MGMT 200 Quest 1 Review
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are the two functions of financial accounting?
Measure businesses activities of a company
Communicate those measurements to external parties for decision-making process
Investors
buy ownership in the company and have the right to share in the company’s profits
Creditors
lend money to a company, expecting to be paid back the loan amount plus interest
What are the types of business activites?
Financing: transactions the company has with investors and creditors
Investing: transactions involving the purchase and sale of resources that are expected to benefit the company for several years
Operating: transactions that relate to the primary operations of the company
Business Structures
Corporation: a company that is legally separate from its owners
Sole Proprietorship: a business owned by one person
Partnership: a business owned by two or more persons
Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ equity
Assets
total resources of the company
Example: cash, equipment, land, supplies, accounts receivable, buildings, inventory, investments
Liabilities
amounts owed to creditors
Example: accounts payable, salaries payable, deferred revenue, rent expense, advertising expense
Stockholders’ Equity
owners’ claims to resources
Example: common stock, retained earnings, dividends, service revenue, salaries expense
Revenue
the amounts recognized when the company sells products or provides services to customers
Expenses
the cost of providing products and services and other business activities during the current period
Net Income
the difference between revenues and expenses
Dividends
cash payments to stockholders (not expenses)
Financial Statements
periodic reports published by the company for the purpose of providing info to external users
Income Statement
reports the company’s revenues and expenses over an interval of time
If revenues > expenses; net income
If revenues < expenses; net loss
Compares revenues and expenses for the current period to assess the company’s ability to earn a profit from running its operations
Heading: At the top of the statement including company’s name, title of financial statement, and the time period covered
Revenues: Total revenues
Expenses: Typical costs such as rent, supplies, salaries, etc.
Net Income/Loss: Final total
Underlines: single underline represents subtotal, double underline represents final total

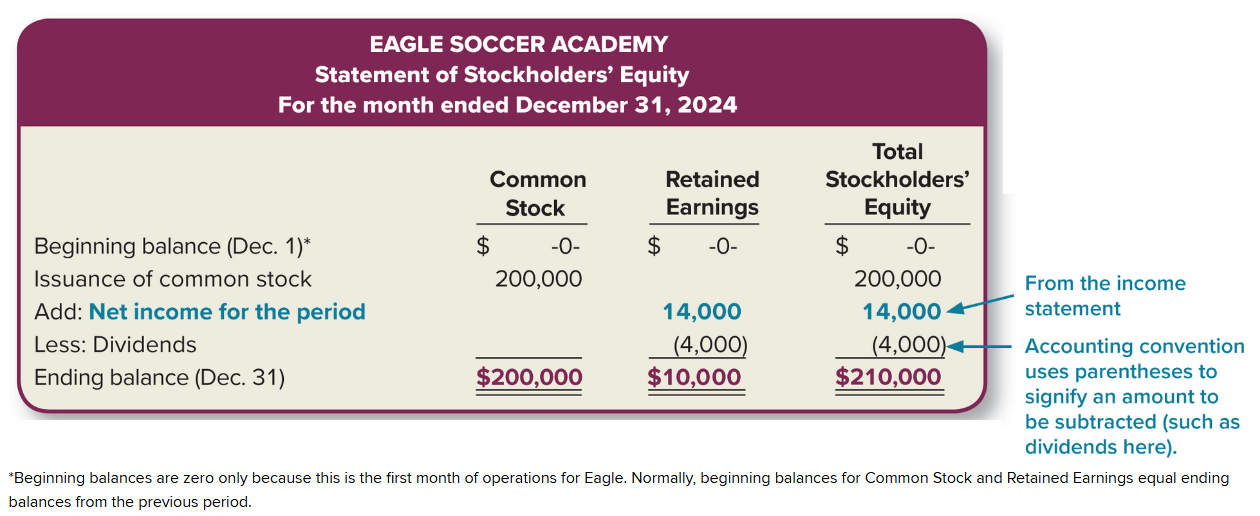
Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
summarizes the changes in stockholders’ equity over an interval of time
Heading: reports the activity for common stock and retained earnings over an interval of time
Issuance of Common Stock: shows starting common stock and the issuance of common stock (first column)
Add (Net income for the period): adds net income under retained earnings (second column)
Less (Dividends): decreases retained earnings (second column)
Ending Balance: sums up the totals for each column (common stock, retained earnings, stockholders’ equity)
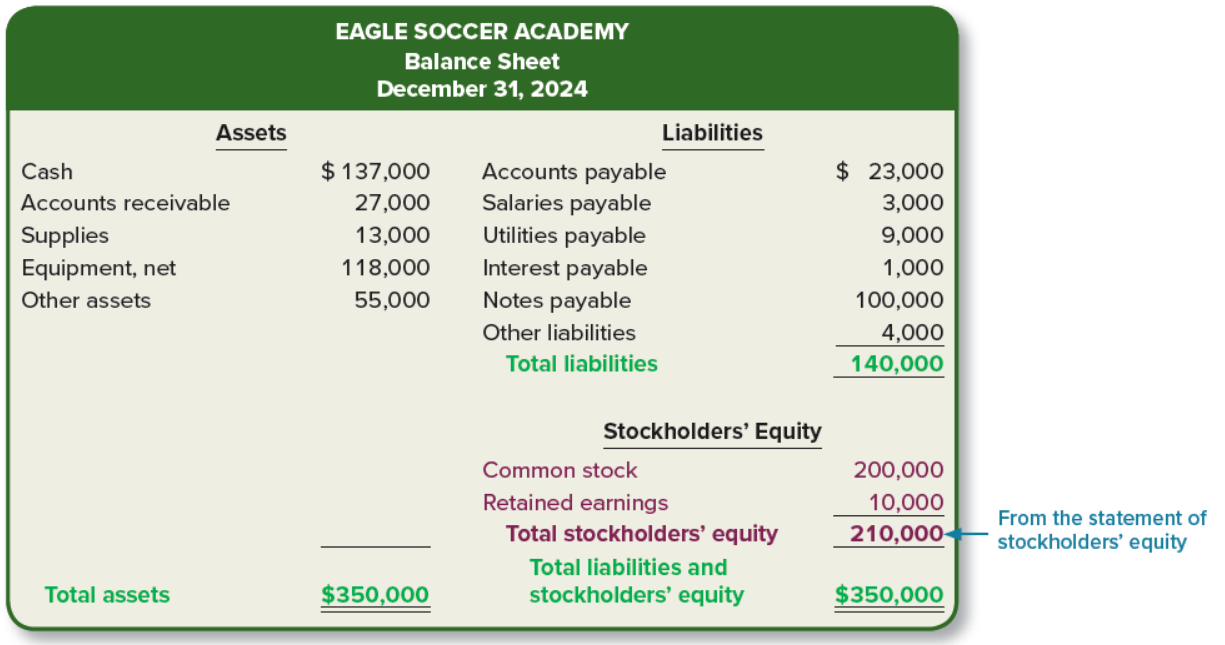
Balance Sheet
presents the financial position of the company on a particular table
Heading: reports assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity at a point in time
Assets: resources of the company
Liabilities: amounts owed by a company
Stockholders’ Equity: difference between assets and total liabilities
