1, 2 - Defining Health and Health Promotion
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
traditional medicine/allopathic medicine/treatment based would define health as the
absence of disease
What is the traditional/allopathic/treatment-based medicine more specific definition of health?
- Absence of the 5 D’s
- Death
- disease
- discomfort
- Disability
- Dissatisfaction
Primitive view of health
- Believed Spirits were responsible for health.
- Consequence of personal doings
Change in health with industrial revolution-rural transition to urban
overcrowding, lack of clean water, poor food supply, disease
18th and 19th century engineering advances
sewage control and food preservation
1900s advances in health
vaccinations and antibiotics
prevent morbidity and mortality
control over diseases like tuberculosis, diphtheria, pneumonia, syphilis, tetanus
simple preventative measures such as washing hands and food preparation
the late 20th century introduced
chronic diseases because people were living longer
What is the definition of health and sickness: Defined by extremes?
- Absence of disease
- Good hygiene
What is the 1947 world health organization definition of health?
- Complete physical, mental, social well being, not just the absence of disease or infirmity
- First time health meant more than an absence of illness. to more holistic
How has the “cause of death” changed over the years?
- shift from infectious to chronic diseases
- decreased morbidity and mortality rates.
Based on the average Canadian child born in 2003, who has a longer life expectancy, males or females?
- Females longer (82.4)
- Males shorter (77.4)
Mortality rates indicate people are living ______. Morbidity rates indicate ______ people suffer from infectious disease.
- longer
- fewer
Even though people are living a longer life, are they living a healthy life?
- Healthy life 66 years
- Impaired life 11.6
- Although living longer, not whole life is quality.
WHO definition of healthy life
- Healthy life expectancy is based on life expectancy but includes an adjustment for time spent in poor health.
Male LE = 77.2, HLE = 70.1
Female LE = 82.3, HLE = 74
What is the most current definition of health?
- The dynamic, ever-changing process of trying to achieve individual potential in the following 7 dimensions:
1. Physical
2. Social
3. Mental
4. Emotional
5. Spiritual
6. Environmental
7. Occupational
The current definition of health also implies what 4 things: health is a _______, people _______ their own health, health is related to? Health is a _____ state.
- Health is a process.
- People can influence their own health.
- Health is related to our environment (social, physical, psychological)
- Health is a relative state (state of mind is crucial)
What is the difference between health and wellness?
- Health: dynamic, multi-dimensional, adaptability to life situations
- Wellness: achieving a high level in each dimension of health
holistic health
a view of health in terms of its physical, emotional, social, intellectual, and spiritual make up
not a fad or quack medicine
not incompatible with conventional medicine
Describe physical health.
- Susceptibility to disease
- Body weight/composition
- Visual
- Strength, endurance, coordination
- Functioning and ability to perform activities of daily living.
Describe social health.
- Ability to have satisfying interpersonal relationships and adapting to various social situations.
- Interactions in friendship, work, school, family
- Communication, listening, conflict management.
What is mental/intellectual health?
- Ability to think clearly, act on information, clarify values and beliefs, analyze critically, decision making capacity.
Occupational health
- Employment satisfaction
- Feeling good about their jobs -> themselves -> healthier lifestyle
- Work and leisure balance
Emotional health
feelings
Ability to: cope with stress, remain flexible, compromise, goals.
Self efficacy, confidence
Describe environmental health.
- The appreciation of external environment
- Individual role in preserving, protecting, and improving environment.
- Can include home or study environment (desk, room, lighting, noise level, comfortable atmosphere)
Describe spiritual health.
- Guiding sense of meaning in life
- Can include religion, beliefs.
- Sense of belonging, community, familiar practices
- Can enhance by engaging in new experiences with nature, art, music.
How might one enhance their health in each of the 7 dimensions of health?
To enhance health in each of the 7 dimensions of health, consider the following:
Physical: Engage in regular exercise, maintain a balanced diet, and get enough sleep.
Emotional: Practice stress management techniques, seek support from loved ones, and engage in activities that bring joy.
Mental: Stimulate your mind through reading, learning new skills, and engaging in critical thinking.
Social: Build and maintain healthy relationships, participate in social activities, and communicate effectively.
Occupational: Find satisfaction and fulfillment in your work, set goals, and maintain a work-life balance.
Environmental: Create a safe and clean living environment, connect with nature, and practice sustainable habits.
Spiritual: Engage in activities that align with your values and beliefs, practice mindfulness or meditation, and seek spiritual guidance if desired.
