Introduction to Amino Acids - lecture 9
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Biochemistry
the scientific discipline that seeks to explain life at the molecular level
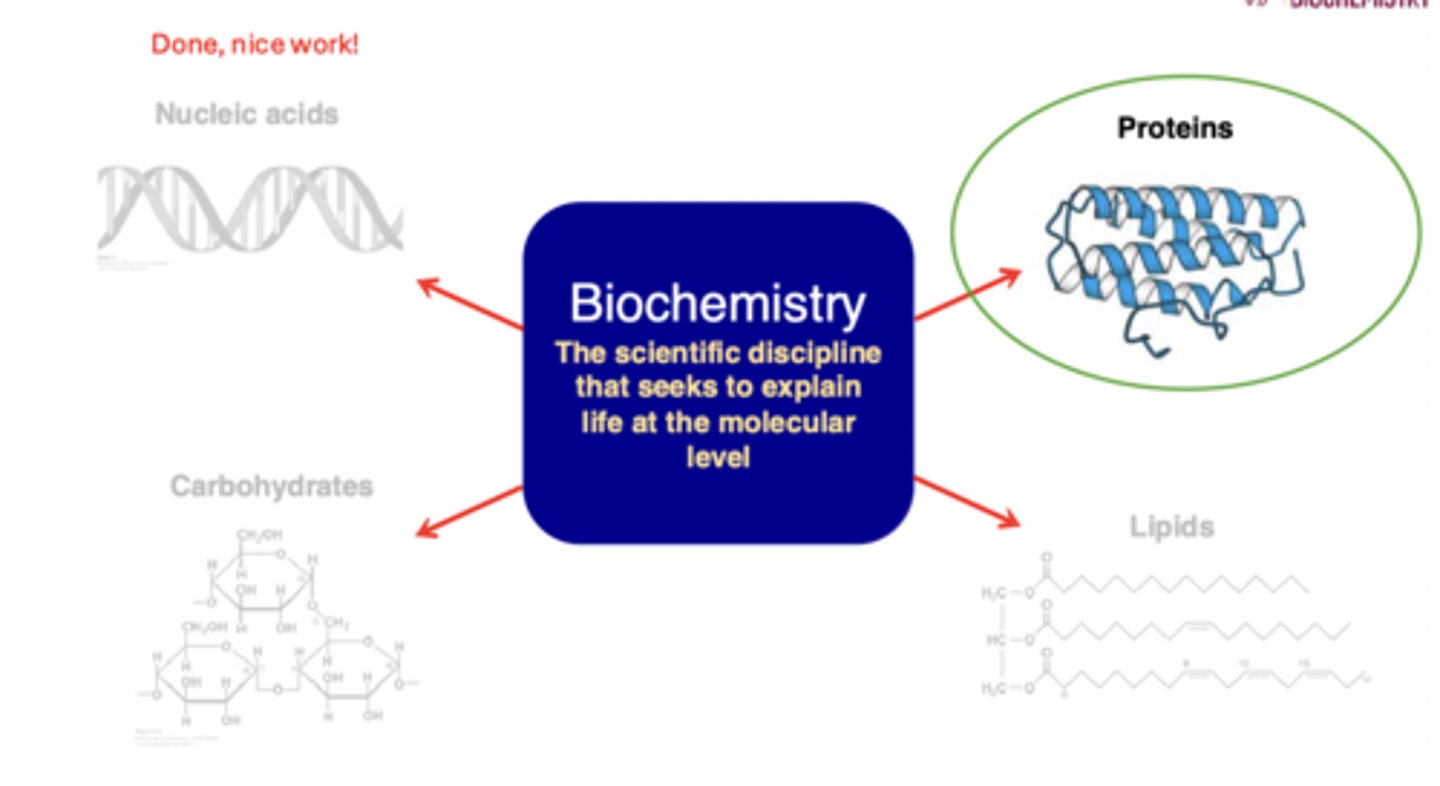
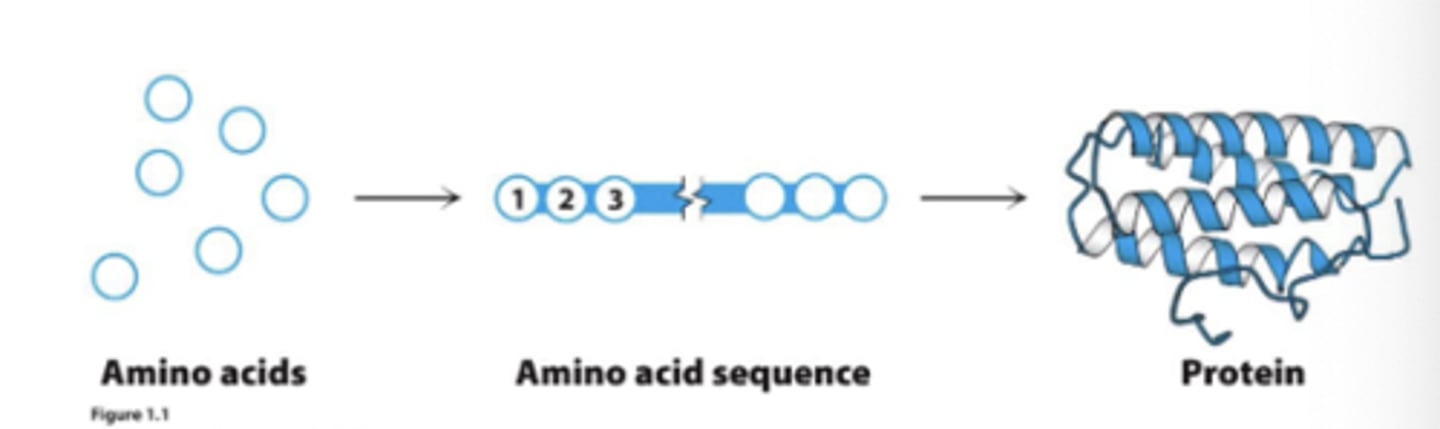
Proteins
are true polymers comprised of amino acids (_______ monomers)
3D structure
water solubility of proteins depends on this
physical properties
amino acids within proteins differ in ________ properties, like polarity
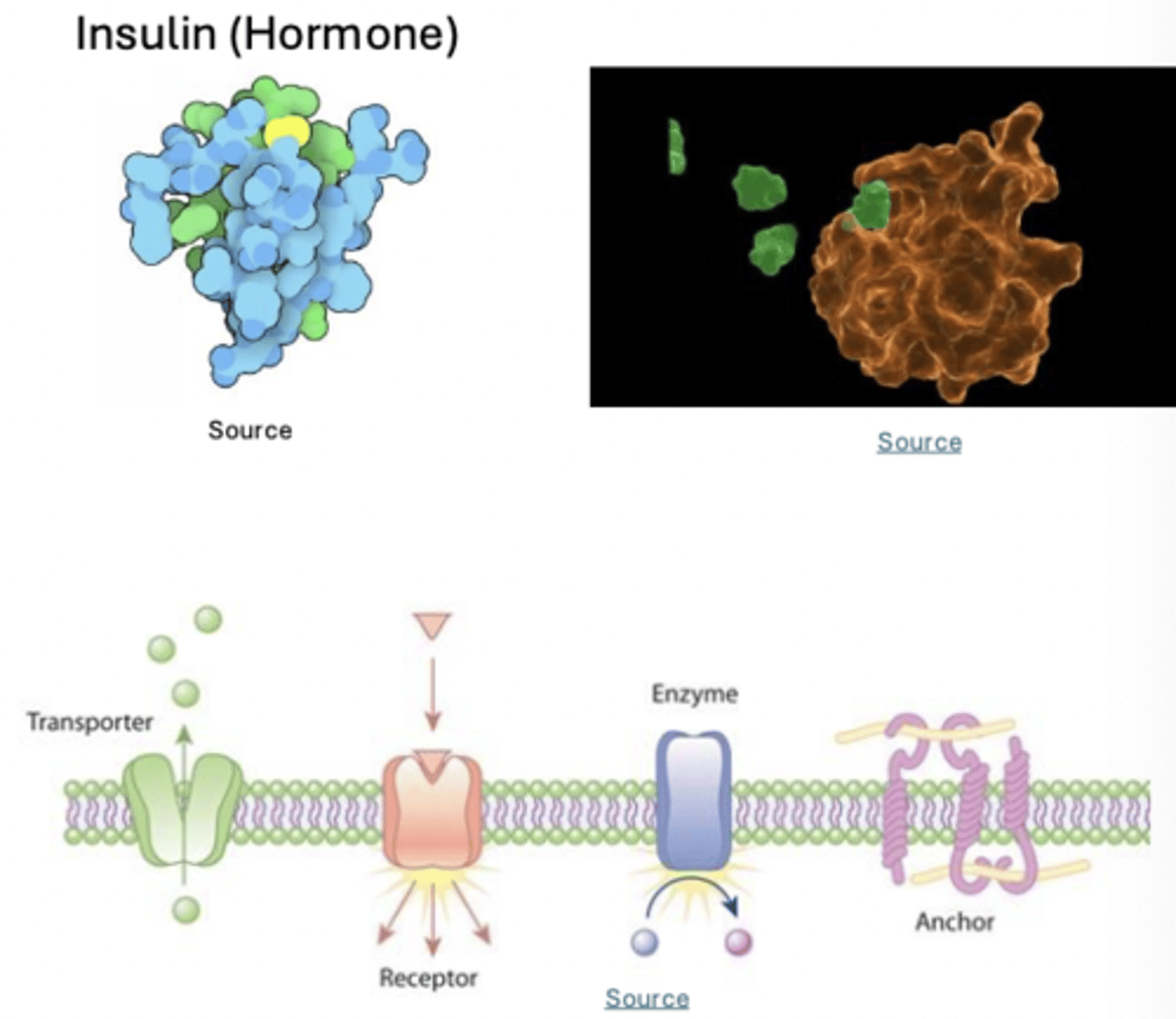
enzymes, histones and peptide derived hormones
water soluble components of proteins
collagen and lamina (within nuclear membrane)
water insoluble components of proteins
lipids (proteolipids) or carbohydrates (glycoproteins)
