01 Egypt: The New Kingdom
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
New Kingdom
The period in ancient Egyptian history between the 16th century BCE and the 11th century BCE that covers the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of Egypt. Considered to be the peak of Egyptian power.
Thutmose III
The sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty, who greatly consolidated political power through a series of military conquests.
Hatshepsut
The fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty, who expanded Egyptian trade.
Hatshepsut ruled Egypt in the Eighteenth Dynasty (1478-1458 BCE), and brought wealth and a focus on large building projects. She was one of just a handful of female rulers
Akhenaten
Pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty known for his religious fervor to the god Aten.
Tutankhamun
An Egyptian pharaoh of the 18th dynasty (ruled c. 1332 BC-1323 BC in the conventional chronology), during the period of Egyptian history known as the New Kingdom. He is popularly referred to as King Tut.
Aten
The disk of the sun in ancient Egyptian mythology, and originally an aspect of Ra.
Ramesses II
The third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, who made peace with the Hittites. Often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the Egyptian Empire.
Bust of Akhenaten
Akhenaten, born Amenhotep IV, was the son of Queen Tiye. He rejected the old Egyptian religion and promoted the Aten as a supreme deity.
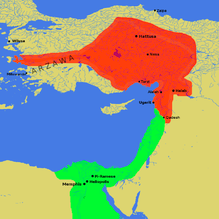
Egyptian and Hittite Empires
This map shows the Egyptian (green) and Hittite (red) Empires around 1274 BCE.
Temple of Ramesses II
Detail of the Temple of Ramesses II
Ramesses II had a large number of children, and he built a massive funerary complex for his sons in the Valley of the Kings. The Nineteenth Dynasty ended in a revolt led by Setnakhte, the founder of the Twentieth Dynasty.
Kohl
A black powder used as eye makeup
Obelisks
Stone pillars, typically having a square or rectangular cross section and a pyramidal tip, used as a monument.
co-regent
The situation wherein a monarchical position, normally held by one person, is held by two.
Statue of Hatshepsut
This statue of Hatshepsut is housed at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City.
Female Rule
Hatshepsut was not the first female ruler of Egypt. She had been preceded by Merneith of the First Dynasty, Nimaathap of the Third Dynasty, Nitocris of the Sixth Dynasty, Sobekneferu of the Twelfth Dynasty, Ahhotep I of the Seventeenth Dynasty, Ahmose-Nefertari, and others. However, Hatshepsut’s reign was longer and more prosperous; she oversaw a peaceful, wealthy era. She was also proficient at self-promotion, which was enabled by her wealth.
Hieroglyphs of Thutmose III and Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut, on the right, is shown having the trappings of a greater role. Often portrayed herself as a male in order to be taken more seriously as an Egyptian ruler, as seen in the statues outside of her temple where she is shown as Osiris, an Egyptian god often connected to the pharaohs
Nubia
A region along the Nile river, located in northern Sudan and southern Egypt.
Assyrians
A major Mesopotamian East Semitic-speaking people.
High Priests of Amun
The highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the Ancient Egyptian god, Amun. Assumed significant power along with the pharaoh in the Twenty-First Dynasty.
Third Intermediate Period
Spanning the Twenty-first to Twenty-sixth Dynasties. A period of Egyptian decline and political instability
Nubian Pharaoh Statues
Statues of the Nubian Pharaohs of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty.
hieroglyphics
A formal writing system used by ancient Egyptians, consisting of pictograms.
pagan
A person holding religious beliefs other than those of the main world religions, Christianity, Judaism, and Islam.
Hellenistic
Relating to Greek history, language, and culture, during the time between the death of Alexander the Great and the defeat of Mark Antony and Cleopatra in 31 BCE.