1st Law of Thermodynamics
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Thermodynamic system
Part of the physical universe with a specified boundary for observation

Open system
Can exchange heat and matter

Closed system
Can only exchange heat
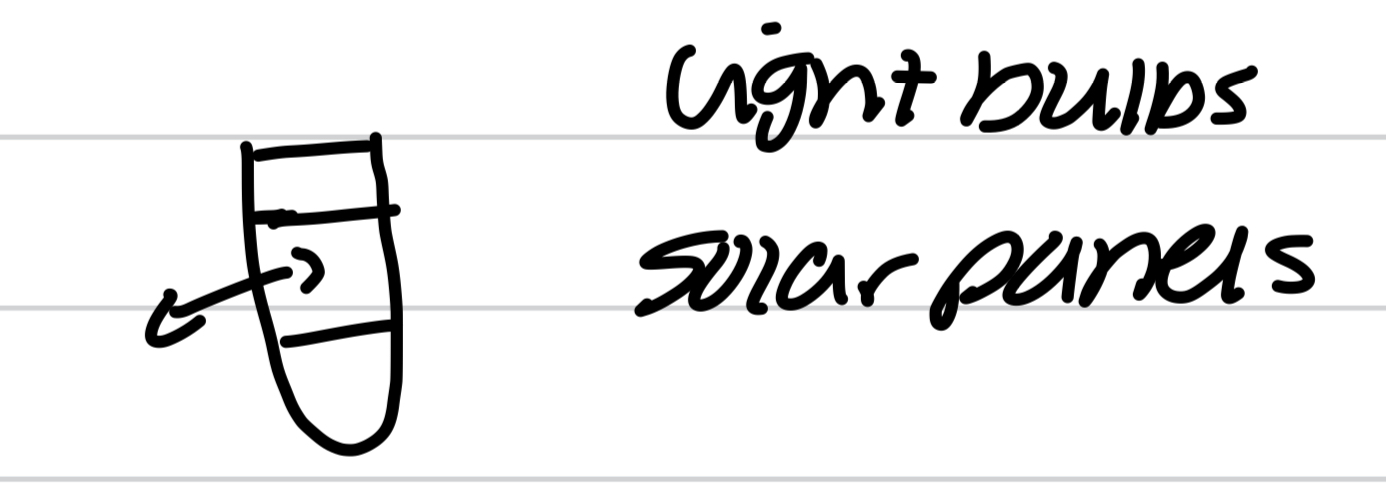
Isolated system
Can’t exchange heat or matter

Isothermal change
Temperature of the system stays the same as the surroundings
Only closed system
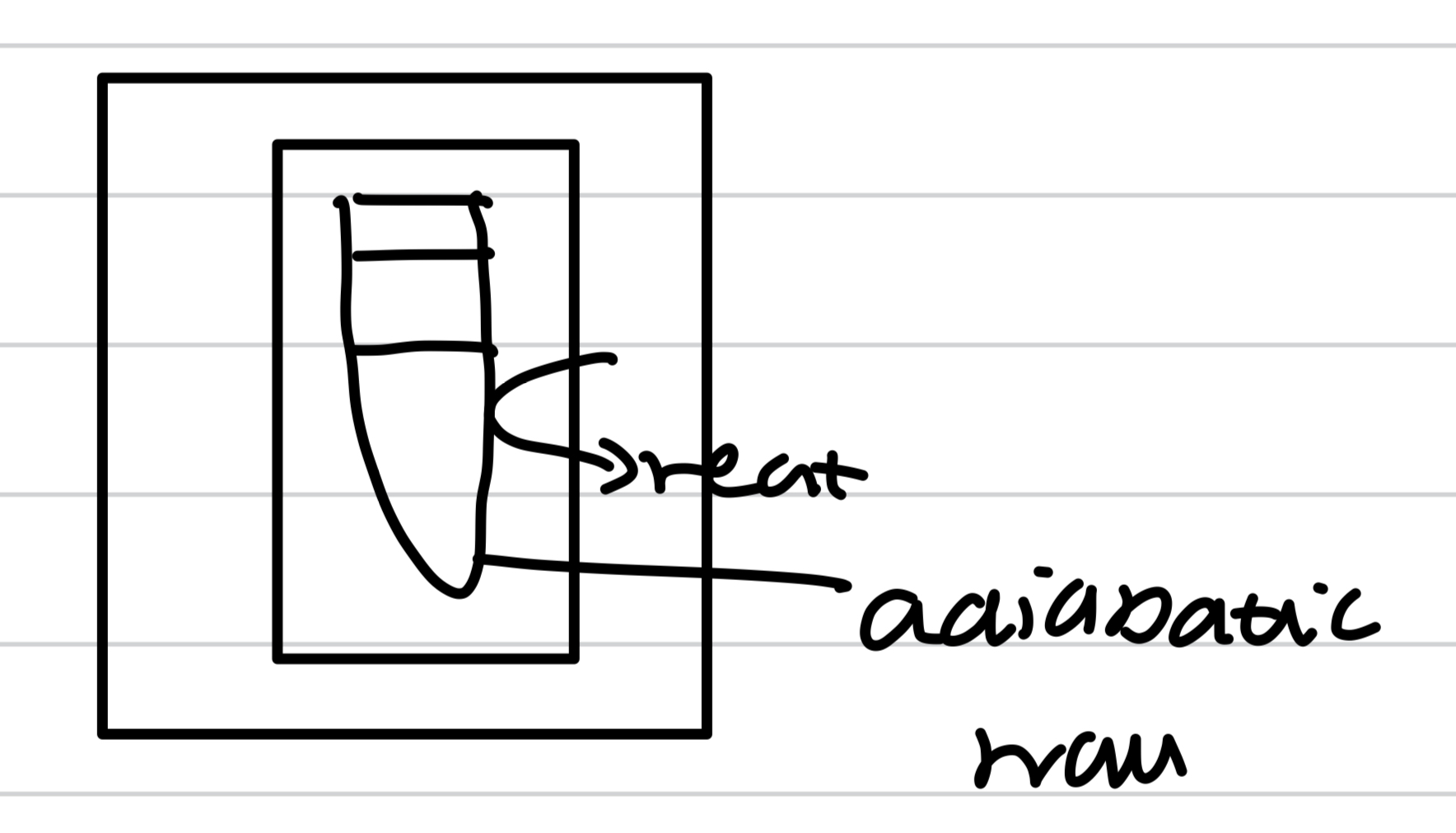
Diathermal wall
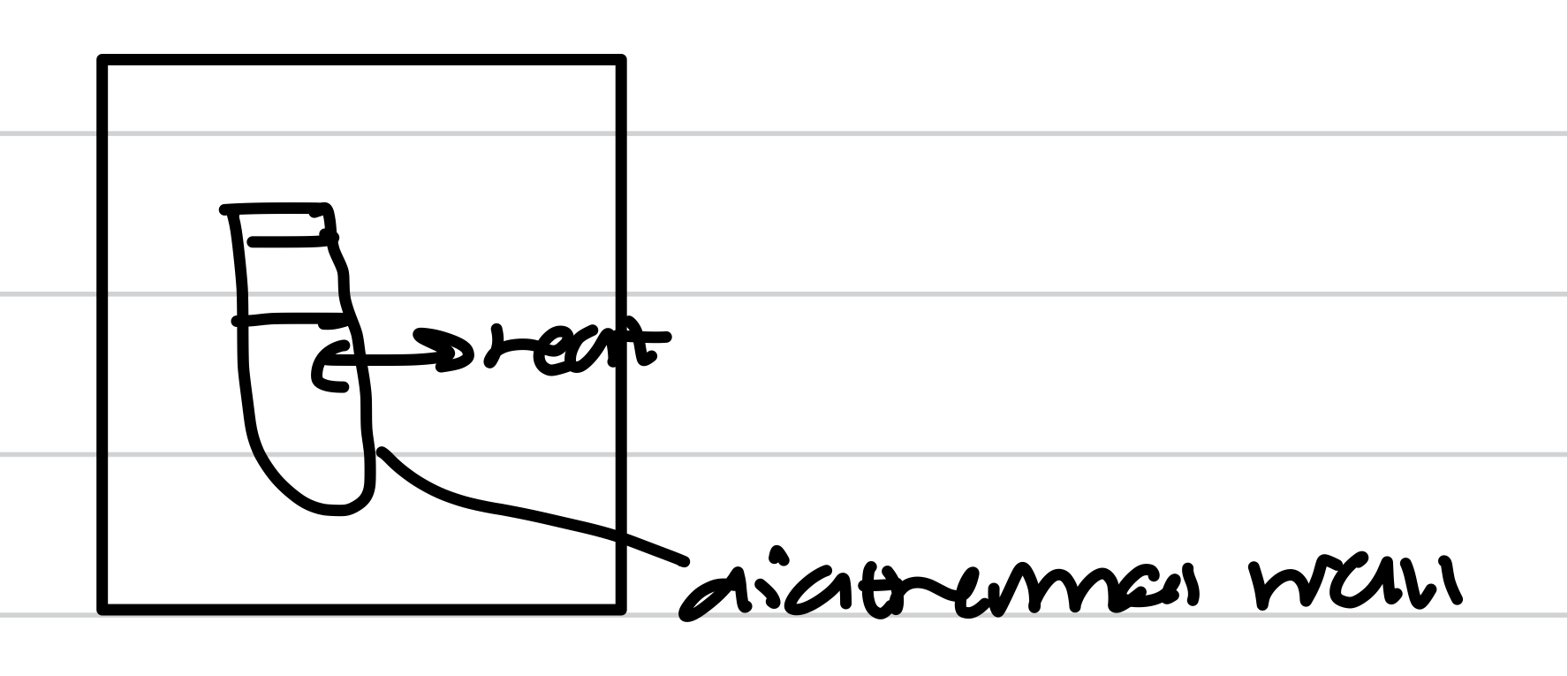
Adiabatic change
No heat exchange between the system and the surroundings
Only isolated system
Adiabatic wall
Earth
Closed system
Exchanging light and heat with the surroundings
Only have very minor exchange of matter
First Law of Thermodynamics
The law relates the internal energy, U, of a system to the amount of heat added to the system and the amount of work done on the system
Work
Work is done when a force is applied to an object and that causes that object to move a distance
Work = distance x opposing force
Opposing force
Mass x -gravity
Total internal energy, U
U of an isolated system is constant
ΔU = q+w
change in internal energy = heat added + work
Conservation of energy
The total internal energy of an isolated system is constant; energy can be transformed from one form to another but can be neither created or destroyed