things proteins may be attached to
Proteins have a variety of biochemical roles
serve as signaling molecules, transporters and receptors
Serve as enzyme catalysts; enhancing rate of chemical reactions
Maintain cell shape/provide structural support
General structure of amino acid in neutral pH
Central atom (α carbon) atom
primary / α carboxyl group (COO-)
primary / α amine group (NH3+)
Hydrogen atom (H)
Side chain (R)
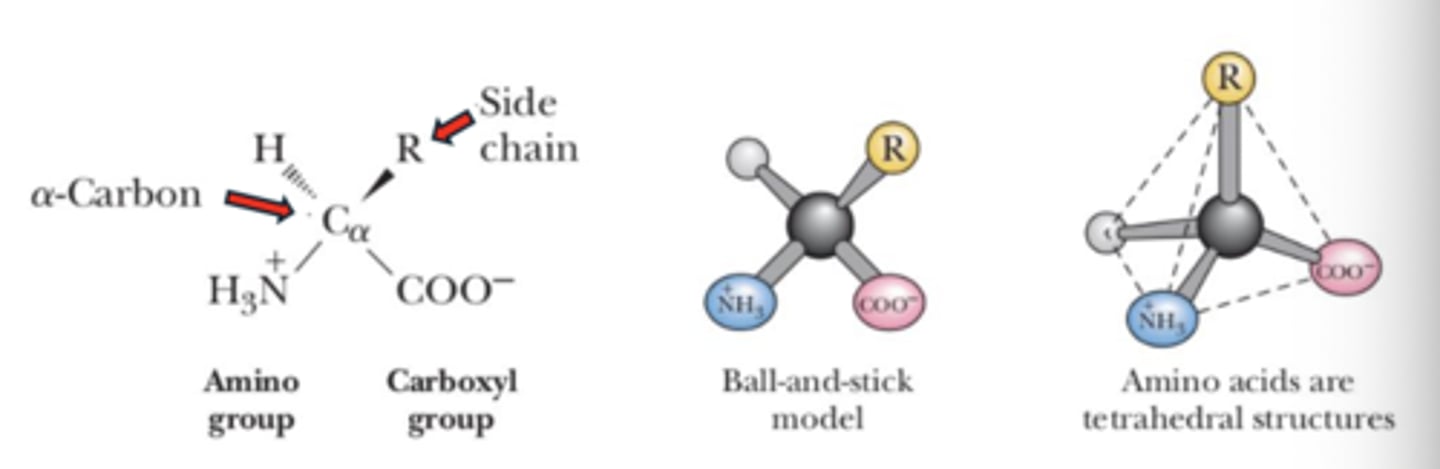
Tetrahedral structure
what shaped molecule an amino acid is
carboxyl and amine
at neutral pH these protein structures are ionizable groups
- can gain or lose electrons, which alters charge of free amino acid
20 standard proteinogenic amino acids
these amino acids differ by side chain, whether humans can synthesize, etc.
