C2
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IGCSE chemistry: : Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, Isotopes, Atomic Structure, Electronic Configuration, and Metallic Bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Define element and give an example
A pure substance that cannot be broken down chemically into a simpler substance, made of only one type of atom.
Ex: Hydrogen (H), and Iron (F)
Define compound and give an example
A pure substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together.
Ex: CO2 (carbon dioxide), and H2O (water)
Define mixture and give an example
Substance, physically combined, made up of two or more elements/compounds
Ex: Coffee and seawater
Define isotope
Different forms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
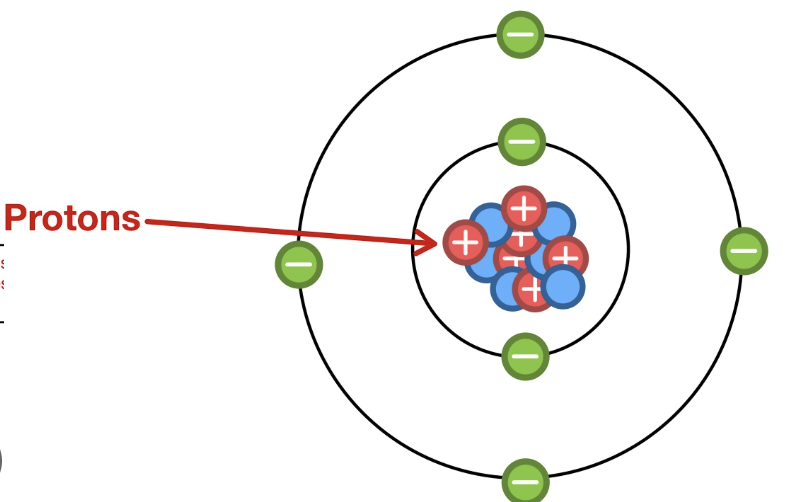
What is the location, mass, and charge of a proton?
It’s located in the nucleus, it has a mass of 1, and a charge of 1
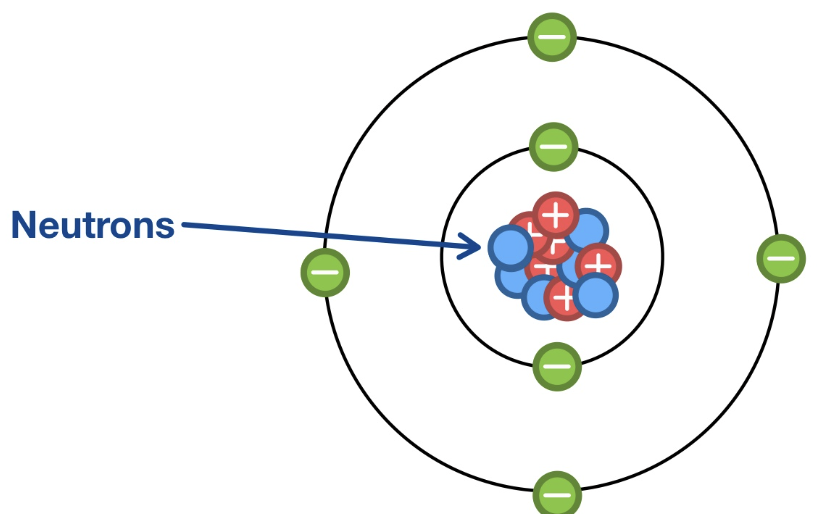
What is the location, mass, and charge of a neutron?
It’s located in the nucleus, it has a mass of 1, and it has no charge

What is the location, mass, and charge of an electron?
It’s located in the shell, it has a mass of 0, and a charge of -1
Define atomic number
The total count of protons found within an atom’s nucleus (number of protons=number of electrons)
Define atomic mass
The actual mass of a single atom
How do you calculate atomic mass?
number of protons + neutrons in an atom
What is the neutron equation?
