Exam 3 Textbook Questions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms

Which shows greater deviation?
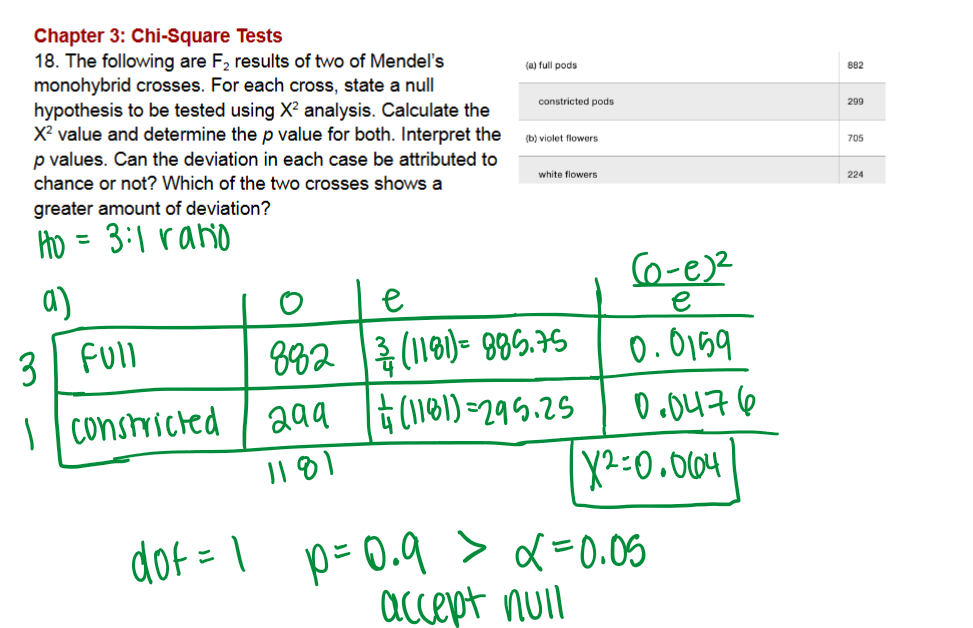
Cross (b), because it has the larger χ2\chi^2χ2 (0.39 > 0.064).
both show no significant difference

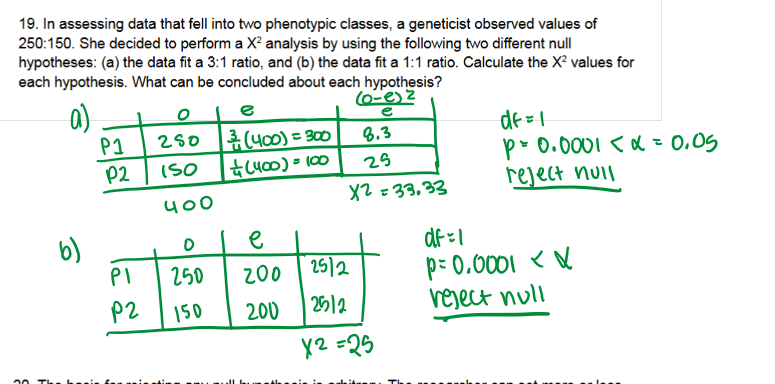

Using p = 0.10 as the critical value is more stringent about not rejecting the null hypothesis. Increasing the critical p value means that a smaller χ² value is sufficient to reject the null hypothesis, so less difference between observed and expected values is needed for rejection. Therefore, it becomes harder to fail to reject the null hypothesis, increasing the stringency of failing to reject it.


