eukaryotic cells
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
don’t have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles, whereas eukaryotes do.
Ultrastructure
the small structures discovered since using the electron microscope.
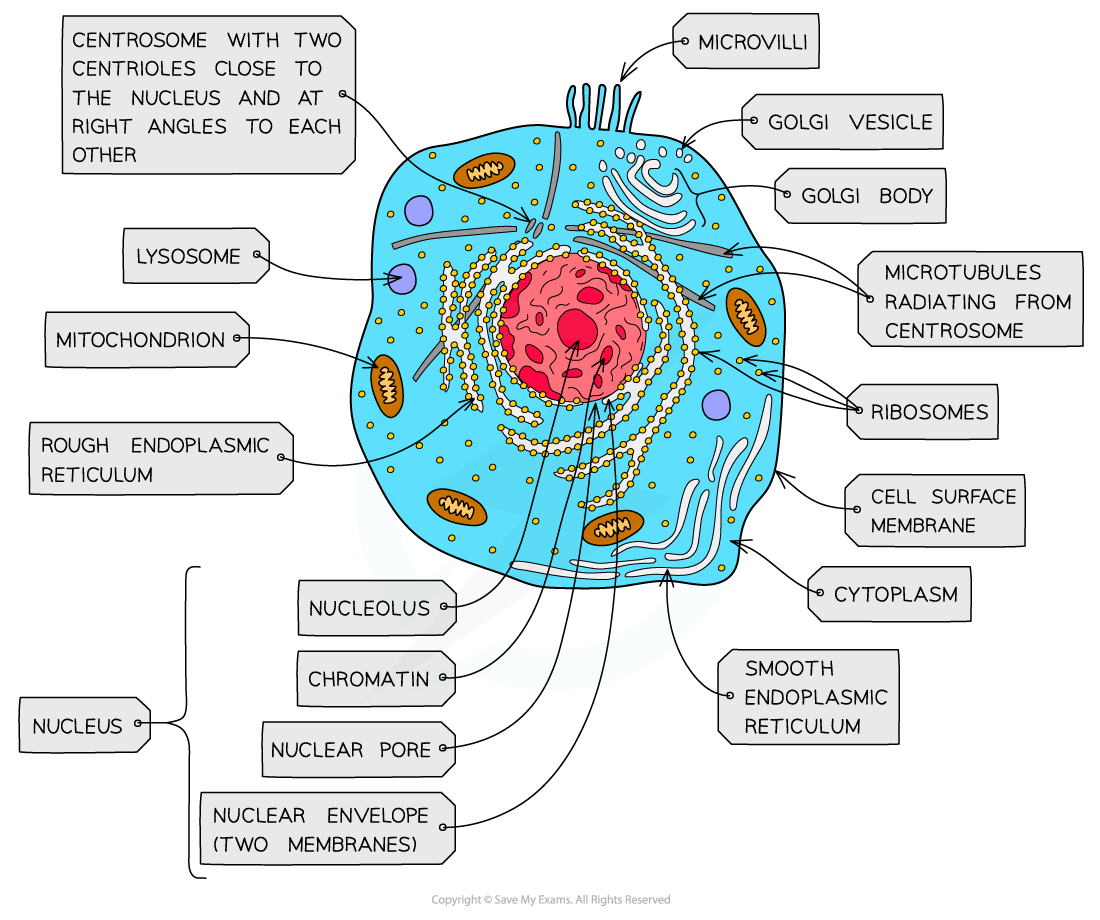
Nucleus
•Largest organelle.
•Surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
•This has pores in it called nuclear pores.
•The fluid inside is called the nucleoplasm
•Contains DNA which is in the form of chromatin when not dividing and chromosomes when it is.
Contains the nucleolus inside.
