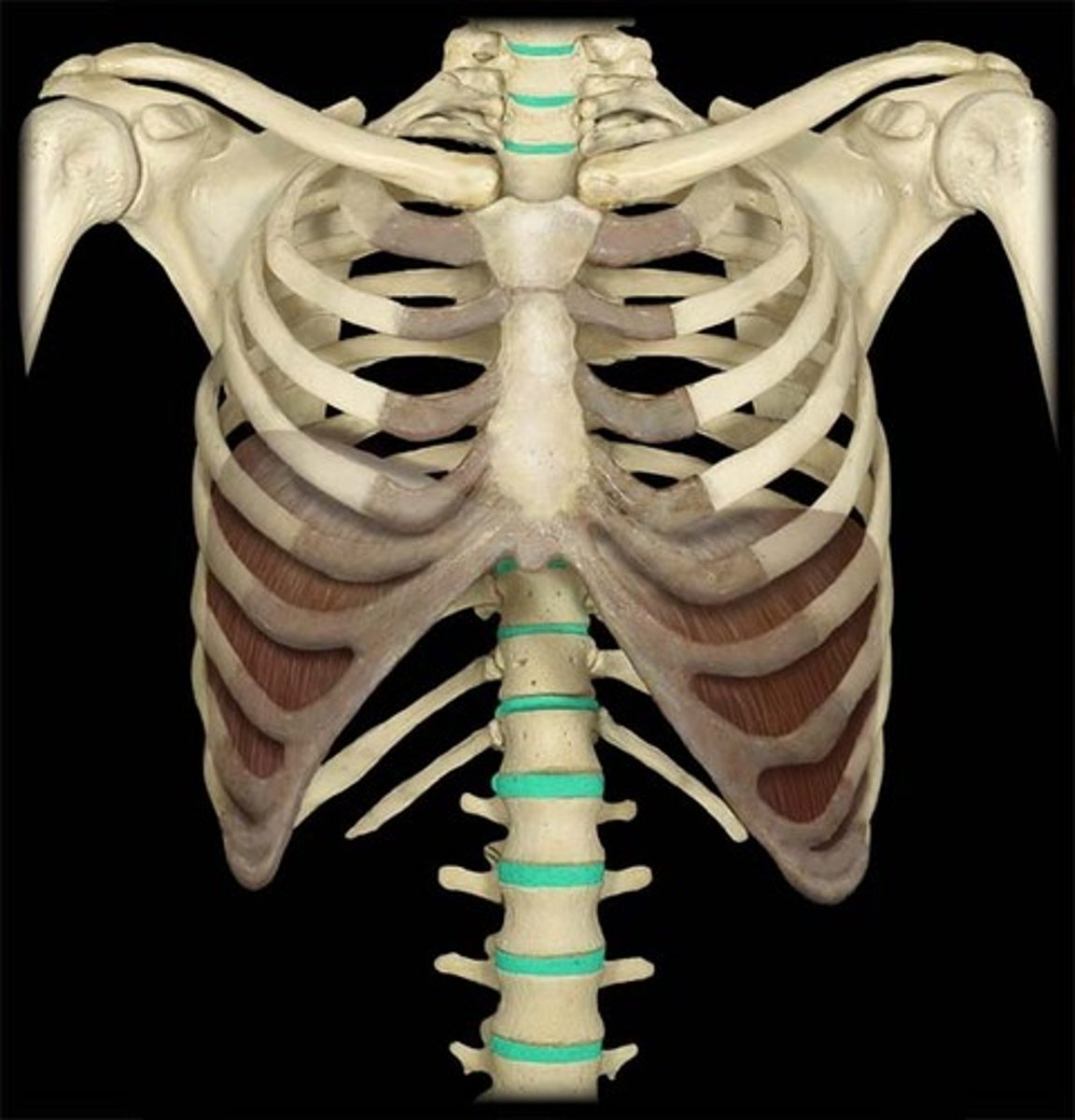
Which structure is highlighted?
