Module 2: Target Tissue Toxicity
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
what nerves are in the PNS? what are the major subdivisions?
* cranial & spinal nerves
* somatic (skeletal muscle) & visceral (autonomic)
* somatic (skeletal muscle) & visceral (autonomic)
2
New cards
inorganic Pb toxicity is very dependent on _
* Pb can also pass in the _?
* Pb can also pass in the _?
age
* placenta, breast milk, bones
* placenta, breast milk, bones
3
New cards
At low Pb concentrations, children can see decreases in:
IQ, Hearing, growth
4
New cards
Lead neurotox history
* known since Roman times
* 1900s: Australia had 1st epidemic of Pb poisoning in children bc of lead paints
* 1970s: widespread subtle cognitive/behavioral deficits in kids exposed to low Pb
* 1900s: Australia had 1st epidemic of Pb poisoning in children bc of lead paints
* 1970s: widespread subtle cognitive/behavioral deficits in kids exposed to low Pb
5
New cards
Methyl mercury neurotox history
* 1950: in men w/occupational exposure, used as fungicide for beaver pelts
* 1960s: in Japan, mothers contaminated consumed fish → infants were blind, retardation
* 1990: New Zealand & Seychelles, lower doses assoc’d w/dec IQ, memory, attention, language
* 1960s: in Japan, mothers contaminated consumed fish → infants were blind, retardation
* 1990: New Zealand & Seychelles, lower doses assoc’d w/dec IQ, memory, attention, language
6
New cards
Thalidomide neurotox history
* in Europe, a pregnant nausea treatment
* in Europe, a pregnant nausea treatment
1950s: congenital limb defects
1970-80: exposure in utero → mental retardation & autism spectrum disorder
1970-80: exposure in utero → mental retardation & autism spectrum disorder
7
New cards
neurodevelopment stages
1. proliferation
2. differentiation/migration
3. growth/synaptogenesis & glial fxn/myelination
4. xs neurons are pruned → apoptosis
8
New cards
mechanism of developmental neurotox
* altered cell proliferation, differentiation, or apoptosis
* interference w/neurotransmission
* alteration of morphogenetic process
* changes in cell shape
* epigenetic (DNA methylation, histone acetylation)
* interference w/neurotransmission
* alteration of morphogenetic process
* changes in cell shape
* epigenetic (DNA methylation, histone acetylation)
9
New cards
why is timing everything in dev neurotox?
1. later stages dep on success of earlier ones
2. indiv events may be differentially vulnerable to a substance
3. different brain regions develop according to different time lines during pregnancy & postnatal life
1. ex) alcohol fetal syndrome
4. expression or fxn of neurotoxin targets may vary by dev stage
\
10
New cards
ex of timing of neurotox
fetal alcohol syndrome
* if early → hypothalamus affected → executive fxn issues
* if later → cerebellum affected → motor fxn issues
\
glycine receptor alpha-subunit + strychnine
* neonatal isoform is resistant while adult is susceptible
\
AchE also as a axonal morphogen during dev
* helps guide outgrowth of axon
* OPs target AchE → axon won’t grow right
* if early → hypothalamus affected → executive fxn issues
* if later → cerebellum affected → motor fxn issues
\
glycine receptor alpha-subunit + strychnine
* neonatal isoform is resistant while adult is susceptible
\
AchE also as a axonal morphogen during dev
* helps guide outgrowth of axon
* OPs target AchE → axon won’t grow right
11
New cards
non-dioxin like (NDL) vs dioxin-like PCBs
NDL PCBs
* more stable, predominate over DL PCBs
* non-coplanar
* don’t bind AhR → but have neurotox via the RyR
\
DL PCBs
* coplanar
* bind strongly to aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) which regulates dioxin-responsive genes
* similar tox as dioxin (liver, skin, immune)
* more stable, predominate over DL PCBs
* non-coplanar
* don’t bind AhR → but have neurotox via the RyR
\
DL PCBs
* coplanar
* bind strongly to aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) which regulates dioxin-responsive genes
* similar tox as dioxin (liver, skin, immune)
12
New cards
Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) and NDL PCBs
* fxn?
* types? found where?
* fxn?
* types? found where?
