organic chemistry
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is a hydrocarbon?
- A compound which contains hydrogen and carbon atoms ONLY
What does the molecular formula show?
- Exact number of atoms of each element present in a compound
What does the empirical formula show?
- Simplest ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound
What does the general formula show?
- Relationship between the number of atoms of each element within a molecule
What does the structural formula show?
- How the atoms in a compound are joined together
What does the displayed formula show?
- A drawing of the bonds within a compound
What is a functional group?
- An atom or group of atoms which determine the chemical properties of a compound
What is a homologous series?
- Group of compounds with same chemical properties because they have same functional group
- e.g. alcohols (-OH), alkenes (C=C)
What do members of the same homologous series have in common?
- Same chemical properties
- Trend in physical properties
- Same functional group
- Same general formula
What does isomerism mean?
- Compounds with same molecular formula but different displayed/structural formula
What is crude oil made up of?
- Mixture of hydrocarbons
What is a fraction?
- Group of substances with similar boiling points
How is crude oil separated into its various fractions?
- Fractional distillation
- Crude oil is heated
- Crude oil boils and vaporises
- Vapour passed into bottom of fractionating column
- Column hottest at the bottom - longest chain fractions condense here e.g. bitumen
- Column coolest at the top - shortest chain fractions condense here e.g. refinery gases
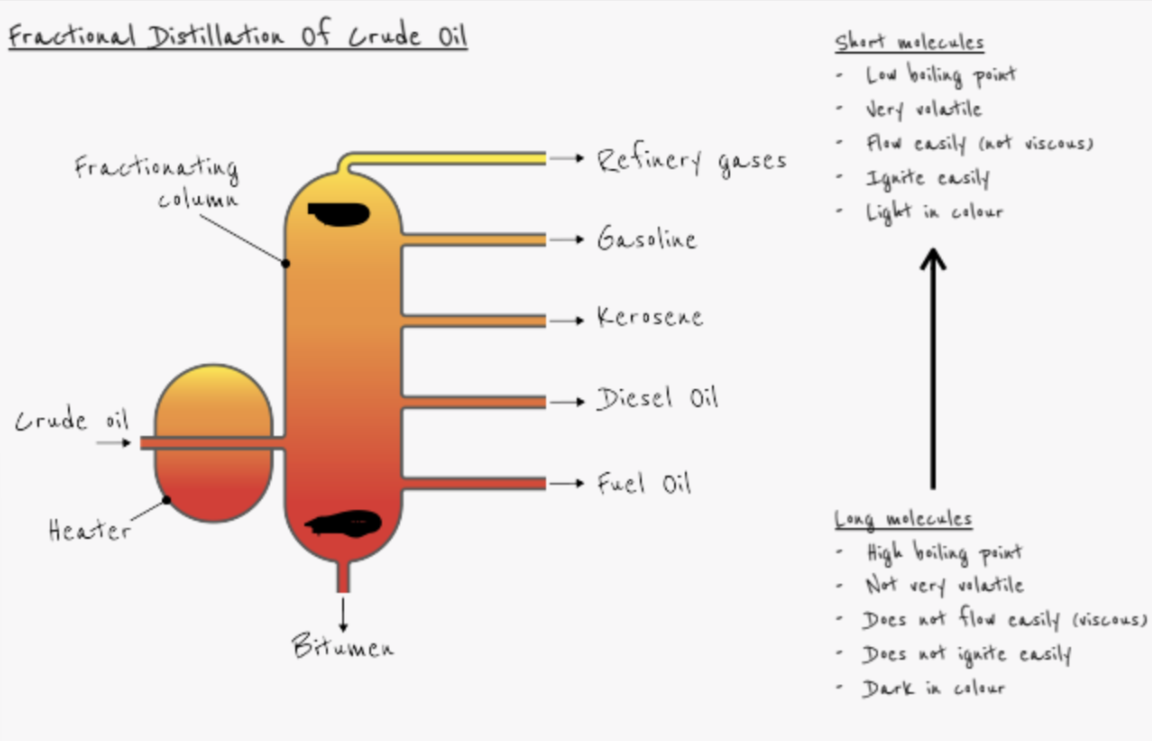
What are the main uses of the following fractions:
- Refinery gases (mixture of methane ethane, propane) - bottled gas
- Gasoline - fuel for cars
- Kerosene - fuel for planes
- Diesel - fuel for buses, lorries
- Fuel oil - fuel for ships
- Bitumen - road surfacing
What does viscosity mean?