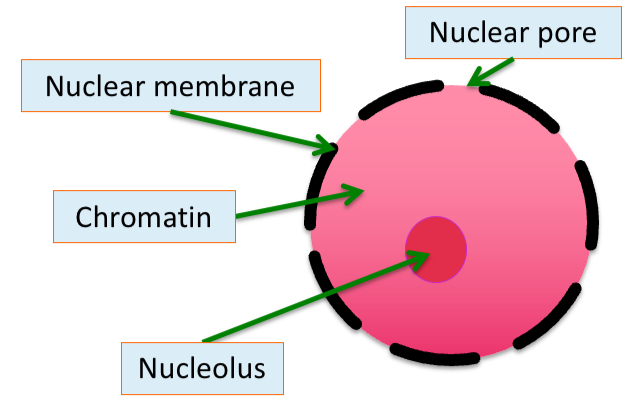
Nucleolus
•Dense, darker staining area of the nucleus.
Produces ribosomes and RNA .
Ribosomes- eukaryotic
•They are made of ribosomal RNA and protein.
•They are used in the process of protein synthesis to assemble the polypeptide.
•The type found in eukaryotic cells are 80S ribosomes.
These are made from a 60S subunit and a 40S subunit.
Free in the cytoplasm and attached to Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
•Endoplasmic reticulum is made from flattened sacs of membrane called cisternae.
•The RER also has ribosomes dotted along the surface as this is the location of extracellular protein synthesis.
•Once a protein has been made the membrane can pinch off to form a vesicle and be transported around the cell.
The RER is usually found next to the nucleus of a cell and sometimes joined to the nuclear envelope.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
•manufacture lipids and steroids such as certain hormones.
It has the same structure as RER but without the ribosomes
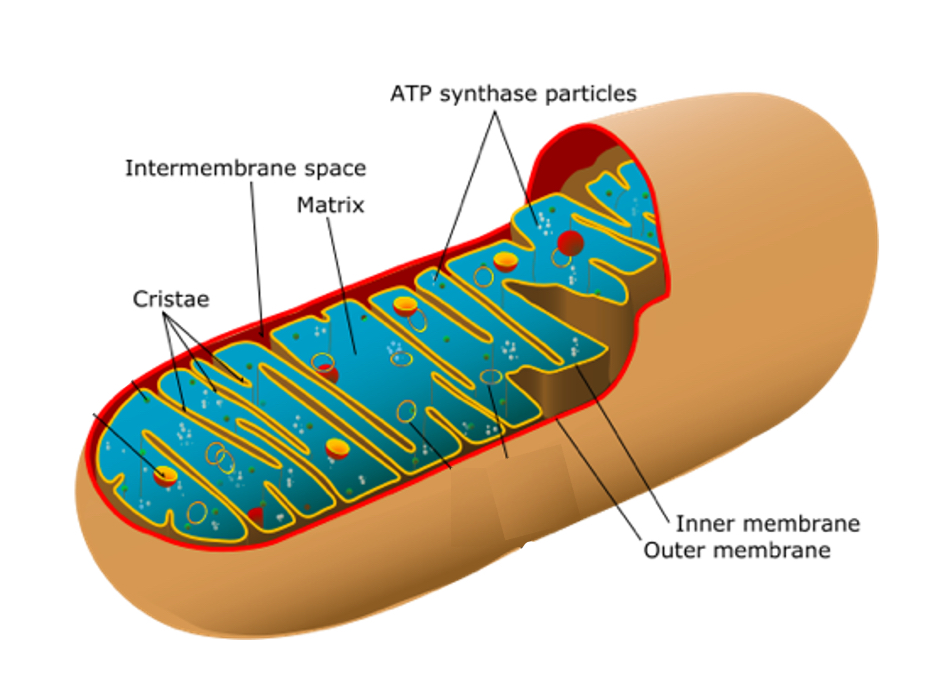
Mitochondria
•Mitochondria are often referred to as the ‘powerhouse of the cell’
•Much of the process of aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria to produce ATP.
•Cells that require more ATP have more mitochondria.
•Capsule shaped or spherical made from a double membrane filled with a fluid called matrix.
The inner membrane is folded into cristae to provide a large surface area.
Centrioles
•Only found in animal cells, not plant.
•Found in a pair near the nucleus, usually at right angles to each other.
•Each one is a bundle of nine microtubules.
•They are used when the cell divides.