3 letter code
1 letter code
how each amino acid can be abbreviated
Glycine
abbreviation is Fly or G
chemical characteristics
what classification and categorization of amino acids relies on
Group 1
hydrophobic amino acids
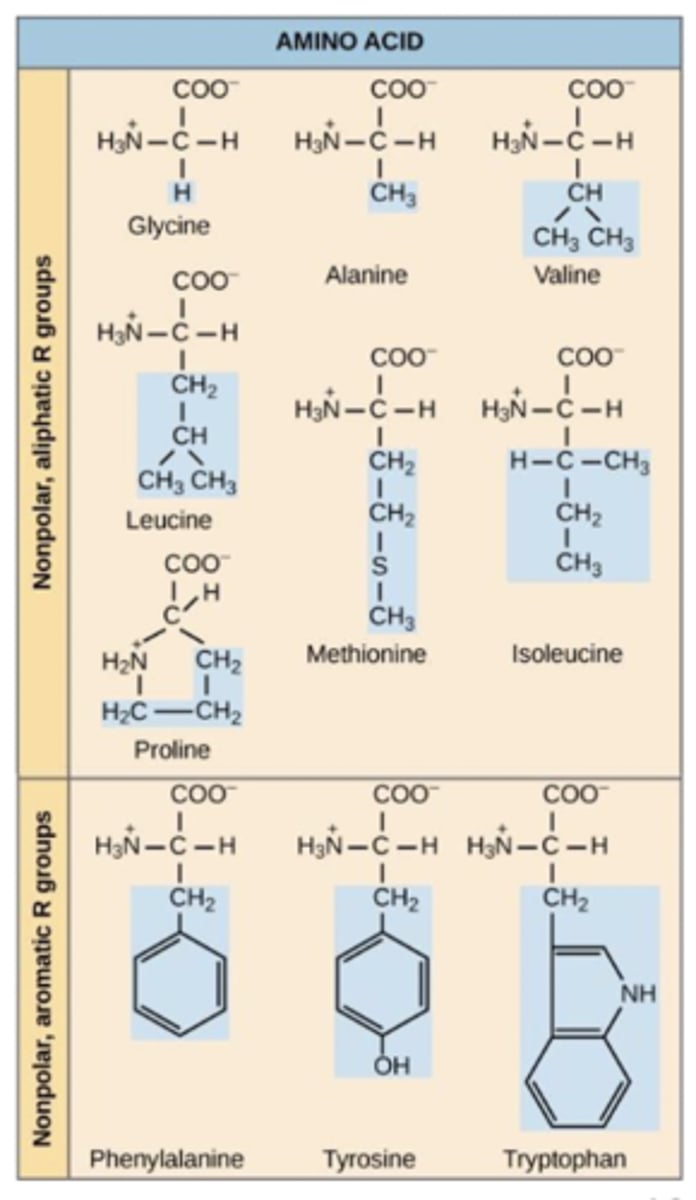
hydrophobic amino acids
have non polar R groups that mainly consist of hydrocarbon side chains
differ in length of side chains; may have aromatic side chains (like phenylalanine)
