ITE 484 Adv. Network Management - Final Exam Study Guide
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What does it mean if a server is connectionless and iterative?
Connectionless - UDP
Iterative - only one customer served at a time
What does it mean for a server to be connection-oriented and concurrent?
Concurrent - can serve more than one process (custeomer) at a time -- every time it gets a request, it spawns off a child process (know what a Zombie is)
Connection Oriented - Protocols like TCP
Zombie Process
A process that has finished executing, but whose parent has not yet released its PID; the zombie retains a spot in the kernel's process table.
DHCP packet format
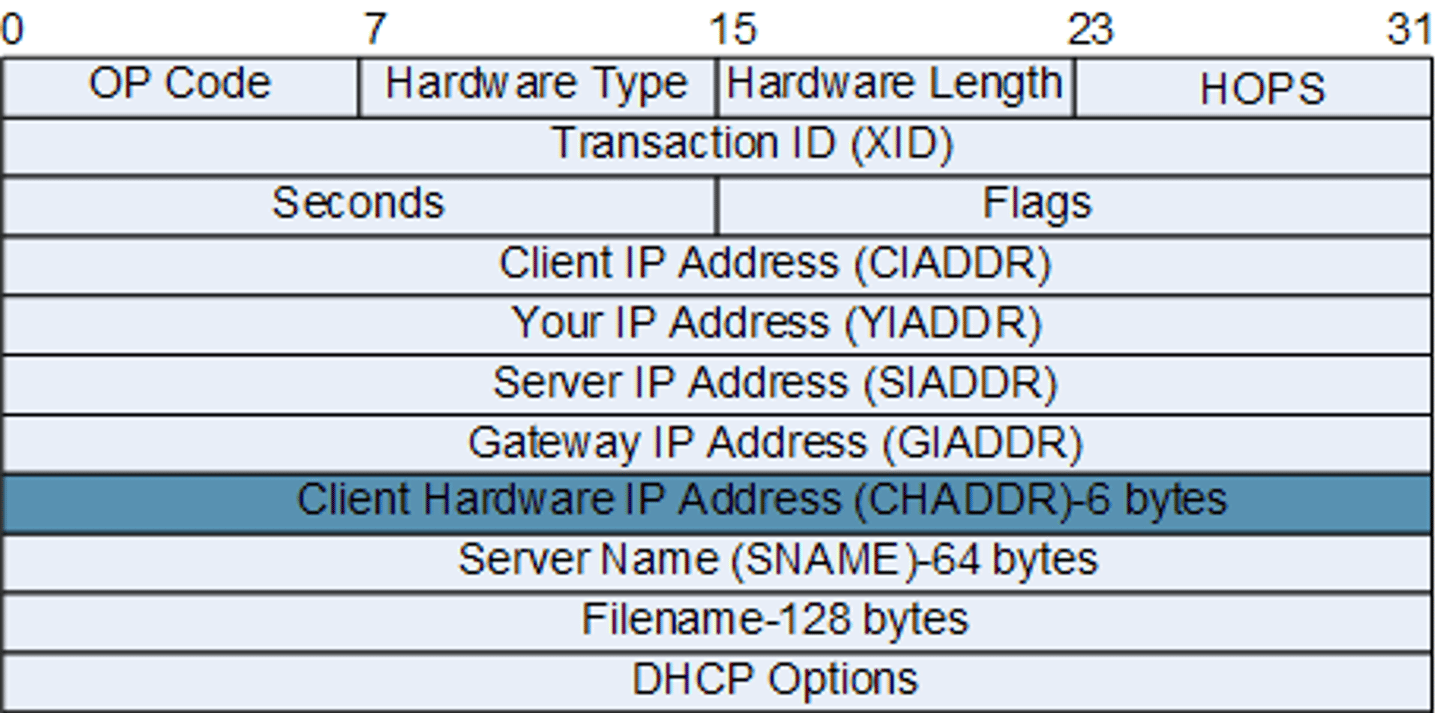
DHCP
Dynamic host configuration protocol
udp/67/68
assigns IP address settings to local machines
When does the client IP get added into the DHCP packet?
The client IP address is added to the DHCP packet by the DHCP server in the "Offer" or "Ack" message after the client has requested an IP address.
Who adds your IP to the dhcp packet?
the server
Who adds the client IP to the DHCP packet?
the client
DHCP Tags
DHCP tags are the options included in DHCP packets that provide additional information to the DHCP client, such as the IP address of the default gateway or the DNS server.
12 - Host Name
43 - Vendor Info
etc.
Magic Cookie
The Magic Cookie is a four-byte field used in DHCP to identify a vendor or protocol. It's located at the beginning of the options field and is always set to the value 0x63825363.
DHCP Tag 53
Indicates the DHCP Message type
(discover, offer, request, ask)
DHCP Exchange
the DHCP client sends a DHCP Discover message to the server to request an IP address lease. The server then responds with a DHCP Offer message containing an available IP address. The client then requests the IP address by sending a DHCP Request message, and the server confirms the assignment by sending a DHCP Acknowledgement message.