- How readily a liquid flows
- e.g. honey - very viscous
- e.g. water - not very viscous
What does volatile mean?
- Evaporates readily
Compare the colour of bitumen and refinery gases
Bitumen = Dark
Refinery = Light
Compare the viscosity of bitumen and refinery gases
Bitumen = Very viscous
Refinery = Not viscous
Compare the boiling point of bitumen and refinery gases
Bitumen = High
Refinery gases = Low
What is a fuel?
- Substance which releases energy when burnt
What is complete combustion?
- Burning in plentiful oxygen
- Produces carbon dioxide and water
What is incomplete combustion?
- Burning in insufficient oxygen
- Produces carbon monoxide and water
- e.g. ethane + oxygen → carbon monoxide + carbon + water
Why is incomplete combustion a problem?
- Carbon monoxide is made - poisonous gas
- Combines irreversibly with haemoglobin
- Less oxygen transported in blood
How are oxides of nitrogen formed?
- High temperatures in car engines
- Cause nitrogen to react with oxygen
- Forms nitrogen oxides
- e.g. nitrogen oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
Which sulfur oxides are formed by burning sulfur impurities found in crude oil?
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Sulfur trioxide (SO3)
How is acid rain formed?
- Nitrogen oxides from car engines dissolve in rain water → nitric acid
- Sulfur impurities in crude oil → sulfur dioxide → dissolve in rain water → sulfuric acid
What environmental issues does acid rain (H2SO4) cause?
- Plants die
- Fish die
- Limestone buildings corrode
What is cracking?
- The breaking down of long alkane chains
- Into smaller chain alkanes and alkenes
What reaction conditions are needed for cracking?
- 600-700°C
- Alumina or silica catalyst
Explain why cracking is important
- Produces shorter chain molecules
- Shorter molecules more useful as fuels
- Used to make petrol/diesel for vehicles
- Crude oil richer in long chain molecules
- Alkenes also produced by cracking
- Used to make alcohols / polymers / plastics
What is the general formulae of an alkane?
- CnH2n+2
Why are alkanes classified as ‘saturated’ hydrocarbons?
- All carbons form 4 single bonds
- No C=C double bonds
Describe the reaction of alkanes with halogens
- Substitution reaction
- UV radiation required
Give the equation for the reaction of methane with bromine
- Methane + bromine → bromomethane + hydrogen bromide
- CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr
What is the functional group of the alkenes?
C=C
What is the general formulae of an alkene?
- CnH2n
What does the ‘1’ in but-1-ene mean?
- Double bond attached to the first carbon in the chain
Why are alkenes classified as ‘unsaturated’ hydrocarbons?
- Contain C=C double bonds
What is the test for an unsaturated compound (an alkene)?
- Add compound to bromine water
- Orange colour turns colourless
- This is an addition reaction
- Dibromoalkane formed as product
Give the equation for the reaction of ethene with bromine water
- Ethene + bromine → dibromoethane
- C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
Describe how to use bromine water to distinguish between an alkane and an alkene
- Add bromine water to each compound
- If bromine water turns colourless → compound is an alkene
Why don’t alkanes turn bromine water colourless?
- Alkanes have no double bond (they’re saturated)
Define monomer
A small molecule that joins together to form a polymer
Define polymer
A long chain formed from many small molecules joined together
What is an addition polymer?
- A polymer made from the joining up of many monomers
How are addition polymers formed?
- One bond in the double bond break
- Monomers join together
- Form a long chain containing only single bonds
Give a use for common addition polymers
- Poly(ethene) - plastic bags
- Poly(propene) - plastic water pipes
- Poly(chloroethene) - window frames (PVC)
- Poly(tetrafluorine) - non-stick pan coating
What does biodegradable mean?
Can be broken down using microorganisms
What are the difficulties with the disposal of addition polymers?
- Inert (unreactive)
- Means they do not-biodegrade
- When burned give off toxic gases