Bacteriology
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
bacterium/bacteria
single celled organisms
ubiquitous and the majority of bacteria are beneficial or harmless
some can invade the body and cause diseases
bacteria are prokaryotes
no nucleus
single celled organisms with a single circular chromosome and a rigid complex cell wall
they reproduce asexually though binary fission (cell*2)
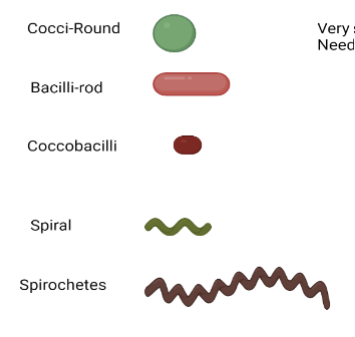
bacteria shapes
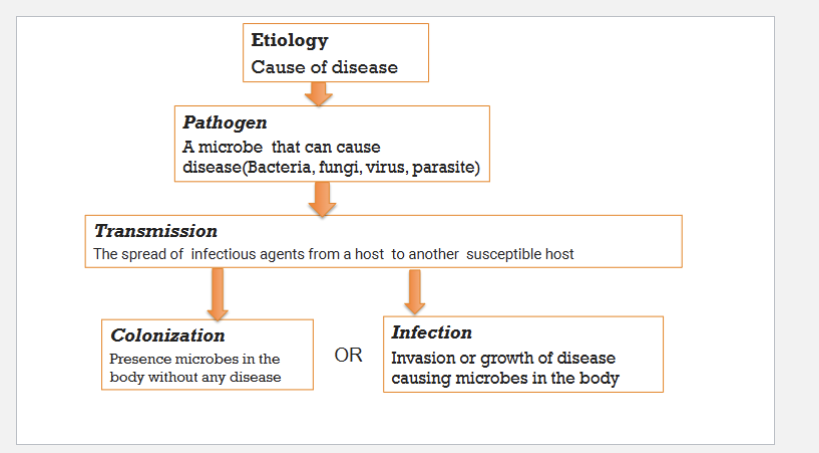
etiology
cause of disease
pathogen
microbe that can cause disease (bacteria, fungi, virus, parasite)
transmission
the spread of the infectious agents from a host to another susceptible host
colonization
presence of microbes in the body without any disease
infection
invasion or growth of disease causing microbes in the body
transmission of disease diagram
pathogenesis
mechanisms by which a pathogen causes a disease
pathogenicity
ability of a pathogen to cause disease in a host
predisposition
condition of the host that makes it susceptible to infections
virulence
a pathogen’s ability to cause disease or damage
virulence factors
properties or traits found in isolates that cause disease but not found in isolates of the same species that lack the ability to cause disease
consequences of pathogen-host interaction
no colonization or colonization—the presence of bacteria on body surface without causing disease
infection
invasion of a host organism’s tissues by disease-causing organisms
what follows after infxn
disease followed by recovery
disease, death, or disability
disease followed by persistence:subclinical/chronic infection
obligate pathogen
obligatory—required
highly virulent microbe
small number of bacteria is enough to cause infection and a distinct dz without any host predisposition can cause a distinct dz
ex. Bacillus anthracis=Anthrax
primary pathogen
moderately virulent bacteria in moderate numbers with some level of host predisposition can cause a distinct dz
ex. Staphylococcus aureus skin infxn
opportunist pathogen
a bacteria with no virulence can cause nonspecific dz where this is host predisposing factors
ex. wound and burn infections caused by nonpathogenic bacteria
invades and then causes infxn; wide variety
endotoxin
bacteria has to die for toxin to be released in the body
sequence of events in bacterial pathogenesis
entry into host
evade host defenses
colonize the host systems
multiply
exert damage in host
transmission to other others
infectious vs contagious
🦠 Infectious
Definition: Refers to diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms (like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites) that invade and multiply in the host.
Key Point: Not all infectious diseases are easily spread from person to person.
Examples: Tetanus (caused by Clostridium tetani) is infectious but not contagious—it enters through wounds and doesn’t spread between individuals.
🤝 Contagious
Definition: A subset of infectious diseases that are easily transmitted from one individual to another.
Key Point: All contagious diseases are infectious, but not all infectious diseases are contagious.
