MRIQUIZ rapid fire
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Page
of 6
WCUI MRI REGISTRY REVIEW
SESSION #5 – MR SAFETY & INSTRUMENTATION
Who should be screened before entering the MR scan room?
Identify the four zones of the MRI environment:
Define the following and describe the sticker associated with them:
MR safe:
MR conditional:
MR unsafe:
Identify Level 1 and Level 2 personnel:
Define fringe field:
SAR stands for ______________________________. What units is it measured in? ________
What are the FDA guidelines for SAR?
How can an MRI technologist manage the SAR effects?
Define magnetohydrodynamic effect and what does it cause?
What are the hazards of radiofrequencies?
How can an MRI technologist reduce the RF deposition?
Describe the effects of time-varying magnetic fields (TVMF) and the cause:
How should the cables and gating leads be positioned?
What happens during a quench? When should an MRI technologist quench the magnet?
List the primary safety concerns associated with cryogens:
The MRI scan room humidity should be ______%. The room temp should be ______%.
Diamagnetism:
Paramagentism:
Ferromagnetism:
1 Tesla = _______ gauss
Permanent magnet:
Resistive magnet:
Superconducting magnet:
What does the RF system do?
What does the RF amplifier do?
What does the gradient amplifier do?
Gradient strength or amplitude:
Rise time:
Slew rate:
Duty cycle:
______Active shimming a. Surrounds magnet with steel plates, used in high field systems
______Passive shimming b. Adjusts uniformity of field over specific body part
______Active shielding c. Uses metal discs/plates to reach optimal field homogeneity
______Passive shielding d. Solenoid electromagnets at each end of bore creating 5gauss line
Describe the following coils:
Receiver coil:
Volume coil:
Surface (linear) coil:
Phased array coil:
Define homogeneity:
____Theories of MRI a. Has magnitude and direction
____Hydrogen b. Secondary spin of proton
____Atomic number c. Primary MR signal
____Mass number d. Application of RF causing resonance to occur
____Free induction decay e. Number of protons in nucleus
____Vector f. Classical and quantum
____Precession g. Magnetic field induced around nucleus
____Magnetic moment h. Sum of protons and neutrons in nucleus
____Excitation i. Most abundant element in body, 1 proton
____ Net magnetization factor j. Number of H protons per unit volume
____ Proton density k. Excess of H protons aligned with magnetic field
Hydrogen has ______________________ because it is charged and ________________.
When atoms are in magnetic field, they will align ____________________________________.
Define:
Faraday’s Law of Induction:
Larmour equation:
Resonance:
Relaxation:
Gyro-magnetic ratio of hydrogen at 1 Tesla is ________________.
Define T1 relaxation:
Define T2 decay:
When does the slice selection occurs and what does it determine?
When does the phase encoding and frequency encoding occur?
Short axis of anatomy is normally the ___________encoding direction.
For small FOV in frequency direction, _________ frequency encoding gradient is applied.
Determine what gradient performs each function:
Plane Slice Selection Phase encoding Frequency encoding
Sagittal
Axial (body)
Axial (head)
Coronal
Define receive bandwidth:
Define transmit bandwidth:
K-space is defined as:
The center of K-space is responsible for _________________, whereas the outer portions are for
_________________. Phase encoding steps determines number of ______________________
that must be filled. Phase encoding gradient changes amplitude from _____________________
to encode a new line of data.
Name the different types of K-space filling
A ___ is a instrument that allows a patient to appoint an agent to make healt care decisions in the event that the primary individual is incapable of executing decisions
Health care proxy
This ___ weighted image axquire in the __ scan plane
t2, Sagittal
Reducing the flip angle yields images with what change in image contrast?
Less T1 information
Doubling field strength will result in what impact on SAR potential, if any?
Quadruple SAR
This is an example of a weighted sequence acquired in the scan plane
t2 , coronal
Normal Oxygen Sat levels should be between?
