Chapter 17: Blood (Erythrocytes)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what are the functions of erythrocytes
- delivering O2 and nutrient throughout the body
- transporting metabolic wastes to lungs and kidneys for elimination
- transporting hormones
what does blood regulate
body temp, pH, fluid volume
T or F: Blood is the only fluid tissue in body
true
Matrix is a nonliving fluid called what?
plasma
cells are living blood cells called what
formed elements
what are the three formed elements
erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
blood is composed of
1. plasma (nonliving fluid, least dense component)
2. formed elements
- Buffy coat: leukocytes and platelets (<1% of blood)
- erythrocytes (most dense component)
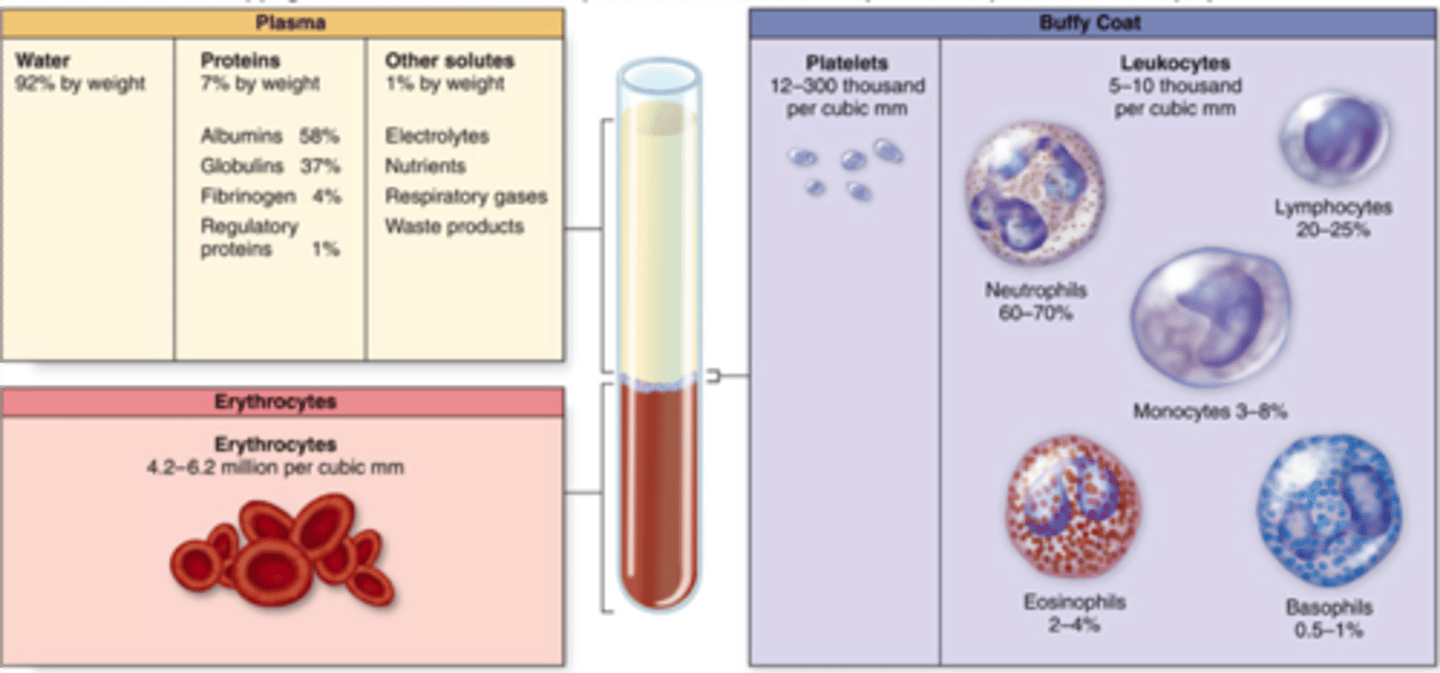
blood plasma is about 90% water with over 100 dissolved solutes. Name the major dissolved solutes
