Unit 6: EVOLUTION
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/62
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
evolution
change in genetic make up of a population over time
2
New cards
evolutionary fitness
favorable variations for survival and reproduction, populations can evolve not individuals
3
New cards
mutations
random changes to DNA, errors in mitosis/meiosism or in environmental change
4
New cards
sexual reproduction
mixing alleles, genetic recombination (new arrangement in offspring)
5
New cards
what creates new phenotypes
new genetic recombinations
6
New cards
dawrins idea of natural selection
a) variation exsists in populations
b) over-production of offspring (more than the environment can handle)
c) competition (food/mates/escape predators)
d) differential surival
e) differential reproduction (adaptations become more common
b) over-production of offspring (more than the environment can handle)
c) competition (food/mates/escape predators)
d) differential surival
e) differential reproduction (adaptations become more common
7
New cards
Lamackian view of evolution
adaptations were created by environmental necessity
8
New cards
Darwin view of evolution
adaptations are inherited traits/genes
9
New cards
Is natural selection random
NOT RANDOM, those with the most FIT traits are selected for SURVIVAL and reproduction
10
New cards
Changes in the average trait of a population (3 types)
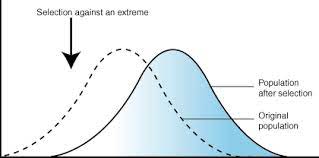
a) directional selection
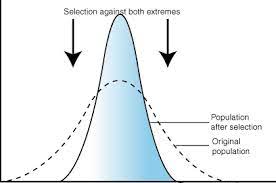
b) stabilizing selection
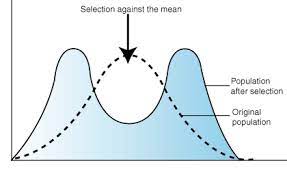
c) disruptive selection
b) stabilizing selection
c) disruptive selection
11
New cards
Heterozygote Advantage
keeps the recessive alllele in the population (ex: sickle cell anemia)
12
New cards
Artificial Selection
hidden variations can be exposed through selections (ex: breeding dogs)
13
New cards
Genetic Drift
Chance events changing frequency of traits in a population (NOT adaptation to environmental conditions, not selection)
14
New cards
what is the founder effect
small group splinters off and starts new colony (random who joins new colony)
15
New cards
what does bottleneck mean
disaster reduces population to small # and then population recovers and expands again but from a limited gene pool
16
New cards
Human impact on: artificial selection/in-breeding
loss of alleles in gene pool
17
New cards
Human impact on: loss of genetic diversity
reduces adaptability
18
New cards
Human impact on: overuse of antibiotics/insecticides
resistance increased
19
New cards
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
created idea of hypothetical, non-evolving population (preserves allele frequencies), natural populations are NEVER in H-W equilibrium
20
New cards
H-W conditions that ocurs in non-evolving populations
a) very large population (no genetic drift)
b) no migration (no gene flow in or out)
c) no mutation (no genetic change)
d) random mating (no sexual selection)
e) no natural selection (everyone equal fit)
b) no migration (no gene flow in or out)
c) no mutation (no genetic change)
d) random mating (no sexual selection)
e) no natural selection (everyone equal fit)
21
New cards
Populations and Gene pools
a) a population is a localized group of interbreeding individuals
b) gene pool is a collection of alleles in the population
c) allele frequency is how common is that allele in the population
b) gene pool is a collection of alleles in the population
c) allele frequency is how common is that allele in the population
22
New cards
what is a species
a population whose members can interbreed and produce viable, fertile offspring
23
New cards
how do new species orginiate
when 2 populations become reproductively isolated from each other
24
New cards
speciation model: allopatric
geographic separation
25
New cards
speciation model: sympatric
still live in the same area
26
New cards
Sympatric speciation example
disruptive selection can cause this or polyploidy events
27
New cards
Pre-==zygotic== barriers
obstacle to mating or fertilization if mating occurs
28
New cards
Pre-zygotic barriers: types of isolation
geographic, ecological, temporal isolation, behavioral, mechanical, gametic
29
New cards
Post-Zygotic Isolation
a) hybrid inviability - aborted fetus
b) hybrid sterility - offspring are infertile