95-100%
Hemangiomas in the liver are typically bengin leisons, are best visualed with what
Delayed images
Isotropic voxel refers to a ___ voxel shape
Cubic
risk factors of MR exposure with reguards to SAR absorption include all the following except
Hypotension
In a contrast enhanced MR angiography of the abdomial arteries , the IV gadolinium would enhance in which order
Celiac, Superior mesenteric, renal, inferior mesenteric
Kienbock’s disease is a condition of osteomalacia in the Lunate bone of the wrist
Lunate bone of the wrist
The substances that bind to gadolinium ions are defined as
Chelates
Which colon is below the liver
Ascending colon
formula for effective TR( BPM question)
Effective TR=Heart Rate (bpm)/60
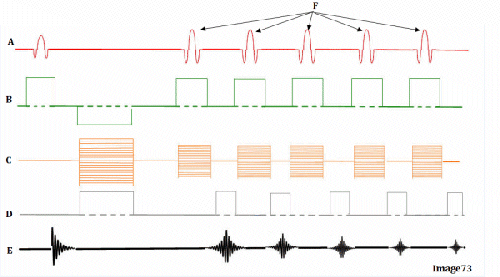
What kind of pulse sequence is this
Gradient echo sequence. Due to small repeated excitation, and no 180
Best imaging view for spinal stenosis
sagittal
Which tendon torn the most in rotator cuff tear?
Supraspinatus
Primarily stemming from active RF coil, elements out side the scan FOV, ____ aritfacts can be fixed by de selecting the elements out side the scanning range
Annefact
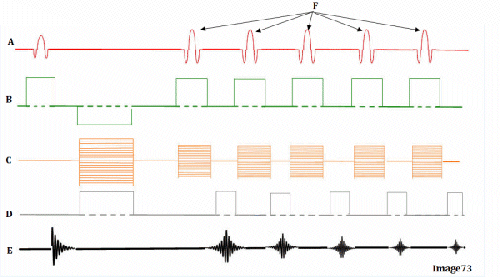
what kind pulse sequence is this ?
Fast spin echo
Where does the common carotid artery bifurcate at?
C3-4 disc space
____ measures 20 feet long and is made of duodenum, jejunum, an dthe ileum
Small intestine
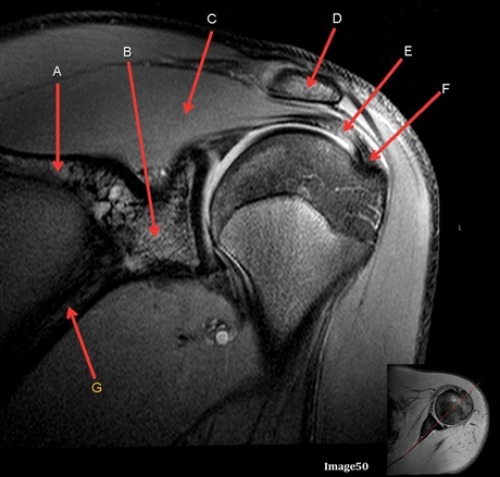
letter E is pointing at?
Supraspinatus tendon
What specifically is a SPGR sequence spoiling
Transverse magnetization
What parameter woild affect a cardiac function study
Heart rate
Most optimal veiw for evaluation of th eovaries is
Coronal
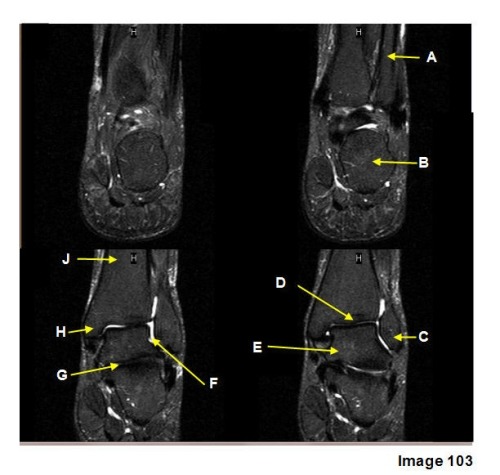
B is pointing to what?