* RyR regulates Ca2+ release from ER
* RyR1 = skeletal
* RyR2 = cardiac
* RyR3 = brain
* all 3 found in brain
* 1&2 predominate in skeletal and cardiac
* RyR1 = skeletal
* RyR2 = cardiac
* RyR3 = brain
* all 3 found in brain
* 1&2 predominate in skeletal and cardiac
13
New cards
how does PCB 95 (NDL-type) exposure lead to behavioral deficits
* learning & memory
* psychomotor
* attention
* learning & memory
* psychomotor
* attention
* normal neurodev: glutamate would enter post-synaptic neuron via NMDAR, AMPAR, or mGluR → depolarization → RyR opens to release Ca2+ → signaling pw triggered → CREB trxn factor → dendrite growth
* PCB 95 binds to RyR → won’t close → xs Ca2+ in cytoplasm → inc Ca2+ oscillations in hippocampal neurons → triggers same pw → xs dendrite growth/spine formation → inc neuronal apoptosis
* proving PCB 95 is RyR dependent
* PCB 66 (same chem properties as 95) shows no RyR activity
* siRNA: KO of RyR gene → no arborization
* PCB 95 binds to RyR → won’t close → xs Ca2+ in cytoplasm → inc Ca2+ oscillations in hippocampal neurons → triggers same pw → xs dendrite growth/spine formation → inc neuronal apoptosis
* proving PCB 95 is RyR dependent
* PCB 66 (same chem properties as 95) shows no RyR activity
* siRNA: KO of RyR gene → no arborization
14
New cards
what are the reactions of making ACh and degrading ACh?
choline + acetyl-CoA → ACh + CoA
* via choline acetyltransferase
\
ACh + H2O → choline + acetate + H2O
* acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
* via choline acetyltransferase
\
ACh + H2O → choline + acetate + H2O
* acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
15
New cards
how do SNARE proteins facilitate neurotransmission?
help vesicles of NT fuse w/post-synaptic terminal membrane
* AP arrives to terminal → Ca2+ enters → V- & T-SNARE bind → vesicle of NT fuse w/membrane → NT diffuses to post-synaptic neuron
* AP arrives to terminal → Ca2+ enters → V- & T-SNARE bind → vesicle of NT fuse w/membrane → NT diffuses to post-synaptic neuron
16
New cards
how do botulinum toxins cause muscle paralysis?
* botulinum (heterodimer) binds to receptor via its heavy chain → vesicle → its light chain leaves vesicle & cleaves SNARE → prevents ACh release
* reason why botox causes paralysis
* reason why botox causes paralysis
17
New cards
what are the 2 hypothesized mechanisms of A-Latrotoxin? This causes what?
1. channel forming: causes xs ACh release by forming a Ca2+ channel in the presynaptic neuron
2. receptor mediated (Latrophilin/CIRL): inc fusion of ACh-vesicles to inc ACh release
\
* xs ACh → muscle tetany
18
New cards
Uses/Exposures of Organophosphorus Esters (OPs)
* insecticides
* petroleum additives
* plasticizers
* warfare
* pharm
\
* exposures
* terrorist/suicide
* occupational
* environmental
* oral, dermal, inhalation
* petroleum additives
* plasticizers
* warfare
* pharm
\
* exposures
* terrorist/suicide
* occupational
* environmental
* oral, dermal, inhalation
19
New cards
how do OPs cause toxicity? how does this affect autonomic neurochemistry?
target catalytic triad of AChE → ACh accumulation in synapse in …
\
in somatic NS
* skeletal muscles
\
in autonomic NS
* parasympathetic: at ganglion synapse
* sympathetic: at ganglion synapse & adrenal medulla
* → overstimulation of NE and Epi → smooth or cardiac, muscles, glands or GI overstimulated
\
\
in somatic NS
* skeletal muscles
\
in autonomic NS
* parasympathetic: at ganglion synapse
* sympathetic: at ganglion synapse & adrenal medulla
* → overstimulation of NE and Epi → smooth or cardiac, muscles, glands or GI overstimulated
\
20
New cards
Acute Cholinergic Crisis effects on PNS and CNS?
* SLUDGE
* DMBBELLS
* SLUDGE
* DMBBELLS
\
PNS (muscarinic)
* resp: wheezing, bronchoconstriction
* GI: anorexia, nausea, vomit, diarrhea
* cardio: bradycardia, hypotension
* urinary: incontinence
* glands: hypersalivation, hyperlacrimation, inc xs sweating
* pupils: constricted (miosis), unreactive to light
\
PNS (nicotinic)
* muscles: fasciculations, twitching, weakness
* sympathetic ganglia: tachycardia, hypertension
\
CNS
* headache, drowsiness, confusion, blurred vision, slurred speech, ataxia, depression
* lethal: coma, convulsions, respiratory center block
\
SLUDGE = salivation, lacrimation, urination, diarrhea, GI distress, emesis)
DUMBBELLS = diarrhea, urination, misosis, bronchorrhea, bronchospams, emesis, lacrimation, taxation, sweating)
PNS (muscarinic)
* resp: wheezing, bronchoconstriction
* GI: anorexia, nausea, vomit, diarrhea
* cardio: bradycardia, hypotension
* urinary: incontinence
* glands: hypersalivation, hyperlacrimation, inc xs sweating
* pupils: constricted (miosis), unreactive to light
\
PNS (nicotinic)
* muscles: fasciculations, twitching, weakness
* sympathetic ganglia: tachycardia, hypertension
\
CNS
* headache, drowsiness, confusion, blurred vision, slurred speech, ataxia, depression
* lethal: coma, convulsions, respiratory center block
\
SLUDGE = salivation, lacrimation, urination, diarrhea, GI distress, emesis)
DUMBBELLS = diarrhea, urination, misosis, bronchorrhea, bronchospams, emesis, lacrimation, taxation, sweating)
21
New cards
major classes of neurotoxic chemicals
* natural neurotoxins
* neuroactive drugs
* organic solvents
* metals
* pesticides
* gases
* persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
* neuroactive drugs
* organic solvents
* metals
* pesticides
* gases
* persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
22
New cards
what are the extraneural factors influencing neurotoxicity?
