Tooth Extractions
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What are the indications for extractions?
Fractures, advanced periodontal disease, tooth resorptive lesions, inflammatory diseases, persistent deciduous teeth, un-erupted teeth, nonvital teeth, malocclusions, strategic extractions to prevent dz, carious lesions where restoration is not an option, failed endodontic treatment
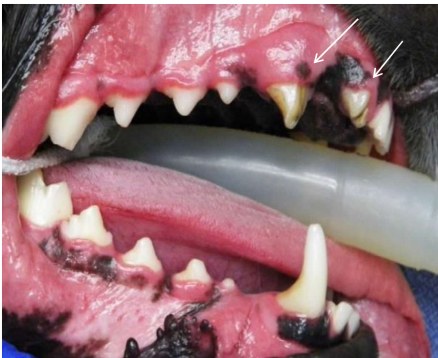
Tooth fracture, endodontic dz (pulp is visible)
Advanced periodontal dz
Tooth resorptive lesions
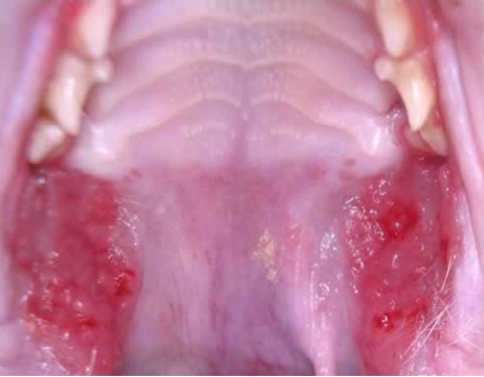
Feline chronic gingivostomatitis
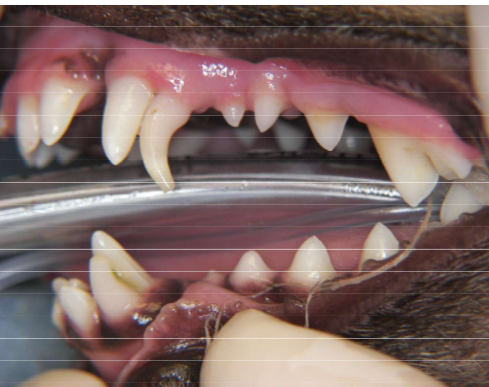
Persistent Deciduous teeth (604 and 704)
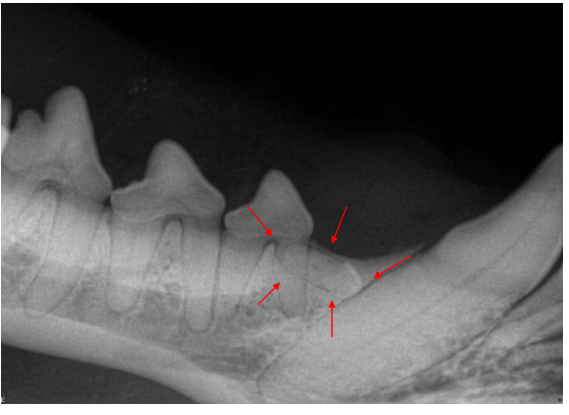
Unerupted tooth
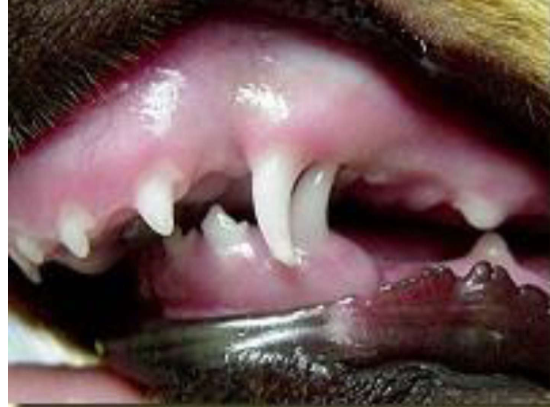
Malocclusion
What are the advantages to saving the teeth instead of extracting them?
Preserve function
Prevent occlusal trauma
Aesthetics
What does the client need to understand?