mass number - atomic number
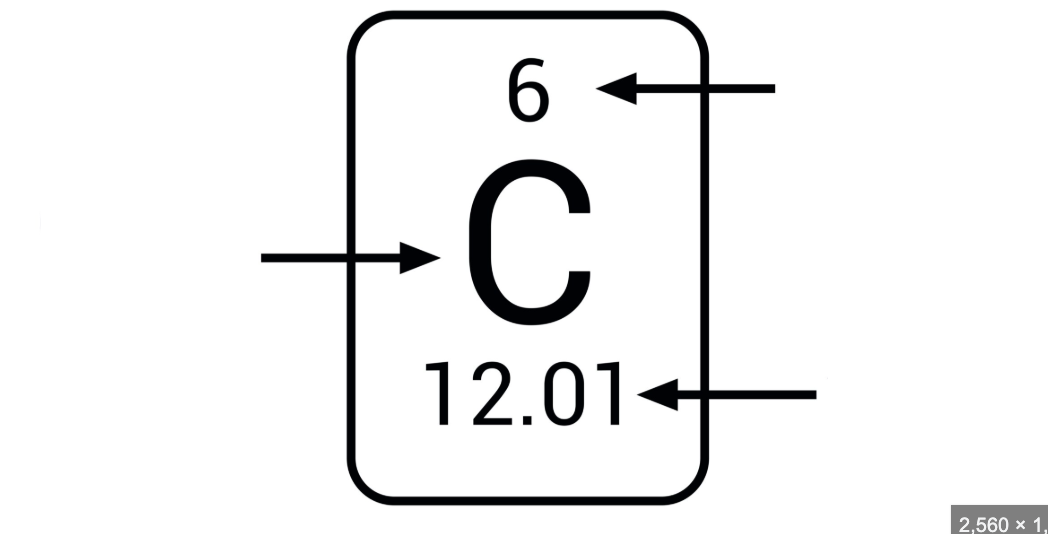
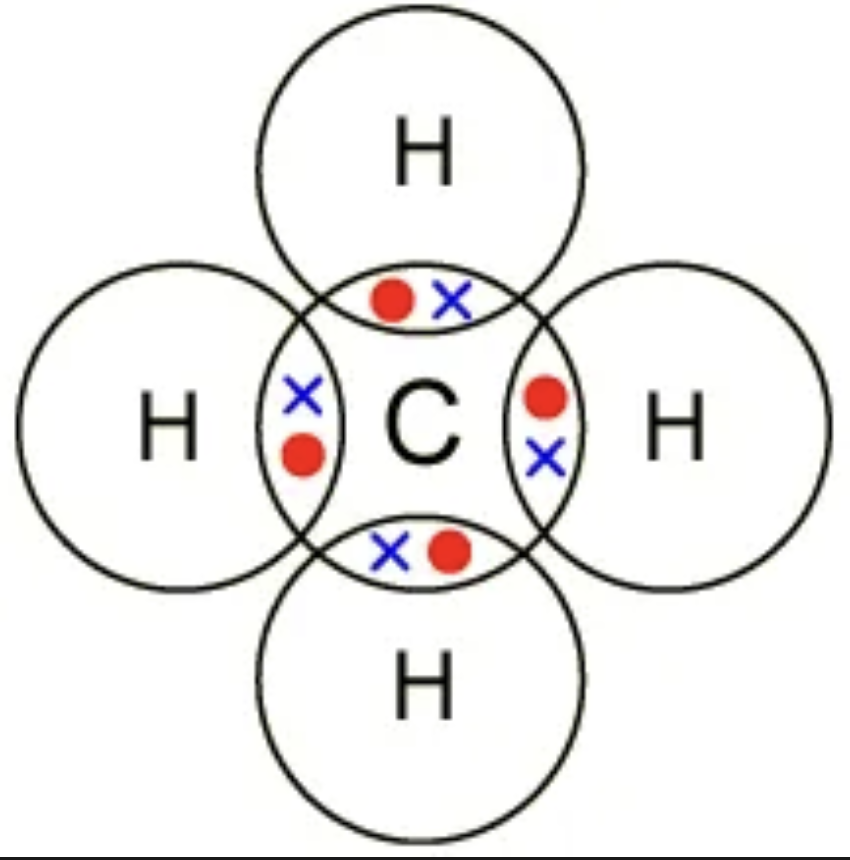
Label the image

How is the periodic table arranged?
In order of increasing atomic number, from left to right and top to bottom
What do the groups in the periodic table tell is?
Elements with the same number of valence electrons
Define valence electrons
Electrons in the outer shell of an atom
What do the periods in the periodic table tell us?
The number of electron shells an atom has
Define ions
Atoms or molecules with a positive or negative charge
How are ions formed?
Due to the gain or loss of electrons
What ion charges will be formed from atoms in the groups 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7?
1: 1+
2: 2+
3: 3+
4: 4+/4-
5: 3-
6: 2-
7: 1-
Ionic bonds form between what?
Negative and positive particles
How are the ions involved bonded to each other?
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between their opposite charges cf
If an atom gains an electron, what charge will it have?
A negative charge
If an atom loses an electron, what charge will it have?
A positive charge
Why do atoms of elements have a neutral charge?
Because they contain an equal amount of positively and negatively charged electrons
Describe the structure of an ionic lattice
Three dimensional, repeating arrangement of positively and negatively charged ions
What do covalent bonds form between?
Oppositley charged ions
How are the atoms involved bonded to each other?