Calcaneus
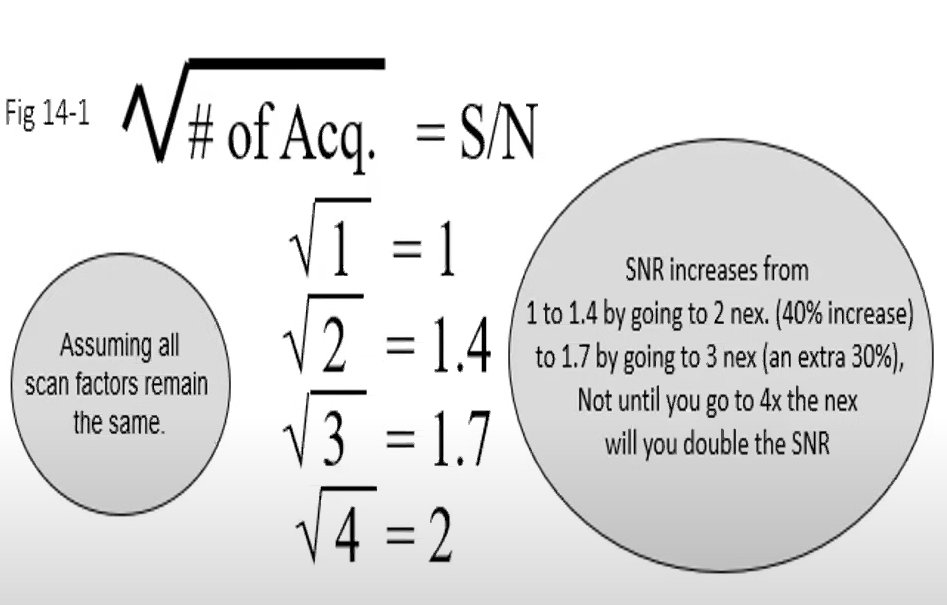
what kind of artifact is this
Moire
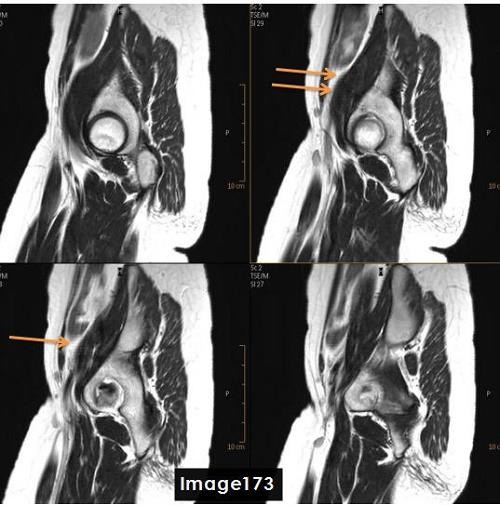
The artifact indentified by the orange arrows in this image is a ___ artifact
FID Crushing
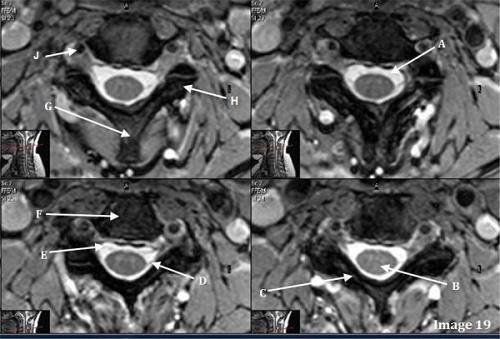
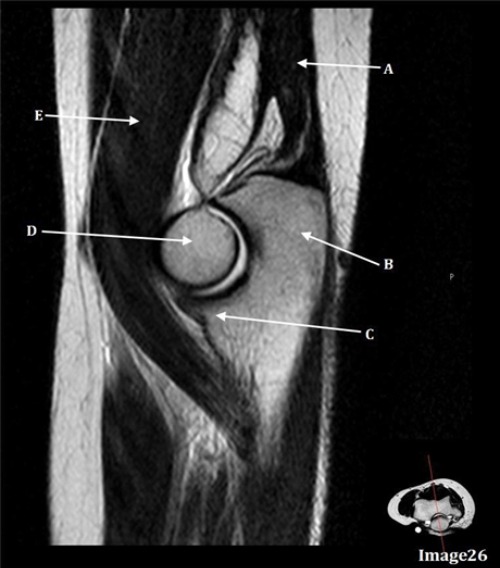
D is pointing to
Dorsal nerve root
An example of parenteral method of drug delivery is taking a drug by mouth
false
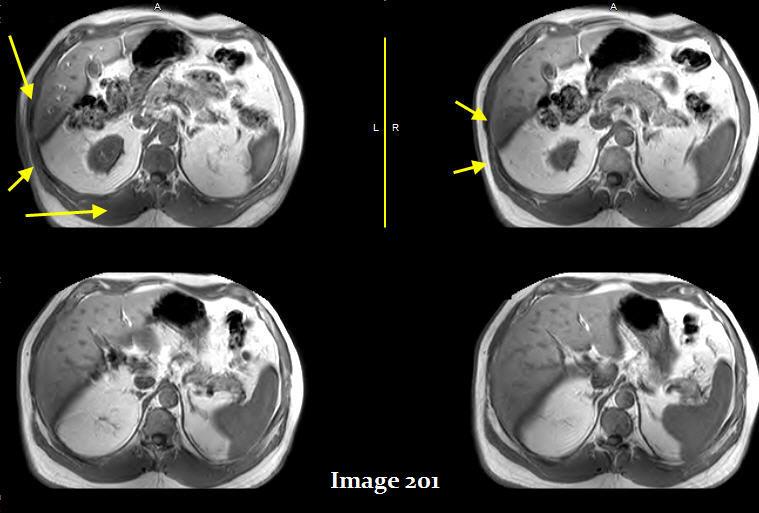
The yellows arrows point to what kind of artifact
Dielectric effects
What parameter combination will yield the best spatial res
3mm slice thickness, 256 × 256 matrix
The first major branch of the abdominal aorta is the celiac trunk, which branches into ___ arteries
Gastric, hepatic, and splenic
Standard dose for the adminstration of IV gad chelates is
0.1 mmol/kg
Which imaging plane would best display both the dorsal ventral nerve roots?
Axial
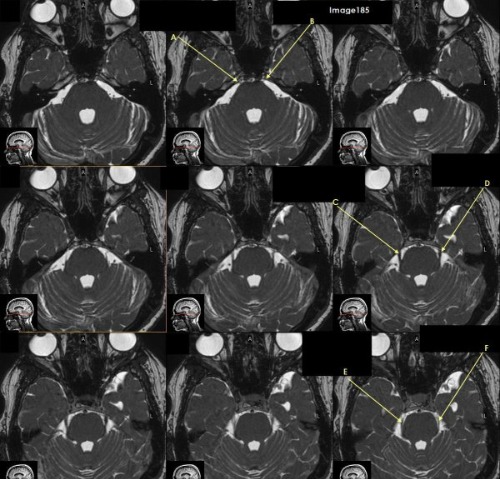
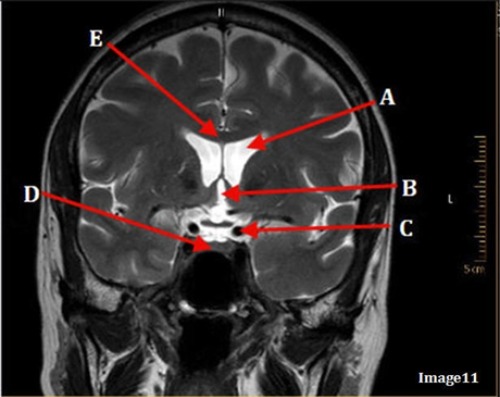
letter C is pointing to which cranial nerve
Trigeminal nerve ( CV V)
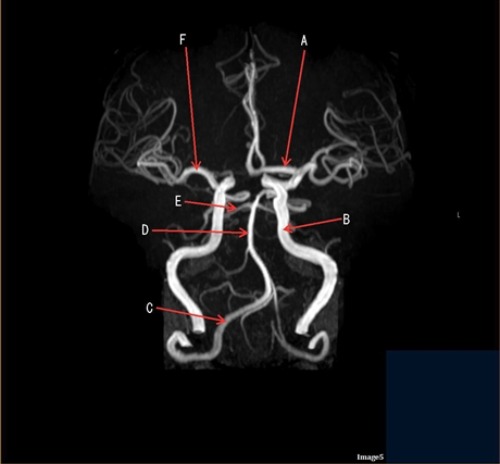
Letter F is pointing to
Middle cerebral artery
In an IR recovery sequence, the time interval between the 180 RF pulse and the 90 RF pulse is the
TI
Most optimal view for evalutation of the uterus is the
Sagittal
Remedy for Gibbs truncation artifact would be