nutrient, gases, hormones, wastes, proteins, inorganic ions, plasma proteins
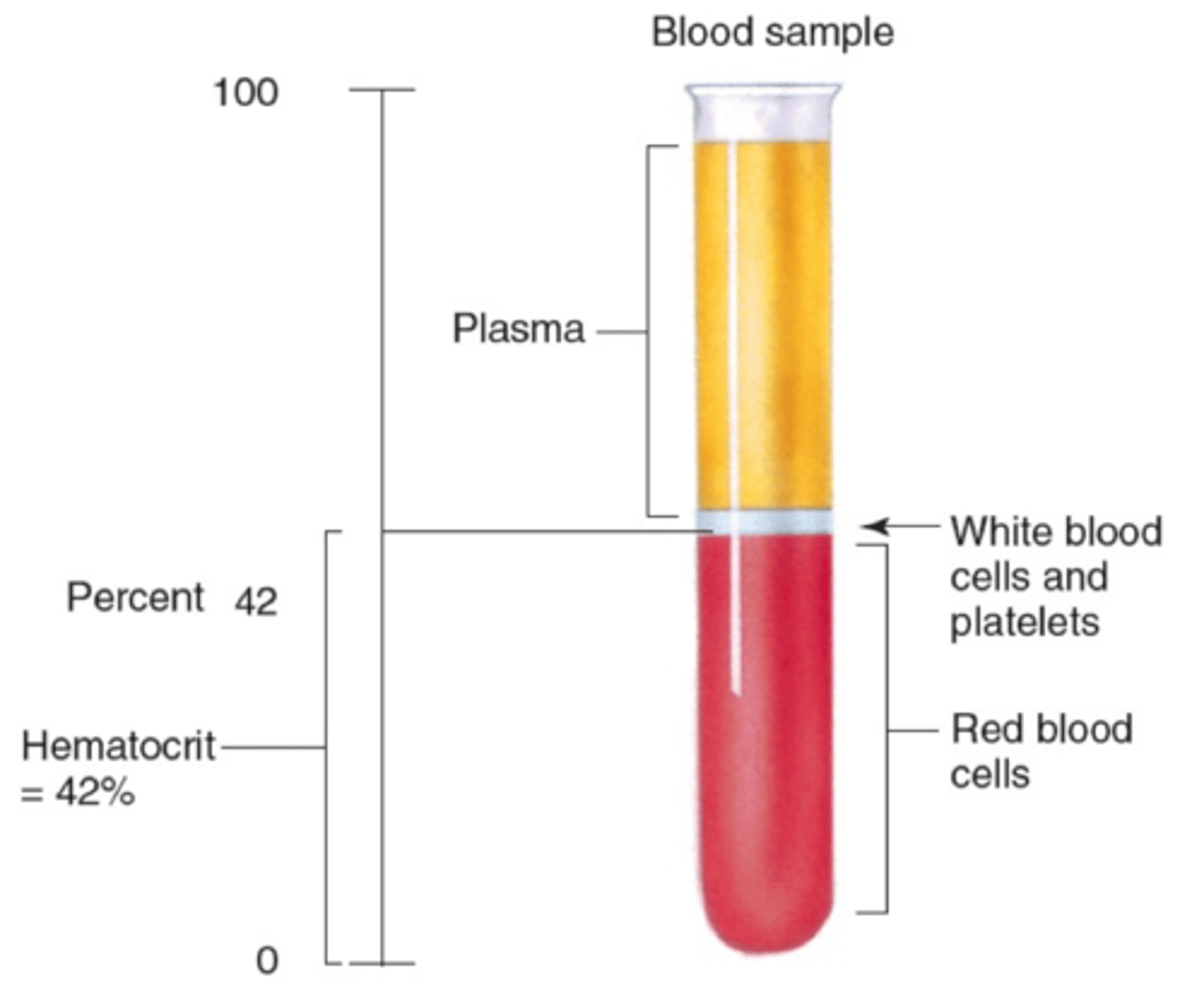
what is hematocrit
percent of red blood cells in your blood
what is the most abundant plasma solute
plasma proteins (8%)
- it stays in your blood
- NOT taken up by cells
what is the most abundant plasma protein
albumin (60%)
- made in the liver
albumin function
maintain osmotic pressure and a carrier of other molecules
do formed elements divide
NO, they are replaced by the red blood marrow
main function of erythrocytes
gas transport
erythrocyte structure
biconcave disc shape, anucleate, essentially no organelles
- filled with hemoglobin (Hb) for gas transport
What protein gives erythrocytes its flexibility
spectrin
how does the structure of RBC's help with its function
biconcave shape: huge surface area compared to volume for gas exchange