intervertebral discs
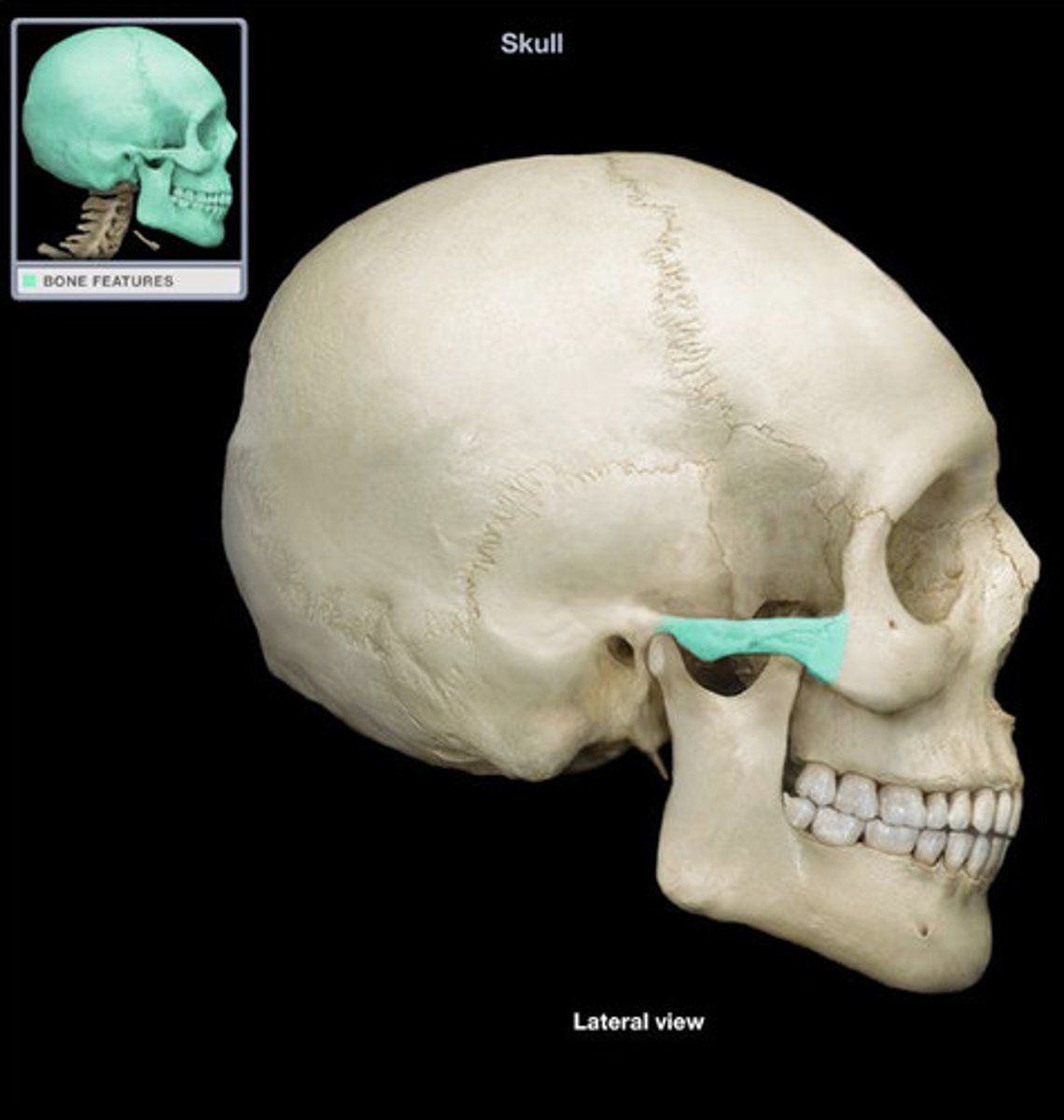
Which structure is highlighted?