Energy, E with units of Joules, J
Interconvert energy
Kinetic energy
Chemical energy
Nuclear energy
Heat, work and light
Applies to:
atoms and molecules
chemical bonds
photons and electrons
biology, engineering, Earth science
Work and heat
Energy can be exchanged between systems/surrounds as work, w or heat, q
U, w, q are key to thermodynamics
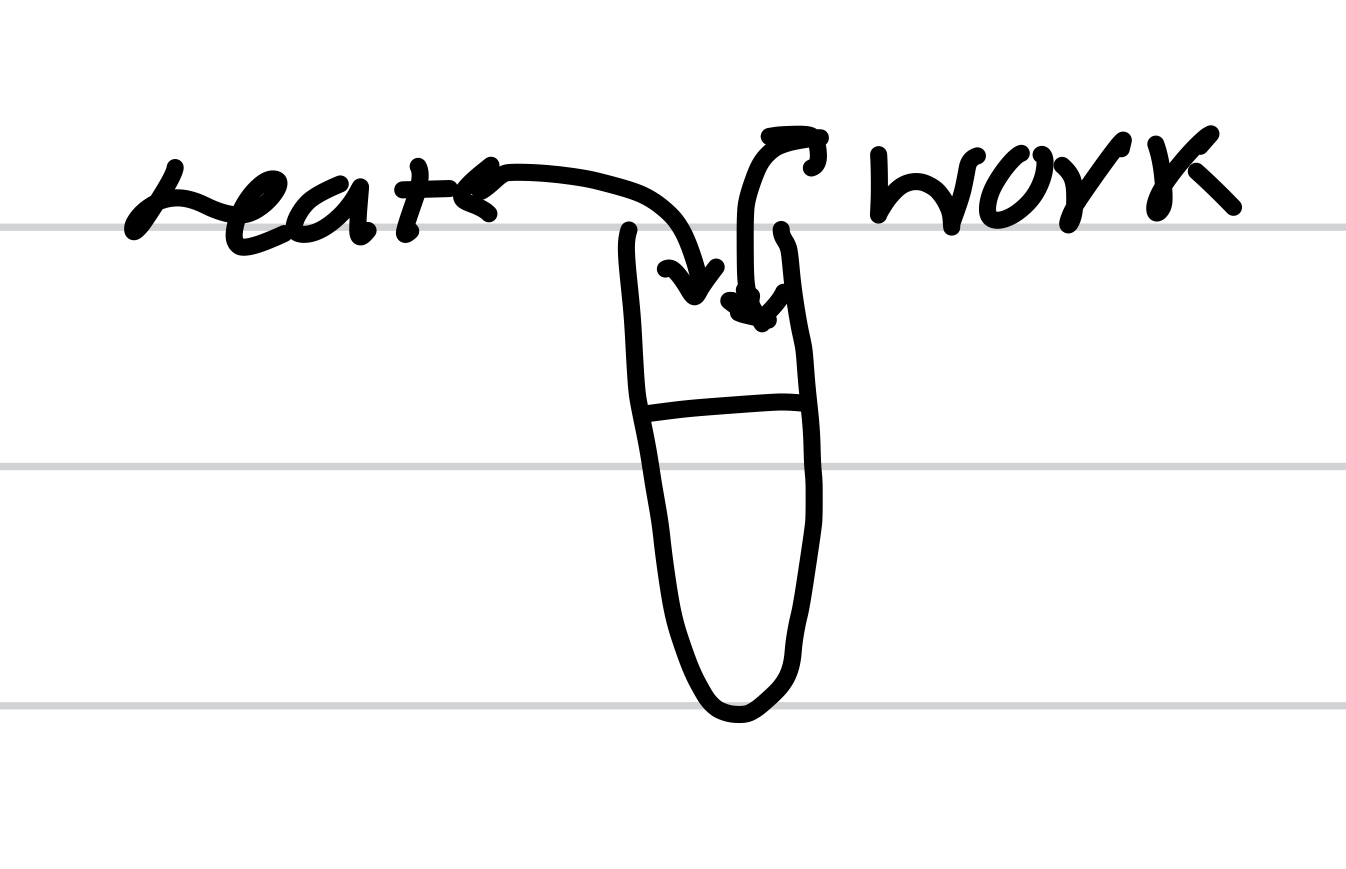

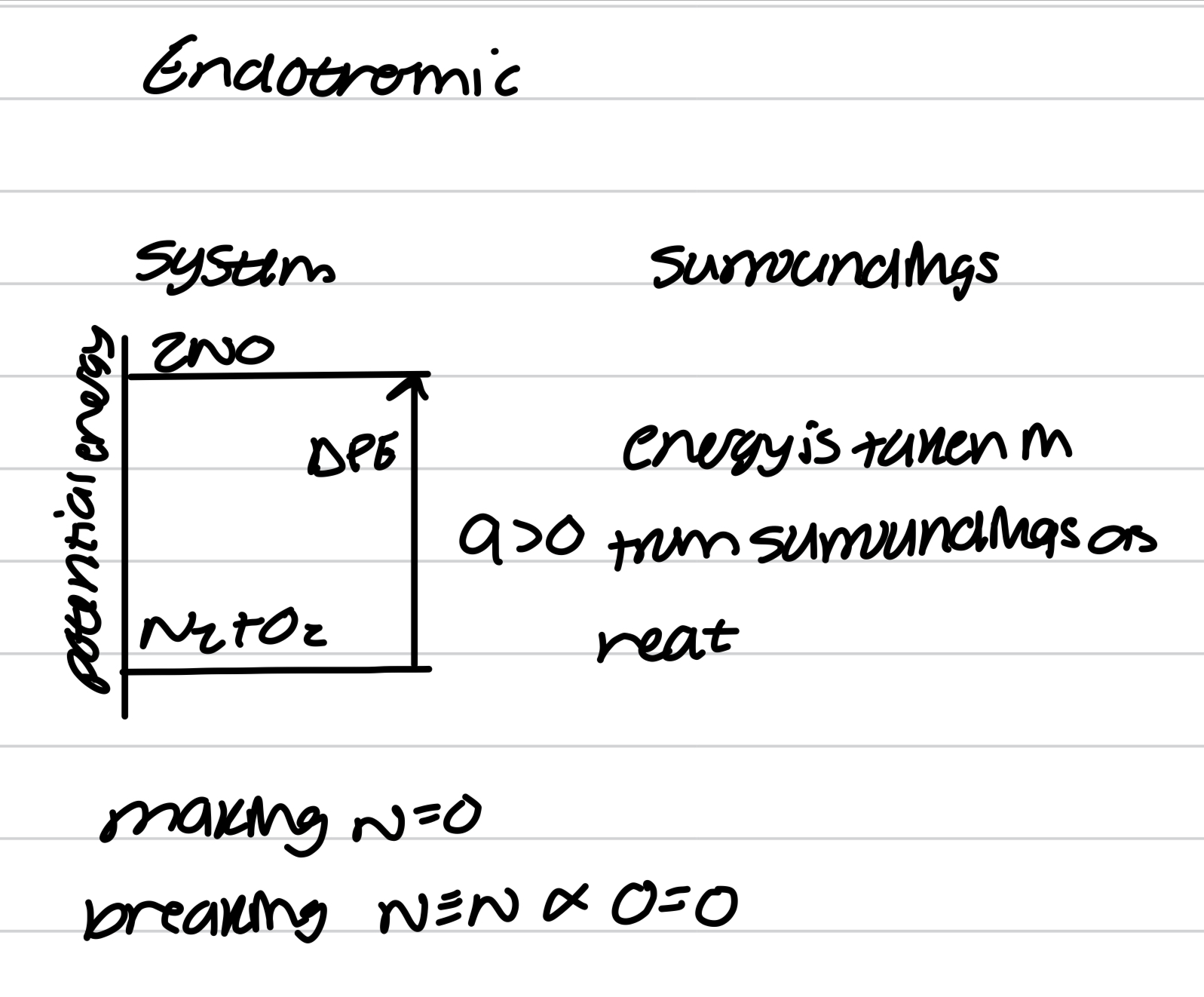
Exothermic exchange of heat

Endothermic exchange of heat
Work and heat in terms of molecular motion
Molecules in uniform motion, energy is transferred to surroundings as work
Molecules in chaotic motion, energy is transferred to surroundings as heat
Energy is the capacity to do work
In an open system, the CO2 would push the air out of the way so still doing work on the surroundings
Work is done by the system on the surroundings because the gas pushes the weight upwards as it expands. The weight represents the pressure of the atmosphere → w<0
w>0 when gases are being consumed → the surroundings are doing work on the system
Expansion work
A gas expands and does work against external pressure, Pex
Opposing force = Pex x area
Work = force(F) x distance(s)(height,h)
= (Pex x A) x h
= Pex x ΔV
When w<0 system loses energy → w=-PexΔV