- no mitochondria: at production is anaerobic, so they do not consume O2 when transporting
T or F: Hemoglobin binds reversibly with oxygen through bicarbonate based (ph dependent)
true
T or F: hemoglobin consists of a red heme pigment bound to the protein globin
true
what is globin composed of
4 polypeptide chains (2 alpha and 2 beta chains)
- a heme pigment is bonded to each globin chain
- each heme's central iron atom binds to one O2
a single red blood cell contains ________ hemoglobin molecules and ________ oxygen molecules per red blood cell
250 million, 1 billion
hematopoiesis
formation of all blood cells
where does hematopoiesis occur
red bone marrow
- mostly in axial skeleton and girdles; proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur
hematopoietic stem cells (hemocytoblasts)
stem cell that give rise to all formed elements
stages of erythropoiesis
1. hematopoietic stem cell
2. myeloid stem cell
3. proerythroblast: divides many times
4. basophilic erythroblast: synthesizes ribosome (stain blue)
5. polychromatic erythroblasts: synthesize large amounts of red-hued hemoglobin (stain BOTH purple and red)
6. orthochromatic erythroblasts: nucleus degrades, organelles are ejected, causes concave shape
7. reticulocytes: contains small amount of ribosomes
8. erythrocytes: ribosomes degrade, transforming into mature RBCs
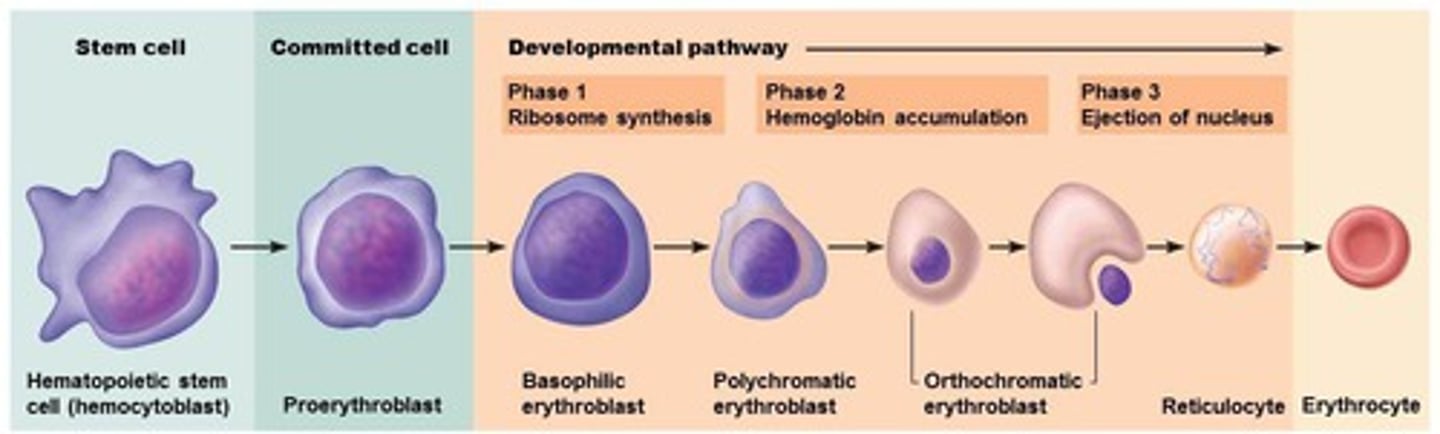
mnemonic devices to remember erythropoietic stages
1. hungry monkeys prefer bananas picked only right & easy
2. happy people buy pretty orange red eggs (MISSING MYELOID STEM CELL STAGE)
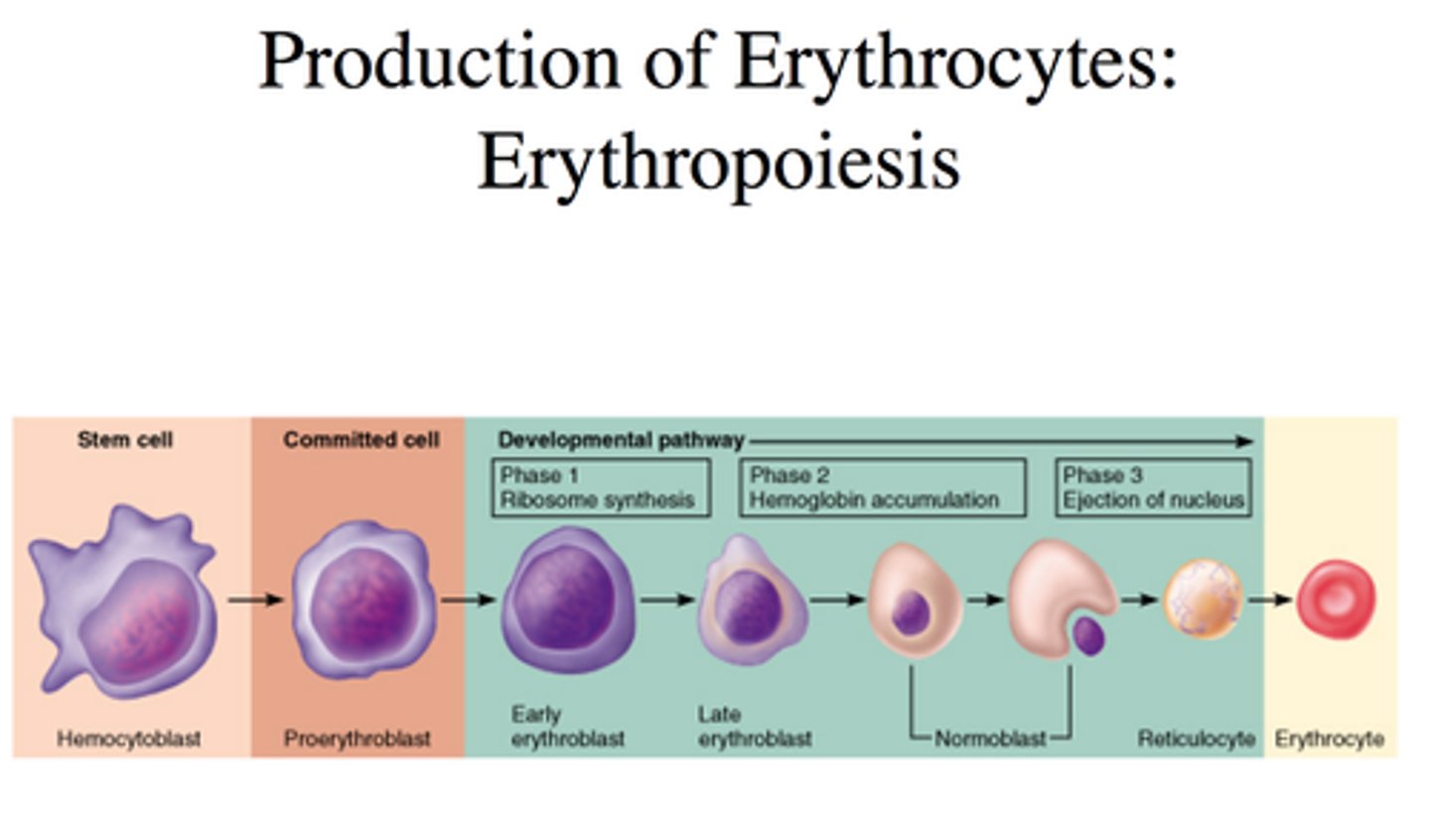
what stage of erythropoiesis indicates the RATE OF RBC FORMATION
the reticulocyte count