Increase phase encodings
Depression in the base of the skull where the pituitary gland is located is called
Sella turcica
SNR does not increase with
Decreasing pixel sizeThe
timing of RF pulses controls
Image contrast
Who developed math equation to analyze the heat transfer between solid bodies
Joseph fourier
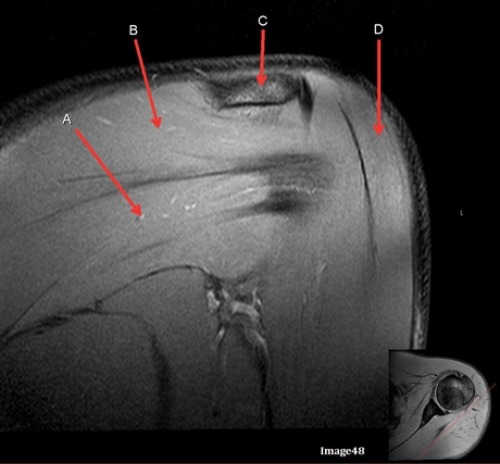
Letter B is pointing to
Infraspinatus muscle
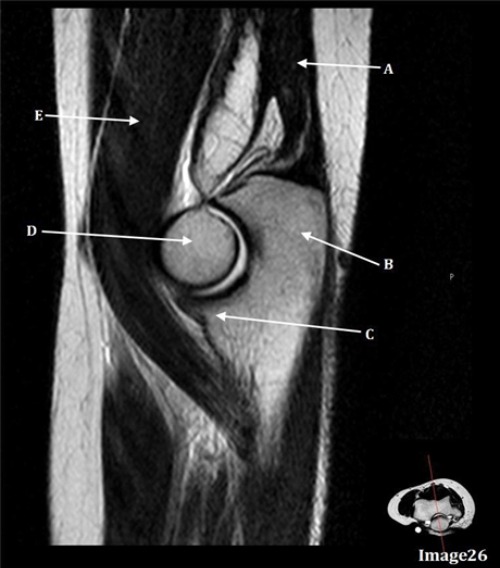
C is pointing to
Coronoid process
Extracranial MRA exam is defined as MRA of the
Carotid arteries
Ernest angle can be defined as optimal ___ that yeilds the ____ signal for a particular spin the least amount of time
F/A, Maximum
In lumbar spine images through the intervertebral disc spaces, slices should be
Oblique
Metastic lesions enhance after injecting gado chelate b/c of
The breakdown in the blood brain barrier
When parallel imaging techniques are utilized, a low res ___ is acquired prior to the acquistion
Calibration
A sign that a pt may be in cardiac arrest might include
Not having a pulse
What can result in the highest SAR factor in an MR oulse sequence
Short RF transmit pulse ( vendor fast sequence )
With reguards to k-space, the data containing high res are located
The outer lines
What parameter adjustments reduce the overall SNR
Decrease TR, Reduce pixel size, Decrease FOV, Increase rBW, decrease NEX, and increase ETL