group with most members (10 our of 20)
hydrophobic amino acid charge
overall neutral charge at physiological pH (approximately 7.4)
Group 2
polar amino acids
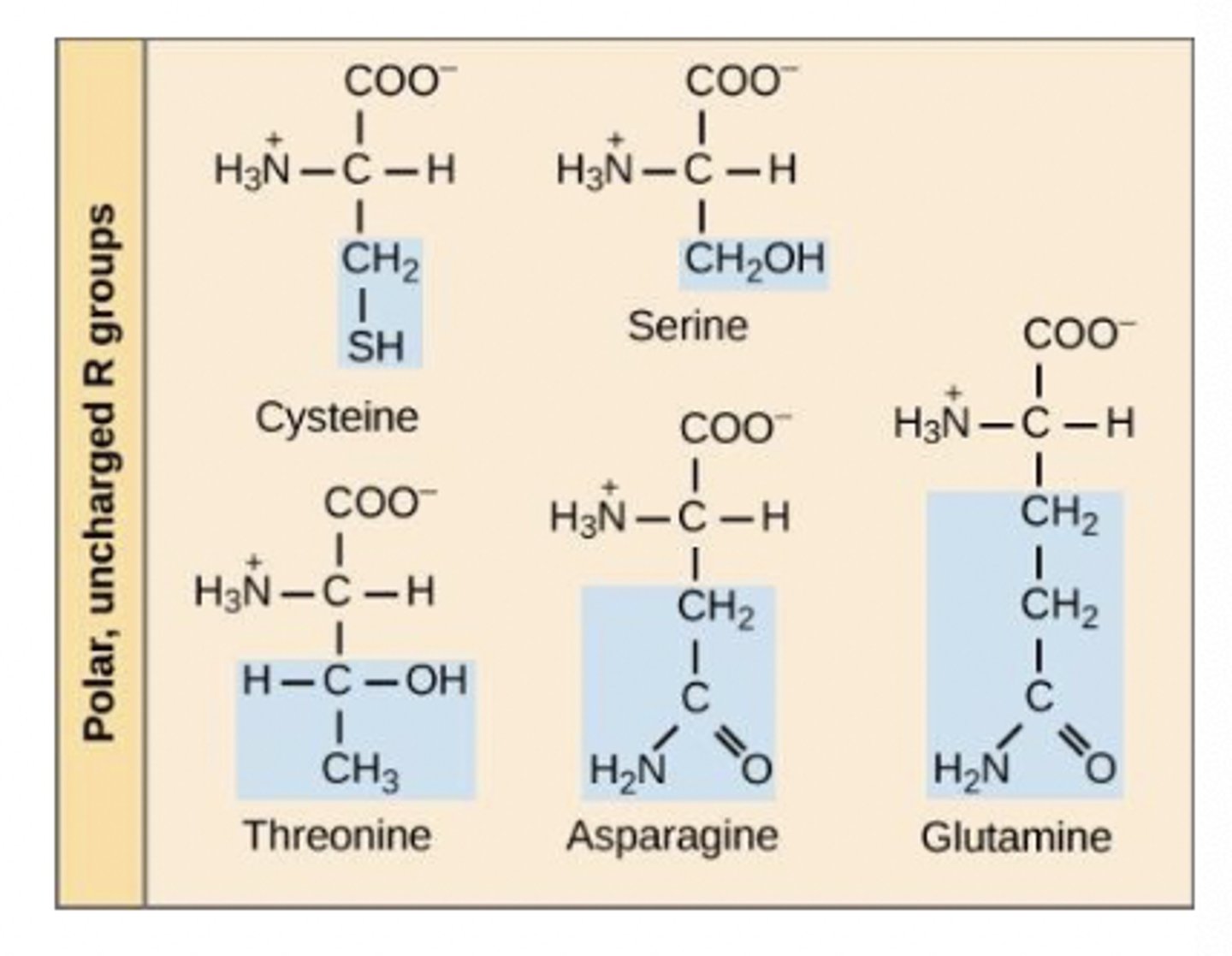
polar amino acids
have polar R groups as electron distribution uneven; overall neutral charge
some (i.e. serine, threonine and tyrosine) can be phosphorylated - a post-translational modification
