Plasma Membrane PAL session questions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
amphipathic
describes something with a hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic regions
phosphoglyceride
type of lipid with two fatty chains linked to glycerol via an ester bond
saturation
absense of double bond between C atoms in the hydrocarbon chain of a fatty acid
sphingolipid
type of lipid with a long hydrocarbon tail with a fatty acid chain attached to the amine group
cholesterol
type of lipid made up of inflexible rings
fluidity
describes the property of plasma membrane that allows components to move freely within the membrane
a membrane is a continuous
lipid bilayer
lipid bilayers are populated by
proteins and carbohydrates
proteins and lipids make up the
bulk of the plasma membrane
the head of a phospholipid is
hydrophilic
the tail of a phospholipid is
hydrophobic
what diffusion is the movement of membrane lipid to the other side of the bilayer
transverse
what diffusion is the movement of lipids within the same side of the bilayer
lateral
integral proteins often take the shape of an
alpha helix
Glycolipids are lipids that have
sugars attached to their heads
what are the 6 functions of the plasma membrane?
compartmentalization: separates inside and outside; encloses intracellular compartments
scaffold for biochemical activities: organizes enzymes for effective interaction
selectively permeable barrier: allows exchange of specific substances
respond to stimuli: receive and produce signals that change cell activity
interactions with other cells: signaling, exchange, and adhesion
energy transduction: converting one type of energy into another
what are the three types of membrane lipids