DHCP Exchnage Diagram
~Client sends request (BC)
~Since BC message cannot be routed, DHCP service must be on first router, or a default route to a DHCP server
~Server sends offer back to the requesting MAC address
~client fills in IP
~server affirms with an ACK
Be able to interpret a DHCP Config file
Available IP address range
Number of IP Addresses
Lease Times
Lease Time
A time limit on the validity of a DHCP-issued IP address.
Give an example of when you would employ a short lease time and when you would employ a long lease time and explain why for each example.
§ If you have an office where people are working for hours a day, you want the lease time to be longer than at McDonalds for example.
§ If a customer has a lease for an IP, and they walk off so their computer does not get to release, it'll lock up that IP address, becuase the protocol was never able to close out that lease. You would have to wait until that long lease time is up. Thats why it's better to have a shorter on in that scenario
DNS
Domain Name System
The service that translates URLs to IP addresses.
UDP (sometimes TCP) 53
Iterative DNS
Iterative DNS is a type of DNS resolution in which a DNS client requests information from a DNS server, and the server responds with the best information it has available. The client then uses that information to make another request, and the process continues until the client has obtained the complete answer to its query.
The client goes to the server. If that server is not the final destination where the IP address is located, it sends back the IP of the server that it thinks will be able to help.
Recursive DNS
Recursive DNS is a type of DNS query in which a DNS resolver queries other DNS servers on behalf of the client to provide the requested domain name resolution, and then returns the resolved IP address to the client.
more effecient, less traffic overhead, less work for the client, faster
forward lookup
resolving domain name --> IP address
reverse lookup
Resolves IP --> domain names
*Nslookup 8.8.8.8 = Google
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name
What is significant about the FQDN?
has a .
signifies the root
location of a resource within the DNS hierarchy that include the top-level domain (TLD), the domain name, and any subdomains
Generic Domain
not associated woith country or region
.com
.net
.org
country domain
Usually two letters, such as .us (United States) or .ca (Canada), that define the location of the domain server for a country
inverse domain
AKA Reverse DNS
resolving IP address to domain name
DNS Port
53 (both udp and tcp but usually udp)
DNS Header
identification number of the DNS query, the DNS query type, the DNS query class, the number of records in the answer section, and the number of records in the authority section and the additional records section.
DNS Header ID Number
help match the DNS query with the corresponding response message that the client receives from the server
Authoritative Answer
A DNS server that hosts a primary or secondary zone containing a particular record can issue the following response to a query for that record:
DNS Flags
AA - Authoritative Answer
TC - Truncated
RD - Recursion Desired (set by client)
RA - Recursion Available (set by server)
Question record vs resource record
A question record is a DNS query sent by a client to a DNS server to request information about a domain name or resource record, while a resource record is a DNS response from the DNS server that provides the requested information, such as an IP address associated with a domain name.
When does DNS use TCP?
When transmitting more then 512 bytes
zone transfers
DNS troubleshooting
Check if issue on single or multiple clients.
One client: Get DNS server IP, check connectivity between, flush cache or switch DNS server, verify A/CNAME records, verify TTL
systemctl status
config files
FTP
File Transfer Protocol
TCP 20 --> data trasnfer
TCP 21 --> control
FTP transfer
Client Server ---------------- ---------------- | User | | FTP Server | | Application | | Application | ---------------- ---------------- | | | Establish connection | | -----------------------> | | | | Send authentication credentials | | <----------------------- | | | | Change to binary mode | | -----------------------> | | | | Send commands | | <----------------------- | | | | Transfer data | | <----------------------- | | | | Close connection | | -----------------------> | | |
Active FTP
-Client sends FTP request on port 21
-Server makes connection from port 20 to the clients random data port
-If client uses NAT, the router has no idea where to send the incoming packet
-Firewall also views it as an intrusion attempt since nothing on the client end initiated the link on port 20
mode of FTP communication in which the FTP server initiates a connection to the client's data port, which requires the client to open an additional inbound port on its firewall.
Passive FTP
-Client sends FTP request on port 21
-server then sends back a random port number telling the client which port to listen on
-the client then sends the data on the specified port
a mode of FTP connection where the client opens a control connection to the server and sends a PASV command to request the server to open a data connection back to the client for file transfer.
Active vs Passive FTP
In active FTP, the client initiates the connection to the server's port 21, and the server initiates a data transfer back to the client's data port. In passive FTP, the client initiates both the control and data connections, and the server responds on the data connection.
Active is the OG version: you send the PORT cmd with the ftp cmd and you connect to that port
Passive sends the PASV cmd with ftp cmd and teh serevr sends a port that the client can connect tp
Is active or passive FTP more secure?
PASV
FTP cpmmands
open
close
user
ls
cd
put
get
quit
DDNS
Dynamic Domain Name System
service that maps domain names to IP addresses, automatically updating the DNS records as IP addresses change.