* sex (endocrine disruptors, P450)
* sp, genotype
* nutrition
* protein defic → sulfur groups dec needed to detoxify cyanide
* folate defic → exacerbate MetOH intoxication
* age: the most important factor!
* sp, genotype
* nutrition
* protein defic → sulfur groups dec needed to detoxify cyanide
* folate defic → exacerbate MetOH intoxication
* age: the most important factor!
23
New cards
major cell types in NS
1. neuron
2. glial cells: equal # as neurons, support neuron dev, signaling
3. ependymal & endothelial cells: regulate passage b/t brain parenchyma & CSF (ependymal) & blood (endothelial)
\
24
New cards
glial cell types & role in neurotox
macroglia
* oligodendocytes (myelinating)
* astrocytes (non-myelinating, CYPs, NT uptake)
microglia
* phagocytic cells
* synapse stabilization & elimination/pruning
\
role in neurotox
* targets for neurotox
* protects neurons
* facilitates neurotox
* oligodendocytes (myelinating)
* astrocytes (non-myelinating, CYPs, NT uptake)
microglia
* phagocytic cells
* synapse stabilization & elimination/pruning
\
role in neurotox
* targets for neurotox
* protects neurons
* facilitates neurotox
25
New cards
how do astrocytes facilitate MPTP toxicity?
* MPTP small, uncharged exits capillary
* MAO-B on astrocyte → MPDP+ now charged → trapped in brain → MPP+
* MPP+ resembles dopamine → interferes w/complex I of mitochondrial ETC → dopaminergic neuron can’t make ATP → neuron dies
* MAO-B on astrocyte → MPDP+ now charged → trapped in brain → MPP+
* MPP+ resembles dopamine → interferes w/complex I of mitochondrial ETC → dopaminergic neuron can’t make ATP → neuron dies
26
New cards
VG ion channels are targets for neurotox
* pore blockers
* allosteric modulators that alter gating kinetics
* voltage sensor trapping neurotoxins
* bind for pyrethroid pesticides
* allosteric modulators that alter gating kinetics
* voltage sensor trapping neurotoxins
* bind for pyrethroid pesticides
27
New cards
mechanism for terminating neurotransmitters in synapse
* reuptake by presynaptic neuron
* enzymatic degradation
* diffusion from synapse
* enzymatic degradation
* diffusion from synapse
28
New cards
ACh is used where? excitatory or inhibitory NT?
* used by spinal cord neurons to control muscles, brain- memory, autonomic fxn
* excitatory mostly
* excitatory mostly
29
New cards
what are the major inhibitory and excitatory NT in the brain?
GABA = inhibitory
Glutamate (Glut) = excitatory \[glutes are exciting\]
Glutamate (Glut) = excitatory \[glutes are exciting\]
30
New cards
chemical synapses as targets of neurotox examples
* levodopa: precursor for dopamine
* fenclonine (PCPA) inhibits Tryptophan hydroxylase
* Maneb blocks transport of Glut into vesiscles → inhibit excitatory NT
* Curare: inhibits ACh receptors on skeletal muscle (natives used on arrowheads to paralyze)
* Amitraz: activates autoinhibitory alpha2 NE receptors
* cocaine: inhibits reuptake of dopamine
* fenclonine (PCPA) inhibits Tryptophan hydroxylase
* Maneb blocks transport of Glut into vesiscles → inhibit excitatory NT
* Curare: inhibits ACh receptors on skeletal muscle (natives used on arrowheads to paralyze)
* Amitraz: activates autoinhibitory alpha2 NE receptors
* cocaine: inhibits reuptake of dopamine
31
New cards
how can excitotoxicity occur?
1. xs release of Glut or aspartate from presynaptic cells
2. xs stimulation of NMDA, AMPA, or KA (kainate) GlutR by substances other than presynaptic NT
3. dec activity of Glut transporters
4. altered balance of excitatory to inhibitory neurotransmission
1. inhibit GABA → removes disinhibition of excitability
32
New cards
how does domoic acid (DA, shell fish poisoning) cause excitotoxicity?