Examples: Influenza, COVID-19, and measles are both infectious and highly contagious.
disease triangle of tragedy
host
pathogen
environmental
how do microbes cause disease
combination of specific virulence determinants that will allow them to invade, multiply, and persist in the host and conditions of the host that permits their survival
infection may result in
changing physiology by direct damage to the host cell (toxins)
depleting the host’s nutrients by using them
as a result of immune response (inflammation) to the infecting agent
a combination of all the above affects
microbiome
collection of all microbes, such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and their genes that naturally live on our bodies and inside a living body
they play a role essentially in all aspects an individual’s development immunity, mood, and disease development (obesity, chronic inflammation)
gram positive bacteria
thick peptidoglycan cell wall
lipoteichoic acid
no outer membrane
colored pink
gram negative
thin peptidoglycan wall
outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
colored purple
acid fast bacteria
mycolic acid
they are **gram positive as they do not have an outer membrane
during gram-negative bacterial infection, bacteria dies and release
lipid a component or endotoxin to the bloodstream>stimulate the immune system>resulting in endotoxin or septic shock
what happens during gram negative bacterial infections
endotoxin releases immune factors
exceptions of bacteria without a cell wall
mollicutes: mycoplasm ureaplasma L forms are cell wall deficient bacteria
cannot see them using gram stain
cannot use cell well targeting therapy when treating infections caused by this bacteria
some bacteria have this type of flagella
endoflagella
pili/fimbrae
small thread-like structures on the bacterial surface
virulence factor
facilitate adherence to the host tissue through specific receptors
contibute to antigenicity and protection, and can be used as components of diagnostic test and vx
capsule
some bacteria have an outer coating usually made of a polysaccharide
capsule helps bacteria evade phagocytosis
a significant virulence factor
components of diagnostic test and vx
endospores
dormant form of bacteria
highly resistant to destruction
produced when bacteria are expose to adverse conditions and when essential nutrients are depleted
survival mechanism during adverse conditions
exotoxins
proteins produced inside pathogenic bacteria which are secreted into the surrounding medium
ex. tetanus
endotoxins
constitutive elements of the bacteria membrane
they are only liberated when the bacteria die
heat stable—components of bacteria that can induce inflammation by stimulating the immune system
superantigens
produced by pathogenic microbes (bacteria, mycoplasma, and viruses)
bind and crosslink indiscriminately to MHC class II molecule on the antigen presenting cells (macrophages) and T helper cell receptor
results in T cell activation and massive cytokine release leading to nausea, vomiting, fever and may end up in shock
ex. staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1)
biofilms
extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) produce when bacteria come together in masses and allowing bacteria to cling to surfaces
promote chronicity and reduce antimicrobial penetration and susceptibility and difficult to treat
ex. dental plaque, biofilm formation in implants, Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilsm in cystic fibrosis patients
quorum sensing
molecular communication systems used by to synchronize the expression of certain genes
more likely to attack the host—individual behaviors vs group behaviors ex. fire ants
plasmids
circular extrachromosomal elements containing virulence factors
transferred between bacteria through a process called conjugation
ex. Tetanus neurotoxin
staphylococcus enterotoxin
bacteriophages
virus particles which attack bacteria
they transfer virulence factors or mutate virulence factors through a process called transduction
ex. Diphtheria toxin
Botulinum toxin
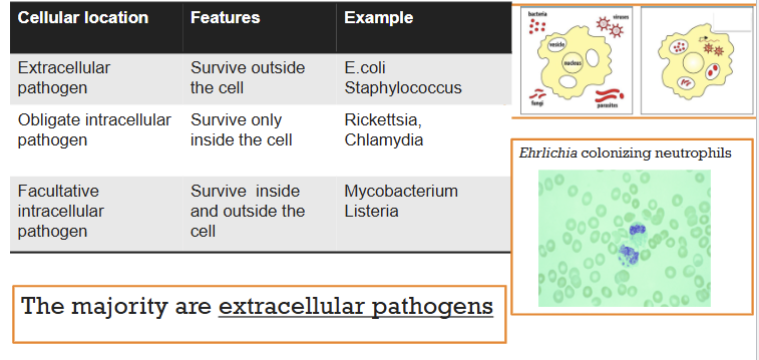
bacterial location
classification (taxonomy) of bacteria
best achieved by evaluating both genotypic and phenotypic properties (polyphasic taxonomy)
classification and nomenclature are subject to change
phylogeny
science dealing with evolutionary relationship between living organisms based on the sequences of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and protein
highly conserved **16s ribosomal gene is used most commonly