Problem, what you recommend, why you recommend, cost, complications, post op needs, follow ups
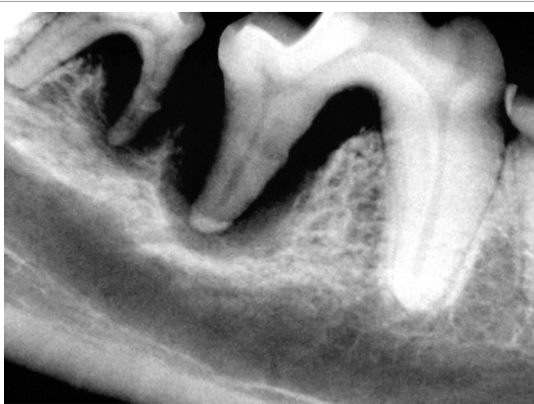
Why do you need radiographs before pulling teeth?
See anatomy
Look for complicating factors
What are the blocks used for dental extractions?
Infraorbital
Maxillary
Mental
Inferior alveolar
Describe the infraorbital block
Place in infraorbital foramen to block buccal bone, teeth, and soft tissue
What determines which teeth are numbed with infraorbital blocks?
How far caudally the anesthetic agent diffuses
What animals have a very short infraorbital canal?
Small toy dogs, cats, and brachycephalics
What does the maxillary block?
Blocks maxillary nerve before it enters the infraorbital canal
What anatomical features do you need to be careful of during a maxillary block?
Maxillary artery eye
What does the mental block?
Rostral mandible, lip, and teeth
Why is reliability of the mental block questionable?
Anesthetic depends on diffusion of drug
What animals have a difficult mental block to do?
Small dogs and cats
What does the inferior alveolar block?
Lower arcade
What are the general instruments you need?
Scalpel, handle, scissors, periosteal elevators, tissue forceps, tissue retractor, drill, elevator and luxator, alveolar curette, suture, saline, gauze, cotton tip applicator, suction
What are the types of extractions?
Closed and open
Describe a closed extraction
No gingival flap, sectioning of teeth, or removal of buccal bone
When do you do a closed extraction?
Incisors, single rooted premolars and single rooted molars
What are the steps of a closed extraction
Incise attached gingiva with a scalpal
Insert elevator or luxator into periodontal ligament space
Apply rotational or wedge forces
Extraction forceps for tooth removal
Close with a simple interrupted or cruciate
When do you do an open/surgical extraction?
Multi-rooted teeth
Single-rooted tooth with large roots (canines)
Teeth with fragile roots
There is a complication in a closed fracture
What is the steps of an open extraction?
Mucoperiosteal flap is made for increased exposure of buccal bone
Some buccal bone over tooth root is removed
Multi rooted teeth are sectioned into single rooth
Extraction of entire root
Alveoloplasty and curettage
Closure of flap
What is an alveolotomy?
Removal of buccal bone to add in extraction of individual roote
How much do you remove with a alveolotomy?
1/3-1/2 of the bone covering length of the root
What burs are used for a alveolotomy?
Round, pear, and tapered
Why do you section the bone into individual roots?
It makes it easier to remove
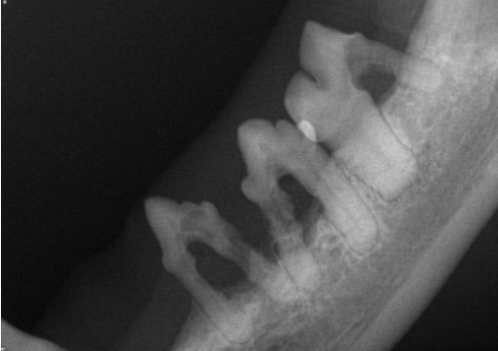
What is the problem with removing the first molar?
It has variable roots so you sometimes have to section it sometimes dont
Need to use radiographs to identify roots
What do you use to divide the tooth into single root segments?
Cross-cut taper or pear bur
What is a must on a elevator or luxator when removing a tooth?
Using a short finger stop
What should the tooth socket feel like after removing a tooth?
Smooth and round
If you feel a tooth socket after removing a tooth and it is gritty what do you need to do?
Remove your fragment or look for underlying disease
When do you use extraction forceps?
After tooth is mobile
What are some complicating factors of tooth removal?
Diseased teeth may be fragile and break, ankylosis, tooth resorption, dilaceration of roots, fused roots, extra roots, amount of supporting bone present, placement of teeth in mouth, shape of mouth
What is ankylosis?
Fusion of tooth to surrounding alveolar bone
Common in older patients
What do you do after removing a tooth?
Radiograph to make sure that there are fragments left
What is an alveoloplasty?
Contouring the bone so no sharp edges that can damage the flap are present
What do you use to do a alveoloplasty?
Diamond burr, football or taper shape
Why do you use a curette on the alveolus after removing a tooth?