Ionic, covalent, or metallic bonded

Draw the dot and cross diagram for H2 (Hydrogen)
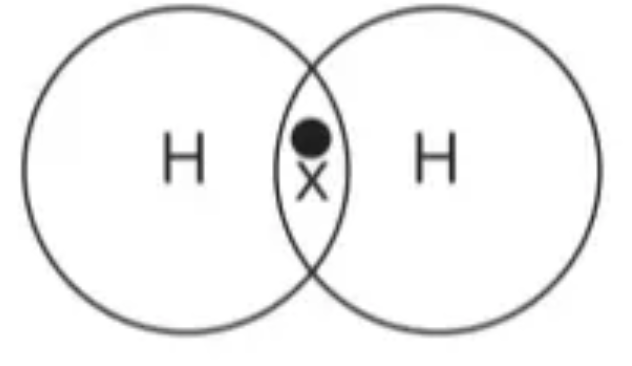
Draw the dot and cross diagram for Cl2 (Chlorine)

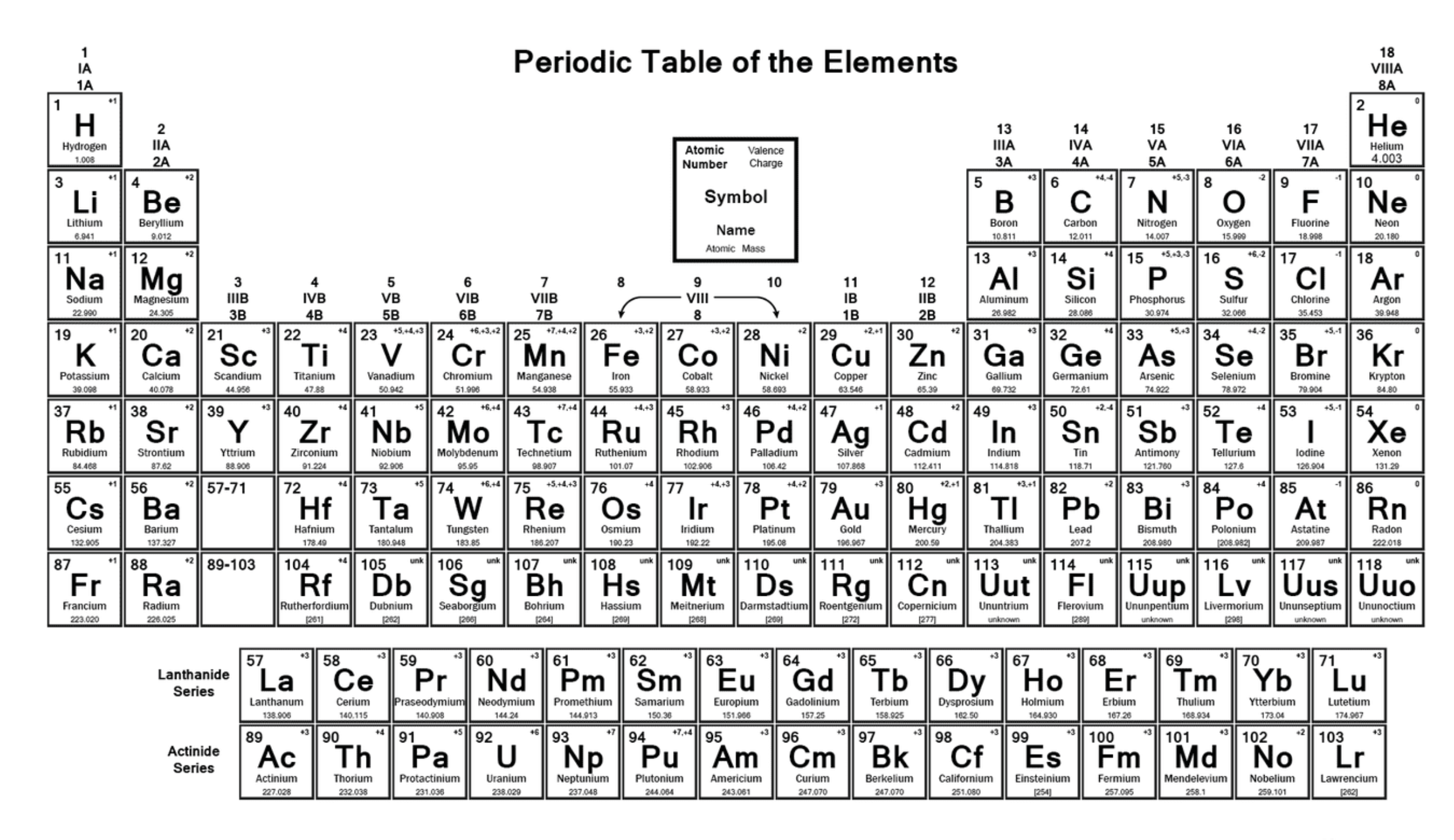
Draw the dot and cross diagram for CH4 (Methane)
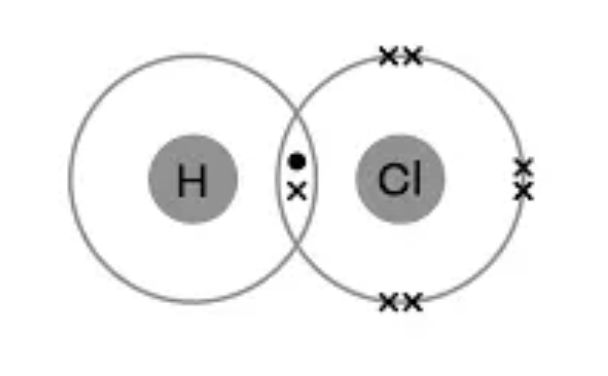
Draw the dot and cross diagram for HCl (Hydrochloric Acid)

Draw the dot and cross diagram for N2 (Nitrogen)

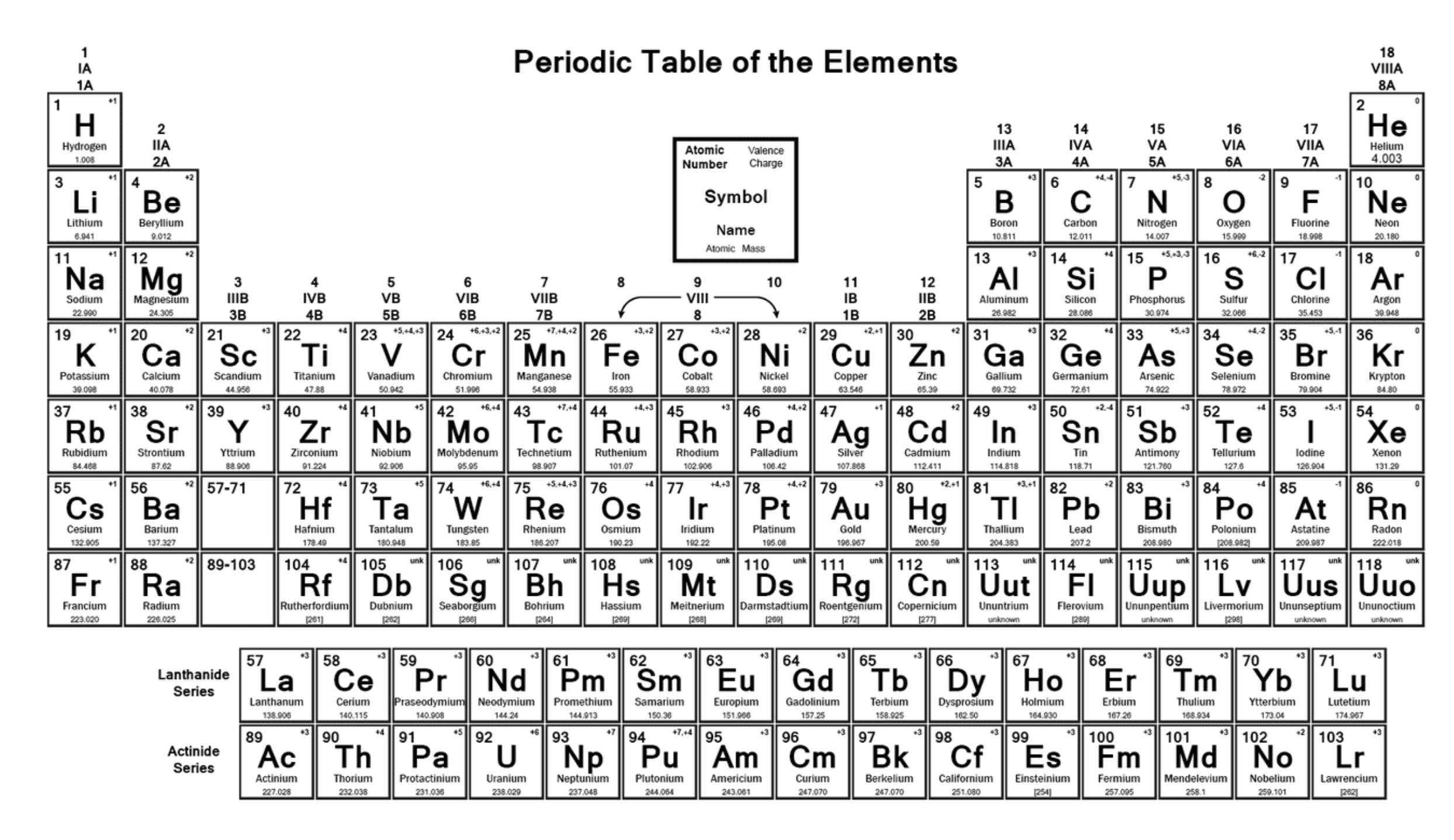
Draw the dot and cross diagram for C2H4 (Ethene)
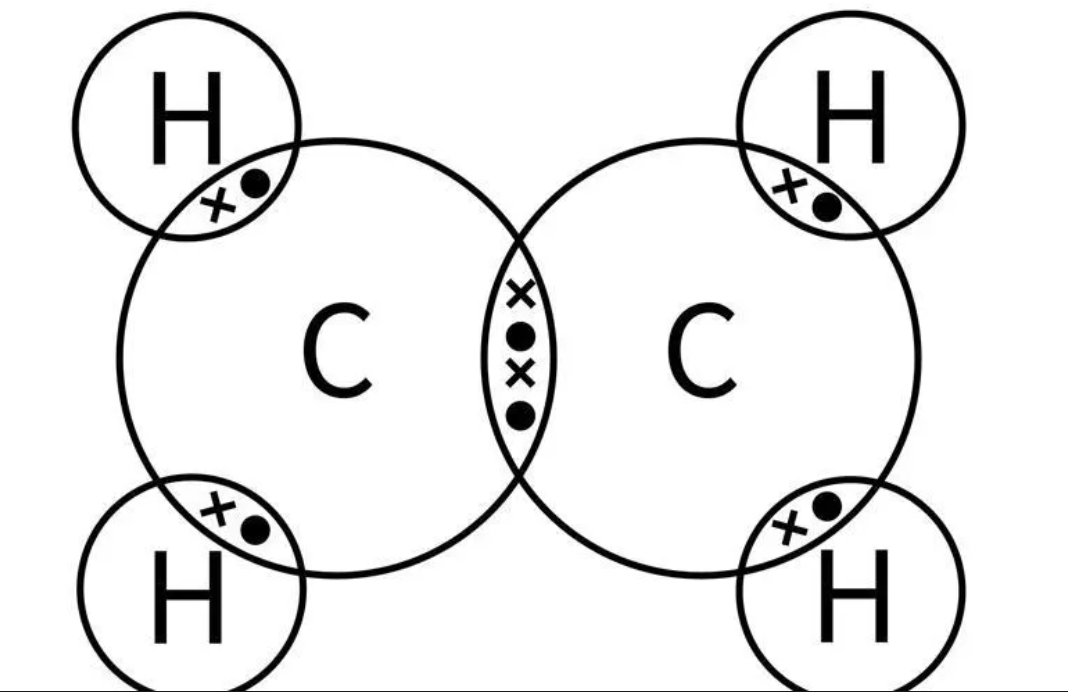

Draw the dot and cross diagram for CH3OH (Methanol)
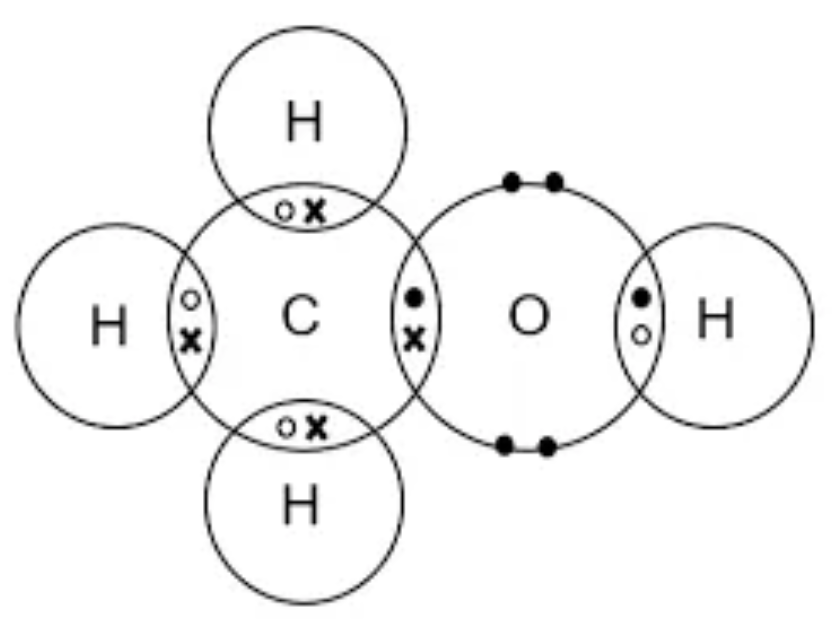
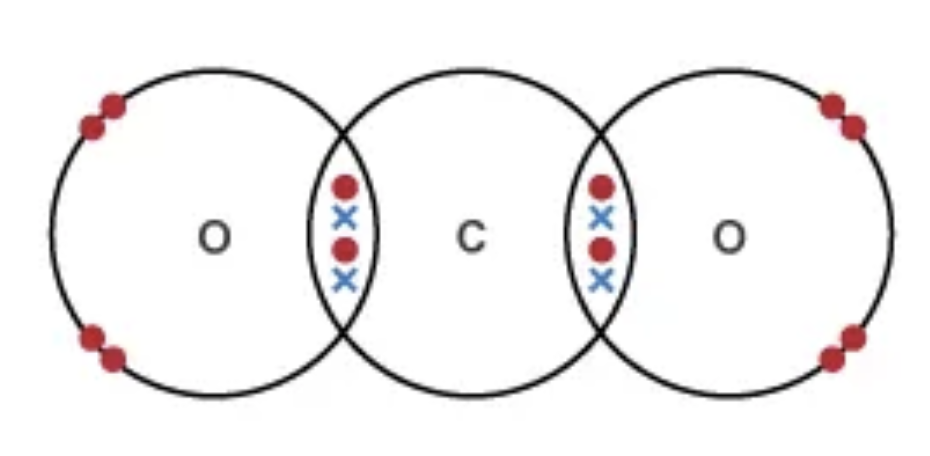
Draw the dot and cross diagram for CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