For health promotion, you need to create optimal conditions for successful behaviour change through:
educational supports
organizational supports
environmental supports
financial supports
Pan-Canadian Healthy Living strategy
supports Canadian health-care system
uses a population health approach
living and working conditions need to be addressed to achieve change by individuals
emphasizes physical activity and nutrition and their relationship to healthy weight
primary prevention
actions designed to stop health problems before they start
ex. physical activity, participaction
prevent
secondary prevention
intervention early in development of health promotion to decrease symptoms or stop progression
ex. Physical activity to decrease risk of high blood pressure
at risk
tertiary prevention
treatment or rehab to limit the effects of a disease someone already has
ex. physical activity to help manage arthritis
treatment
what are the trends in leading causes of death in Canada, 2005
Malignant neoplasms (29.3)
Diseases of the heart (22.4)
factors reflecting sex biases in medical research
androcentricity
overgeneralization
sex insensitivity
double standards
androcentricity
tendency to look at something from male perspective
ex. having male only participants/researchers
overgeneralization
findings use to treat EVERY group, even though finding were only based on males
Sex insensitivity
ex. pregnancy guidelines for physical activity (researchers had no experiences with topic and scared to harm women ) → being insensitive to that life stage
double standards
how information is expected and shared
creating physical activity guidelines
2 factors that are targeted in improving your health: key behaviours to
help lengthen life
quality of life
key behaviours to help lengthen life
good sleep
healthy eating habits
PA regular
oral hygiene
safe sex
avoid tobacco
limit alcohol
regular medical exams
key behaviours to help improve quality of life
control stress
maintain meaningful relationships
time for yourself
fun activities
value each day
learn from mistakes
factors influencing behaviour change
predisposing factors
enabling factors
reinforcing factors
predisposing factors to behaviour change
sex, race, income, family education, knowledge, beliefs
enabling factors of behaviour change
skills, abilities, physical/emotional/mental capabilities
reinforcing factor
support, encouragement from others (ex. workplace has a gym)
belief
an appraisal of the relationship between some object, action, or idea and some attribute of that object, action, or idea (what you think)
attitude
a relatively stable set of beliefs, feelings, and behavioural tendencies in relation to something or someone
health belief model
explains how beliefs may or may not influence behaviours
factors that support belief that change is needed:
perceived seriousness of the health problem
how big of a deal you think it is
perceived susceptibility to the health problem
if you think you are to get it
cues to action
places to be physically active
what is theory of resoned action
suggests that behaviours result from intentions, which are influenced by:
attitudes towards the behavior
subjective norms
perceived behavioural control
It posits that people are more likely to engage in a behavior if they have a positive attitude towards it and perceive social pressure to perform the behavior.
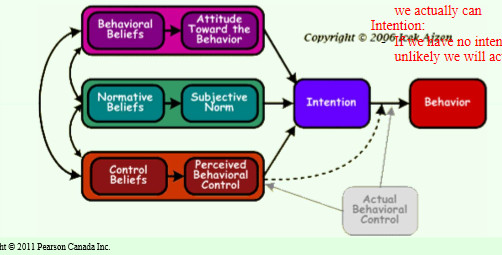
Theory of reasoned action: What is attitude toward the behaviour?
how we think about the action will affect if we try it
does it sound fun, do we like it, are we good at it?
Theory of Reasoned Action: subjective norm
what you think other people will think of you doing this behaviour
pressure of what others want you to do
theory of reasoned action: perceived behavioural control
do you think you have control over this action
sometimes perceived different than actual (think we can’t but can)
manage it? equipment? time?
theory of reasoned action: attitude toward the behaviour
does it sound fun
how we think about the action will affect if we try something
sources of efficacy
mastery experience
verbal persuasion
vicarious experience
physiological/affective states
mastery experience
actual experience
verbal persuasion
positive encouragement
vicarious experience
seeing similar others do well in it
physiological/affective states
positive mood and how you are feeling in the moment
what source of efficacy is most related to norms
vicarious experience most related to norms
knowing similar others can do it, so can you
behaviour change techniques
shaping: developing new behaviours in small steps
visualizing: the imagined rehearsal
modeling
controlling the situation
reinforcement
changing self-talk
self-assessment: antecedents and consequences
analyzing the behaviours you want to change
decision making: choices for change
goal setting and behaviour change: Super SMART
describe Shaping: developing new behaviours in small steps
start slowly
keep steps small and achievable
be flexible
refuse to skip steps
reward yourself for meeting short and long term goals
Visualizing: The imagined rehearsal
visualizing the perfect turnm how to stand up from a fall
modeling
careful observation of other (role model)
controlling the situation
situation inducement
pack gym runners in bag before work, avoid going home, signing up for a class at a specific time
reinforcement
types of positive reinforcers to reward behaviour
Consumable (treat)
Enjoyable activity (show, movie)
Manipulative incentives (companies paying for memberships, bonus for being active)
Possessional (medal)
social
Pros and Cons of reinforcement
pros:
gets people started
Cons:
don’t want to get reliant on rewards
compare rewards to previous times
can become expectation
only focuses on external motivation, need internal motivation to continue long term
changing self talk
Rational emotive therapy
close connection between what people say to themselces and how they feel
meichenbaum’s Self-instructional methods
self instructions and positive affirmation
blocking or thought stopping
purposely stopping negative thoughts
self talk example
negative
I hate going to the dentist, it’s scary
positive
while it might involve temporary pain, I’ll feel much better long term once I have this toothache looked at
analyzing the behaviours you want to change
frequency
duration
seriousness
basis for the problem behaviour
antecedents
what comes before this event that caused it?
skipping a workout because tired of work
decision making: choices for change (DECIDE)
decide in advance what the problem is
explore the alternatives
consider the consequences
identify your values
decide and take action
evaluate the consequences
Super smart goals
Self-controllable
Public
Rewards
Specific
Measurable
Adjustable
Realistic
Time based
mid-late 20th century implementation of health education
only effective for those in upper middle class
some people do not have the same lifestyle choices as others
determinants of health
gender
race
income and income distribution
education
social exclusion
early life
indigenous health
food security
social safety net
health services employment and working conditions
housing
unemployment and job security
disability
income and income distribution
strong link between SES and health
influences other determinants of health
affects overall living conditions, psychological functioning, and influences health related behavior like diet, physical activity, alcohol
hollowing out of the middle class
relationship of life expectancy and income