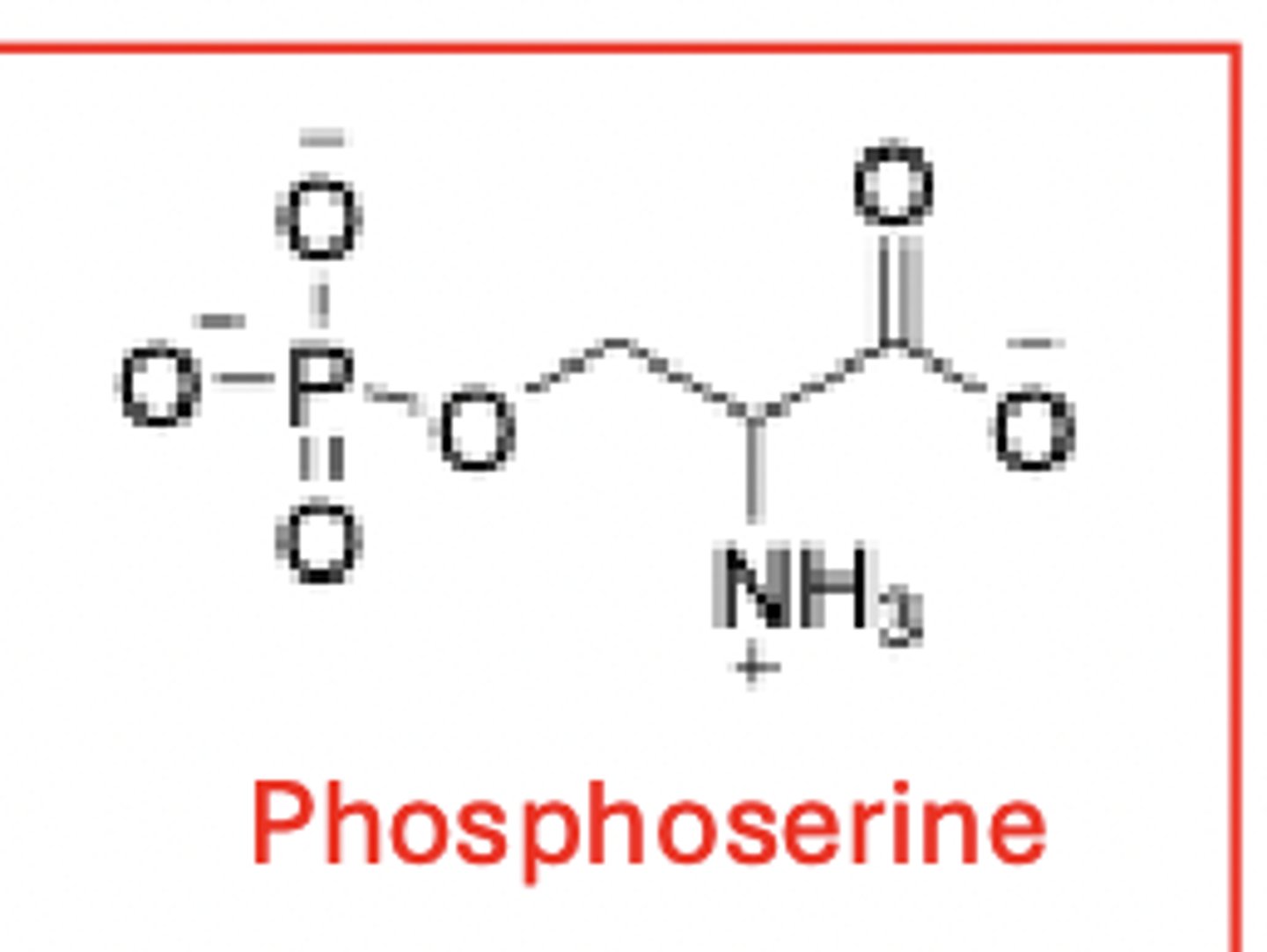
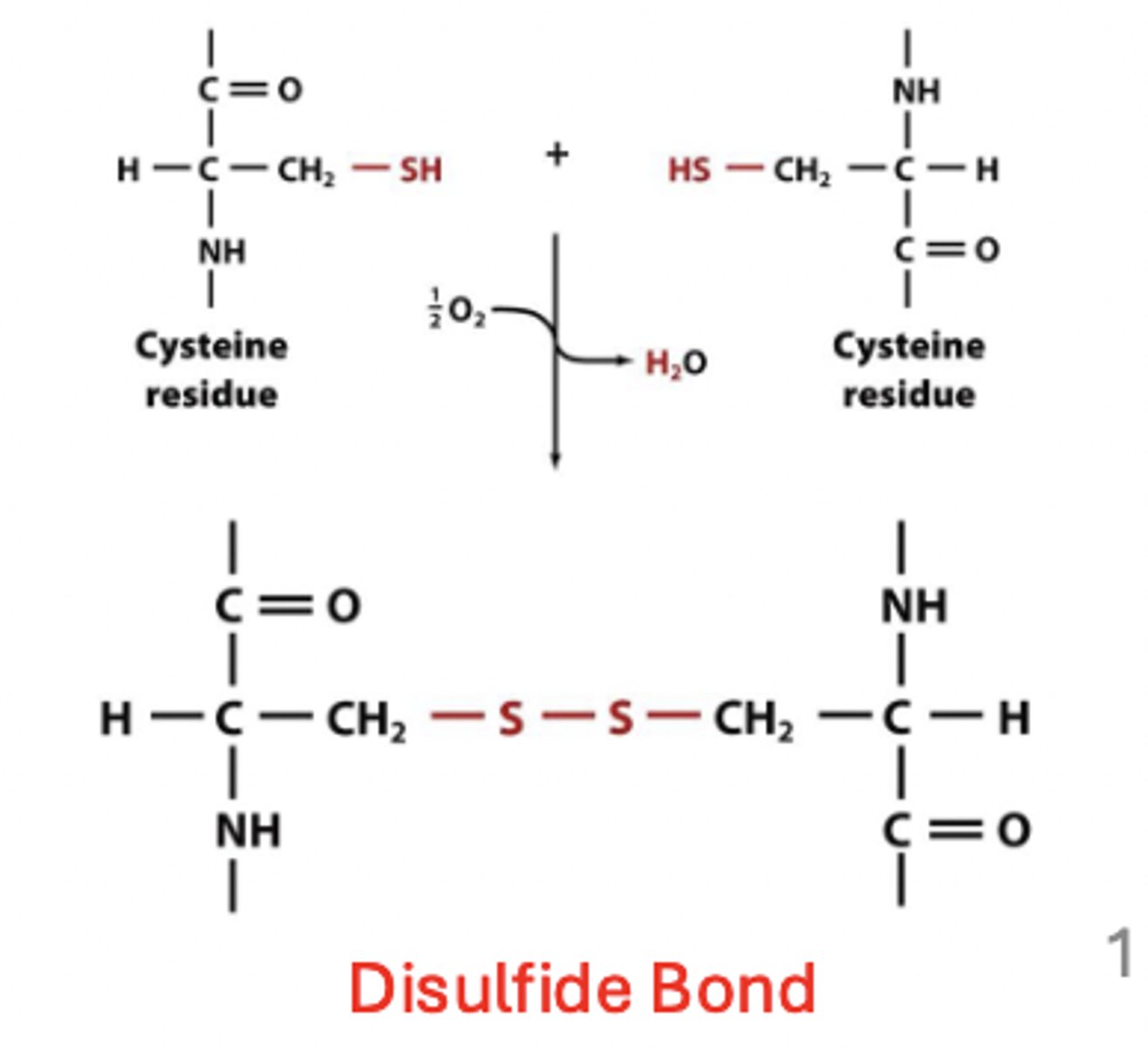
polar amino acids - cytosines thiol (SH) group
this group can form covalent disulfide bonds, which help stabilize protein structure
Groups 3 & 4
charged amino acids
charged amino acids
hydrophilic with R groups that retain a charge at physiological pH
- often involved in protein ion channels
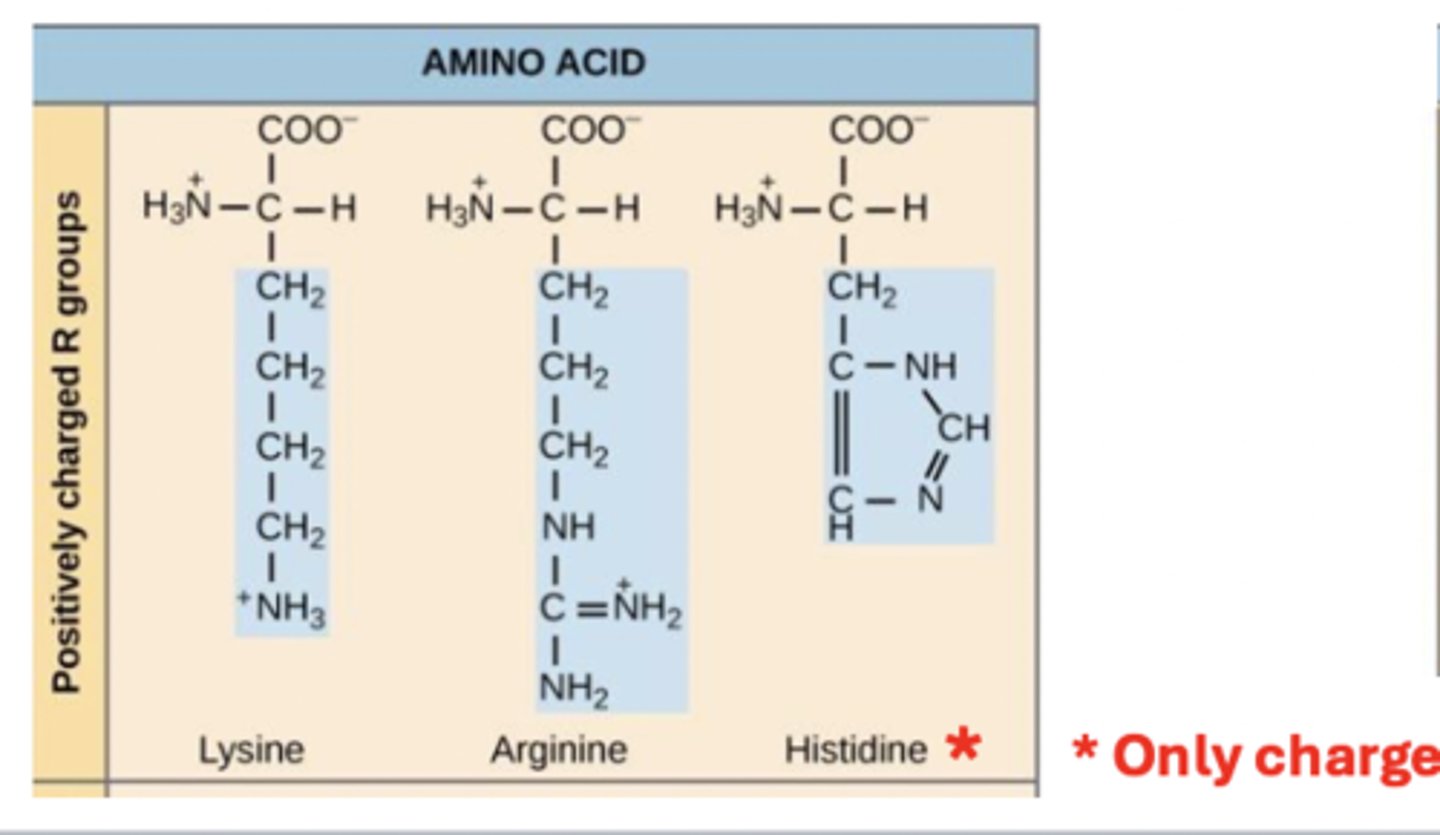
