(8) The Carbon Budget + impacts on land/ocean/atmosphere
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
The Carbon Budget
= uses data to describe the amount of carbon that is stored and transferred within the carbon cycle
Areas where carbon is stored = carbon sinks
As carbon moves from one store to another = carbon flux
Carbon = measured in peta-grams (Pg)
1 peta-gram = 1000,000,000,000,000 grams
1 Pg = 1 x 1015 g
Patterns within the Carbon Budget
- the vast majority of carbon is stored in the earth's crust and oceans
- relatively small amounts of carbon are stored in the atmosphere and in plants
... carbon transfers are extremely active and carbon fluxes are continuous between the atmosphere and the land (BIGGEST PHOTOSYNTHESIS)
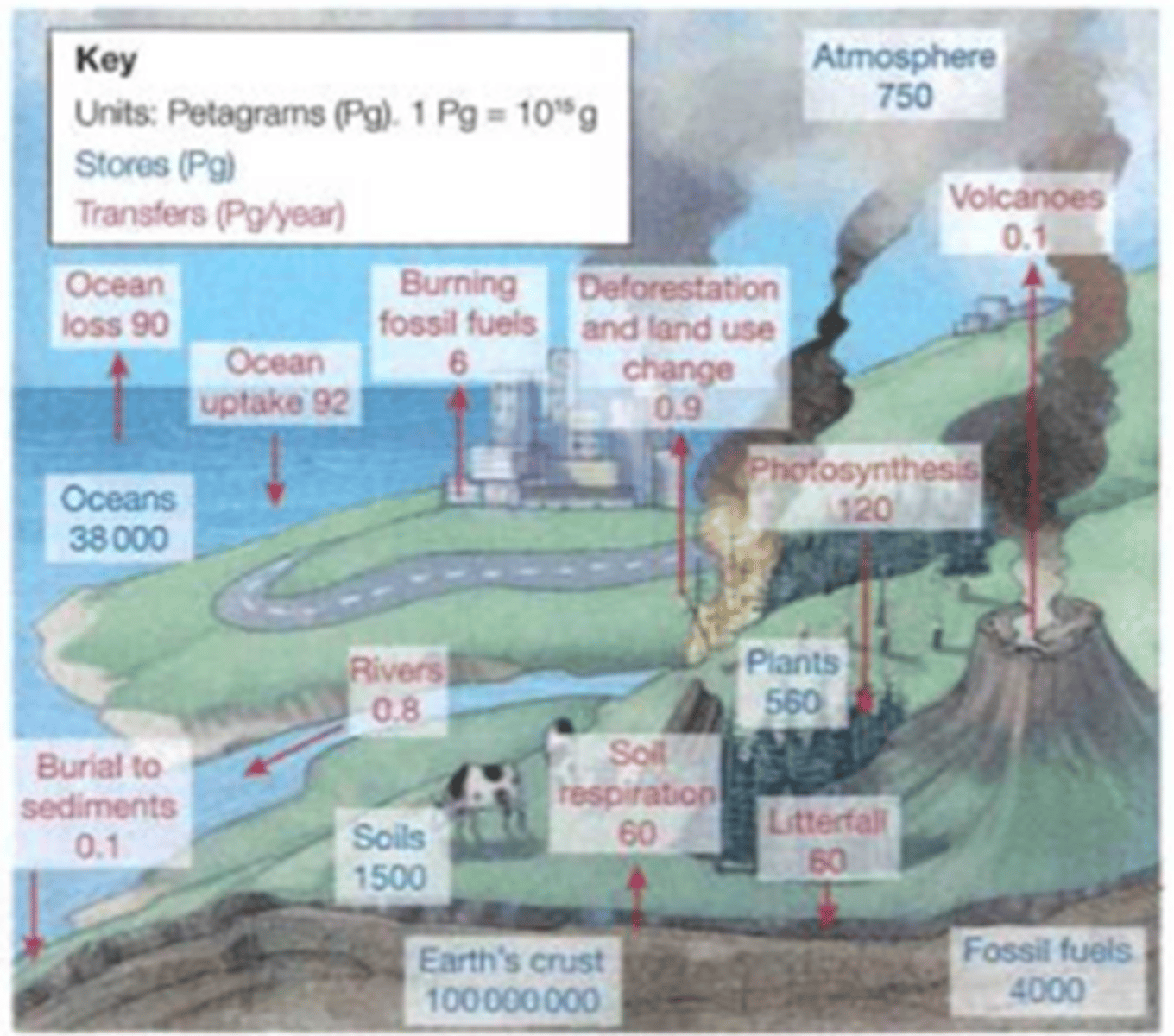
Natural Sources of Carbon
... ocean outgassing = the largest source of CO2 in the atmosphere
- Dissolved CO2 is released (particularly from warm tropical waters) into the atmosphere
- Oceans also absorb CO2
= the ocean carbon pump
... volcanic activity = releases CO2
- Small but significant amounts from the asthenosphere
- Both terrestrial and submarine
... photosynthetic stores
- Largely responsible for a net loss of carbon in the atmosphere
Absorb more CO2 than they release
Natural Offset
1. Ocean sink
2. Soil and land-based sinks
=> balance the emissions from the release of CO2 to form the carbon budget
Impact of the Carbon Cycle
... most important role = release of CO2 + other gases (methane) into atmosphere
=> these gases absorb long-wavelength radiation from the earth and warm lower atmosphere, enabling life to exist
=> Surface absorbs heat, which is re-radiated as long- wavelength infra-red (absorbed more readily by atmospheric greenhouse gases)
= the greenhouse effect
Enhanced greenhouse effect = more greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere, making it more effective in trapping radiation from earth
=> caused by increased emissions resulting from anthropogenic activities
e.g., Burning fossil fuels, deforestation
Impacts on Land
- Carbon cycle is responsible for the formation and development of soil
- Carbon in the form of organic matter introduces important nutrients and provides a structure to the soil