At constant pressure and temperature
Pex=Pgas
pΔV= -nRT → ideal gas equation
w=-nRT → only when we have perfect reversibility and theoretical max work obtained
Δn = (nfinal - ninitial) is the change in the number of moles of gas
Reversible expansion
Constant P+T conditions rarely realistic → complex maths
Maximum work obtained is when expansion reversible otherwise energy lost (wasted) as external heat, sound, etc
Process can be reversed with minimum effort
Key assumptions for reversible expansion
No temperature or pressure gradients - constant
System at equilibrium throughout
Internal energy
A measure of all of the energy reserves of a system
Um = molar internal energy → energy of 1 mol Jmol-1
ΔU = change in internal energy
Enthalpy changes
Measured at constant pressure in open systems
Standard states and standard conditions
ΔUθ/AU° = standard conditions
Gas - pure gas at 1 bar (1×10^5 Pa)
Liquid - pure liquid at 1 bar
Solid - pure solid at 1 bar
Solution 1moldm-3 concentration
Temperature unless stated but 298.15K
Enthalpy changes of state
ΔvapHθ - liquid to gas → -ΔconHθ
ΔconHθ - gas to liquid
ΔfusHθ - solid to liquid
Reference state
Is the most stable state at standard temperature and pressure
Enthalpy change of formation, ΔfHθ
When 1 mole of substance is formed from elements in their reference states at stated temperature