charged amino acids group 3
positively charged (basic)
side chain contains amine group
*Histone only charged when pH is ~6.1 or below
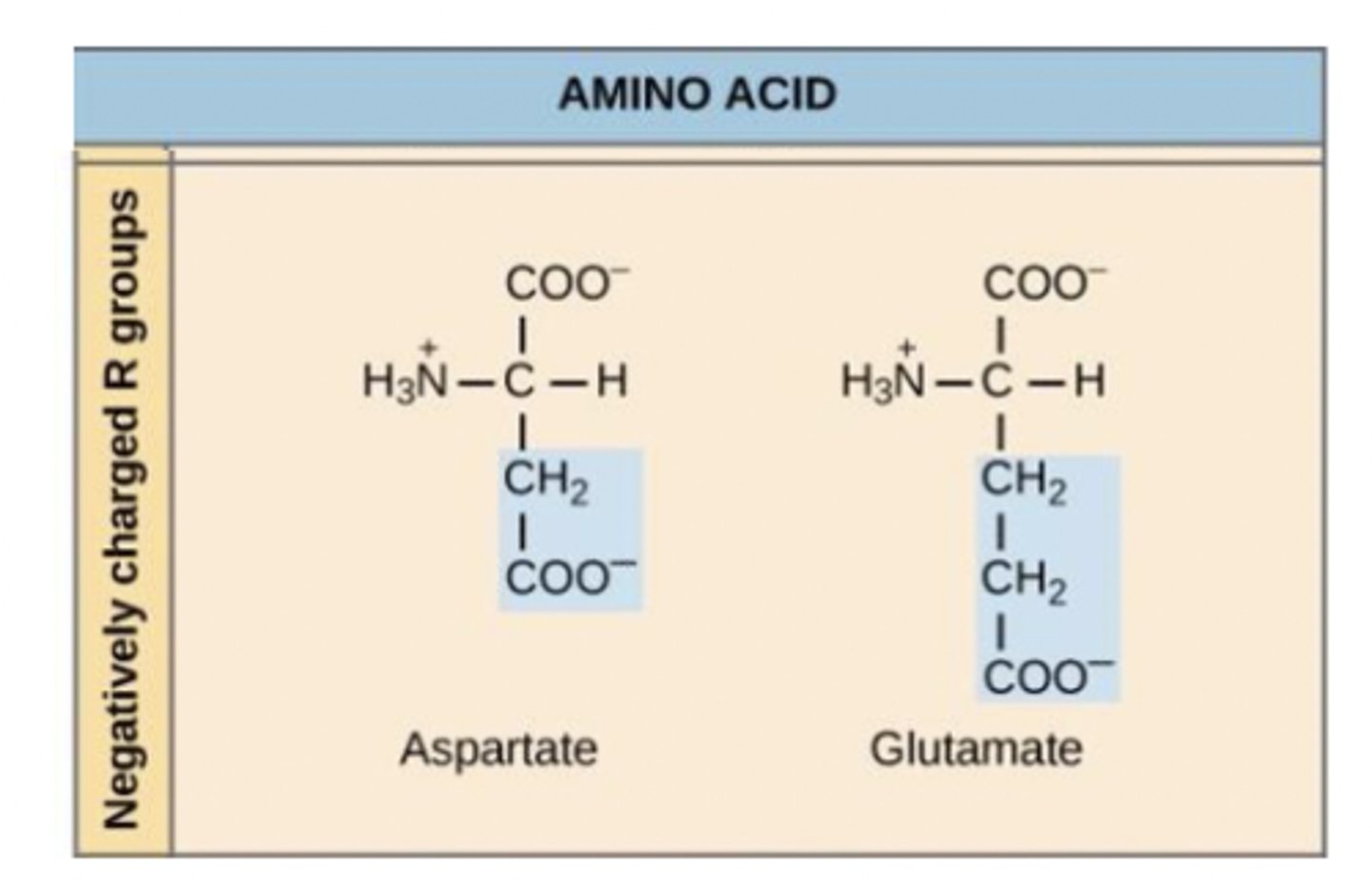
charged amino acids group 4
negatively charged (acidic)
side chain contains carboxyl group
Ionic form of amino acids - acid-base behavior of glycine
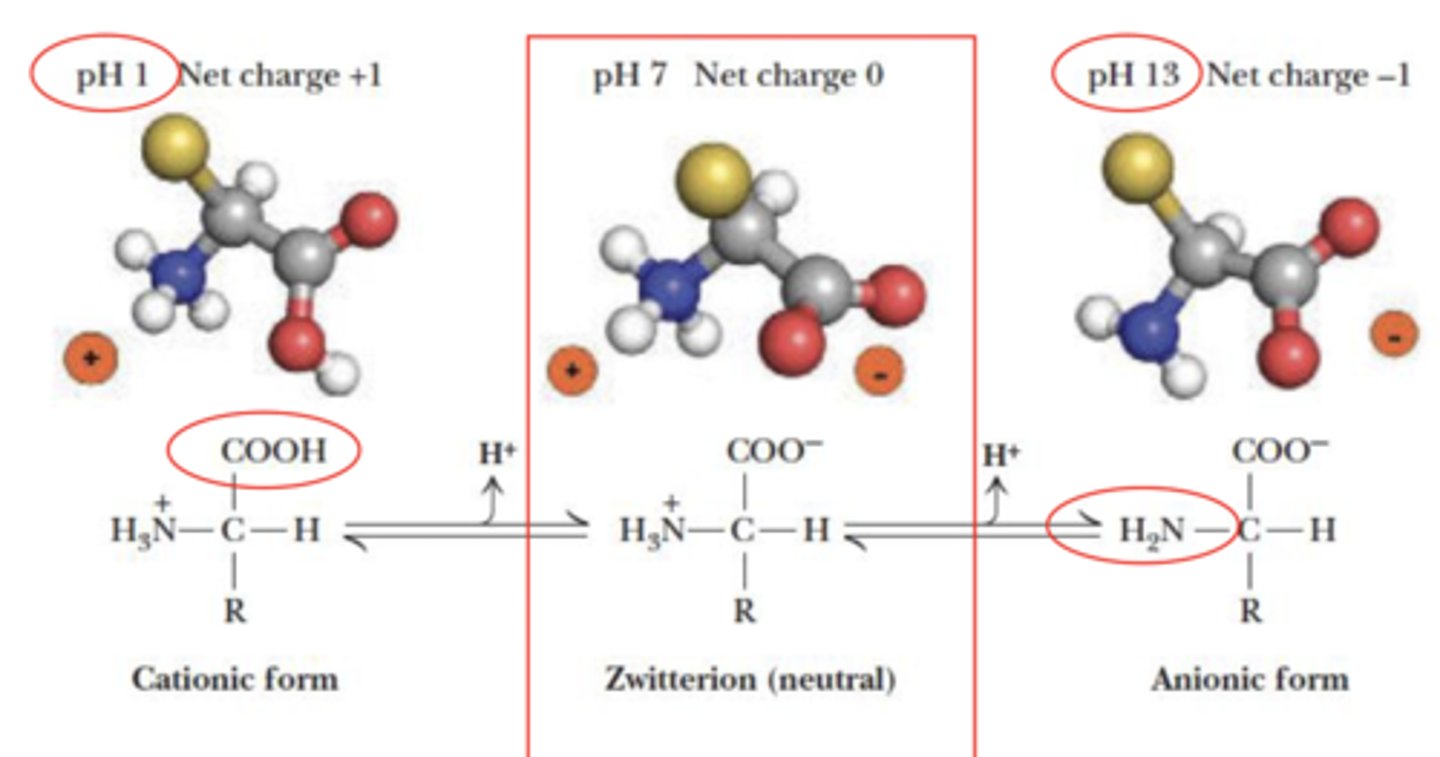
Why do charge states of amino acids change?