They move to opposite ends and produce the microtubule spindle that will attach to the chromosomes and pull them apart.
Lysosomes
•Dark spherical organelles in the cytoplasm.
digestive enzymes.
•Use for breaking down old organelles and in some simple organisms, digesting nutrients.
•Can fuse with cell membrane and release enzymes out of the cell.
Also used in programmed cell death (apoptosis) when a cell self destructs!
Golgi apparatus
•Stacks of membrane bound sheets called cisternae.
•Small membrane bound transport sacks (vesicles) fuse with it and also get pinched off.
•The Golgi receives vesicles containing proteins made in the RER.
•The Golgi modifies the proteins, folds them up, or adds extra parts to make them ready for their role.
Then they release them in a vesicle to be transported around the cell or released at the cell membrane by exocytosis.
Cytoskeleton
•A fibrous network that fills the cytoplasm.
•Gives cells structure.
•Moves and holds structures like organelles .
-made from microtubules and protein microfilaments like actin
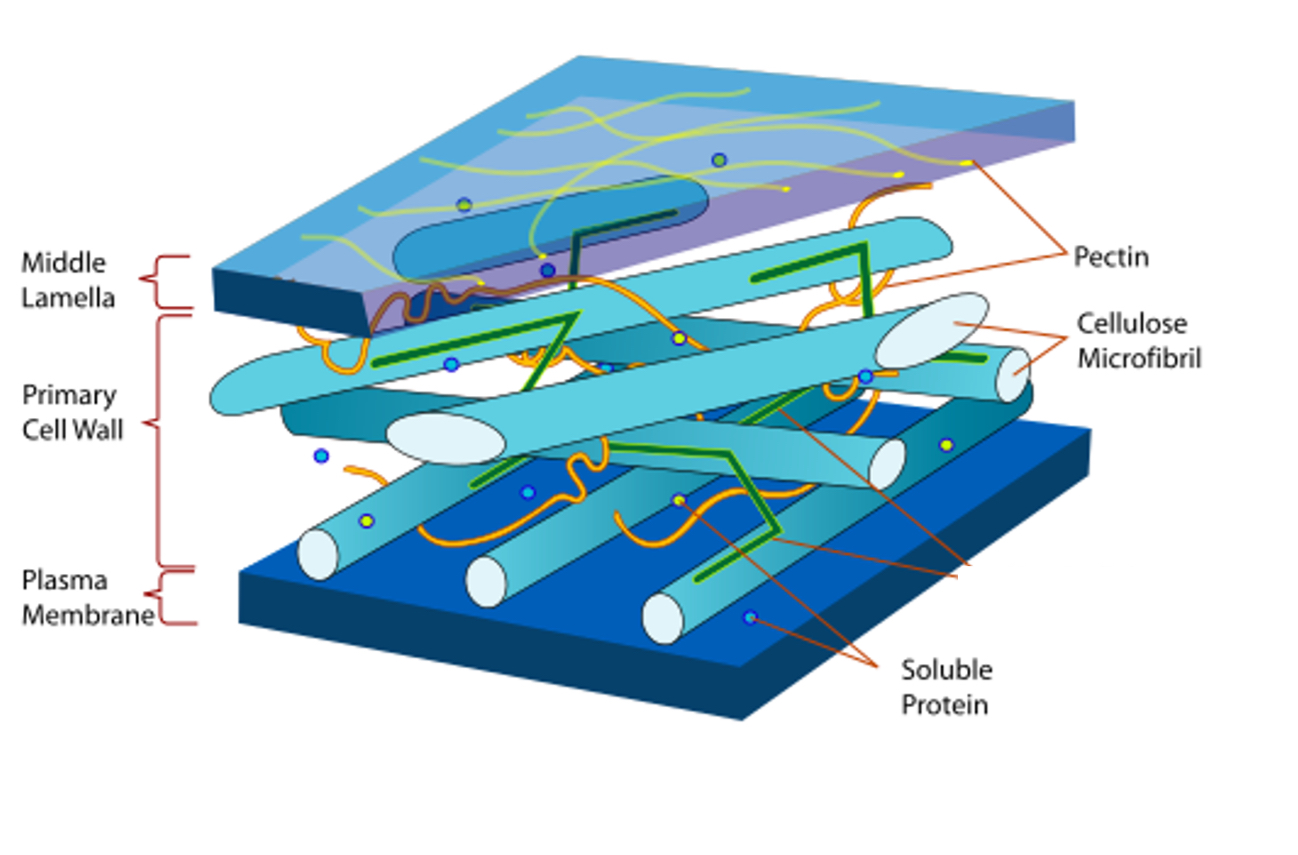
Cell wall
•Surrounds entire cell giving it a regular shape.