Draw the dot and cross diagram for H2O (Water)

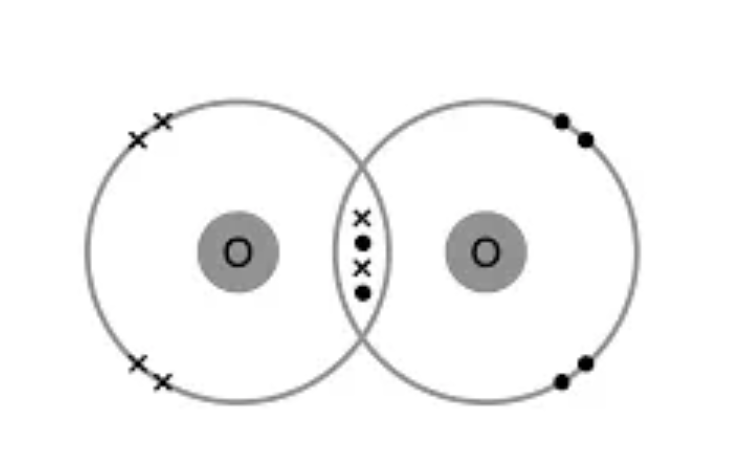
Draw the dot and cross diagram for O2 (Oxygen)
Describe the volatility of ionic compounds
Low volatility due to strong electrostatic attractions between their ions
Describe the solubility of ionic compounds
Most dissolve in water because water molecules are polar and they can surround and separate ions, but some are insoluble and form a precipitate
Describe the electrical conductivity of ionic compounds
They can’t condunce electricity in solid state because the ions are fixed in a crystal lattice form, but molten or dissolved ions become mobile
Describe the volatility of simple covalent compounds