Telnet
network protocol used to provide remote access to a server or other network device, allowing a user to control it as if they were physically present at the device.
Define Telnet and explain why it isnt secure
Telnet is a clear text authentication protocol
It was the old way to cpnnect to a machine, but it is not encrypyted so it is not considered safe.
SSH
clear text authentication protocol, creates a secure tunnel, encrypted traffic, secure alternative to Telnet
TCP port 22
How does telnet know what is a data and a control character
control has a 1
data has a 0
how does Telnet recognize a control character?
It has an "interpret as command" - the next character you see will be a cmd
How do you read an ls -l
owner, group, world
how big, who group, who owner
How do you do chmod numbers work?
777 is full permission to everyone
umask
A special variable used to alter the permissions on all new files and directories by taking away select default file and directory permissions.
Jailing users
locks users in their home directory
what are the limitations of jailing users?
You only have access to what is in you rhome directory
CUPS
Common Unix Printing System
URL
Uniform Resource Locator
Parts of a URL
protocol - Host - Port - Path
Static and Dynamic Documents on a web server
Ststic - HTML, nothing will chnage if you click on it
Dynamic - usually has links or interactive controls that you can send/receive info from the server
HTTP and HTTPS ports
How does HTTP get a file
80
443
GET
HTTP Cookie
Small piece of data that is sent from the web server and is stored in the user's web browser while the user is browsing
Message Transfer Agent
A messaging component that routes, delivers and receives e-mail.
Message Access Agent
which is a software program that retrieves email messages from a server and delivers them to a user's local mailbox or email client.
User Agent
Locally accessed software that allows the receipt of and response to communication.
POP3 vs IMAP
POP3 downloads the email from a server to a single computer, then deletes the email from the server. On the other hand, IMAP stores the message on a server and synchronizes the message across multiple devices.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
which is a software program that retrieves email messages from a server and delivers them to a user's local mailbox or email client.
Why is UDP a better choice than TCP for streaming video and audio?
UDP is a better choice than TCP for streaming video and audio because it provides faster and more efficient transport of the data. UDP has less overhead and does not require the same level of error-checking and retransmission that TCP does, making it more suitable for time-sensitive and real-time data like streaming media
Reliability
Multimedia applications require reliable data transmission to ensure that all the data is delivered to the receiver in the same order that it was sent. Loss or corruption of data packets can result in degraded audio or video quality or even complete loss of the transmission
Delay
Delay refers to the amount of time it takes for a data packet to travel from the sender to the receiver. High delay can cause audio or video to be out of sync, which can be especially noticeable in live streaming applications.
Jitter
Jitter is the variation in delay that can occur between different data packets. In multimedia applications, this can cause audio or video to stutter or buffer, leading to a poor user experience.
Bandwidth
andwidth is the amount of data that can be transmitted in a given amount of time. Multimedia applications require high bandwidth to ensure that audio and video can be streamed without interruption or degradation in quality.
Weightage Queueing
Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) is a network queuing technique used to allocate bandwidth to streams of data flows based on their assigned weight in order to achieve fairness and reduce congestion in the network.
Traffic Shaping
A QoS mechanism that introduces some
amount of delay in traffic that exceeds an
administratively defined rate.
AD
Active Directory
DC
Domain Controller
Active Directory
system that MS uses to control access to different resources
Domian Controller
server that is running AD
Symmetric Key Encryption
involves one key for both encryption and decryption.
Assymetric Key Encryption
an encryption method that uses different keys to encrypt and decrypt the data
Explain how we can use Asymmetric-Key Cryptography to do the following:
o Sign a document
o Provide non-repudiation
o Create a session key
Signing a document: The sender of the document can use their private key to sign the document, and the receiver can verify the signature using the sender's public key. This ensures that the document has not been tampered with and that the sender is who they claim to be.
Providing non-repudiation: Non-repudiation is the assurance that the sender of a message cannot later deny having sent the message. To achieve this, the sender can sign the message with their private key, and the receiver can verify the signature using the sender's public key. This way, the receiver has proof that the message came from the sender and cannot be denied later.
Creating a session key: Asymmetric-key cryptography can also be used to securely create a session key that can be used for symmetric-key cryptography. The two parties can exchange their public keys, and each can use the other's public key to encrypt a secret value. When the other party receives this encrypted value, they can use their private key to decrypt it and obtain the secret value. Both parties can then use the secret value as a session key for symmetric-key cryptography. This allows for secure communication without the need to exchange the session key in plaintext.
SDN
Software defined network. A method of using software and virtualization technologies to replace hardware routers. SDNs separate the data and control planes.
Northbound vs Southbound Traffic
In Software-Defined Networking (SDN), the northbound traffic refers to the communication between the SDN controller and the applications or services that use the network. This traffic flows from the controller to the applications and services, and it carries information about network topology, performance, and policies.
On the other hand, southbound traffic refers to the communication between the SDN controller and the network devices such as switches and routers. This traffic flows from the controller to the network devices, and it carries instructions on how to configure, manage, and control the network.