Chapter 4 Flashcards
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
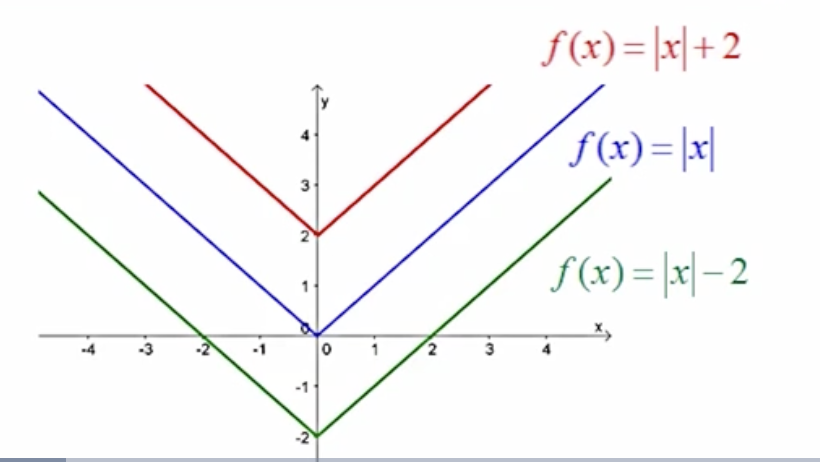
f(x)+ k means . . .
The graph is shifting upwards
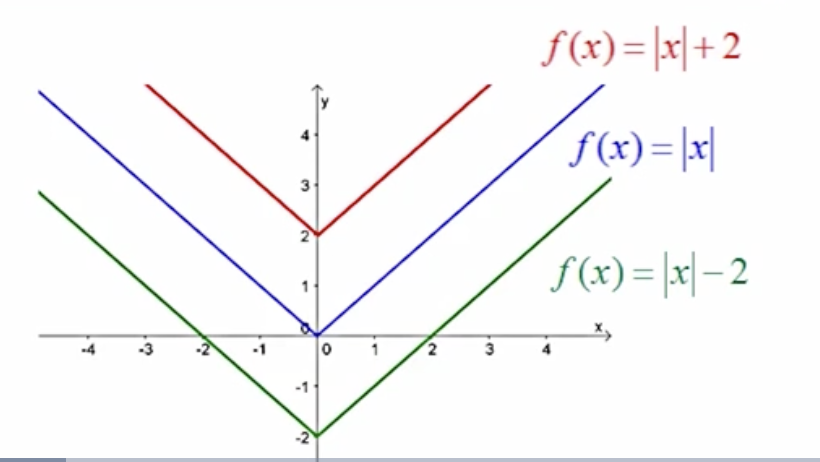
f(x) -k means. . .
The graph is shifting downwards.
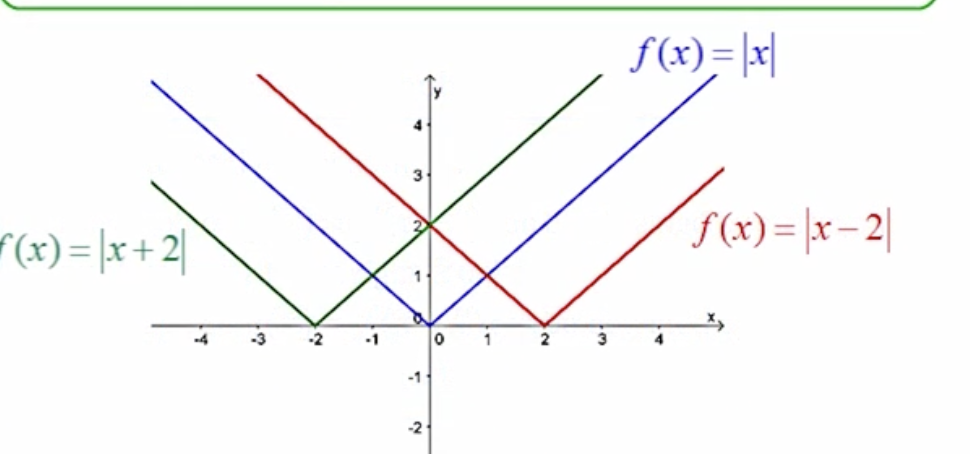
f(x-k) means . . .
The graph is shifting to the right.