Technique used to supress fluids, utilizing a long echo time coupled w/ long inversion time is known as
FLAIR
The height of a peak on MR spectrum correlates to the __ of a substance that was detected
Amount
The ___ mag field poses risks to patients and staff, due to the torpedo effect when a ferromagnetic object becomes magnetized and attracts to the large magnet
Main Static
The major bifurcation of the abdominal aorta is the
Right and left iliac arteries
Mag field inhomogeneity is expressed in
PPM
Brain exam to evaluate crainal nerves VII & VIII due to pt symptoms of tinnutis
IAC exam
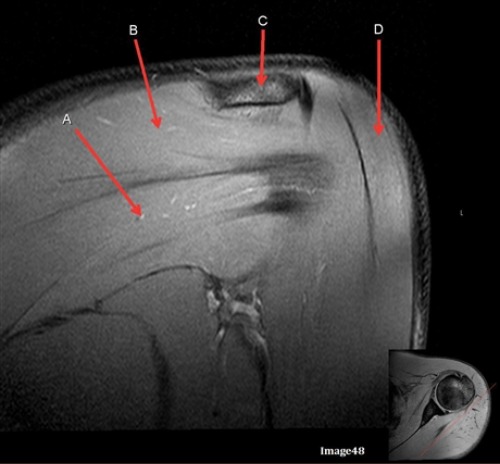
D is pointing to
Delotid muscle
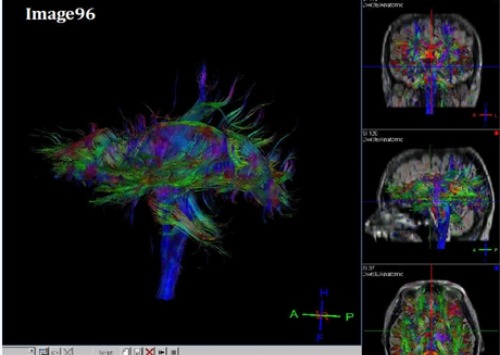
This is an example of
Diffusion tensor imaging ( tractography)
The FDA set of mag field clinical use limits of for the entire population and over 1 month of age
4 T and 8 T
__ occurs when tissue outside FOV is undersampled, causing opposite side of anatomical location
Aliasing artifact, aka Wrap
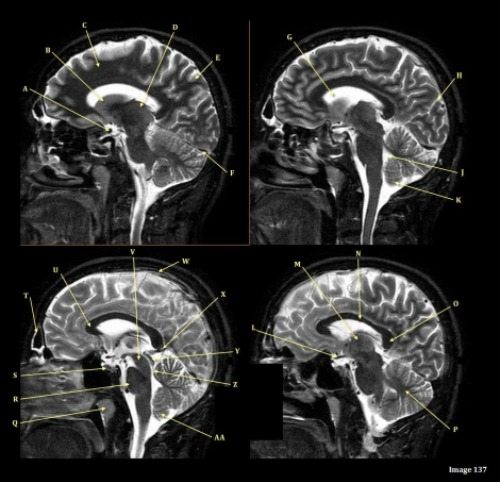
J is pointing at
Fourth ventricle
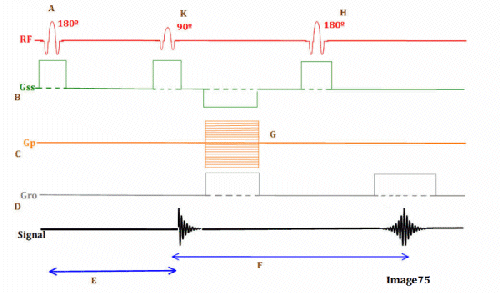
This graph represents
TI ; inversion time ( look at RF)
The ___ is posterior to the vertebral body and consists of two pedicles and two laminae
Vertebral arch