High volatility because they have weak intermoecular forces between their molecules
Describe the solubility of simple covalent compounds
They generally dissolve in water. becuase most of them are nonpolar
Describe the volatility of simple covalent compounds
They are poor electrical conductors because they lack charged particles
Describe the structure of a diamond
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 4 other carbon atoms around it. 3D tetrahedral arrangement
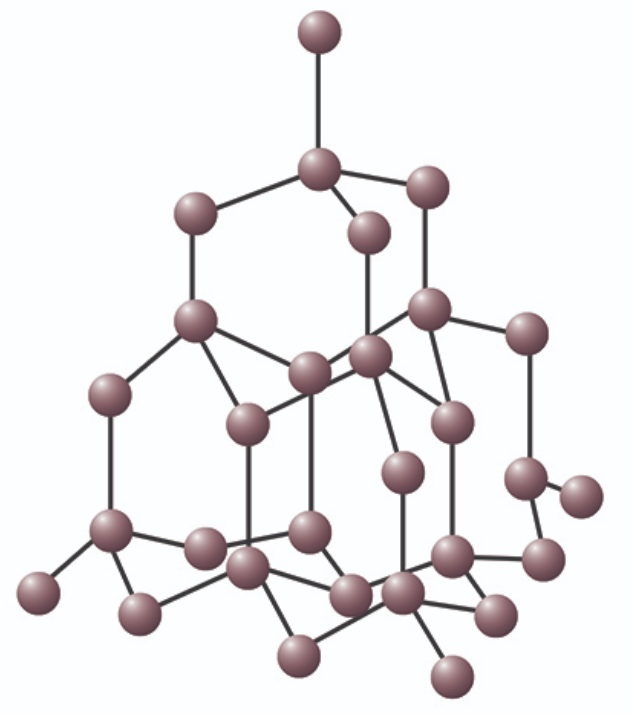
Why is diamond so strong? Provide an example of what it is used for
Diamond is strong because each carbon atom forms 4 strong, covalent bonds with 4 neighbouring carbon atoms, forming a dense network where stress is evenly distributed, making it really hard.
