AP Psychology - Sleep
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Conciousness
Our awareness of ourselves and our environment.
Circadian Rhythm
A regular sequence of biological processes, such as temperature and sleep, that occurs every 24 hours.
Sleep Cycle
A period of sleep lasting about 90 minutes and including one or more stages of NREM sleep, followed by REM sleep.
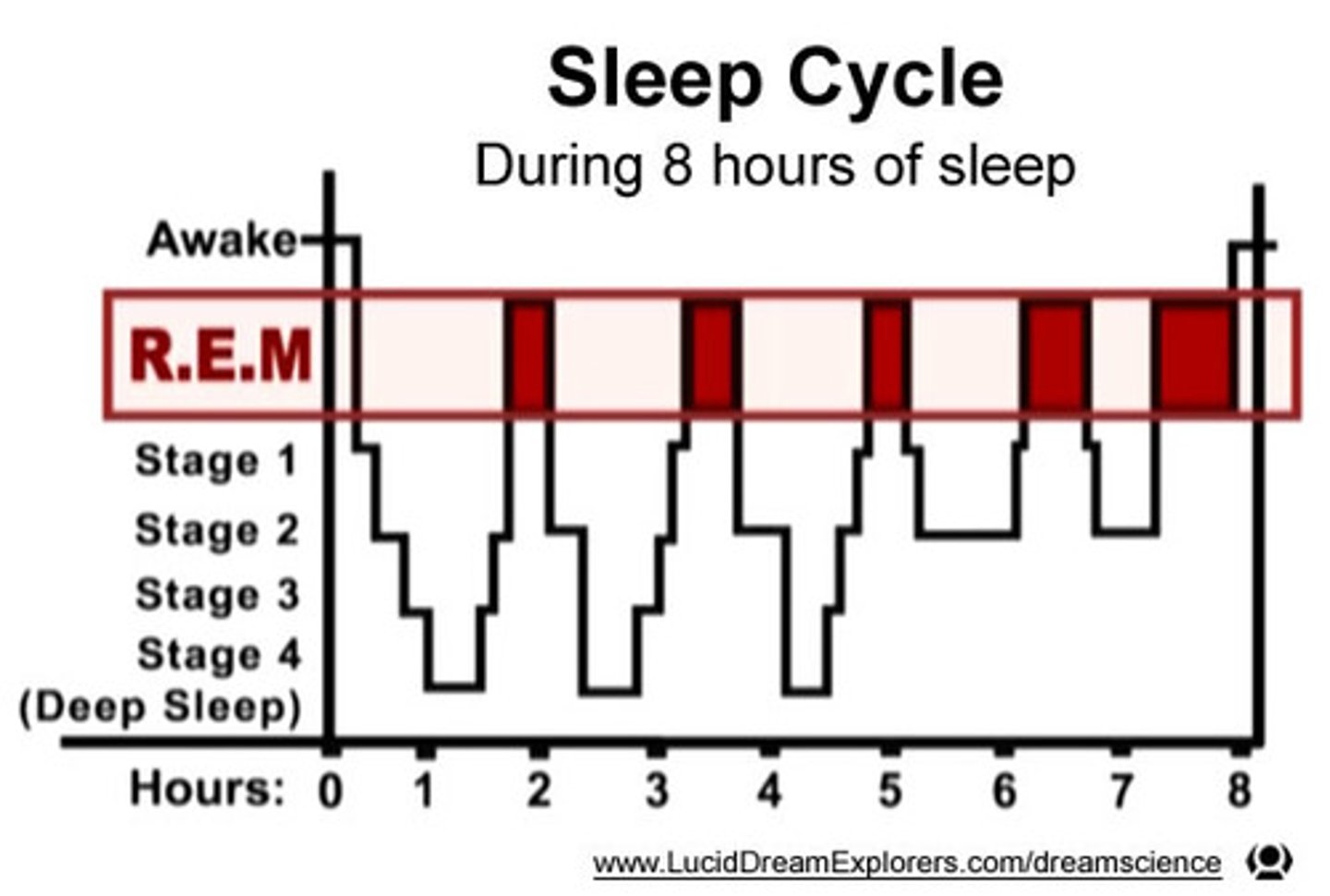
REM Sleep
A recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
Alpha Waves
The relatively slow brain waves of a relaxed, awake state.
Delta Waves
The large, slow brain waves associated with deep sleep.
Insomnia
Recurring problems in falling or staying asleep.
Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times.
Sleep Apnea
A sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings.
Night Terrors
A sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares,these occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep, and are seldom remembered.
Occurs usually in small children
Manifest Content
According to Freud, the remembered story line of a dream.
Latent Content
According to Freud, the underlying meaning of a dream.
REM Rebound
The tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation.
Posthypnotic Suggestion
A suggestion, made during a hypnosis session, to be carried out after the subject is no longer hypnotized; used by some clinicians to help control undesired symptoms and behaviors.
Dissociation
A split in consciousness, which allows some thoughts and behaviors to occur simultaneously with others.
Depressants
Drugs (such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions.
Barbituates
Drugs that depress the activity of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment.
Opiates
Opium and its derivatives such as morphine and heroin; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety.
Stimulants
Drugs (such as caffeine, nicotine, and the more powerful amphetamines, cocaine, and Ecstasy) that excite neural activity and speed up body functions.
Amphetamines
Drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing speeded-up body functions and associated energy and mood changes.
Methamphetamine
A powerfully addictive drug that stimulates the central nervous system, with speeded-up body functions and associated energy and mood changes; over time, appears to reduce baseline dopamine levels.
Hallucinogens
Psychedelic ("mind-manifesting") drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input.
LSD
A powerful hallucinogenic drug; also known as acid.
THC
The major active ingredient in marijuana; triggers a variety of effects, including mild hallucinations.
Onset Sleep
-brain emit beta waves
-muscles, heart relax
-brain transitions slightly to slow alpha waves
-awareness of sensations continue - faster brainwaves, muscle volume supresses
Stages 1 & 2
very aware of your environment, scientifically asleep, less concious the longer you're in
Stage 3 & 4
Delta Sleep, no awareness of environment, growth hormones are released, illnesses are cured, all the chemicals you lost during the day are replenished.
REM Sleep
rapid eye movement sleep, a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
Freud's Wish Fulfillment
Dreams provide a "psychic safety valve"—expressing otherwise unacceptable feelings; contain manifest (remembered) content and a deeper layer of latent content—a hidden meaning.
Information Processing
Dreams help us sort out the day's events and consolidate our memories
Activation Synthesis
the idea that dreams are the result of the cerebral cortex interpreting and organizing random flashes of brain activity, originating in the lower brain structures, especially the pons
State Theory (hypnosis)
A theory that hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness.
Role Theory (hypnosis)
According to this theory, subjects under hypnosis merely act in accordance with the hypnotized role. They are not in a special state
posthypnotic suggestion
a suggestion that is made to a person who is hypnotized that specifies an action he will perform (usually in response to a cue) after he has awakened
Subconciousness
is a store of information that was registered in memory without being consciously attended.
Preconciousness
Ideas that are not in your awareness presently, but you could recall them if you had too.
Nonconciousness
things like heartbeat, blood pressure, breathing, blinking, etc
Unconciousness
Repressed thoughts, kept from emerging