Which MR technique assesses the mechanical properties of tissues
Magnetic resonance elastogrpahy ( MRE)
Readout gradient is usually turned on during the sampling or readout of the peak echo and during which other process
Frequency encoding
Array processor is responbile for
Reconstructing the images using the Fourier transform
Does gadolinium chelates readily pass the blood brain barrier
False
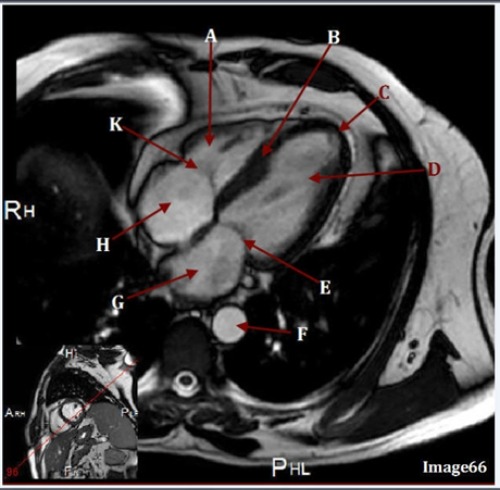
Letter B is pointing to
Septum
MR tech is permitted to administer how much oxygen to the pt in emergency
2L/min
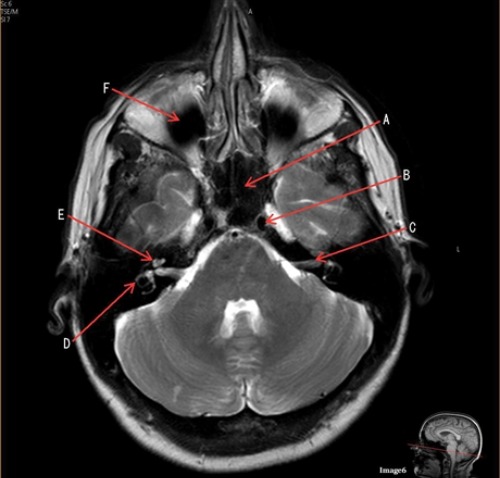
D is pointing to what
Semicircular canal
For intracranial arterial blood flow sequence, a pre sat pulse would be applied where
Superior to slice group
Narrow receiver bandwidth
Increases susceptibility artifact
gradient moment nulling is used to compensate for what
First order motion, slow flowing vessels
FDA whole body SAR absorption rate
4 watts/ kg for 15 min
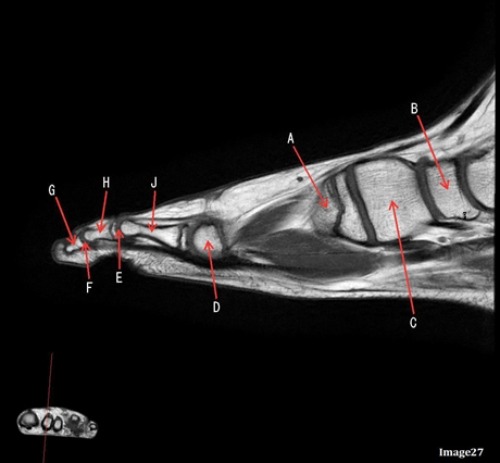
J is pointing to what
Proximal phalanx
Remedy for Gibbs truncation artifact is
Increase # of phase encodings
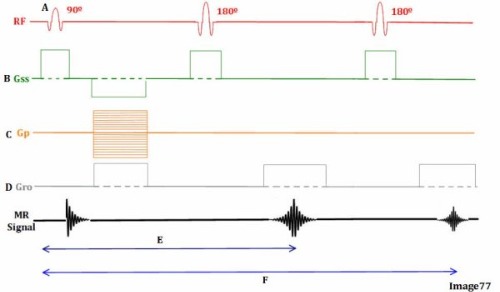
If this is a FSE, the number of lines of K space filled for each TR period would be
2 ( each 180 represents a line of k space )
The ___ to reduce chemical shift artifacts
rBW increased
____ is simply defined as the distance between echos
Echo spacing