pKa values of the ionizable groups (α-COOH, α-NH3+ and R group)
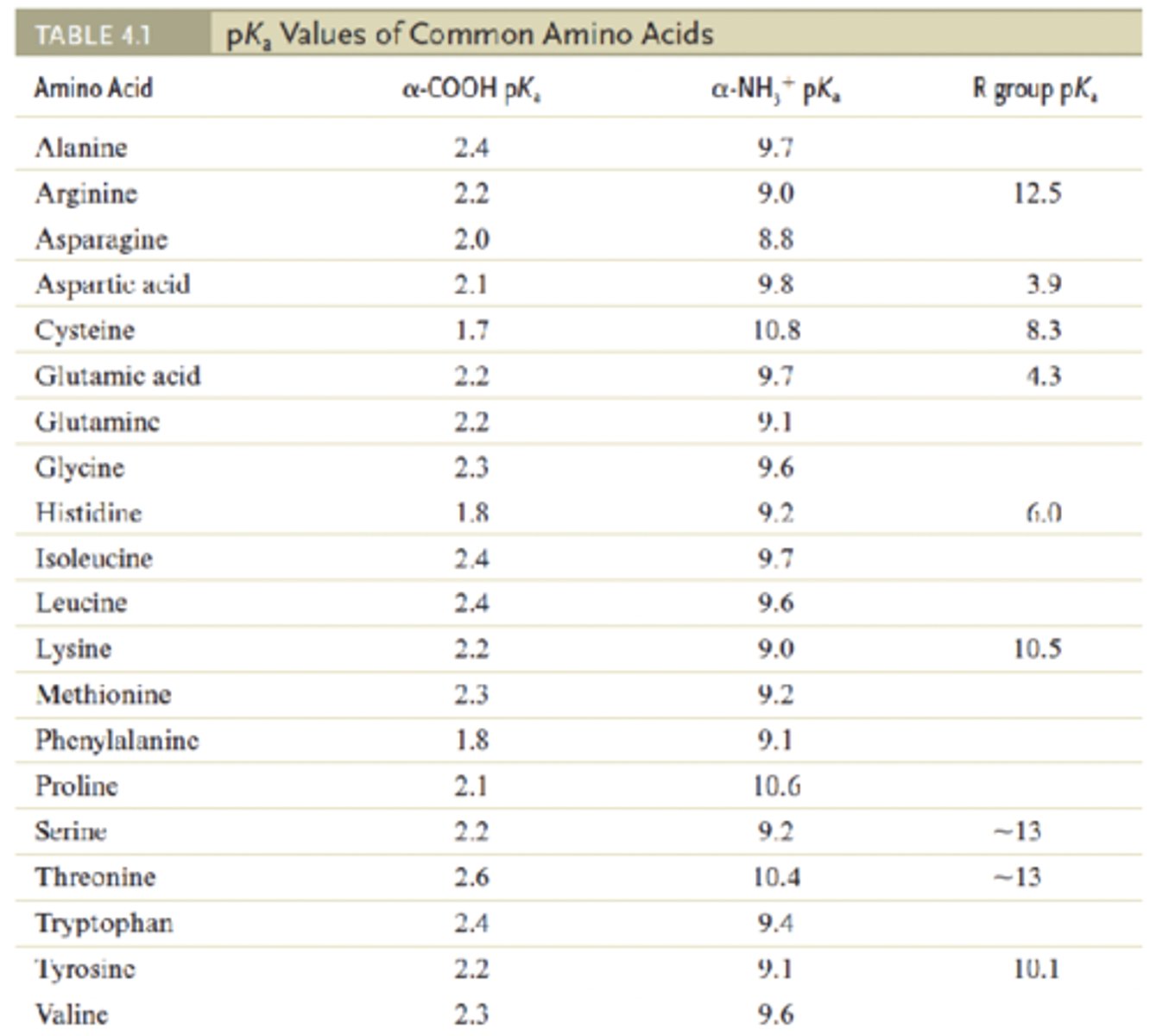
pKa
negative base-10 logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of a solution
lower pKa = stronger acid
lower pKa = (stronger or weaker) the acid
Ka equation
__ = 10^-pKa
pKa equation
___ = -logKa
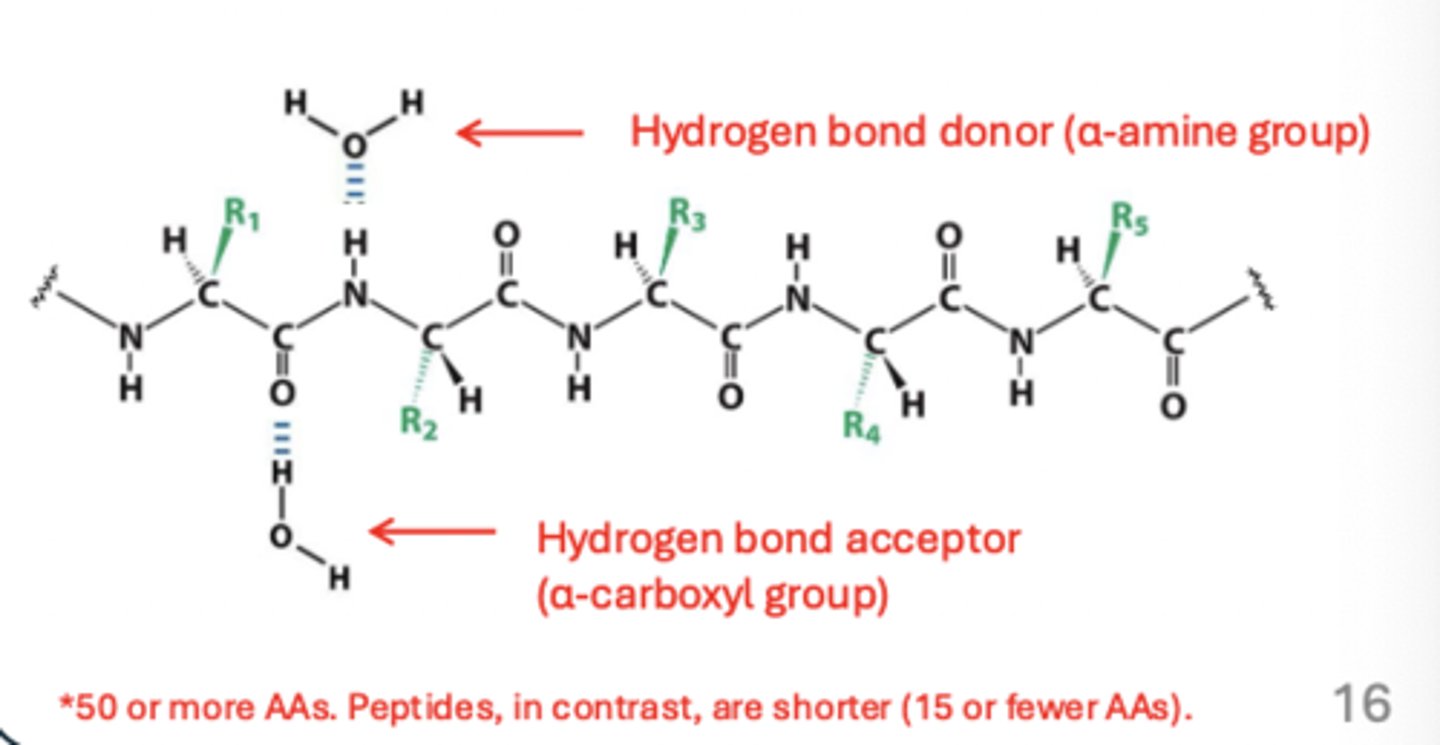
How are amino acids connected to one another
linked by covalent peptide bond between the carboxyl group and amino group, formed in condensation reaction by a ribosome
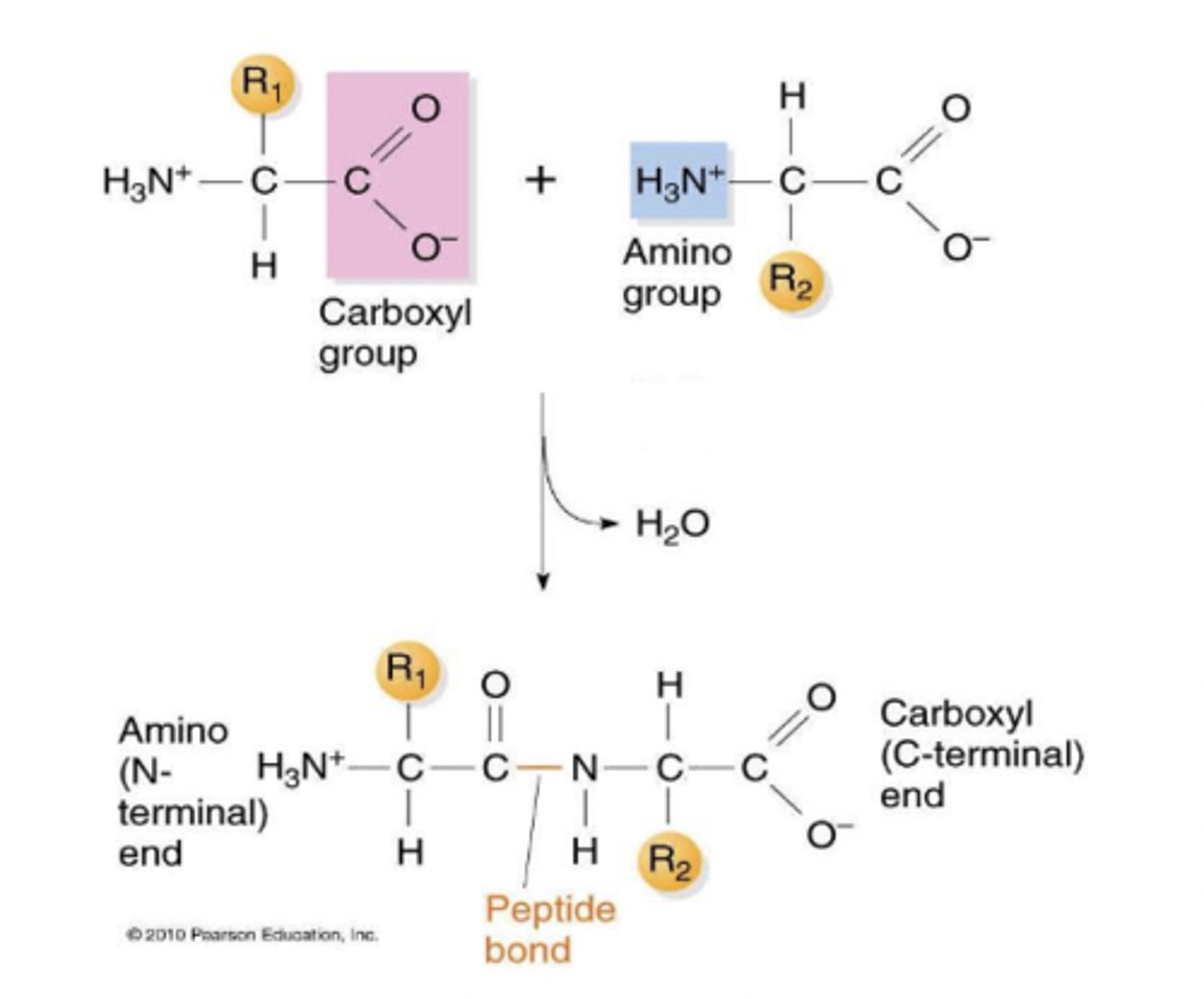
polypeptide
longliner chain made of many amino acids
amino acid residues
name for amino acids within a molecule
Directionality of a polypeptide chain
Beginning: α-amine group (N-terminus)
End: α-carboxyl group (C-terminus)