c) hybrid breakdown - future generations have less fertility/viability
b) hybrid sterility - offspring are infertile
c) hybrid breakdown - future generations have less fertility/viability
30
New cards
Divergent Evolution
2 or more species are separating from a common ancestor
31
New cards
what is adaptive radiation in terms of divergent evolution
large number of species formed
32
New cards
convergent evolution
2 or more species sharing similar traits but NO COMMON ANCESTRY (also analogus)
33
New cards
Evolution evidence: paleontology
fossils show change in a species over time
34
New cards
Evolution evidence: biogeography
study of geographic distribution of species
35
New cards
Evolution evidence: morphology
comparing structure
36
New cards
Homologous structure
body parts with similar structure but possible different function (shows common ancestry, divergent evolution)
37
New cards
Analogous structure
same function, different structure (different ancestry, convergent evolution)
38
New cards
Evolution evidence: biochemical or molecular (DNA)
similarities in gene sequences, protiens, DNA
39
New cards
Vestigal Organs
remnants of structures that were functional in ancestral species
40
New cards
Speed of Evolution: gradualism
species are slowly evolving (fossil evidence)
41
New cards
speed of evolution: punctuated equilibrium
short periods of fast evolution followed by periods with little to no change
42
New cards
Coevolution (2 living things in response to each other)
two or more species reciprocally affect each other’s evolution
a) predator-prey
b) competitive species
c) mutualism (pollinators and flowers)
a) predator-prey
b) competitive species
c) mutualism (pollinators and flowers)
43
New cards
Primitive Earth: Atmosphere
all chemicals/compounds necessary are thought to have originated on Earth
44
New cards
Primitive Earth: Inorganic Precursors
water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, small amounts of hydrogen and carbon monoxide
45
New cards
What were inorganic precursors used for
were used as the monomers for forming complex molecules
46
New cards
Is it possible to form organic molecules from inorganic molecules
yes
47
New cards
What is abiotic synthesis
1953 miller and urey tested the hypothesis: formed organic compounds (amino acids and adenine)
48
New cards
Key events in the origin of life: origin of cells
protocells, lipid bubbles →separate inside from outside → metabolism & reproduction
49
New cards
Key events in the origin of life: origin of genetics
RNA is first genetic material
50
New cards
what are the functions of RNA
encodes info, self-replicating, enzyme, regulatory molecule, transport molecule (tRNA, mRNA)
51
New cards
does natural selection work upon fitness of RNA or DNA
RNA
52
New cards
Origin of Eukaryotes
Endosymbiosis (symbiosis in which one of the symbiotic organisms lives inside the other)
53
New cards
First Eukaryotes
developent of internal memebranes, create internal micro-environments, advantage: specialization = increase efficiency (natural selection)
54
New cards
sequence of gentic varitation under the influence of natural selection
1) a change occurs in the environment
2) poorly adapted individuals do not survive
3) well adapted individuals leave more offspring
4) genetic frequencies within the population change
2) poorly adapted individuals do not survive
3) well adapted individuals leave more offspring
4) genetic frequencies within the population change
55
New cards
an organism’s relative fitness is measured by its…
contribution to the gene pool of the next generation
56
New cards
what is the only factor that can change allele frequencies in population to produce adaptive evolutionary change
selection
57
New cards
geographic isolation
occurs when two populations are separated by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies of water
58
New cards
mechanical isolation
a type of reproductive isolation where two species physically cannot undergo fertilization
59
New cards
behavioral isolation
occurs when members of a population diverge in their behaviors over time
60
New cards
gametic isolation
a type of prezygotic barrier where the gametes (egg and sperm) come into contact, but no fertilization takes place
61
New cards
directional selection graph
62
New cards
disruptive selection graph
63
New cards
stabilizing selection graph