strength, support.
•It is freely permeable and does not control what comes in and out of the cell, this is the job of the cell membrane.
•It is made up of a few layers, the middle lamella which contains pectin and the cellulose microfibrils.
•Plant cells can be linked together by gaps in the cell walls called plasmodesmata.
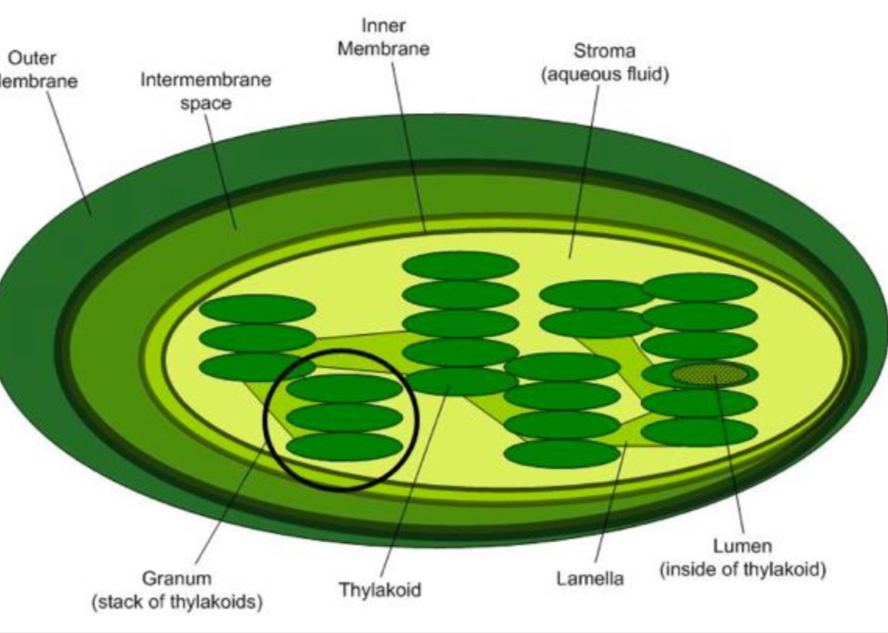
Choloplasts
•The site of photosynthesis.
•Contain chlorophyll which is the green pigment required for photosynthesis.
•Double membrane bound capsule like organelle.
•Inner membrane folded into thylakoids which are stacked up to form a granum.
•This provides a large surface area for chemical reactions to occur.
These are linked by lamella and all surrounded by a liquid called the stroma.
Vacuole
•Animal cells sometimes have a small temporary vacuole, but plant cells have a large permanent vacuole.
•It is filled with cell sap, which is dissolved substances in water.
•Used to help maintain the cell shape.
•Also used for storage.
Tonoplasts
•The tonoplast is the name of the membrane that surrounds the vacuole.
It controls what enters and leaves the vacuole and therefore controls the cell’s osmotic potential.
Cell theory
all living organisms are made up of cells, and all cells are essentially made up of the same fundamental structures. This means that all life is fundamentally the same in terms of structure and requirements for function.
Order of cell structures
Cells → tissues → organs → organ systems
Endosymbiotic theory
The endosymbiotic theory posits that ancient, larger host cells engulfed smaller, free-living prokaryotic cells. These smaller cells survived inside the host and developed into the organelles we know today as mitochondria and chloroplasts
Small, have dna, have ribosomes and double membrane structure