DA binds KAR (no DA clearing mechanism) → Na+ influx → overstimulation of NMDAR (req strong depolarization) → Ca/Na+ influx → Ca2+ accumulation → cell death
33
New cards
Ochratoxin A blocks _ to cause excitotoxicty.
glutamate transporter on astrocyte
34
New cards
what level of skin does most toxicity occur at? what are these mature cells called?
epidermis
* squames = full of hydrophobic keratins and lipid envelope out outside
* squames = full of hydrophobic keratins and lipid envelope out outside
35
New cards
Fick’s Law: penetration through the skin equation
mg absorbed = (hr of exposure)(concentration \[cm/hr\])(surface area \[cm^2\])(flux \[ug/mL\])
* recall: cm^2\*cm = cm^3 = mL
* recall: cm^2\*cm = cm^3 = mL
36
New cards
what are primary irritants?
cause damage at site of contact via direct chemical or physical action; no prior immunologic sensitization required
37
New cards
allergy mechanism or delayed hypersensitivity
* what are some major allergens?
* what is a hapten?
* what are some major allergens?
* what is a hapten?
hapten + tissue protein = complete Ag → sensitized T-lymphocyte
* epoxy resins, Rhus genus of plants, chromates, nickel, rubber chemicals
* hapten = reactive molecules that make protein adducts (complete Ag)
* epoxy resins, Rhus genus of plants, chromates, nickel, rubber chemicals
* hapten = reactive molecules that make protein adducts (complete Ag)
38
New cards
what are some effects on skin from allergic reaction?
* atopic dermatitis
* erythroderma: red skin
* Stevens-Johnson syndrome (dalmatian patches)
* Pyoderma gandrenosum (from tattoo)
* warts (nonsterile tattoo/piercing equipment)
* melanin overproduction
* photodermatitis (lime juice, xs tanning)
* leukoderma (white skin from antioxidant in rubber)
* erythroderma: red skin
* Stevens-Johnson syndrome (dalmatian patches)
* Pyoderma gandrenosum (from tattoo)
* warts (nonsterile tattoo/piercing equipment)
* melanin overproduction
* photodermatitis (lime juice, xs tanning)
* leukoderma (white skin from antioxidant in rubber)
39
New cards
skin whiteners chronic use effects
* cause irregular pigmentation
* commonly have mercury or hydroquinone
* Hg targets NS, liver, kidneys
* \[papaya poisoning NS, liver, kidneys\]
* commonly have mercury or hydroquinone
* Hg targets NS, liver, kidneys
* \[papaya poisoning NS, liver, kidneys\]
40
New cards
what are the targets for acne and folliculitis?
* what are some acnegenic substances?
* what are some acnegenic substances?
acne = sebaceous glands which are blocked → can become cysts by highly chlorinated aromatics → retinoids can’t fix (chloracne)
folliculitis = hair follicle
\
* cutting oil
folliculitis = hair follicle
\
* cutting oil
41
New cards
t/f: tanning can cause radiodermatitis (atrophy) and skin cancer
true
42
New cards
Arsenic exposure causes _
hyperkeratosis
43
New cards
phototoxicity
immediate rxn resembles sunburn, occurs when agent is stimulated by light to produce radicals
* delayed rxns can result from allergic sensitization when agent is stimulated by light to become covalently attached to protein
* delayed rxns can result from allergic sensitization when agent is stimulated by light to become covalently attached to protein
44
New cards
petroleum products contain _ that are phototoxic, acnegenic, and carcinogenic (to the skin).
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)
45
New cards
antioxidants are used where? effects on skin?
* rubber industry
* affect melanocytes → leukoderma
\
* hydroquinone in whitening soap → Hg tox
* affect melanocytes → leukoderma
\
* hydroquinone in whitening soap → Hg tox
46
New cards
thyroid gland anatomy
* basic unit
* which part produces hormone? stores hormone?
* other cell types
* basic unit
* which part produces hormone? stores hormone?
* other cell types
* follicle
* follicular cells; colloid
* parafollicular cells (calcitonin → Ca2+ homeostasis)
* follicular cells; colloid
* parafollicular cells (calcitonin → Ca2+ homeostasis)
47
New cards
what are the steps in thyroid hormone (T3/T4) synthesis?
1. Tg is produced in ER & stored in colloid
2. I- uptake via (Na+/I- symporter aka NIS)
3. Thyroperoxidase (TPO)
1. iodinates tyrosyl residues in Tg
2. couples MIT & DIT
4. intracellular proteases cleave Tg → releases T4/T3 into blood stream
48
New cards
if low T3/4, what is the pw of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis? if high T3/4?