temporal process of zygomatic bone
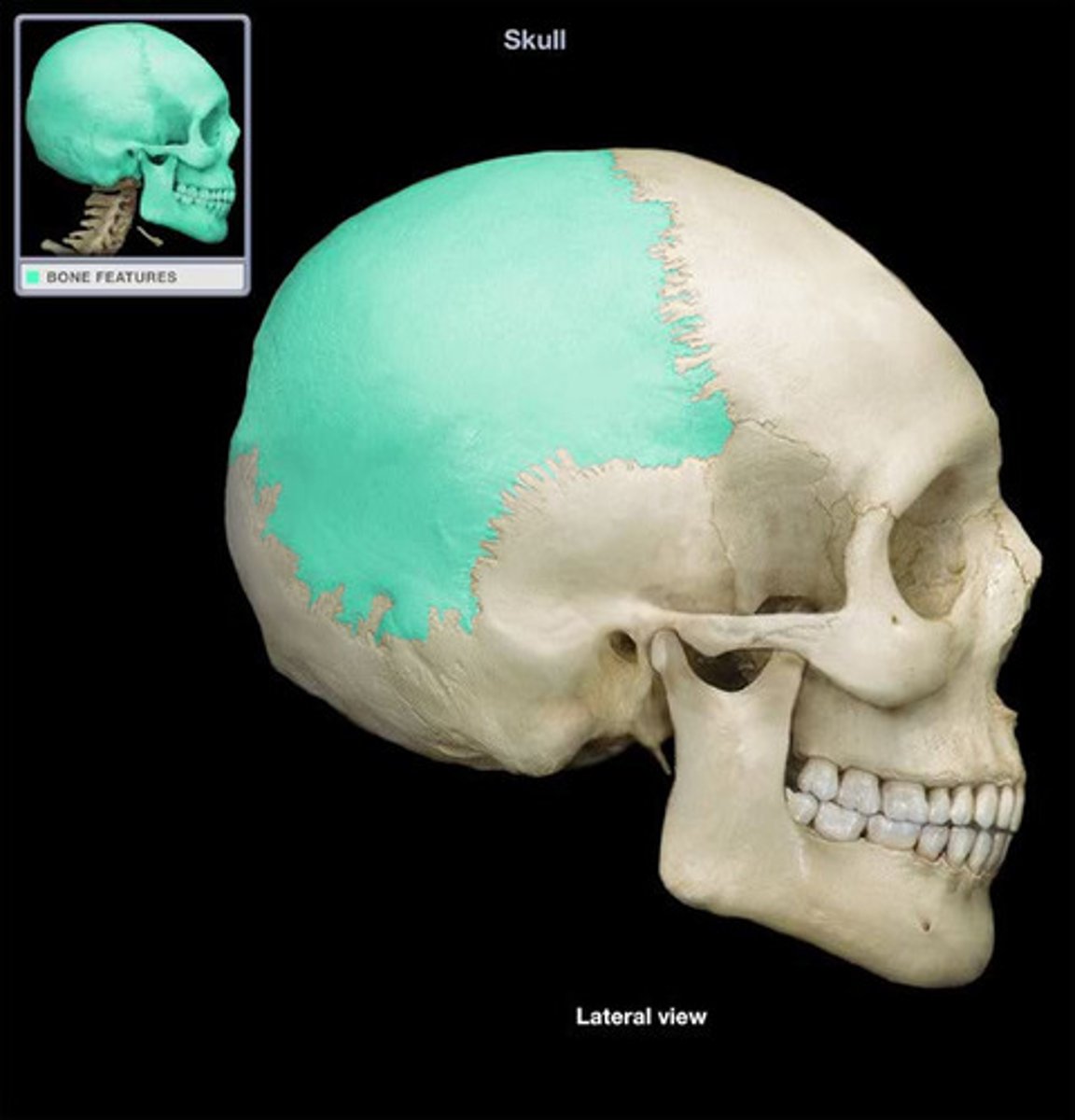
Which structure is highlighted?
parietal bone
Which structure is highlighted?