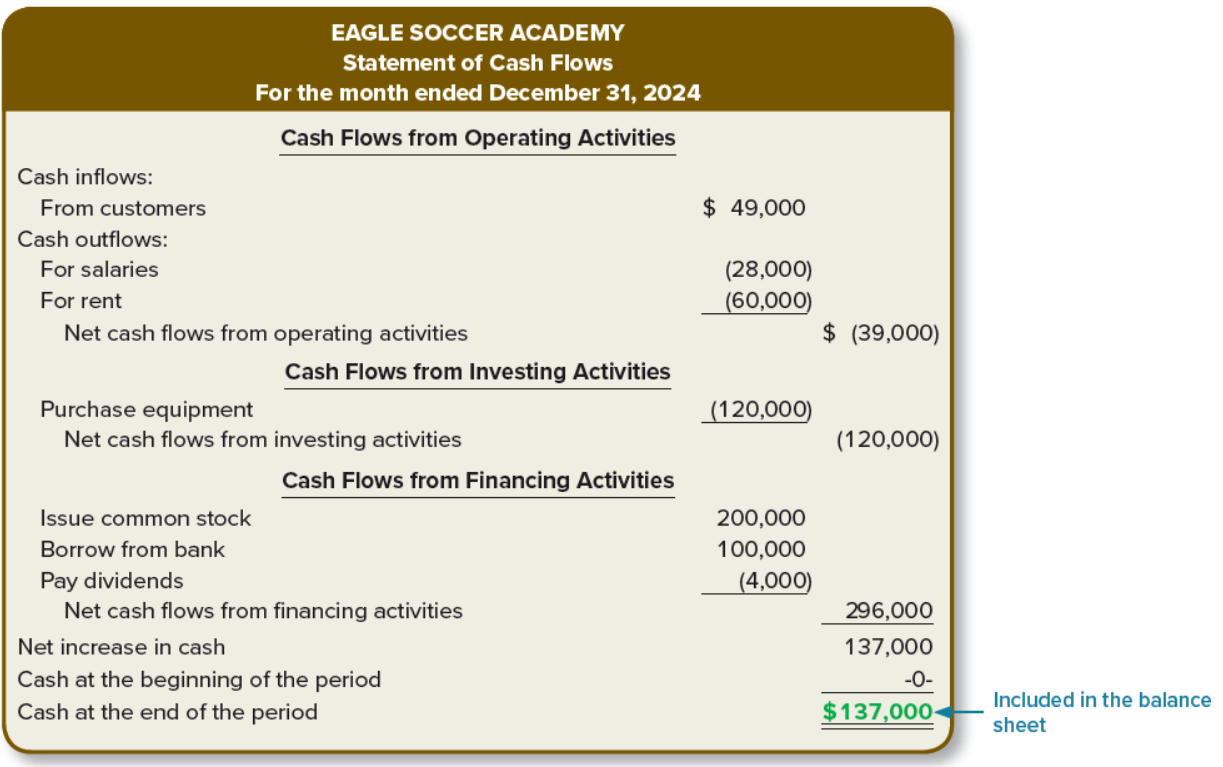
Statement of Cash Flows
measures activities involving cash receipts and cash payments over an interval of time
Operating Cash Flows: cash transactions involving revenue and expense activities (Ex: cash inflows (customers), cash outflows (for salaries, for rent))
Investing Cash Flows: cash transactions for the purchase and sale of investments and long-term assets (purchase equipment)
Financing Cash Flows: cash transactions with lenders and stockholders (issue common stock, borrow from bank, pay dividends,
Reports cash at beginning and end of period, and net increase
Any transaction that affects the income statement ultimately affects the balance sheet through _______ _______.
retained earnings
Change in Cash Formula
operating cash flows + investing cash flows + financing cash flows
Annual Reports
formal document that details a company’s activities and financial performance
Management Discussion and Analysis
includes management’s views on significant events, trends, and uncertainties pertaining to the company’s operations and resources
Note Disclosures
offer additional info either to explain the info presented in the financial statements or to provide info not included in the financial statements
No other single piece of company information better explains companies’ stock price performance that does financial accounting ________ ________.
net income
Company’s _____ ______ is an important indicator of management’s ability to respond to business situations and the possibility of bankruptcy
debt level
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
the rules of financial accounting
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