\
1. HT: low T4/3 signals to brain to release more TRH
2. PG: TRH triggers TSH release
1. Thyroid: TSH triggers proteolysis of Tg → release of T3/4
3. organs: T3/4 bind to nuclear thyroid receptors in different organs to upregulate gene transcription
\
* if high T3/4 → inhibit TRH & TSH (- feedback)
1. HT: low T4/3 signals to brain to release more TRH
2. PG: TRH triggers TSH release
1. Thyroid: TSH triggers proteolysis of Tg → release of T3/4
3. organs: T3/4 bind to nuclear thyroid receptors in different organs to upregulate gene transcription
\
* if high T3/4 → inhibit TRH & TSH (- feedback)
49
New cards
at homeostasis which thyroid hormone predominates?
T4 is 80-90% in blood, but T4 → T3 regularly in liver & brain
50
New cards
hypothyroidism
* cause
* symptoms
* cause
* symptoms
* most underproduction of T4, reduced I- intake
* hyperplasia → Goiter to compensate for dec efficacy of thyroid gland
* dry hair, puffy face, slow HB, weight gain, constipation, possibly infertility
* hyperplasia → Goiter to compensate for dec efficacy of thyroid gland
* dry hair, puffy face, slow HB, weight gain, constipation, possibly infertility
51
New cards
hyperthyroidism (aka thyrotoxicosis)
* overproduction of T3/4
* speeding up of metabolism
* Graves’ disease (eye bulging), hair loss, goiter, rapid HB, weight loss, diarrhea, menstrual cycle effects
* speeding up of metabolism
* Graves’ disease (eye bulging), hair loss, goiter, rapid HB, weight loss, diarrhea, menstrual cycle effects
52
New cards
hyper vs hypothyroidism biomarkers
hyper = low TSH, high T4
\
primary hypo = high TSH, low T4 → thyroid gland issue
secondary hypo = low TSH, low T4 → pituitary gland issue, or tumor/genetic syndromes that prevent PG making TSH
\
primary hypo = high TSH, low T4 → thyroid gland issue
secondary hypo = low TSH, low T4 → pituitary gland issue, or tumor/genetic syndromes that prevent PG making TSH
53
New cards
how do PPB affect thyroid hormone biomarkers?
* T3/4 circulates bound to transport proteins
* globulin >> albumin > TBPA or TTR(=> impt in ex of tox)
* if change levels of these proteins → affects how much T3/4 is measured in blood
* globulin >> albumin > TBPA or TTR(=> impt in ex of tox)
* if change levels of these proteins → affects how much T3/4 is measured in blood
54
New cards
perchlorate & thiocyanate affect on thyroid
* both are competitive inhibitors of I- uptake of NIS
* perchlorate 30x more than I-
* thiocyanate 15x more than I-
* perchlorate 30x more than I-
* thiocyanate 15x more than I-
55
New cards
PTU (propylthiouracil) effect on thyroid
competitive binding to TPO → stops iodination rxn → less T3/4 produced → hypothyroidism
56
New cards
hydroxylated PCBs (dielectric and coolant fluids)
competitive binding to TTR (T4 transporter protein to liver)
* xs unbound T4 → signals state of hyperthyroidism to HT/PG → reduced hormone production → hypothyroidism
* xs unbound T4 → signals state of hyperthyroidism to HT/PG → reduced hormone production → hypothyroidism
57
New cards
hydroxylated PBDEs (brominated flame retardants)
* competitive binding to nuclear thyroid hormone receptors → unregulated mRNA & signaling
58
New cards
what are the lungs’ fxn?
* gas exchange - large surface, thin blood-air barrier
* protection
* air filtration
* humidification/warming of air
* metabolism
* regulates blood content, bioactivation, biosynthesis of mucus
* protection
* air filtration
* humidification/warming of air
* metabolism
* regulates blood content, bioactivation, biosynthesis of mucus
59
New cards
organization of respiratory tract
nasal passage → pharynx → larynx → trachea → main bronchus → bronchiolus → terminal bronchiolus → respiratory bronchiolus → alveoli
60
New cards
respiratory system: humans vs rodents
humans
* simple nasal cavity
* nose/mouth breathers
* more mucous goblet cells, greater # of large airways w/tall epithelial cells & cartilage
* have transitional zone (resp bronchiole)
* 5 lobes- 2 L, 3 R
\
rodents
* convoluted nasal cavity
* obligate nose breathers
* more Club cells
* no transitional zone (respiratory bronchiole)
* 5 lobes - 1 L, 4 R
* simple nasal cavity
* nose/mouth breathers
* more mucous goblet cells, greater # of large airways w/tall epithelial cells & cartilage
* have transitional zone (resp bronchiole)
* 5 lobes- 2 L, 3 R
\
rodents
* convoluted nasal cavity
* obligate nose breathers
* more Club cells
* no transitional zone (respiratory bronchiole)
* 5 lobes - 1 L, 4 R
61
New cards
conducting airways vs alveoli main cells & fxns
airways
* club cells - secretion, P450 metabolism
* goblet cells - secretion/protection w/mucus
* basal cell - adherence of columnar cells, signaling
* ciliated cells - move mucus lining layer/clearance
\
alveoli
* type 2 cells - surfactant
* type 1 cells - blood air barrier
* club cells - secretion, P450 metabolism
* goblet cells - secretion/protection w/mucus
* basal cell - adherence of columnar cells, signaling
* ciliated cells - move mucus lining layer/clearance
\
alveoli
* type 2 cells - surfactant
* type 1 cells - blood air barrier
62
New cards
which lung cells are progenitor capable & have P450?
