Lecture 21: Endemic Mycoses
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Endemic Mycoses Immune Response
PRRs on phagocytes bind fungal PAMPs → Phagocytosis & induction of immune responses
Tissue form survives and replicates inside of phagocytes – are facultative intracellular pathogens of phagocytes
Infection can lead to granulomatous inflammation
Activation of T cells:
Effector Th1 cytokines stimulate a strong CMI response → Resolution in healthy hosts
Th17 cytokines will recruit neutrophils and promote epithelial repair
Antibodies produced participate in clearance
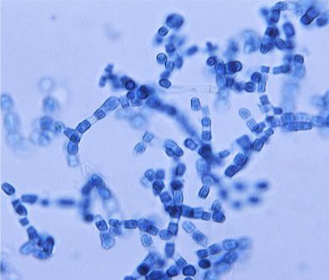
Coccidioides
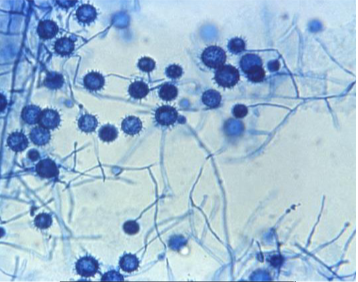
Histoplasma
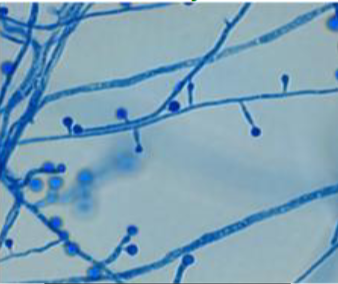
Blastomyces
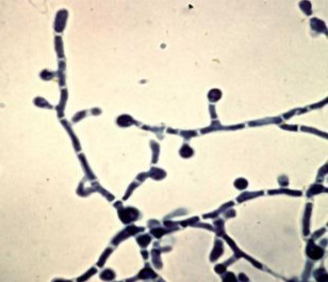
Paracoccidioides
Coccidioidomycosis
Valley Fever
Coccidioides immitis (CA) and Coccidioides posadasii (outside CA)
Dimorphic fungi:
Mold in the environment; hyphae with arthroconidia and mycelia in culture at room temperature
Spherules in the host, containing endospores
Found in lungs; can disseminate to other tissues
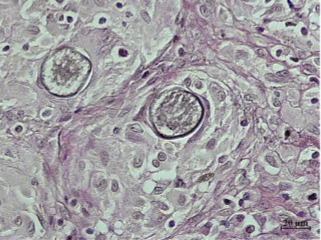
Coccidioides
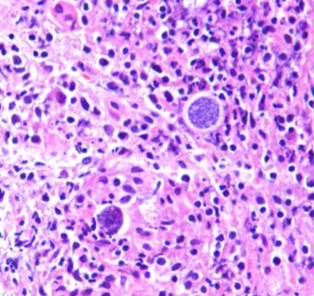
Coccidioides
Erythema Nodosum
Can be triggered by infection with Coccidioides
Often involves lower extremities
Type IV hypersensitivity response to fungal antigens; appears 1-3 weeks after initial respiratory symptoms
Red, tender subcutaneous nodules
Serves as a good prognostic indicator – patient is exhibiting a strong CMI response
Organisms are not present in the lesions
Erythema Multiforme
Can be triggered by infection with Coccidioides
Likely a combination of hypersensitivity responses: Type III = immune complex-mediated & Type IV = delayed-type
Epithelial damage is often due to CMI responses, with a predominance of CD8 T cells and macrophages
Deposits of complement C3, IgM, and fibrin around dermal blood vessels
Red, target-like lesions
Lesions often appear within ~48 hours after initial respiratory symptoms
Higher risk for Coccidioidomycosis Dissemination
Immunocompromising condition, pregnancy, and African-American race or Filipino ethnicity
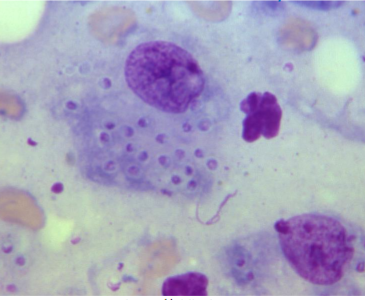
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum
Ohio, Missouri, & Mississippi River Valleys
Soil-based fungus with bird or bat droppings
Mold in the environment and in
culture at room temperature; hyphae with microconidia & tuberculate macroconidia
Yeast form in the host and
culture at 37C
Narrow-based budding yeast often within phagocytes
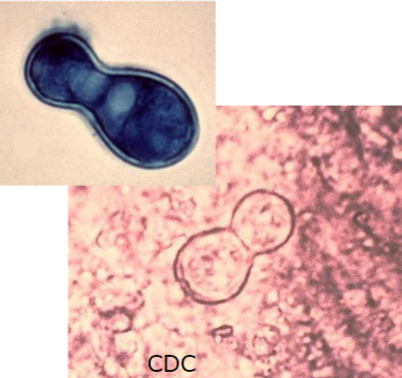
Blastomycosis
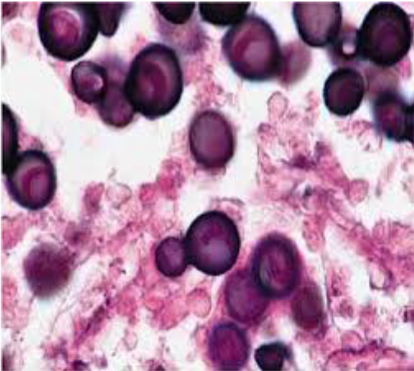
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Midwestern, south-central, and southeastern states
Soil-based fungus
Fungus resides in moist soil & decomposing organic material
Mold in the environment and in culture at room temperature; branching hyphae with conidia on slender terminal or lateral conidiophores
Yeast form in the host & culture at 37 C
Thick-walled, broad-based budding yeast
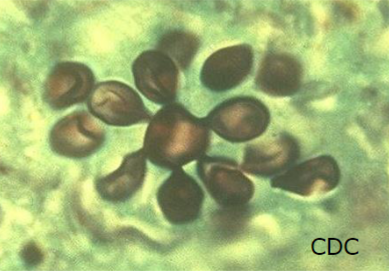
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis complex and P. lutzii
Central and South America (esp Brazil)
Infects lungs & skin
Likely soil-based fungi; agricultural areas
Mold in the environment & in culture at room temperature; hyphae with conidia
Yeast form in the host and culture at 37 C
Large, multiple budding yeast cells; buds attached by a narrow connection – “mariner’s or ship-captain’s wheel” appearance
Triazoles
Inhibit ergosterol synthesis
Amphotericin B
Aggregates with ergosterol, forming membrane pores