an independent, private-sector body with full-time voting members and a very large support staff that establishes financial accounting and reporting standards in the U.S.
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
standard-setting body responsible for eliminating differences in accounting standards around the world
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
government agency that requires companies that publicly trade their stock to prepare periodic financial statements for distribution to investors and creditors
Primary responsible for setting accounting standards to the private sector
Auditors
hired by the company as an independent party to express a professional opinion of the extent to which financial statements are reported in compliance with GAAP and are free of material misstatement
Play a major role in investors’ and creditor's’ decisions by adding credibility to a company’s financial statements
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB)
ensures that auditors follow a strict set of guidelines when conducting their audits of public companies’ financial statements
Sabanes-Oxley Act (SOA)
provides for the regulation of auditors and the types of services they furnish to clients, increases accountability of corporate executives, addresses conflicts of interest for securities analysts, and provides for stiff criminal penalties for violators
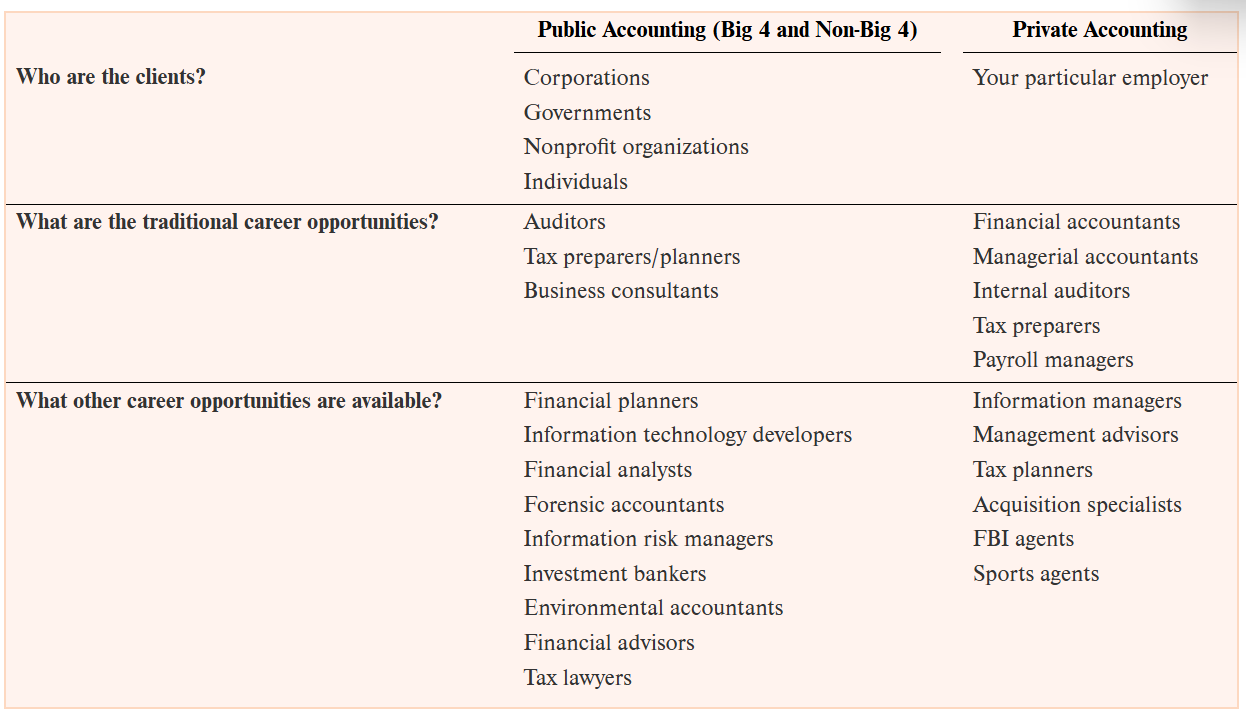
Public and Private Accounting
public: professional service firms that traditionally have focused on three areas (auditing, tax preparation/planning, business consulting)
private: providing accounting services to the company that employs you