progenitors
* club, basal, type 2 cells
\
P450
* club cells >>> type 2 > macrophages, endothelium
* phase I & II
* club, basal, type 2 cells
\
P450
* club cells >>> type 2 > macrophages, endothelium
* phase I & II
63
New cards
which airways are supported by cartiginous rings cover by columar epithelium? which are not
trachea & bronchi
\
not: bronchioles, have smooth muscle, Club cells
\
not: bronchioles, have smooth muscle, Club cells
64
New cards
alveoli: which cells make the blood air barrier?
on top is surfactant layer (from type 2 cell)
\
epithelial cell (type I) + basal lamina + capillary endothelial cell
\
epithelial cell (type I) + basal lamina + capillary endothelial cell
65
New cards
pneumonia
* can be viral or bacteria
* impact depends on lung involvement, treatment, age, history, chemical exposure
* acute: difficult breathing, fever, high WBC
* chronic: chronic atelectasis, fibrosis, bronchitis
* impact depends on lung involvement, treatment, age, history, chemical exposure
* acute: difficult breathing, fever, high WBC
* chronic: chronic atelectasis, fibrosis, bronchitis
66
New cards
chronic bronchitis
* conducting airway narrowing
* inflammation of airway wall
* hypersecretion of mucus
* inflammation of airway wall
* hypersecretion of mucus
67
New cards
emphysema
elastin breakdown → alveolar structure breakdown
68
New cards
asthma
* symptoms
* contributors
* symptoms
* contributors
* reversible airway hyperresponsiveness caused by constriction of smooth muscle & inflammation of airway wall
* inc in stored/secreted mucus, wheezing, inc inflammation (eosinophils/neutrophils)
* most common childhood illness
* genetics, allergies, environmental exposures
* inc in stored/secreted mucus, wheezing, inc inflammation (eosinophils/neutrophils)
* most common childhood illness
* genetics, allergies, environmental exposures
69
New cards
fibrosis
deposition of collagen in process of scar formation in injured lung → assoc’d w/chronic inflammation → stiff lung
70
New cards
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
usual syndrome of advanced lung disease = combo of bronchitis + emphysema + some fibrosis
71
New cards
t/f: lung cancer is the #1 killer of men & women
* causes
* causes
true
* radon gas, asbestos, diesel exhaust, industrial chemicals
* 2nd hand smoke
* air pollution
* radon gas, asbestos, diesel exhaust, industrial chemicals
* 2nd hand smoke
* air pollution
72
New cards
what does FEV1 measure? what is the other primary lung fxn measure?
FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 sec
* FVC
\
how respiratory disease is diagnosed
* FVC
\
how respiratory disease is diagnosed
73
New cards
key consideration for lung study
* lung is dynamic
* in vivo changes → P450s mature postnatally as does detox
* lung is multifaceted - main cell types in microenvironments
* lung has substantial sp differences
* in vivo changes → P450s mature postnatally as does detox
* lung is multifaceted - main cell types in microenvironments
* lung has substantial sp differences
74
New cards
where does ozone (O3) come from?
factory, cars + volatile org cmpds + sunlight → O3
75
New cards
O3 effects on lung
* high levels → damage ciliated epithelium
* lower levels → oxidant stress & inc inflammation
* repeated exposure → remodel lung w/inflammation, mucous, irritate existing lung disease, dec airway size
* lower levels → oxidant stress & inc inflammation
* repeated exposure → remodel lung w/inflammation, mucous, irritate existing lung disease, dec airway size
76
New cards
napthalene sources
cigarette smoke, mothballs, paint, aerosols, vehicle exhaust, pesticides, tar/oil, fire smoke
77
New cards
napthalene is turned toxic when _?
\
what detoxifies napthalene?
\
what detoxifies napthalene?
toxic
* targets Club cells w/CYP2F2 → epoxide → tox
* removing or inhibiting GSH → tox
\
detox
* inc/upregulation of GSH synthesis → dec tox of napthalene
* targets Club cells w/CYP2F2 → epoxide → tox
* removing or inhibiting GSH → tox
\
detox
* inc/upregulation of GSH synthesis → dec tox of napthalene
78
New cards
which vessel type has both for lymph and blood?