Uses: making cutting tools
Why does diamond have such high melting and boiling points?
Becuase of the covalent bonds between the carbon atoms
Describe the structure of graphite
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 3 other carbon atoms, leaving 1 delocalised electron for each atom. Made of layers of carbon atoms arranged in hexagonal rings.
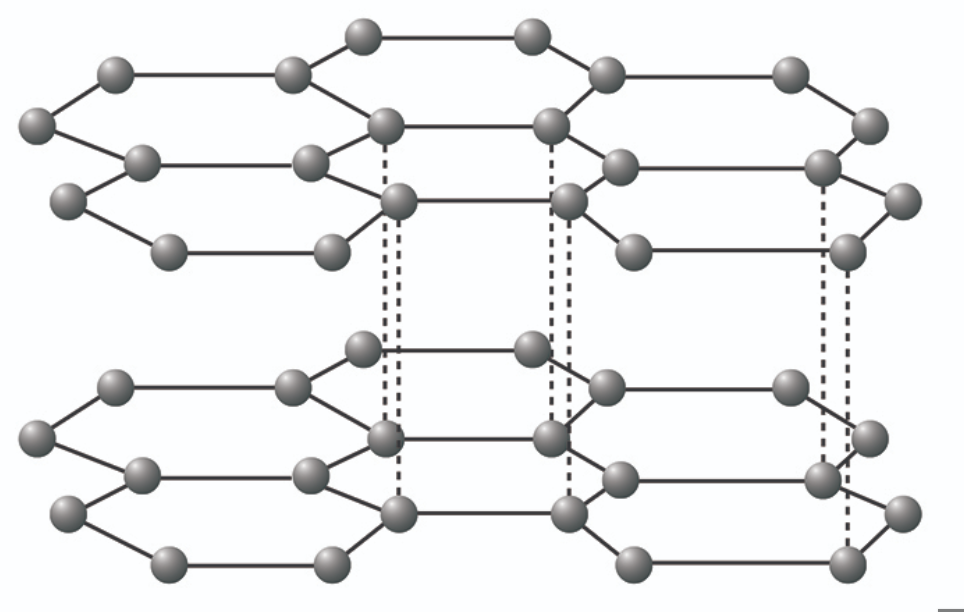
Why is graphite able to conduct electricity?
Because it has 1 free electron for each atom, and they are arranged in a layer structure with delocalised electrons between them
Why is graphite ‘slippery’? Provide an example of what it is used for
Because it is arranged in layers that can slide over each other, and they are joined by weak intermolecular forces.
