GEOGRAPHY EXAM STUDY NOTE
4.0(1)Studied by 11 people
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:38 AM on 6/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
\
WHAT IS GEOGRAPHY?
WHAT IS GEOGRAPHY?
the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments
2
New cards
SENSE OF PLACE
refers to how the physical layout of a space can have an emotional impact on a person
3
New cards
SPATIAL INTERACTION
* refers to how places interact with each other
* how things and people interact inside a space
* how things and people interact inside a space
4
New cards
SPATIAL PATTERN
refers to the layout of a space and how it has changed over time
5
New cards
HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
Focuses on humans, their populations, and how they interact with their environment
6
New cards
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
focuses on the dynamics of landscapes and the environment.
7
New cards
GPS
a device that determines its own location based on the signal from about four satellites
8
New cards
GIS
A system that creates digital maps that help provide an understanding of spatial patterns and relationships
9
New cards
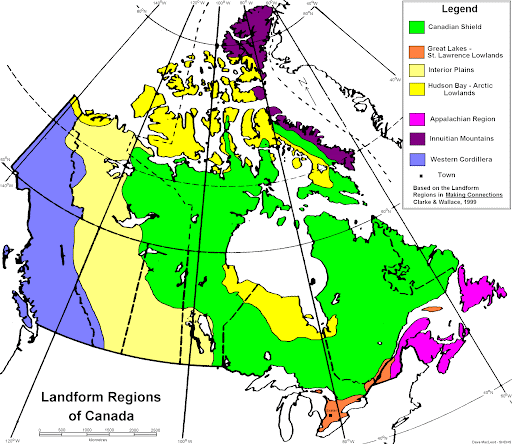
7 LANDFORM REGIONS
* Canadian Shield
* Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands
* Hudson Bay
* Interior Plains
* Appalachian Mountains
* Innuitian Mountains – Arctic Lowlands
* Western Cordillera
* Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands
* Hudson Bay
* Interior Plains
* Appalachian Mountains
* Innuitian Mountains – Arctic Lowlands
* Western Cordillera
10
New cards
WEATHER
conditions of the atmosphere are over a short period of time
11
New cards
CLIMATE
is how the atmosphere “behaves” over relatively long periods of time
12
New cards
FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE
13
New cards
LATITUDE
* distance from the equator
14
New cards
OCEAN CURRENTS
* movement of water from one location to another affects the temperature of the air that passes over it
15
New cards
WIND AND AIR MASSES
four air masses in Canada: Polar – cold, Maritime – moist, Continental – dry, Tropical - warm
16
New cards
ELEVATION(ALTITUDE)
* distance from the water level going up
* higher the elevation, the lower the temperature
* higher the elevation, the lower the temperature
17
New cards
RELIEF
* the change of elevation and that can cause precipitation
* cooling leads to condensation on the windward side leaving the leeward side of the mountain is left dry
* cooling leads to condensation on the windward side leaving the leeward side of the mountain is left dry
18
New cards
NEAR WATER
* climates around bodies of water are moderate
* level of precipitation is relatively high
* those away from the water are likely to have extreme changes in climate
* level of precipitation is relatively high
* those away from the water are likely to have extreme changes in climate
19
New cards
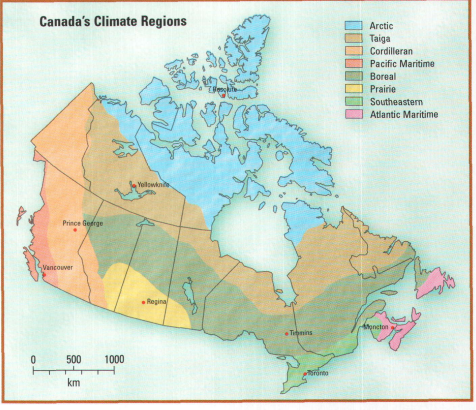
CLIMATE REGIONS
* Arctic
* taiga
* cordillera
* pacific maritime
* boreal
* prairie
* southeastern
* Atlantic maritime
* taiga
* cordillera
* pacific maritime
* boreal
* prairie
* southeastern
* Atlantic maritime
20
New cards
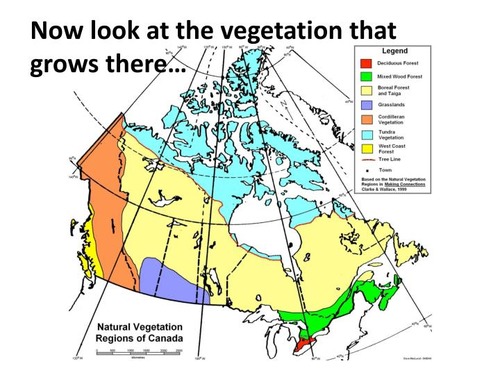
VEGETATION REGIONS
* Tundra
* West Coast Forest
* Cordilleran Vegetation
* Boreal and Taiga Forest
* Grassland
* Mixed Forest
* Deciduous Forest
* West Coast Forest
* Cordilleran Vegetation
* Boreal and Taiga Forest
* Grassland
* Mixed Forest
* Deciduous Forest
21
New cards
LAYERS OF EARTH
22
New cards
THE CRUST
* made up of solid rock
* varies in thickness
* varies in thickness
23
New cards
THE MANTLE
is a thick layer of molten rock (called magma)
24
New cards
THE CORE
made up of an outer liquid layer and a solid center.