* what is the fxn of lymph?
* what is the fxn of lymph?
capillaries
* maintain fluid balance, absorbs fats (chylomicrons), provide immune defense
* maintain fluid balance, absorbs fats (chylomicrons), provide immune defense
79
New cards
blood flow of heart
O2 rich blood into LA → LV → aorta → systemic → tissues → vena cava → RA → RV → lungs
80
New cards
coronary artery blood supply
LCA & RCA (left/right coronary artery)
* RCA delivers blood to SA & AV nodes → regulate HR
* RCA delivers blood to SA & AV nodes → regulate HR
81
New cards
Cardiac Conduction & ECG/EKG
* where is the heartbeat?
* where is the heartbeat?
P wave = atrial cells depolarize
PR = plateau of atrial muscle APs
QRS complex = ventricular cells depolarize & atrial cells repolarize
ST = plateau of ventricular muscle APs
T wave = ventricular cells repolarize
\
R peaks to R peaks = one HB
PR = plateau of atrial muscle APs
QRS complex = ventricular cells depolarize & atrial cells repolarize
ST = plateau of ventricular muscle APs
T wave = ventricular cells repolarize
\
R peaks to R peaks = one HB
82
New cards
cardiomyocyte AP graph
* what are the stages called?
* what ICs open/close when?
* what are the stages called?
* what ICs open/close when?
1. depolarization
2. Na+ ch open, K+ ch close
3. brief repolarization
1. K+ ch open, Na+ close
4. plateau phase
1. Ca2+ ch open, K+ close
5. repolarization
1. Ca2+ close, K+ open
6. refractory period
1. all channels closed (leaky ch → keep resting potential)
\
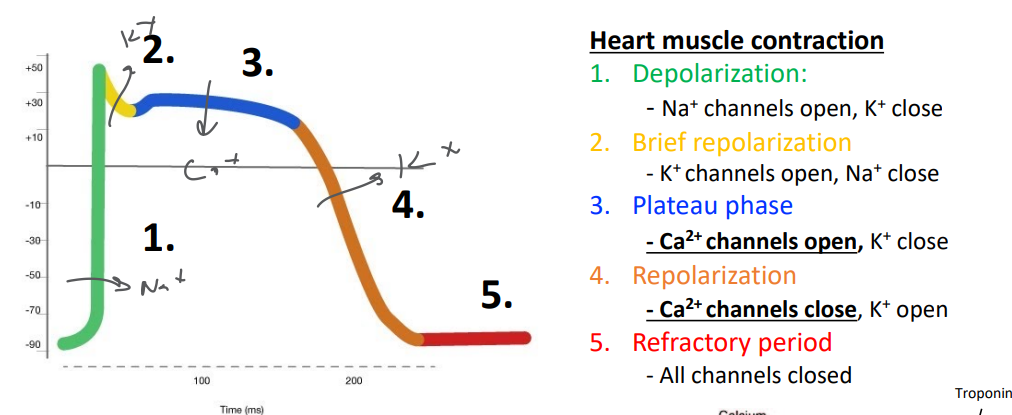
83
New cards
cardiomyocyte depolarization → Ca2+ influx → ?
Ca2+ binds to troponin → actin/myosin binding & power stroke
84
New cards
define:
* heart attack
* myocardial ischemia
* hypertrophy
* heart attack
* myocardial ischemia
* hypertrophy
* heart failure/cardiac arrest/myocardial infarction = pumping failure, lack of tissue perfusion
\
* dec blood flow to heart; usually caused by atherosclerosis or CAD → myocyte death due to hypoxia
\
* enlarged cells & inc tissue vol
\
\
* dec blood flow to heart; usually caused by atherosclerosis or CAD → myocyte death due to hypoxia
\
* enlarged cells & inc tissue vol
\
85
New cards
arrhythmia types = irregular heartbeat
bradycardia = slow HB
tachycardia = fast HB \[fast fashion is tachy\]
\
* QT prolongation = can trigger fast, chaotic HB, delayed ventricular repolarization
* Torsades de pointes (twisting of peaks) = form of ventricular tachycardia
* can lead to sudden death
tachycardia = fast HB \[fast fashion is tachy\]
\
* QT prolongation = can trigger fast, chaotic HB, delayed ventricular repolarization
* Torsades de pointes (twisting of peaks) = form of ventricular tachycardia
* can lead to sudden death
86
New cards
Trastuzumab (Herceptin) mechanism
HER2+ breast cancer → Trastuzumab Ab drug targets receptor Tyr kinase HER2 → Ab binding attracts NK cells
* but ventricular cardiac myocytes also express HER2 → drug binds → cardiomyocyte death
* but ventricular cardiac myocytes also express HER2 → drug binds → cardiomyocyte death
87
New cards
how does cocaine influence cardiomyocytes?
cocaine block funny Na+ ch → reduces depolarization (QRS) → reduces EKG amplitudes → inefficient blood pumping → collapse → myocardial necrosis → death
88
New cards
Di-2-etyylhexy phthalate (DEHP)
* found where?