What does dissociate mean
Separates to infinite distance
Bond dissociation energy
BDE
Enthalpy change when a specific bond in a compound dissociates
Bond energy/enthalpy
BE
Mean bond energy
Mean of the BDE values for similar bonds within a specific compound
Tabulated Average Bond Energies
ABE
Apply yo a type of bond across a range of related compounds
Estimations but some values are annotated with a → true BDE values as there exists only one compound containing the bond
Enthalpy changes of reaction, ΔrHθ
Enthalpy change when molar quantities of the reactants as stated in the end react together under standard conditions with all substances in standard states
Pay attention to:
temp
states
stoichiometry
State functions
Depends only on the current state of the system as defined by the temperature and pressure
Any change in the value of state function depends only on initial and final conditions, not route taken
Hess’s Law
The standard enthalpy change for a reaction is the sum of the standard enthalpy changes to the reactions into which can be divided
Cas use:
bond enthalpies
reaction enthalpies
separate particles
any other reference info
standard enthalpy of formation
ΔrHθ equation
ΣvΔfHθ(products) - ΣvΔfHθ(reactants)
The Zeroth law
If 2 systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other → allows us to do experiments
Only absolute temps
Uses K
Bomb calorimetry
Used to measure temp changes at constant volume
No work can be done at constant V so w=0 and ΔU=q
Isolated system → adiabatic
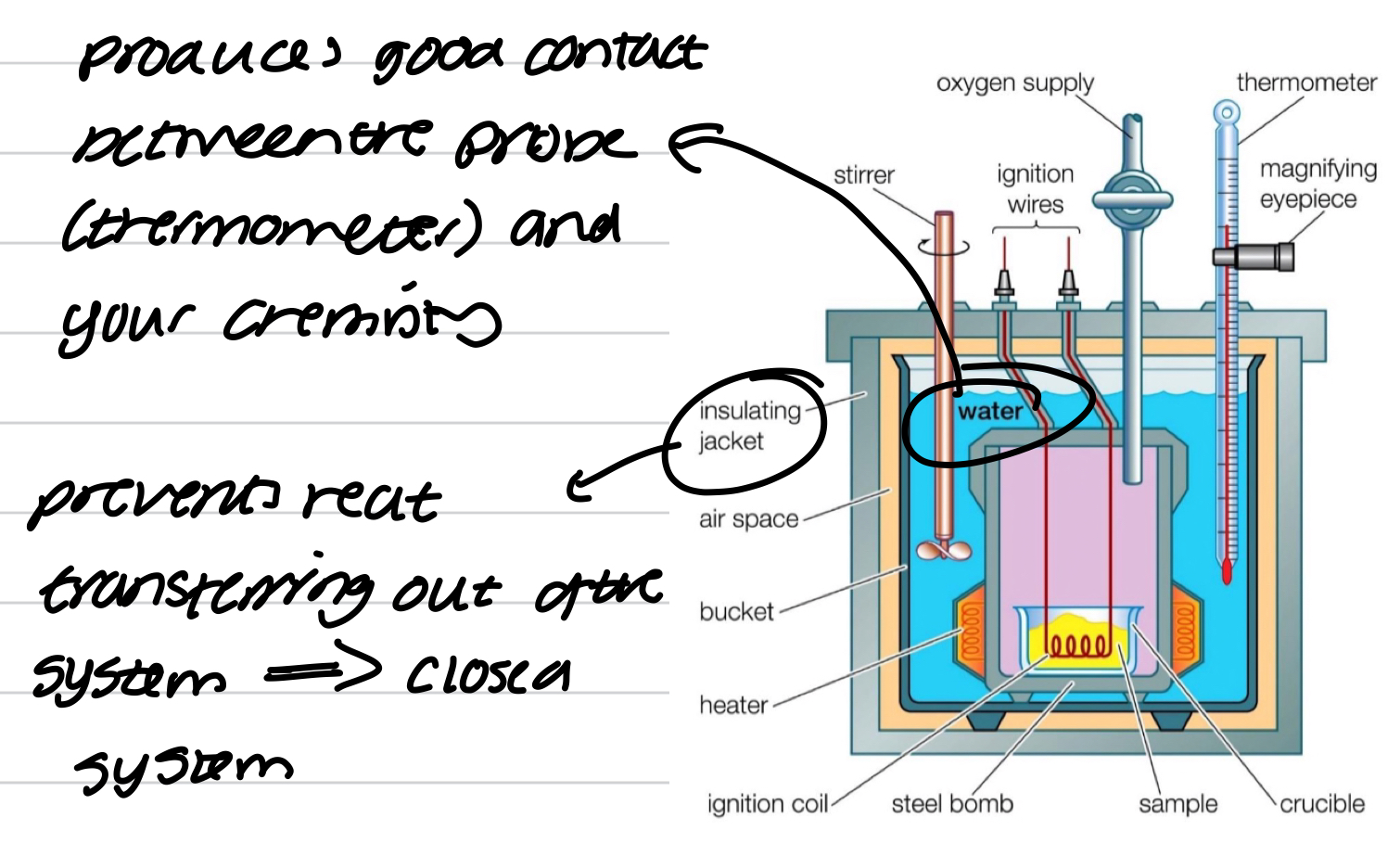
Method for bomb calorimeter
measure heat (temp) evolved by RXN
Use electricity to get to the same temp change again → power
Heat exchange in open systems
Internal energy changes as the energy is rearranged
Energy transferred between the system and surroundings as heat and/or work
ΔU = q + w
ΔU = q + pΔV
Experiments to measure enthalpy change
Everyday chemical changes occur in open systems that have constant pressure, not constant volume
Open calorimeter, q=ΔH
Enthalpy change
Heat transferred at constant pressure
ΔU = ΔH + w
ΔU = ΔH - pΔV
ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT
Δn = moles of gas in products - moles of gas in reactants
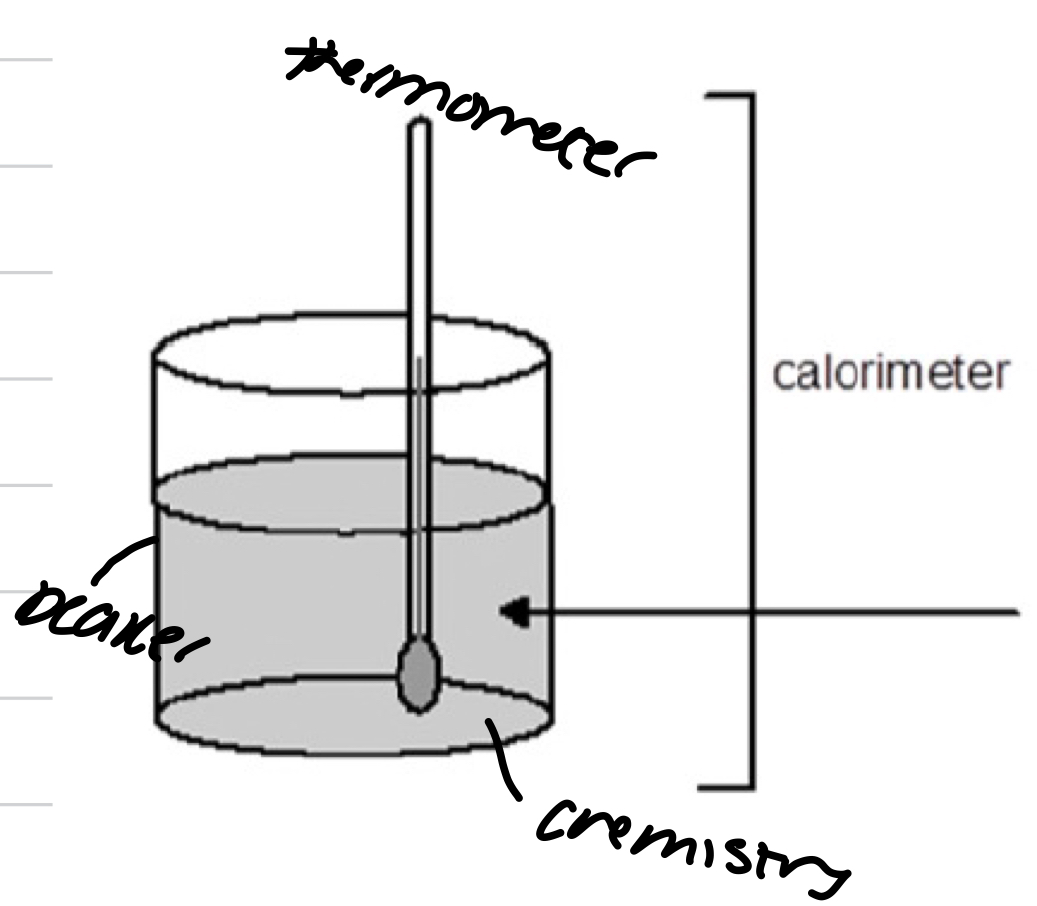
Experiment 1
Open system
Need to take into account for heat leakage
Need to consider heat capacity
RXN takes place in solution and is part of the surroundings
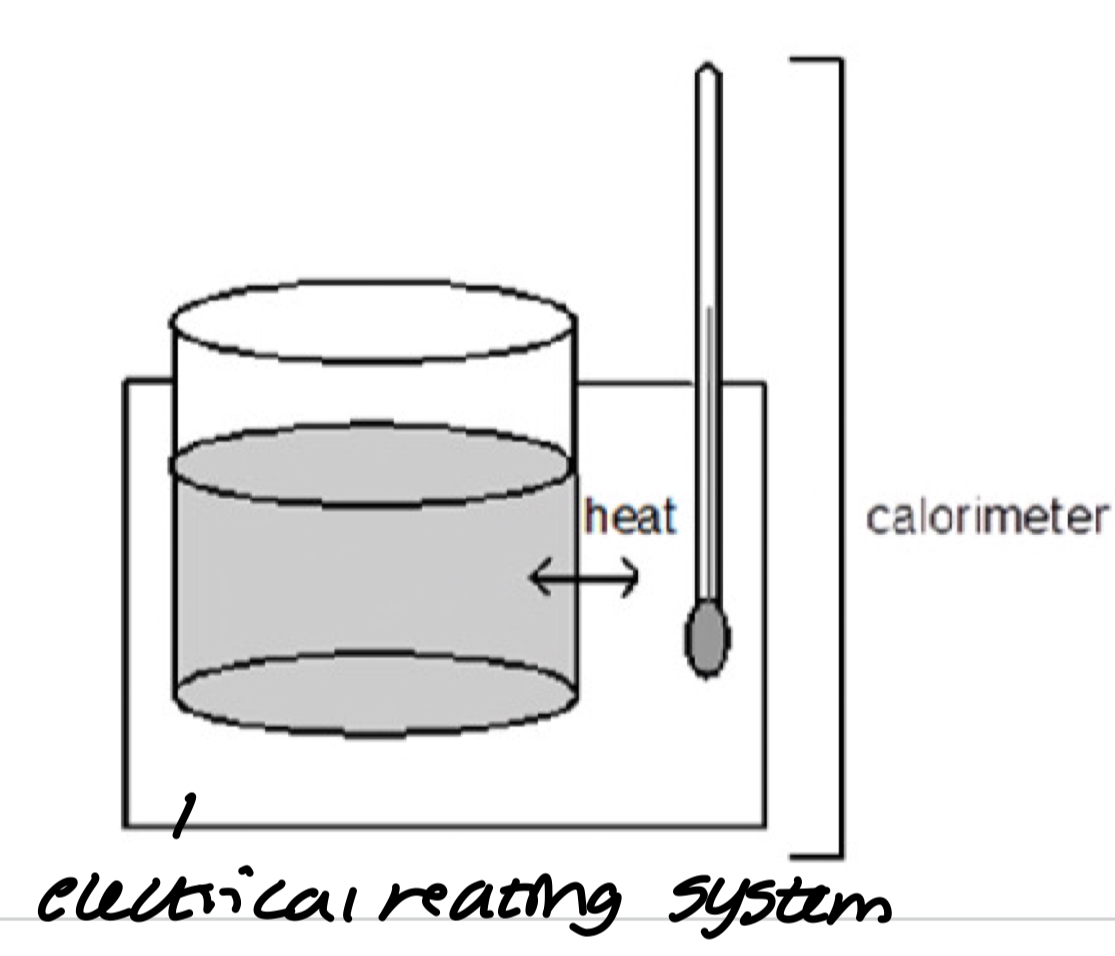
Experiment 2
Improvement on 1
Using electrical heating system to measure the heat capacity of the calorimeter
measure heat rise from the chemistry