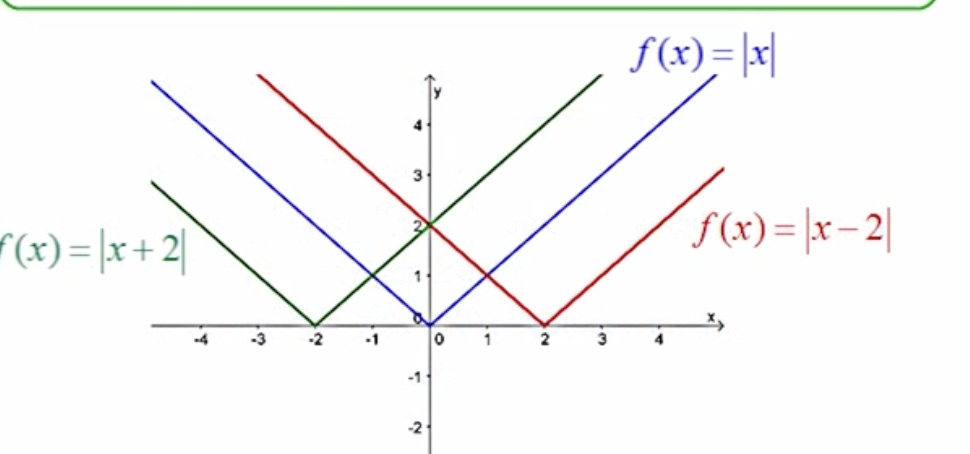
f(x+k) means . . .
The graph is shifting to the left.
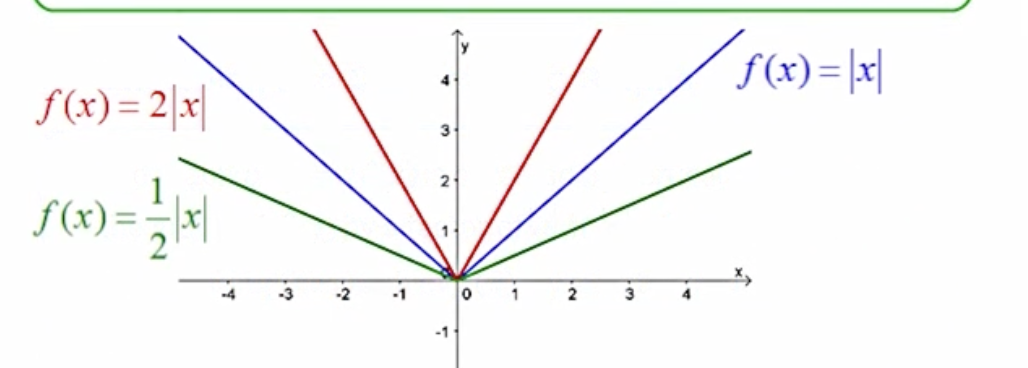
If |a| is greater than one, then . . .
the graph stretches vertically.
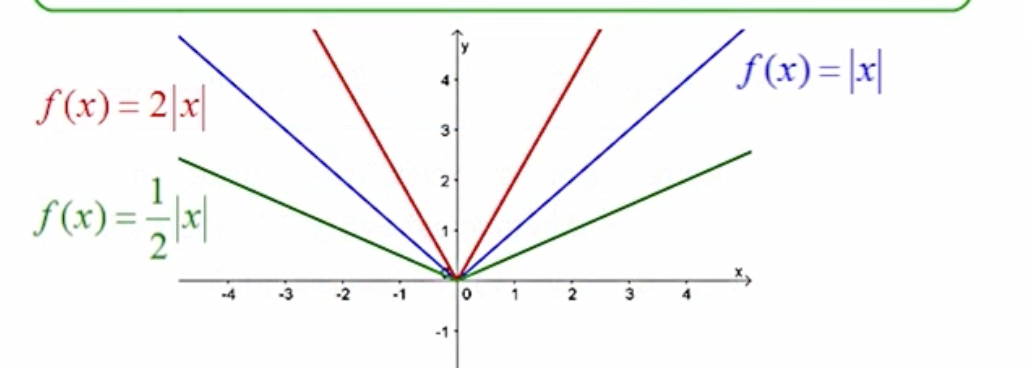
If |a| is greater than 0 but less than 1
the graph compresses vertically.
What happens in y=-f(x)
This is a reflection across the x-axis
What happens in y=f(-x)
This is a reflection across the y-axis.
Describe the symmetry: for every (x,y) point on the graph, there is a (-x,y) point
What is symmetry with respect to the y-axis?
Describe the symmetry: for every (x,y) point on the graph, there is a (-x,-y) point
What is symmetry with respect to the origin?
Describe the symmetry: for every (x,y) point on the graph, there is a (x,-y) point
What is symmetry with respect to the x-axis?
With symmetry to the y-axis, what is this function called?
What is an even function?
With symmetry to the origin, what is this function called?
What is an odd function?