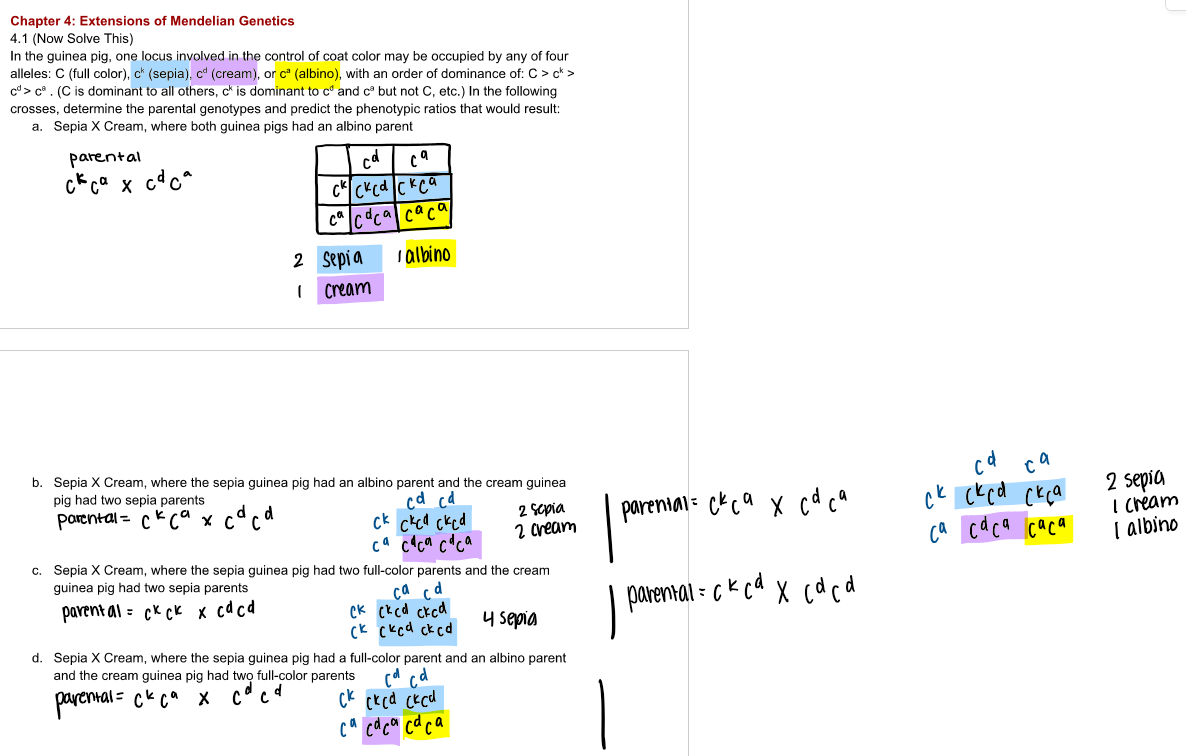



a. consistent
b. consistent
c. not consistent

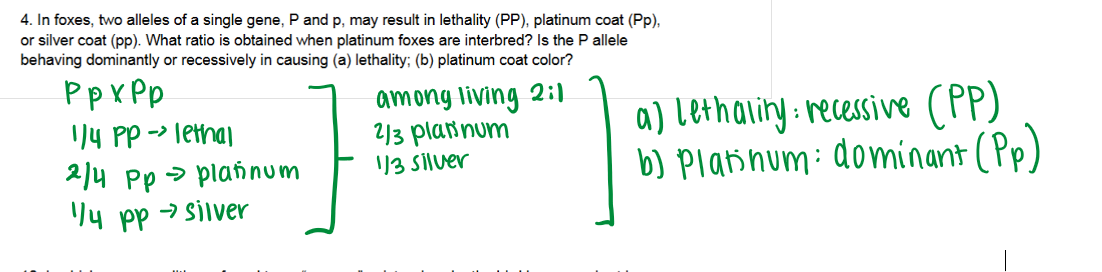

The creeper allele is dominant for the short-leg phenotype but lethal when homozygous.
Let C = creeper, c = normal.
Creeper × normal: Cc × cc → 1/2 Cc (creeper), 1/2 cc (normal) ✅ matches 1:1
Creeper × creeper: Cc × Cc → 1/4 CC (lethal, dies), 1/2 Cc (creeper), 1/4 cc (normal)
Among living chicks: 2/3 creeper : 1/3 normal ✅
So creepers “never breed true” because CC doesn’t survive.

This trait shows incomplete dominance.
CC = chestnut
C Cᶜʳ = palomino
CᶜʳCᶜʳ = cremello
Cremello × chestnut → F₁: all palomino
F₁ × F₁ → F₂: 1/4 chestnut : 1/2 palomino : 1/4 cremello

16a. AACC × aacc
F₁: all AaCc → all agouti
F₂ genotypes (simplified):
9 A_C_, 3 aaC_, 4 __ccF₂ phenotypes:
9 agouti : 3 black : 4 white
16b. Genotypes of agouti females (crossed to aacc males)
8 agouti : 8 white → female = AaCc
9 agouti : 10 black (no white) → female = AaCC
4 agouti : 5 black : 10 white → female = AaCc

Here are the F₁ phenotypic ratios (short, final answers only).
Key rule: cc = albino (epistatic); color only appears if C_ is present.
Phenotypes:
A_B_ → gray
A_bb → yellow
aaB_ → black
aabb → cream
__cc → albino
a. AAbbCC × aaBBcc
All offspring: AaBbCc
→ 100% gray
b. AaBBCC × AABbcc
All offspring are C_, no albino.
A and B segregate.
→ 3/4 gray : 1/4 yellow
c. AaBbCc × AaBbcc
1/2 cc → albino
Remaining 1/2 C_ show A/B colors
Final ratio:
9/32 gray
3/32 yellow
3/32 black
1/32 cream
16/32 albino
d. AaBBCc × AaBBCc
Only gray, black, albino possible.
→ 9/16 gray : 3/16 black : 4/16 albino
e. AABbCc × AABbcc
All A_ (no cream)
1/2 cc → albino
Final ratio:
3/8 gray
1/8 yellow
1/2 albino

a. Mode of inheritance
This is two independently assorting genes with a 9:3:3:1 ratio.
Let:
A_B_ = yellow
A_bb = blue
aaB_ = red
aabb = mauve
All colors can be true-breeding (homozygous).
b. Cross: true-breeding red × true-breeding mauve
Red = aaBB
Mauve = aabb
F₁:
aaBB × aabb → aaBb → all red
F₂ (aaBb × aaBb):
3/4 red (aaB_)
1/4 mauve (aabb)

“Phenotypic expression is dependent on the genome of the organism, the immediate molecular and cellular environment of the genome, and numerous interactions among a genome, the organism, and the environment.”

Penetrance refers to the percentage of individuals among a population who express some degree of a mutant phenotype, whereas expressivity refers to the range of expression of a given phenotype and can vary from individual to individual.”

Labrador coat color is controlled by two genes with recessive epistasis.
Model (gene symbols):
A_B_ = black
aaB_ = brown
__bb = golden (bb is epistatic and blocks pigment)
True-breeding genotypes:
Black: AABB
Brown: aaBB
Golden: any bb genotype (AAbb or aabb)
This two-gene epistatic model explains all the listed mating outcomes and ratios.



Crossing over occurs more often between genes that are far apart because there is more physical space along the chromosome for a crossover to happen between them. Genes that are very close together are less likely to be separated by a crossover, since a single crossover event is unlikely to occur in the small interval between them.

A single crossover involves only two of the four chromatids in a homologous chromosome pair. Even if crossing over always occurs between two linked genes, only half of the chromatids become recombinant, while the other half remain parental. Therefore, the maximum possible recovery of single-crossover (recombinant) products is 50%, which is the upper limit.