replicate change in temp using electrical energy ΔH=ΔEelec
Experiment 3
Accurate research lab-solution
Use a bomb calorimeter to measure ΔU - constant volume
convert ΔU to ΔH using ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT
Explosions with work and enthalpy
Rapid and extreme increase in volume accompanied by energy release
Usually characterised by temperature increase and generation of gases
Explosive effect comes from:
production of gases
Expansion of gases on heating
Standard enthalpy of combustion
The value of ΔrH⦵ for complete combustion of one mole of fuel is the standard enthalpy change of combustion ΔcH⦵
Everyday uses of fuels
Heating - 16% of CO2 emissions
Transport - 21% of CO2 emissions
Electricity generation - lighting
Waste disposal - incineration
Methane and coal
Coal mainly carbon: C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2(g)
Natural gas mainly methane: CH4(g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
To generate power, work must be done → need large ΔnRT → to turn turbines and generate electricity
Use external combustion engine/steam engine to turn water into gas
This assumes all the heat from the RXN is being used to turn water into steam
Fuel metrics
Compare fuels in quantitative way
Economic → price, weight, volume
Environmental → CO2, NOx, O3, particulates
Carbon load of fuels
Energy per unit mass
|ΔcH|/RMM in MJkg-1
By volume: energy density and mass per unit volume in MJm-3
Focus on biofuels
Produced via contempory biological processes eg agriculture or anaerobic digestion
Potentially carbon neutral
Bioethanol added to petrol → reduces carbon load
Larger alcohols show promise as petrol replacements → similar combustion characteristics
Biodiesel used for lorries and heavy vehicles
As O2% increases, ΔcH decreases
Biofuels are already part oxidised
Biofuel issues
Land-use/food vs fuel/ soil erosion/loss of biodiversity
Poor fuel metrics
New chemistry/new engineering
Cryogenic fuels
High energy density
Typically H2 → liquified and stored at low temp sub 33K
Good fuel metrics
Realistic energy densities = taken into account
Inconvenient:
storage
hazardous
need O2 supply
Hypergolic fuels
A two-component propellant combination that spontaneously ignites on mixing
Hypergolic fuel disadvantages
Highly corrosive and toxic
Lots more chemistry to research and understand
Hypergolic fuel advantages
No need for air → good for space
Liquid at 290K → easy storage
Near-instant conversion of chemical energy to heat and work
No need for ignition control
Excellent fuel metrics
Heat capacity
Heat supplied/temp change
For single substance, specific heat capacity, Cs = heat capacity per unit mass JK-1g-1