- Carbon in the form of organic matter is essential for plant growth and food production
- Carbon stored in grass provides fodder for animals
- Carbon provides a valuable source of energy in the form of wood and fossil fuels
Impacts on Oceans
- Carbon can be converted into calcium carbonate, which is used by some marine organisms to build shells
- The carbon cycle has an impact on the presence of the abundance of phytoplankton, which consume CO2 during photosynthesis and carbon is passed along the food chain
Impacts on the Atmosphere
- CO2 in the atmosphere helps to warm the earth through the greenhouse effect, without which there would be no life on earth
- increases in carbon emissions as a result of human activities (anthropogenic) have led to the enhanced greenhouse effect which contributed to global warming
- Carbon stored by vegetation has a significant effect on the atmosphere (deforestation and afforestation)
Carbon cycle & regional impacts on climate
- Vegetation removes CO2 and releases water and oxygen
... regions with dense vegetation experience high rates of photosynthesis and respiration
=> this increases levels of humidity and the amount of cloud cover, which may affect regional temperature and rainfall
- Regions experience widespread deforestation may become drier and less humid
... fewer trees = less photosynthesis
- Volcanic eruptions release CO2 into the atmosphere along with ash and other gases
... these absorb more radiation from the sun and can lead to global cooling effect on earth due to the reflective particles
Marine Sinks
= proliferation of plankton in oceans
- Promotes the formation of clouds through the creation of the chemical substance dimethyl sulphide (DMS)
= temperature + ocean carbon pump
- at higher latitudes CO2 is dissolved into colder seawater
- at lower latitudes CO2 is released from warmer water
- ocean currents transport C02 from ocean surface to the ocean depths by sinking cold water at higher latitudes
- if brought to the surface, e.g., by upwelling, the cold water will warm up and release some CO2 into the atmosphere
= the ocean carbon pump
(being warmed up due to increased ocean temperatures)