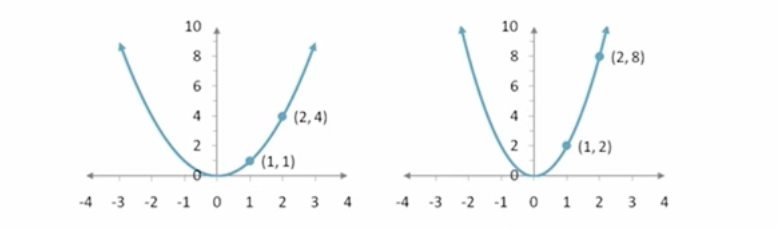
Compare y=x² to y=2x²
Both are parabolic functions, but y=2x² is a vertical stretch of y=x², making it narrower.
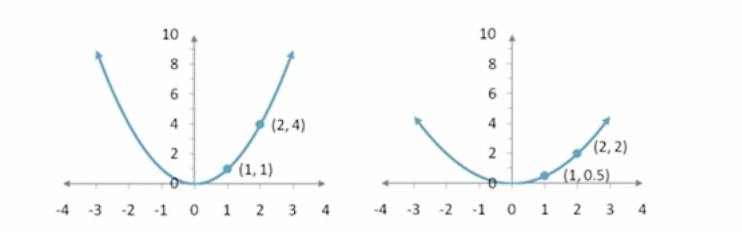
Compare y=x² to y=1/2x²
Both are parabolic functions, but y=1/2x² is a vertical compression of y=x², making it wider.
How do you find the sum of two functions?
What is (f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x)?
How do you find the difference of two functions?
What is (f - g)(x) = f(x) - g(x)?
! Remember to substitute the negative value into g(x)
How do you find the product of two functions?
What is (fxg)(x)= f(x) times g(x)?
Combine like terms.
How do you find the Quotient of two functions?
What is (f/g)(x) = f(x)/g(x), g(x) CANNOT equal zero
f(x): x²-1
g(x): 7+x
Find the sum of these two functions
(x²-1)+(7+x)
x²-1+7+x
x²+x-6
f(x): x²-1
g(x): 7+x
find the difference
(x²-1) - (7+x): Sub negative value into (7+x)
x²-1-7-x: Combine
x²-x-8
f(x): x²-1
g(x): 7+x
Find the product
(x²-1)(7+x): Apply distribution
x³+7x²-x-7
f(x): x²-1
g(x): 7+x
Find the quotient
Definition: ( \frac{x²-1}{7+x} ): Simplify if possible.
x²-1/7+x: Find the domain, vertical ass
7+x=0
x= -7
How do you find the composition of two functions?
(f∘g)(x), substitute g(x) into f(x). f(g(x))
find (fog)(x) when f(x): 8x² and g(x)= 1/x
8 is the starting value
The x of 8x² is where you place g(x)
8(1/x)²= 8/x²
Determine if these two functions =inverses
f(x) 2x-5, g(x) x+5/2
find f(g(x))
2(x+5/2)-5
the 2s cancel out
x+5-5
=x
find g(f(x))
(2x-5)+5/2
The 5s cancel out
2x/2= x
This is when each output of the function corresponds to exactly one input in the domain of the function
What is a one-to-one function?
This is how we test if a function is a one-to-one
What is the horizontal line test?
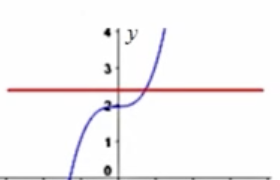
Is this graph a function?
Yes it passes the horizontal line test.
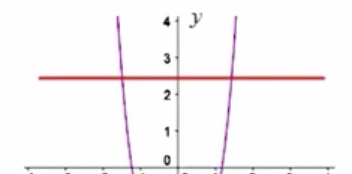
Is this graph a function?
No, it doesn’t pass the horizontal line test.
What is the 1st step of finding the inverse of a function?
What is replacing f(x) with y?
What is the 2nd step of finding the inverse of a function?
what is interchanging x and y within the equation?
What is the 3rd step of finding the inverse of a function?
What is solving for y?
What are graphs of a function and its inverse symmetric with?
What is the line of y=x?
A function cannot have an inverse function if . . .
It is NOT a one-to-one function
What is the 1st step of solving radical equations?
What is isolating the radical?
What is the 2nd step of solving radical equations?
What is squaring both sides?
Solve the radical equation: (x+2)^ 2/5 -1 =0
Add one to both sides
The index of the radical becomes 5 : 5 square root (x+2)²=1
Raise both sides to the power of 5. = square root (x+2)² =1
Since there is still (x+2)² square that side
x+2 = +- square root 1
What is this inequality called: ax²+bx+x > 0?
What are quadratic inequalities?
Solve: x²+2x-3>0
Graph: x²+2x-3
find the x-intercepts (-infinity, -3) U (1, infinity)
if |u| < a . . .
-a< u < a
if |u| ≤ a?
-a ≤ u ≤ a
if |u| > a. . .
u < -a or u > a
if |u| ≥ a
u ≤ -a or u ≥ a