Uses: Lubricant
Define metallic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between cations in a giant metallic lattice and a sea of delocalised electrons (the amount of delocalised electrons depends on the group number (valence electrons))
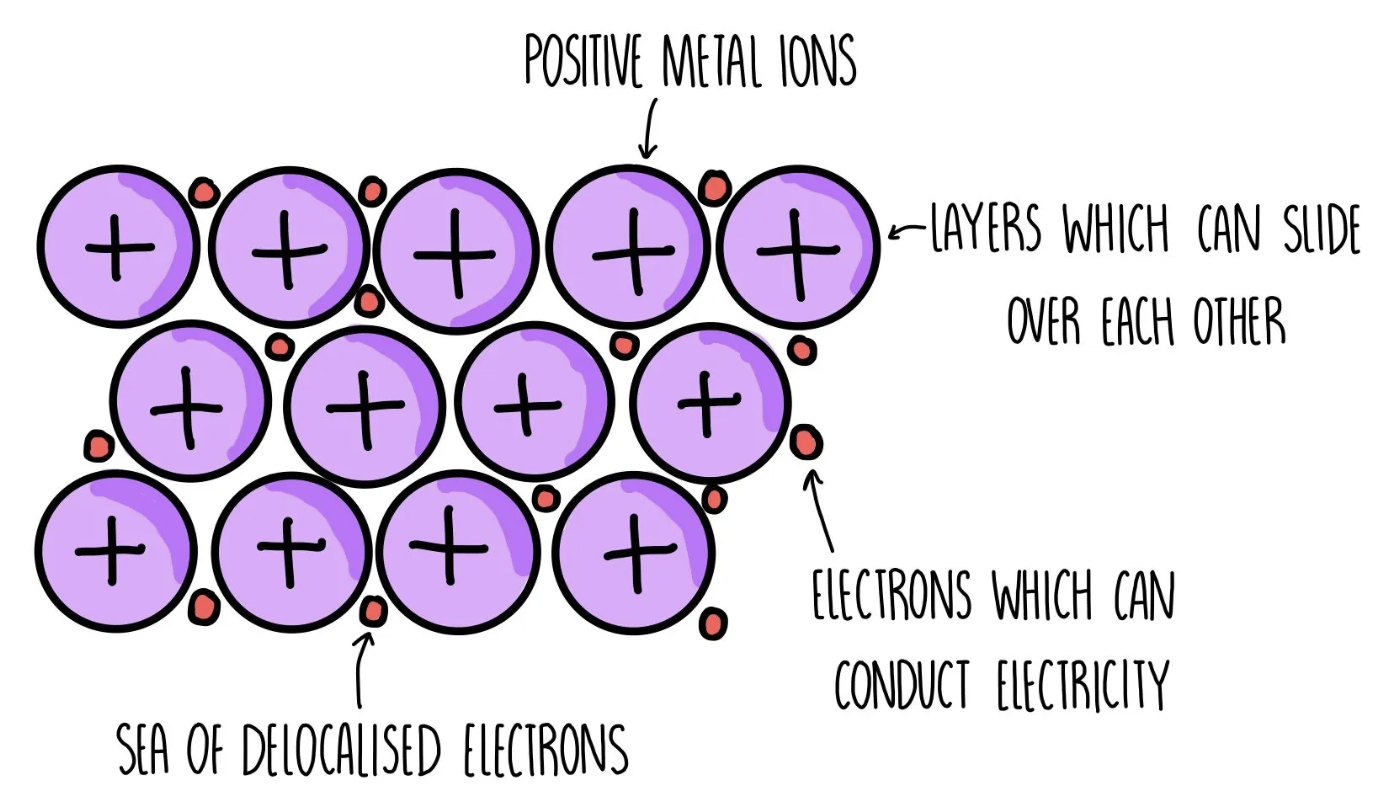
Which are the properties of metallic bonding?
Good conductors of electricity: they have delocalised electrons, which allow them to carry electrical charge
Malleable: the cations are arranged in layers that can slide over each other
High melting and boiling point: they have a strong electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalised electrons, which requires a lot of energy to break
What are physical changes?
A change in the form or appearance of a substance that doesn’t alter its chemical composition
What are chemical changes?
A reaction where new substances with different properties are formed by breaking and making new chemical bonds
What are the differences between chemical and physical changes?