25
New cards
ALFRED WEGENER:
* 300 million years ago all earth’s land masses were in constant motion and collided to form one supercontinent called PANGAEA (“all land”)
* About 200 million years ago Pangaea started to break up
* Pieces drifted in different directions to their present positions.
* About 200 million years ago Pangaea started to break up
* Pieces drifted in different directions to their present positions.
26
New cards
TYPES OF INDUSTRIES
27
New cards
PRIMARY INDUSTRY
* referred to as **extraction**
* industries that extract or produce raw materials
* mining, forestry, fishing, agriculture
* industries that extract or produce raw materials
* mining, forestry, fishing, agriculture
28
New cards
SECONDARY INDUSTRY
* referred to as manufacturing
* changes raw materials into usable products through processing and manufacturing
* manufacturing, engineering, chemical, clothing, brewing industries
* changes raw materials into usable products through processing and manufacturing
* manufacturing, engineering, chemical, clothing, brewing industries
29
New cards
TERTIARY INDUSTRY
* referred to as service industries
* provide essential services and support to allow other levels of industry to function
* finance, utilities, education, retail, housing, medical etc.
* provide essential services and support to allow other levels of industry to function
* finance, utilities, education, retail, housing, medical etc.
30
New cards
QUATERNARY INDUSTRY
* referred to as information industries
* involves advanced technology and the transfer of information
* app creations, software development, experimentations for curing diseases, inquiry-based research
* involves advanced technology and the transfer of information
* app creations, software development, experimentations for curing diseases, inquiry-based research
31
New cards
QUINARY
* responsible for services provided by the highest levels of organization in society
* includes services such as government, military, education, and healthcare decision-making processes
* includes services such as government, military, education, and healthcare decision-making processes
32
New cards
DEPENDENCY THEORY
the idea that resources flow from poor and underdeveloped countries to wealthy countries, enriching the latter at the expense of the former
33
New cards
ROSTOW’S TRADE THEORY
34
New cards
Traditional society
rural, no technology, local trade (no countries in this stage)
35
New cards
Pre-conditions to take off
the beginning of urbanization, transportation systems develop, mechanized farming. (ex. Afghanistan)
36
New cards
Take off
urbanization starting all over the country, international trade has begun (ex Philippines)
37
New cards
Drive to maturity
specialization of industry, investment in social infrastructure, Improved technology. (ex. Brazil, Russia, china)
38
New cards
High mass consumption
advanced technology and communication, skilled workforce. (example Canada)
39
New cards
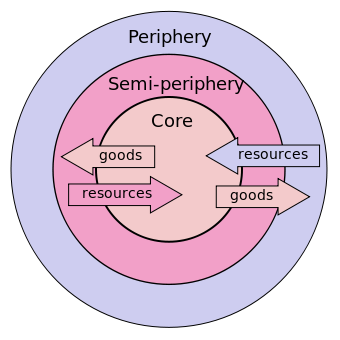
WALLERSTEIN’S WORLD SYSTEMS THEORY
resources from the periphery(underdeveloped countries) and semi-periphery(developing countries) are sent to the core(developed countries) where these resources are converted into goods and sent back into the periphery and semi-periphery
40
New cards
TARIFFS
* Tariffs are taxes on items leaving or entering a country
* tariffs raise revenue, protect domestic industries, or exert political leverage over another country.
* Tariffs often result in unwanted side effects, such as higher consumer prices
* tariffs raise revenue, protect domestic industries, or exert political leverage over another country.