Remove debris like granulation tissue, calculus, or bony fragments
When do you not need to curette the alveolus?
If the alveolus is clean
How do you do a alveolus debridement and flush?
Curette to remove debris
Saline flush after
T/F a tension free closure is a must?
True
How do you prepare the flap for closure?
Fresh margins, shape flap for fit, lengthening incisions may be needed, release periosteum for more mobility
Use gentle tissue handling
What suture do you use to close?
4-0 - 5-0 Monocryl because it is monofilament and glides through tissue easily
How long does monocryl suture take to resorb?
2-4 weeks
What can be helpful when closing a flap?
A small amount of palatal and lingual gingival elevation
What might you have to reduce to close a flap in a cat?
Boney ridge palatally
How do you close a flap?
Simple interrupted 1-3mm apart
2-3 mm from tissue edge
Tag length of 2-3mm
How many throws to close a flap?
4-6 so t the tongue cannot untie
Why do you close a flap?
Keeps blood clot out of alveolus
Improves patient comfort
Faster healing
Prevent food and debris from packing in
What are some complications of extractions?
Fractured roots, root displacement, excessive bleeding, oronasal fistula, fractured alveolus, fractured mandible, damage to surrounding teeth, soft tissue trauma, flap dehiscence, post op infection
Where can roots be displaced while doing an extraction?
Nasal cavity, mandibular canal, retrobulbar area
What is the after care of an extraction?
Soft food
Pain control
Nothing to chew on
E-collar
Rechecks
How long do you give soft food afterwards?
Until follow up
T/F you can give canned or moistened dry food as after care for an extraction?
True
What can you use for pain control after an extraction?
NSAIDs is baseline
Can add in opioids, gabapentin, or tramadol
When should you use antibiotics?
Severe infections of soft tissue or bone
Immunocompromised patients
Sub-aortic stenosis
Recent implants
How long can a patient not have a toy or a chew after an extraction?
Until a recheck
Why can a patient not have toys or chews after an extraction?
Minimize stress on suture line
What do you do at the recheck?
Ensure proper healing
Talk about preventative like tooth brushing, or diet
Behavior modification
What are the approaches for the maxillary block?
intraorally or extraorally
What are the approaches to an inferior alveolar?
intraorally or extraorally
What are mucoperiosteal flaps?
Flaps that allow for access to underlying structures
What do you need to plan ahead for before creating a mucoperiosteal flap?
What type of flap
If and when you need to make a vertical incision
Anatomy that is nearby
How much tissue you have to work with
What are the types of mucoperiosteal flaps?
Envelope
One vertical incision
Two vertical incisions
What flap does not have a vertical incision?
Envelope
What flap is triangle shaped?
One vertical incision
What flap is pedicle shaped?
2 vertical incision
Describe a no vertical incision / envelope flap steps
A sulcular incision is made parallel to the attached gingiva
Periosteal elevator is used to raise a full thickness flap
Buccal bone is exposed
What do you need to avoid with any type of flap?
Mucogingival junction
What does the length of the envelope flap depend on?
Number of teeth that need to be removed
What is the ideal location for a vertical incision of a flap?
Interproximal space between teeth
Where should a vertical incision not be placed?
In the furcational area of adjacent teeth
For a vertical incision flap, where should the suture line be?
Over the bone after closing. You need to plan this while making the vertical incision
What are the steps of a one vertical incision flap?
Sulcular incision made into gingiva parallel to the tooth
One vertical full thickness incision made traversing apically past mucogingival junction
Periosteal elevator used to raise a full thickness flap
Buccal bone is exposed
What are the steps of a two vertical incision flap?
Sulcular incision made into gingiva parallel to the tooth
Two vertical full thickness incision made traversing apically past mucogingival junction
Periosteal elevator used to raise a full thickness flap
Buccal bone is exposed
What is a downside of a 2 vertical incision flap?
It takes longer to close
What are the different forces used to remove a tooth?
Luxation
Elevation
Wheel-and-axle motion
Leverage
Rotation
Traction
What is a luxation motion used for?
Expand alveolar bone and cut periodontal ligament fibers
What is a elevation motion used for?
Expand alveolar bone and cut and stretch periodontal ligament fibers
What is a wheel and axle motion used for?
Elevator is placed perpendicular to 2 roots and handle is rotated to engage the elevator against a tooth root
Lifts tooth from alveolus
What is a rotation movement used for when removing a tooth?
Fatigue remaining periodontal ligament fibers
What is a traction motion used for when removing a tooth?
Removal of tooth from alveolus