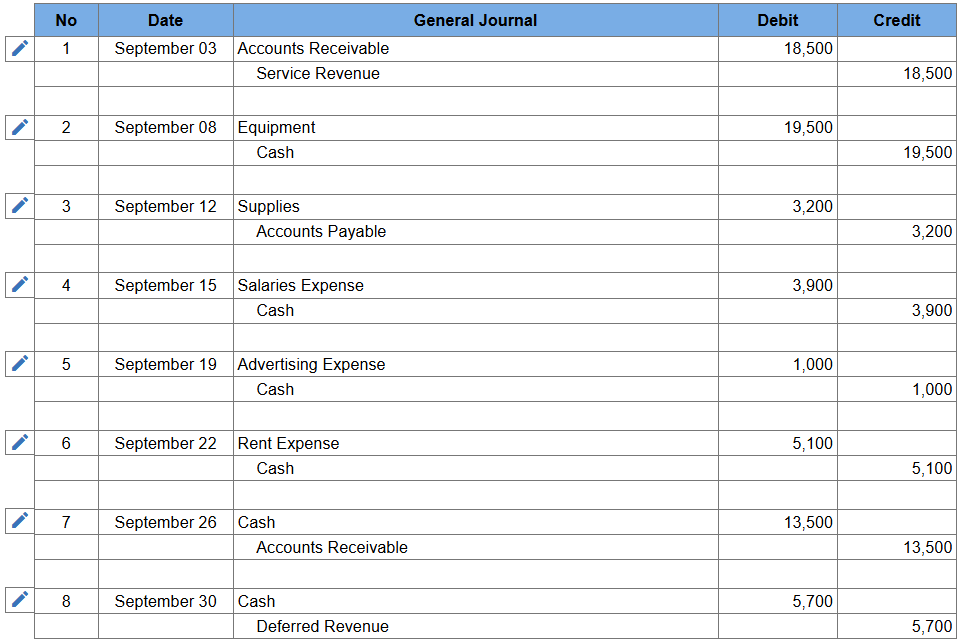
External Transactions
transactions conducted between the company and a separate entity
Steps in Measuring External Transactions
Use source documents to identify accounts affected by an external transaction
Analyze the impact of the transaction on the accounting equation
Assess whether the transaction results in a debit or credit to account balances
Record the transaction in a journal using debits and credits
Post the transaction to the general ledger
Prepare a total balance
Account
record of all transactions related to a particular item over a period of time
Chart of Accounts
list of all account names used to record transactions

Debits
increases in assets, decreases in liabilities and stockholders’ equity
Credits
decreases in assets, increases in liabilities and stockholders’ equity
What type of balance is retained earnings
Normally has a credit balance
Three components: revenue (increases by credits), expenses (increases by debits), and dividends (increases by debits)
Net income increases the balance of retained earnings, dividends vice versa
General Ledger
provides, in a single collection, each account with its individual transactions and resulting account balance
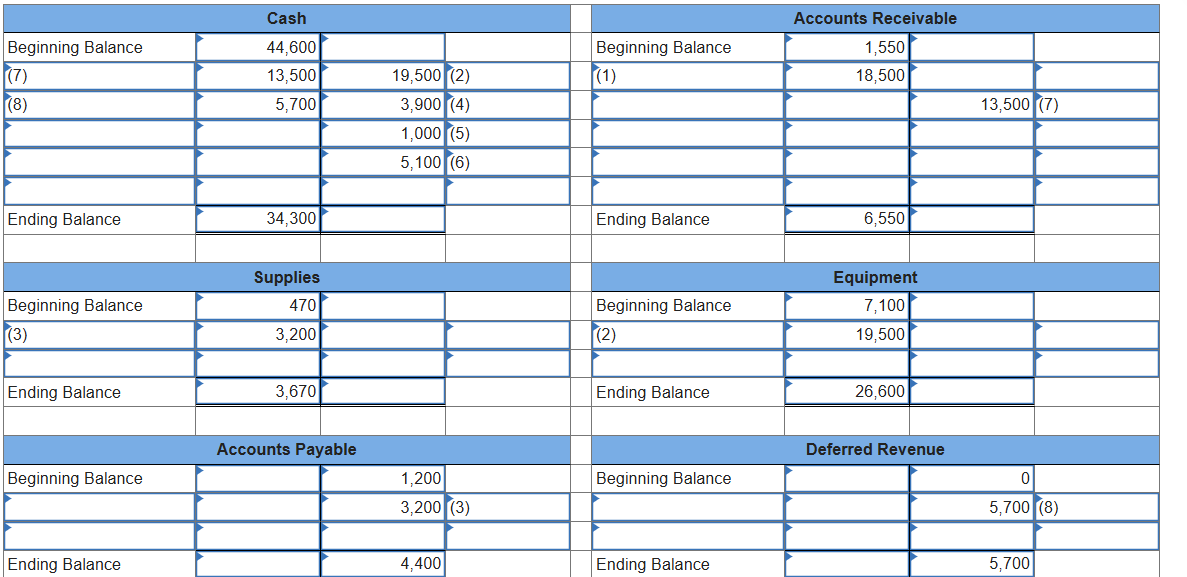
Posting
the process of transferring the debit and credit information from the journal to individual general ledger accounts
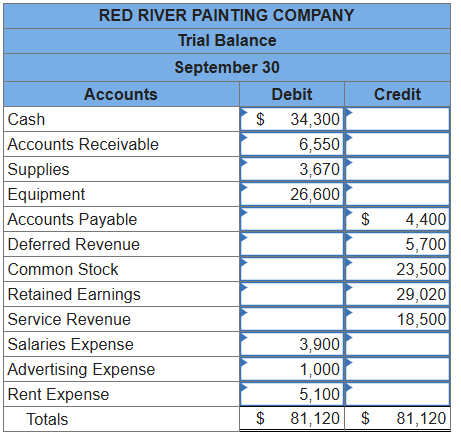
Trial Balance
a list of all accounts and their balances at a particular date, showing that total debts equal total creditsR
Revenue Recognition Principle
companies record revenue at the time goods are provided to customers
Journal
a chronological record of all economic events affecting a firm