* Tariffs often result in unwanted side effects, such as higher consumer prices
41
New cards
COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
The ability of an individual country to specialize in a good or service at a lower cost than trade with other countries who specializes in different good or service at a low cost so both countries can receive goods at a lower cost, overall benefiting them both
42
New cards
DEMOGRAPHY
is the study of populations, population density, and historical trends in population growth
43
New cards
BIRTH RATE
\# of births /population x 1000
44
New cards
DEATH RATE
\# of deaths /population x 1000
45
New cards
EMIGRATION
\# of emigrations/population x 1000
46
New cards
IMMIGRATION
\# immigrations/population x 1000
47
New cards
NATURAL INCREASE
Birth rate − death rate \= rate of natural increase
48
New cards
NET MIGRATION RATE
(Immigration -Emigration ) / Total Population x 1000
49
New cards
POPULATION GROWTH
Natural Increase + Net Migration
50
New cards
POPULATION GROWTH RATE
Population Growth/1000 x 100%
51
New cards
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL
Used to help describe the change from a high birth and death rate to a low birth and death rate
52
New cards
STAGE 1 (PRE-TRANSITION):
birth and death rate are high (some growth)
53
New cards
STAGE 2 (EARLY TRANSITION):
* birth rate is high
* death rate drops dramatically
* results in population explosion
* death rate drops dramatically
* results in population explosion
54
New cards
STAGE 3 (LATE TRANSITION):
* birth rate drops quickly
* death rate continues to decline
* death rate continues to decline
55
New cards
STAGE 4 (POST-TRANSITION):
* birth rate stabilizes
* death rate slightly increases as population ages
* fewer children more senior
* death rate slightly increases as population ages
* fewer children more senior
56
New cards
DECLINING POPULATION
Canada’s population is slowly decreasing due to its large senior population of baby boomers, therefore, increasing death rates
57
New cards
DEPENDENCY LOAD
The part of the population that relies on the working population for support(children 0-15, seniors 65+)
58
New cards
POPULATION PYRAMIDS
A series of stages that countries are assumed to go through the same pattern
59
New cards
STAGE 1 (RAPID)
* High child dependency
* Low senior population
* Low senior population
60
New cards
STAGE 2 (EXPANDING):
* Growing working age group
* Low senior population
* Low senior population
61
New cards
STAGE 3 (STABILIZING):
* Growing senior population
* More even distribution
* More even distribution
62
New cards
STAGE 4 (STABLE/DECLINING/CONTRACTING):
* Low child dependency
* High working population
* High working population
63
New cards
PUSH FACTORS
Factors that cause people to leave the country in which they live
64
New cards
PULL FACTORS
Factors that draw immigrants to a different country
65
New cards
INTERVENING OBSTACLES
Forces that discourage or stop someone from following through on their decision to immigrate.
66
New cards
IMMIGRATION
Migrating into a place (into a place)
67
New cards
EMIGRATION
migrating away from a place (exiting a place)
68
New cards
REFUGEES
a person who has been **forced** to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
69
New cards
CANADA’S POPULATION HISTORICALLY
* The First Nations and Inuit of Canada are the original inhabitants
* Immigrants from Europe came and dominated the land causing a descendant of immigrants in Canada
* Immigrants from Europe came and dominated the land causing a descendant of immigrants in Canada
70
New cards
CANADA’S POPULATION PRESENT
* Aging Population
* High Life Expectancy
* Increasing Death Rate
* Decreasing Birth Rate
* High Life Expectancy
* Increasing Death Rate
* Decreasing Birth Rate
71
New cards
CANADA’S POPULATION FUTURE
* More immigrants
* High senior population
* Low children population
* High senior population
* Low children population
72
New cards
CANADA’S IMMIGRATION PATTERNS
73
New cards
1840s
Irish settlers - left due to the devastating potato crop failure causing starvation.
74
New cards
1905-1914
Eastern Europe - Canadian government offered free land and other incentives to immigrants
75
New cards
1947-1960
Italians - trying to flee the devastation caused by WWII
76
New cards
1956
Hungarians - failed revolt against the Soviet Union
77
New cards
1980-1997
Hong Kong Chinese - searching for political stability
78
New cards
1980-2003
Afghanistans - seeking safety from conflicts in their country.
79
New cards
2015
Syria- 73,000 refugees from due to war.
80
New cards
2022
Ukaine - trying to flee the invading of Russia
81
New cards
IMMIGRATION PROS
* Immigrants help replace the previous working population, the baby boomers,
* Immigrants help provide for the dependency load
* Immigrants help sustain the economy
* Bring education and knowledge from other countries which can benefit Canada
* Immigrants help provide for the dependency load
* Immigrants help sustain the economy
* Bring education and knowledge from other countries which can benefit Canada
82
New cards
IMMIGRATION CONS
* Some people take advantage of the immigration system by claiming refugee status for immediate entry into the country
* Some immigrants may not be qualified to assist in the economy (senior citizens or children)
* Overcrowding, therefore, there is a demand for more necessities such as housing, hospitals, etc
* Some immigrants may not be qualified to assist in the economy (senior citizens or children)
* Overcrowding, therefore, there is a demand for more necessities such as housing, hospitals, etc
83
New cards
URBAN LAND USES
1. Residential (housing developments/ apartments)
2. Transportation (infrastructure= roads, railroads)
3. Institutional and public buildings (schools, government buildings, community centers)
4. Open Space and recreational (parks, forests, lakes)
5. Industrial (factories, plants)
6. Commercial (grocery stores, malls, shops, etc)
84
New cards
URBAN SPRAWL
the spreading of urban structures into areas surrounding a city in order to provide more for a community
85
New cards
SUSTAINABILITY
* when a place can be maintained at a certain level for as long as is needed.
86
New cards
Walkability
is the accessibility to necessary everyday stores and places
87
New cards
BID-RENT FUNCTION
describes the price range that a household (or firm) would be willing to pay at various locations in order to achieve a given level of satisfaction
88
New cards
SUBURBS
Residential areas outside of main urban areas that are connected to the city by main roads.
89
New cards
EXURBS
Residential areas outside main urban areas that are not connected to the city by main roads (e.g. farm/open space).