A physical change alters a substance’s form but not its chemical identity, usually reversible, and involves no new substances, while a chemical change creates new substances with different properties, it is typically irreversible and involves breaking and forming chemical bonds.
Give examples of chemical changes
Combustion, oxidation, cooking, fermentation, decomposition
Give examples of physical changes
Melting ice, boiling water, dissolving sugar in water, crushing a can
List the properties of metals
Positive ions, lose electrons, good conductors, malleable, high melting point, high density, shiny
List the properties of non-metals
Negative ions, gain electrons, poor conductors, brittle, low melting point, low density, dull
Why are noble gases unreactive?
Because they have a full outer electron shell, which makes them very stable
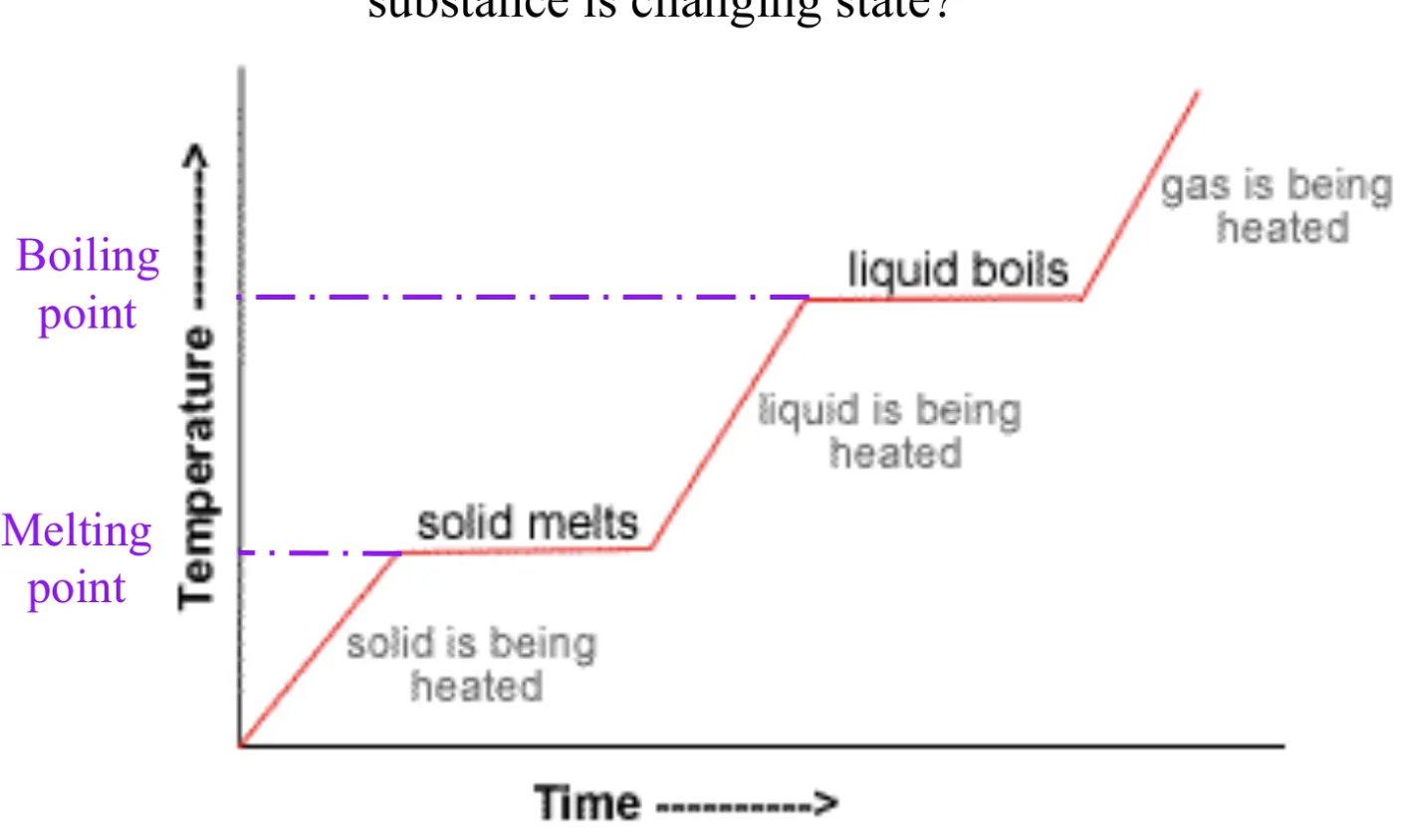
What is this image showing?
A heating curve
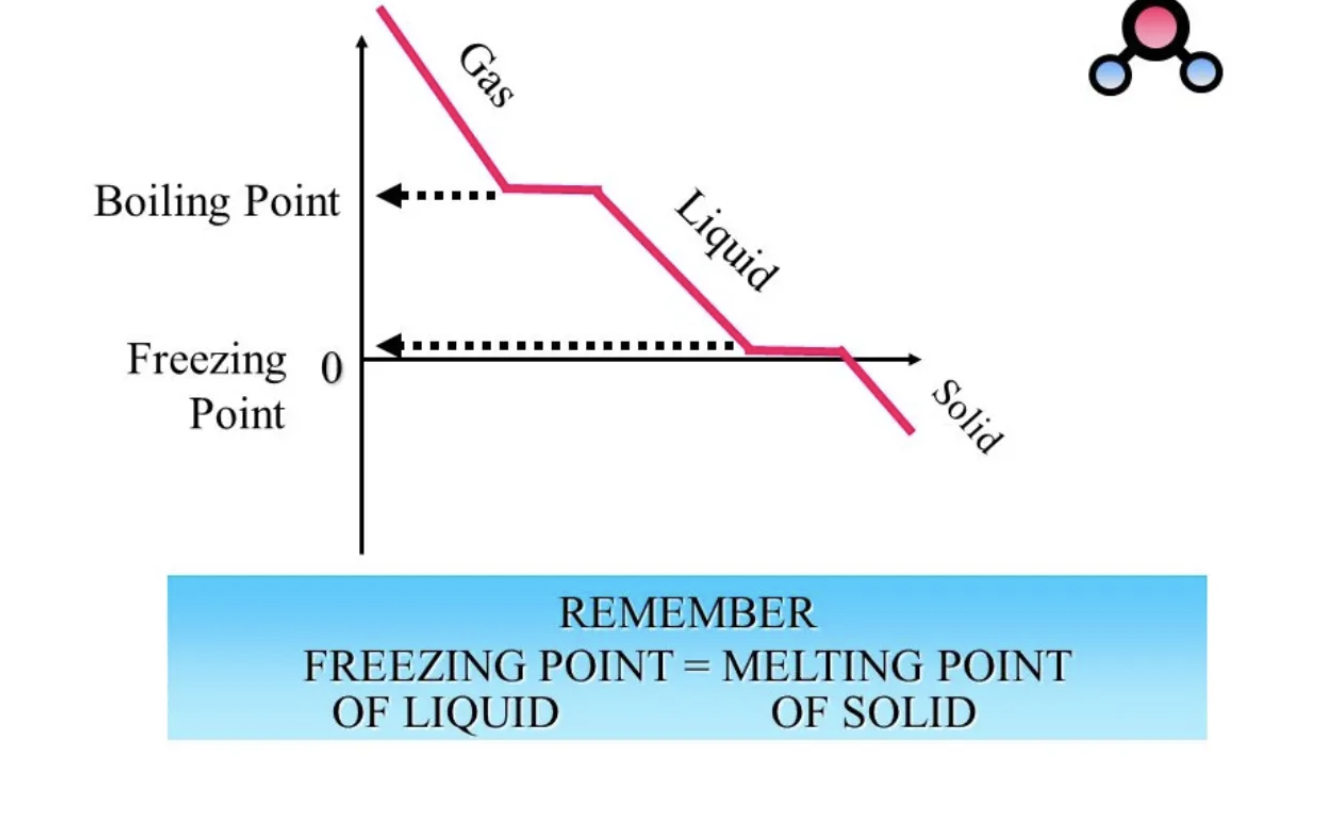
What is this image showing?
A cooling curve