Groups of proteins based on shape
Fibrous (simple shaped)
Globular (complex shape)
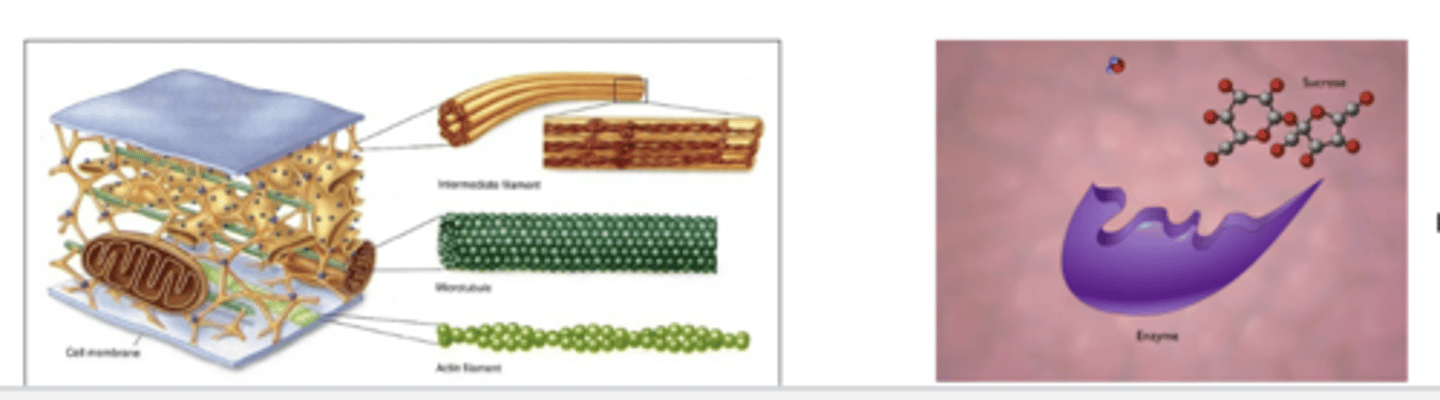

Fibrous proteins
have structural roles and assist with spatial organization
- form sytoskeleton in a cell or anchoring junctions between cells
Globular proteins
have functional or chemical roles
- serve as enzymes, signaling moleciles, transporters and receptors
Proteins based on compositions
Simple (only amino acids)
Conjugated (have non-protein portion)

SImple proteins
include albumin (transports fatty acids) and histones
- (involved in DNA compaction)
Conjugated proteins
include glycoproteins, chromoproteins (hemoglobin, chlorophyll, etc.) and phosphoproteins (tooth dentin , milk casein, etc.)
Hydrophobic effect
drives protein folding