q=m x Cs x ΔT → m is mass of substance
Tells us what is happening to the energy, in molecular terms, when you heat a substance
Water specific heat capacity
Large specific heat capacity
Many everyday applications
Climate
Central heating
Industrial cooling
Molar Heat Capacity
Cm, heat capacity per mole JK-1mol-1
q = n x Cm x ΔT where n is moles of the substance
For gases, two values of Cm:
molar heat capacity at constant pressure Cp, JK-1mol-1
molar heat capacity at constant volume, Cv, JK-1mol-1
H and U changing with temp
Enthalpy and internal energy both increase with temperature
ΔH (increase of enthalpy for ΔT) =CpΔT
ΔU (increase of internal energy for ΔT) = CvΔT
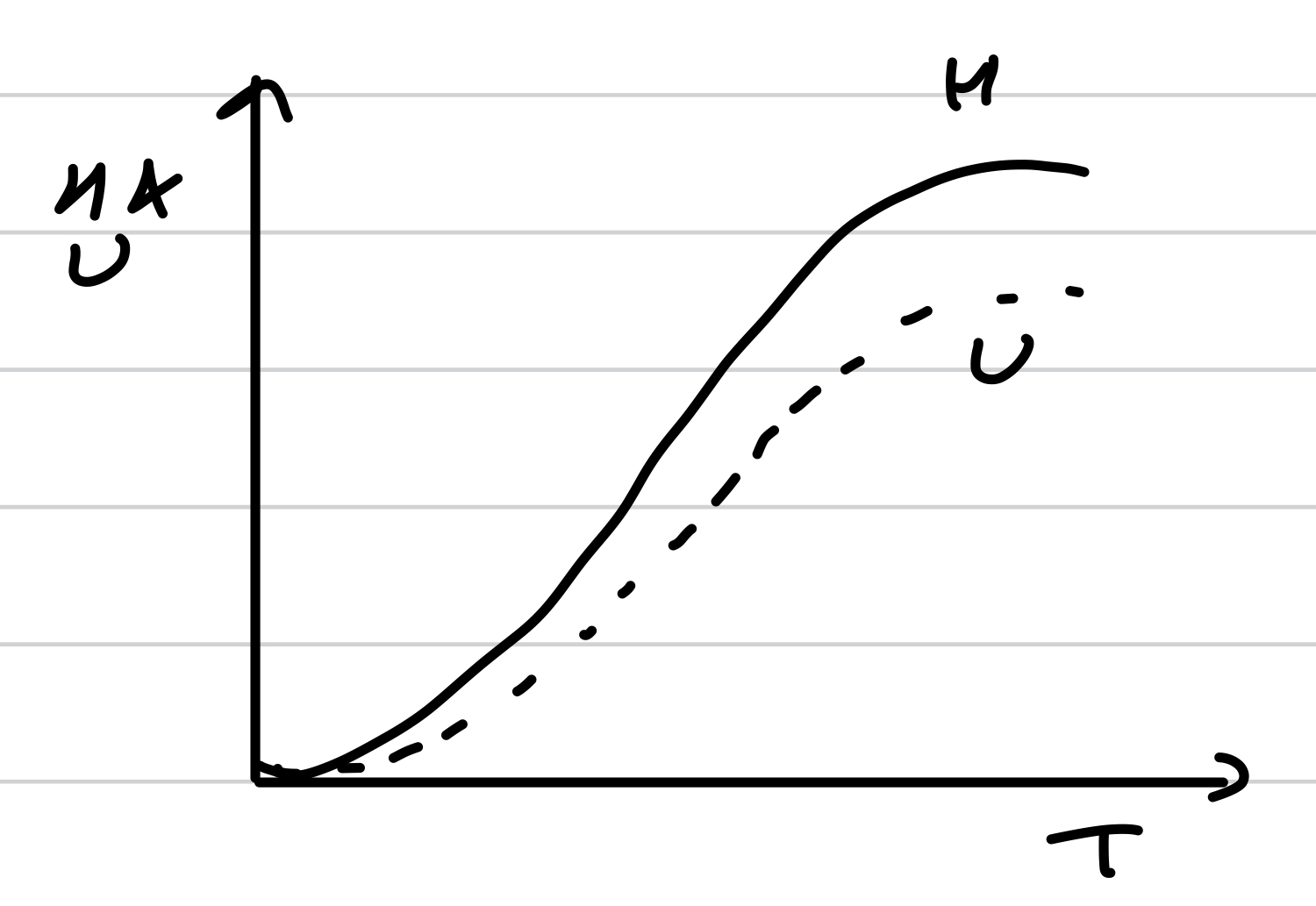
Relation between Cp and Cv for a perfect gas
Hm = Um + pV
Hm = Um + RT
ΔHm = ΔUm + RΔT
ΔHm/ΔT = ΔUm/ΔT + R
Cp = Cv + R
when n=1
Enthalpy change of solution, ΔsolnH⦵
Heat exchanged at constant pressure upon changing to aqueous phase
Change ΔH with temperature
Enthalpy increases with T
H2 = H1 + nCpΔT
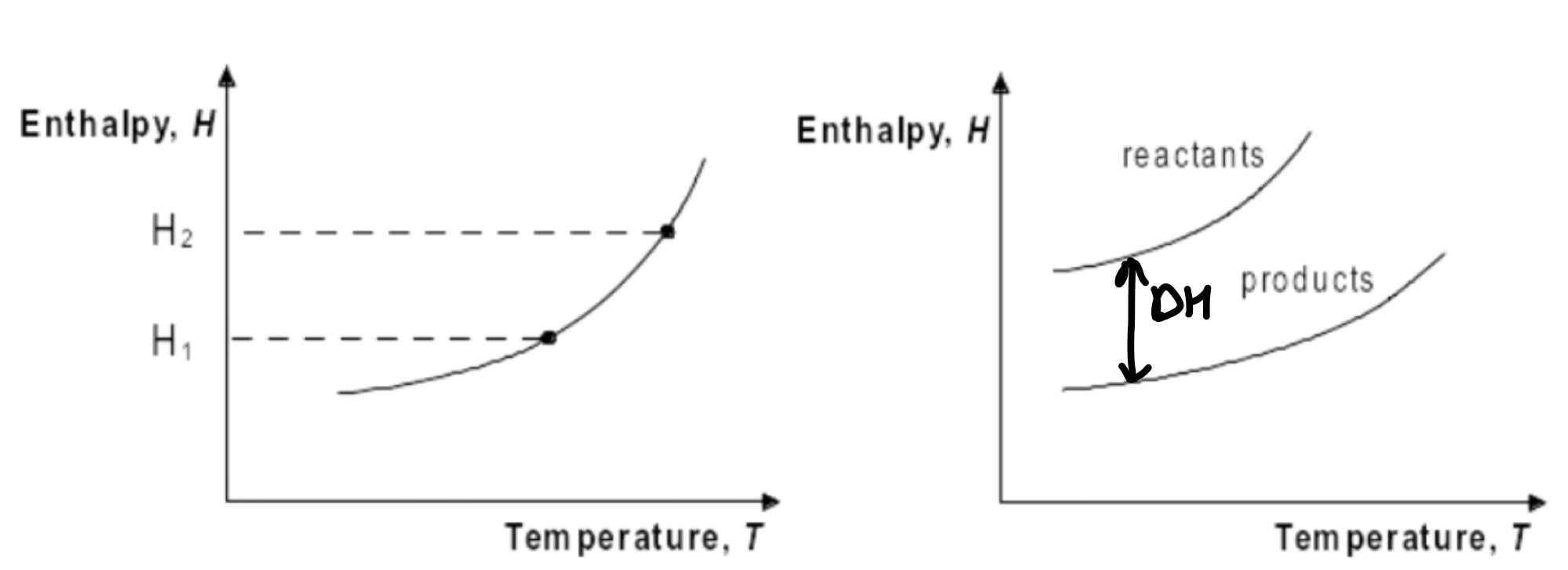
Kirchkoff’s Law
Using to calculate change ΔH with temperature
ΔrHT2 = ΔrHT1 + ΔrCpΔT at constant pressure
ΔrCp = ΣvCp(products) - ΣvCp(reactants) if you cross a phase boundary, will need to adjust the values
This assumes Cp itself doesn’t change with temperature