* main metabolite?
* mechanism
* found where?
* main metabolite?
* mechanism
* plasticizer, PVCs
* MEHP
* DEHP/MEHP blocks connexon protein synthesis → gap junctions in electrical cell-cell coupling blocked → conduction velocity slower
* MEHP
* DEHP/MEHP blocks connexon protein synthesis → gap junctions in electrical cell-cell coupling blocked → conduction velocity slower
89
New cards
what are the specific & nonspecific biomarkers of cardiotox?
specific
* CK-MB (other CK isoforms not unique) = if acute myocardial infarction
* B-type natriuretic peptide - released if MAP too high
* T & I cardiac troponins = inc if myocardial damage
\
nonspecific
* inc myoglobin in plasma
* CK-MB (other CK isoforms not unique) = if acute myocardial infarction
* B-type natriuretic peptide - released if MAP too high
* T & I cardiac troponins = inc if myocardial damage
\
nonspecific
* inc myoglobin in plasma
90
New cards
elimination pathways
1. biliary or fecal (liver & gut)
2. renal or urinary (kidney & bladder)
3. respiratory
4. skin (sweat, tears → incidental)
5. hair/nails/feathers
6. breast milk
91
New cards
nephron: proximal tubule
water, salts, glucose, aa reabsorption (transporters)
\
urea excretion (diffusion)
\
urea excretion (diffusion)
92
New cards
nephron: loop of Henle
descending: water reabsorption (aquaporins)
\
ascending: Na+ reabsorption (transporters)
\
ascending: Na+ reabsorption (transporters)
93
New cards
nephron: distal tubule
ion/mineral reabsorption & secretion (transporters)
94
New cards
nephron: collection duct
water reabsorption (aquaporins)
95
New cards
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System (RAAS)
1. renin (from kidney) released if hypoperfusion, low MAP, distal ‘nutrient loss’
2. renin cleave Angiotensinogen (from liver) → Angiotensin I (AT I )
3. ACE (from lungs) cleaves AT I → AT II
4. AT II acts on adrenals → aldosterone → induce vasoconstriction → inc MAP → Na+/H2O retention
96
New cards
acute vs chronic kidney injury/disease
* cause
* diagnosis
* cause
* diagnosis
AKI = sudden loss of kidney fxn
* renal ischemia, crush injury, inflammation/infection, urinary tract blockage
* inc BUN, creatine, urine output
\
CKD = permanent loss of kidney fxn
* progressive AKI, cardiovasc disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension
* inc creatine, BUN, GFR, urinary abnormalities for at least 3 months
\
* renal ischemia, crush injury, inflammation/infection, urinary tract blockage
* inc BUN, creatine, urine output
\
CKD = permanent loss of kidney fxn
* progressive AKI, cardiovasc disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension
* inc creatine, BUN, GFR, urinary abnormalities for at least 3 months
\
97
New cards
20-25% of AKI are from
* drugs
* renal lithiasis (kidney stones) = form when urine concentrates from:
* calcium oxalate/phosphate (diet- leafy greens)
* uric acid (fluid imbalance)
* struvite (infection) = most damaging to hepatocyte, shArp
* renal pyelonephritis (acute kidney infn)
* UTI eg) E.coli
* permanent damage of kidney → kidney failure
* renal lithiasis (kidney stones) = form when urine concentrates from:
* calcium oxalate/phosphate (diet- leafy greens)
* uric acid (fluid imbalance)
* struvite (infection) = most damaging to hepatocyte, shArp
* renal pyelonephritis (acute kidney infn)
* UTI eg) E.coli
* permanent damage of kidney → kidney failure
98
New cards
t/f: kidney disease is reversible
true, if recovery w/in 24-48h
99
New cards
GFR < _% → increase in mortality
* when is dialysis needed?
* when is dialysis needed?
45%
* at 15% GFR
* at 15% GFR
100
New cards
adaption & repair potential of kidneys
* unilateral nephrectomy & congenital atrophy
* if 1 kidney bad, the other can inc blood flow (via hormones)
* proliferation after tox
* tubular epithelial cells via differentiation, proliferation, migration
* induction of protective proteins
* Metallothionein w/metals (excreted in urine)
* Stress-protein (HSPs) w/toxicants, anoxia, oxidative stress
* if 1 kidney bad, the other can inc blood flow (via hormones)
* proliferation after tox
* tubular epithelial cells via differentiation, proliferation, migration
* induction of protective proteins
* Metallothionein w/metals (excreted in urine)
* Stress-protein (HSPs) w/toxicants, anoxia, oxidative stress