-phosphoglycerides: hydrophobic tails, two fatty acids chains, linked to glycerol with ester bonds, fatty acids are 16 to 22 carbons longs
-sphinolipids: derivatives of amino alcohol sphingoshine, has a long hydrocarbon tail, have a fatty acid chain attached to the amine group, fatty acid chains tend to be more saturated and longer, the hydrophilic head varies
-cholesterol: sterol that makes up 50% of animall membrane lipids, fills space between phospholipid molecules. infleible rings that interfere with movemet of fatty acids tails which stiffen the membrane, membrane with high cholesterol concentrations lose fluidity
list and describe the four groups of membrane proteins
transporters- active or passive transports
anchors- anchor the membrane to macromolecules and adhesion
receptors- receive and transmit signals
enzymes- catalyze reactions
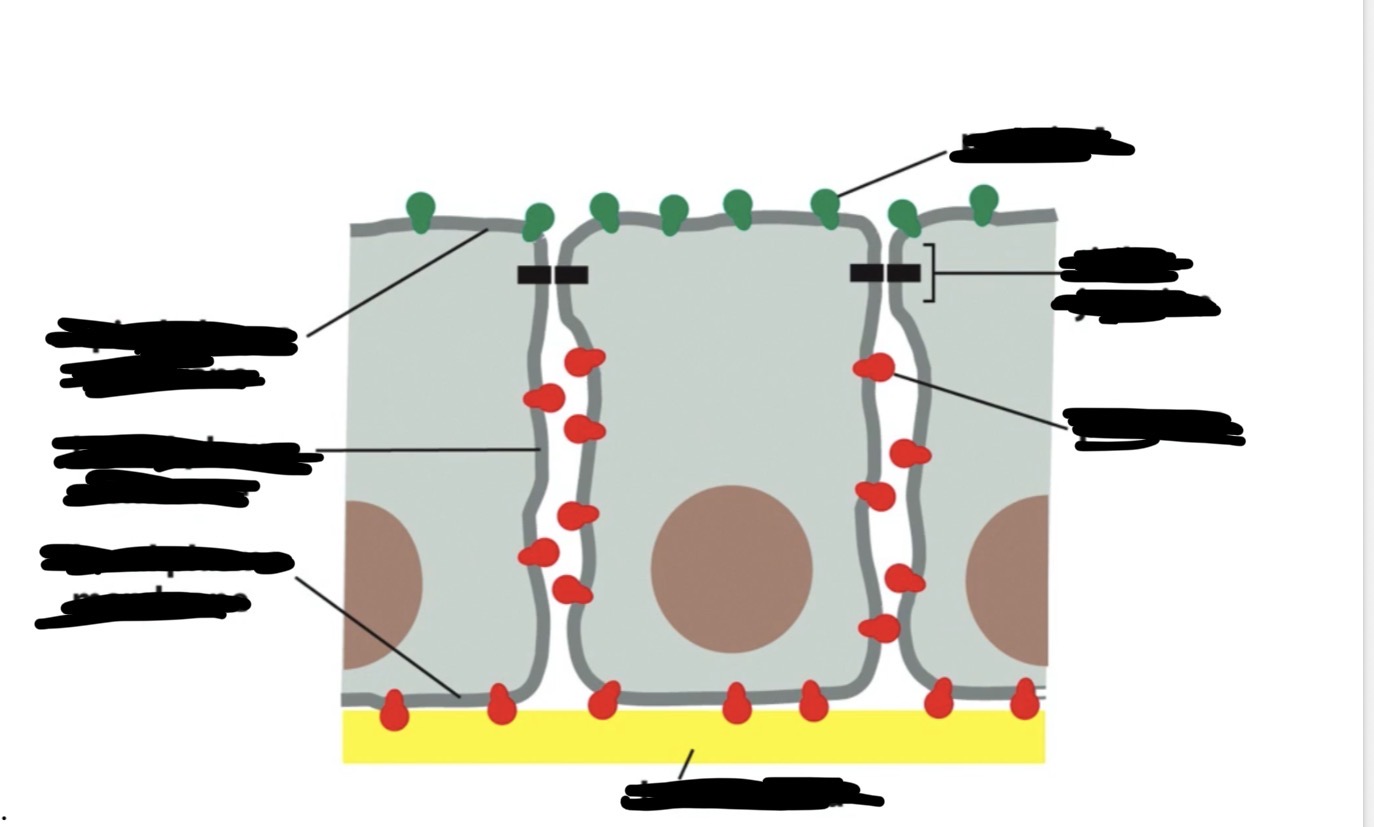
label the following diagram
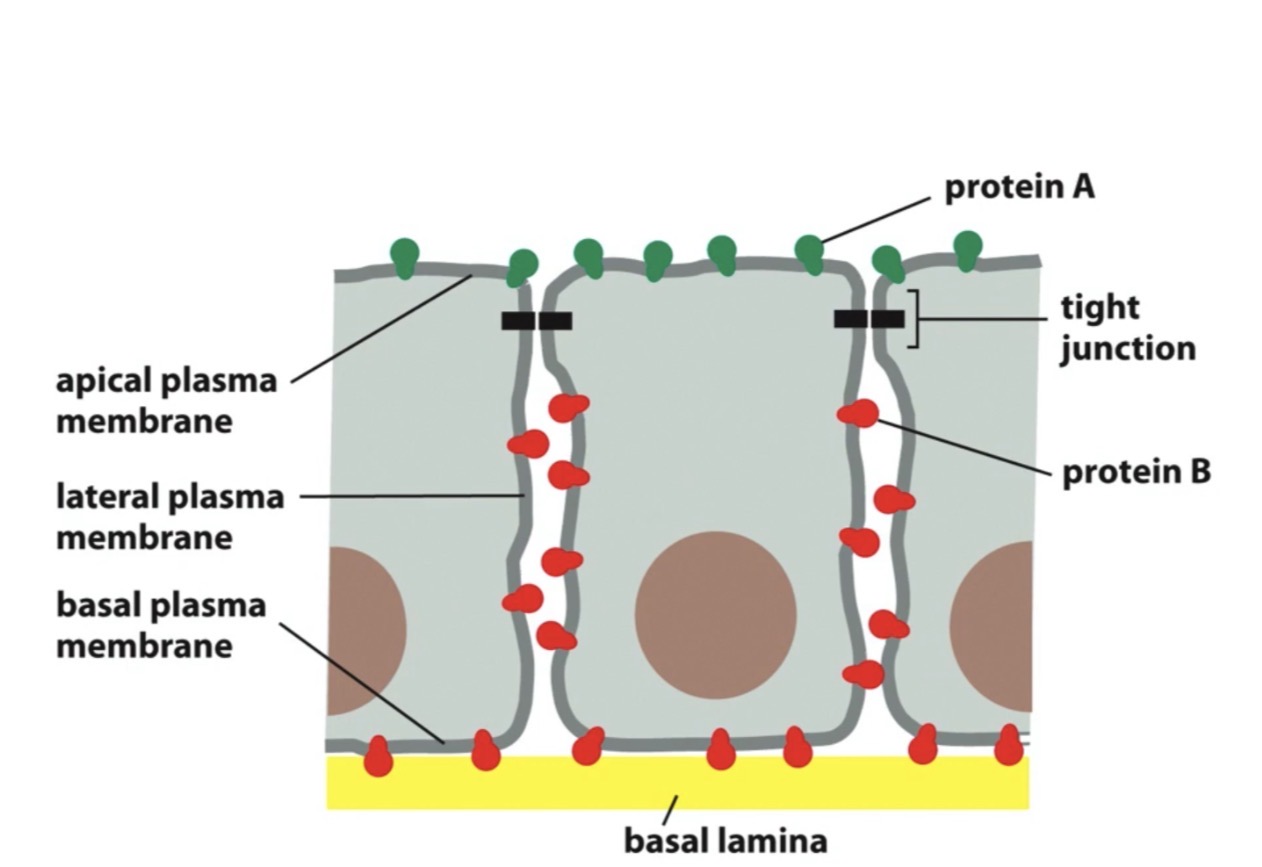
True or false: The function of plasma membrane carbohydrates is to recieve and transmit signals. Explain
false, carbohydrates facilitate cell to cell recognition
what describes the structure of the plasma membrane
a dynamic, fluid mosaic
what type of molecules can diffuse directly through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane?
small hydrophobic molecules
which factor primarily determines the fluidity of the plasma membrane
the concenration of the membrane lipids
what is the primary function of integral membrane proteins
to facilitate the movement of molecules across the membrane
what is the role of carbohydrates attached to proteins and lipids in the plasma membrane
cell to cell recognition
which function is NOT associated with proteins in the plasma membrane
providing energy for cellular activities