foramen magnum
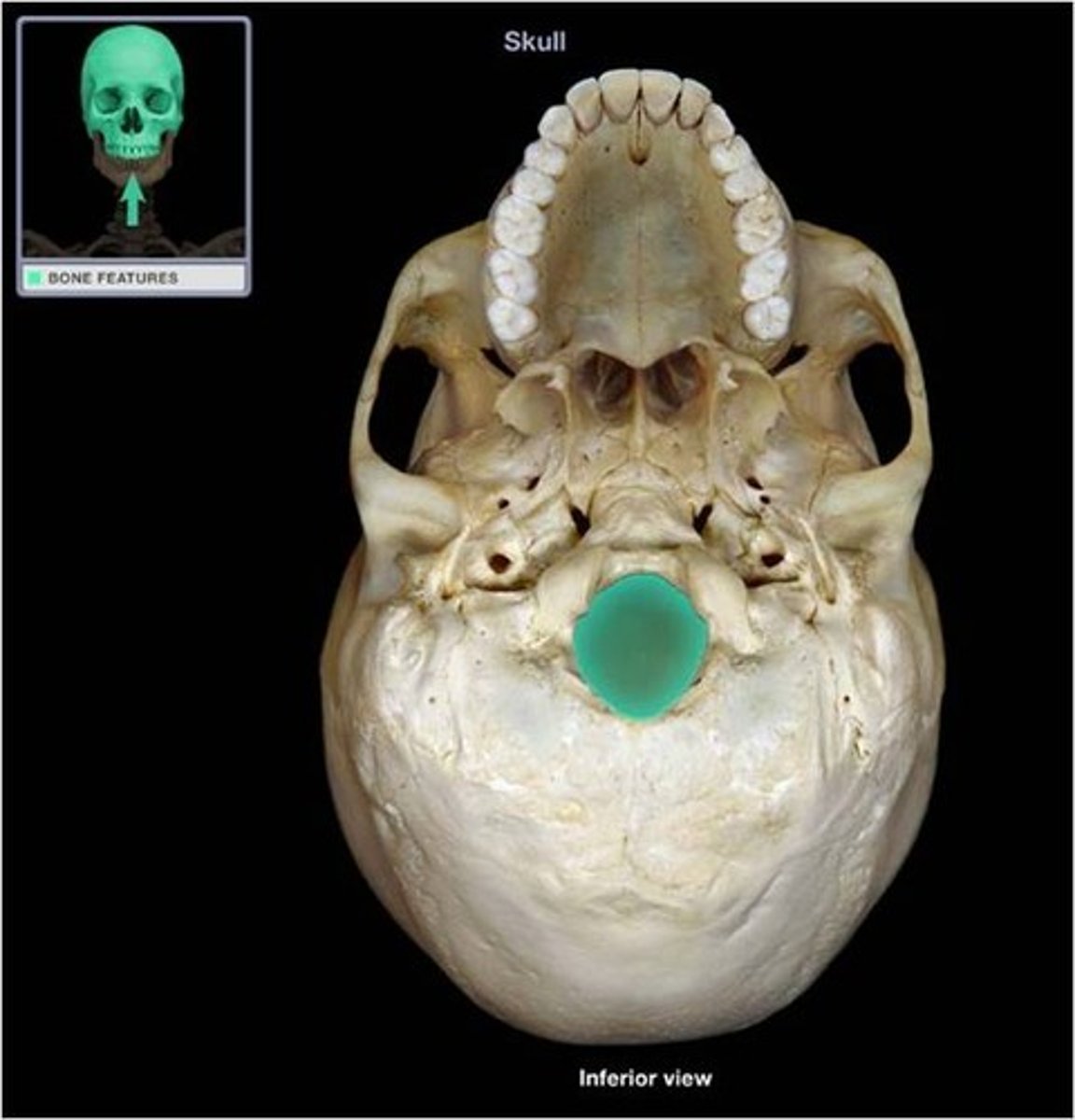
Which structure is highlighted?
mandibular foramen refer to screenshot