Hemosiderin appears ___ to surrounding tissues on t2 weighted images
Hypointense
____ is a condition when blood sugar falls too low often occurring when diabetic patients take too much insuilin
Hypoglycemia
All of following artifacts except ___ occur along the phase encoding axi s
chemical shift
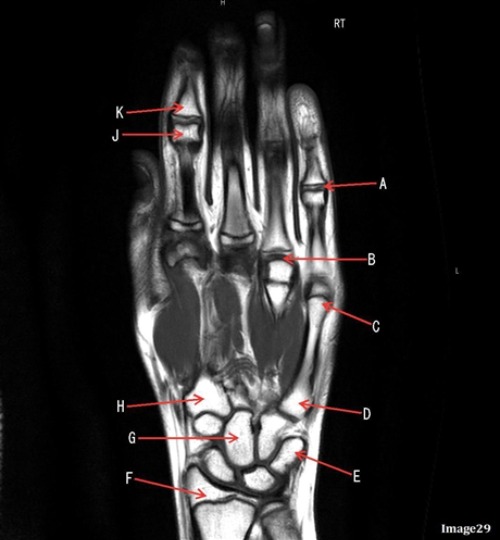
Letter C is pointing to
Head of 5th metacarpal
Reducing FOV by a factor of 2 will reduce the voxel volume by a factor
4
Hydrogen protons is the anti parallel state are referred to as
Spin down/ high energy spins
Active shielding can be defined as
Superconducting windings within the MR scanner, reducing the fringe magnetic field
____ discovered that when a magnet was moved inside a coil of copper wire, a tiny electric current flows through the wire
micheal faraday
What best describes a FSE sequence
A train of spin echos
____, —— gad compounds are considered the least likely to release the gad ion and hence the safest
Cyclical; ionic
On T2 image, edema appears bright because it has a ____-relaxation time
long t2
In FSE, acquired with a long TE, yielding t2 wieghted images, scan time can be reduced by
Using longer ETL
@ 1 T the freq difference between that of fat & water is approx
147hz
Regions of the body that don’t quickly dissipate thermal absorption from sar
Eyes and testicles