what is the hormonal control the stimulate the formation of RBCs
erythropoietin (EPO)
what is erythropoietin
a hormone that stimulates the formation of RBCs
what triggers the release of EPO (erythropoietin)
during hypoxia (low O2) kidneys (and some liver) release EPO
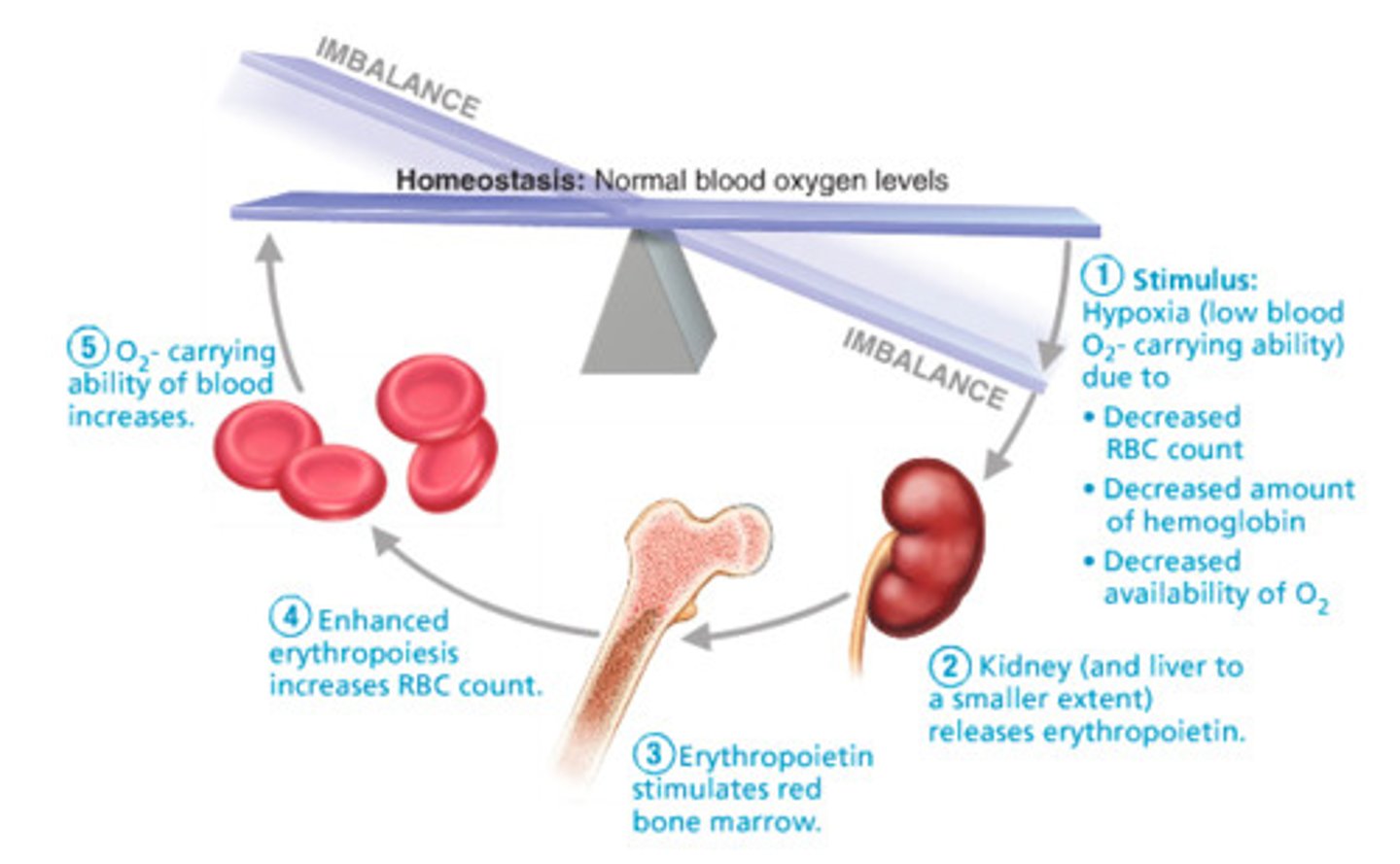
steps for the release of EPO
1. stimulus: hypoxia due to...
- low RBC
- decreased amount of hemoglobin
- decreased availability of oxygen
2. kidney (and liver to a smaller extent) release erythropoietin (EPO)
3. EPO stimulates red bone marrow
4. enhanced erythropoiesis increases RBC count
5 O2 carrying ability of blood rises
what are the dietary requirements for erythropoiesis
- Nutrients: amino acids, lipids, and carbohydrates
- Iron: available from diet
- Two B-complex vitamins: vitamin B12 and folic acid are necessary for DNA synthesis for rapidly dividing cells such as developing RBCs