BIO 202: Chapter 1.3 - 1.5 Endocrine System Histology, Feedback Loops, and Blood
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
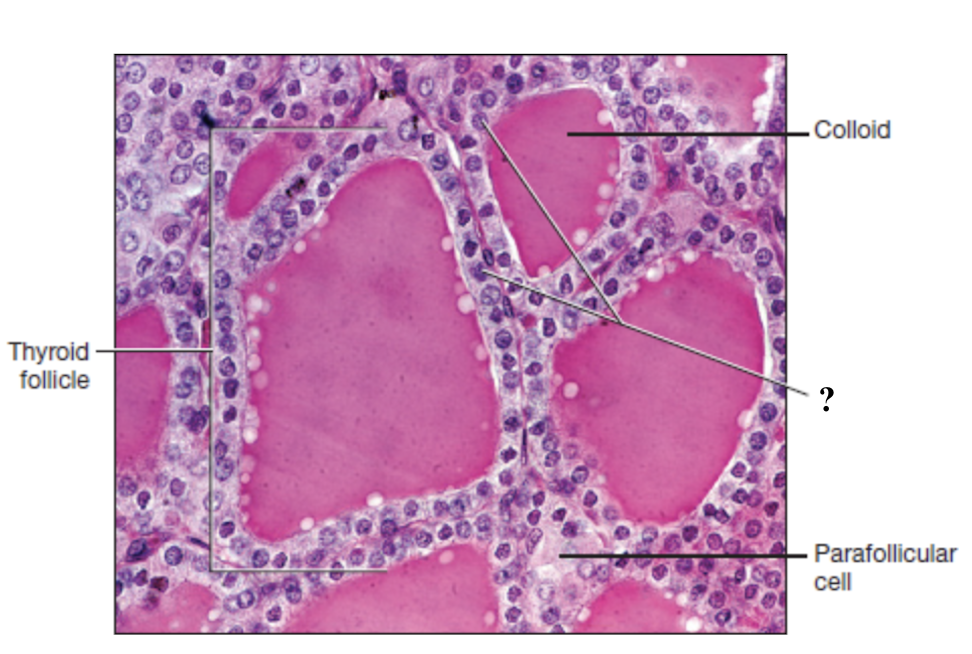
thyroid gland
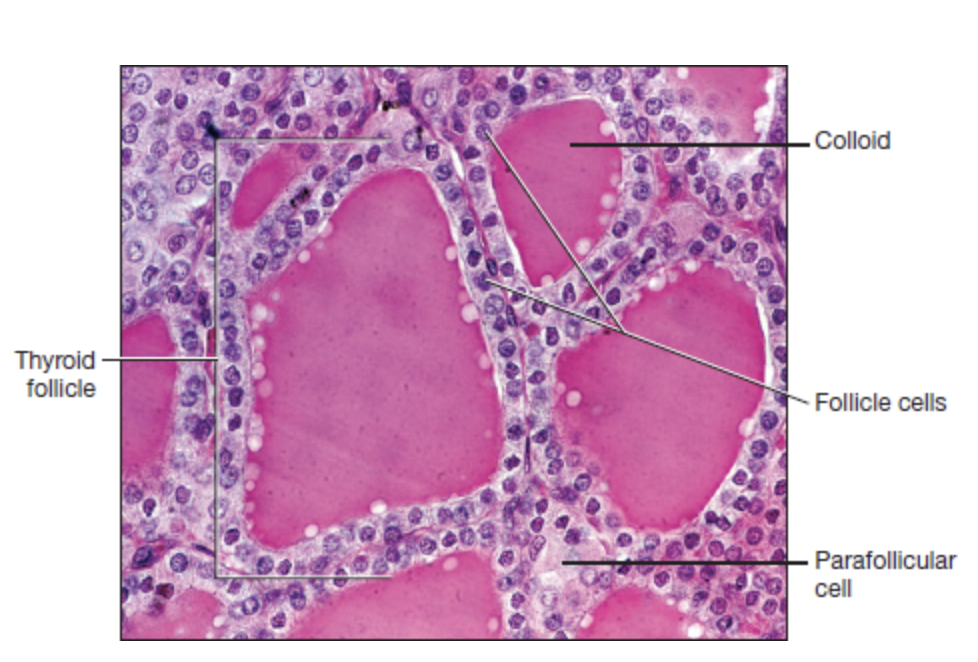
parafollicular cells
large, pale stained cells between or adjacent to the follicles
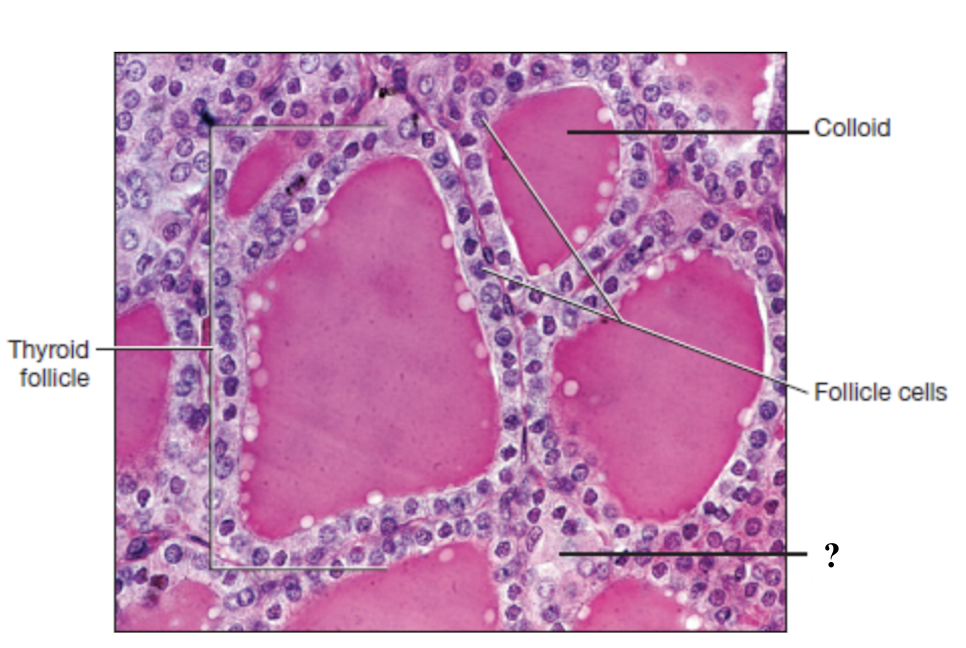
follicle cells
form a ring of simple cuboidal epithelium that surround the colloid
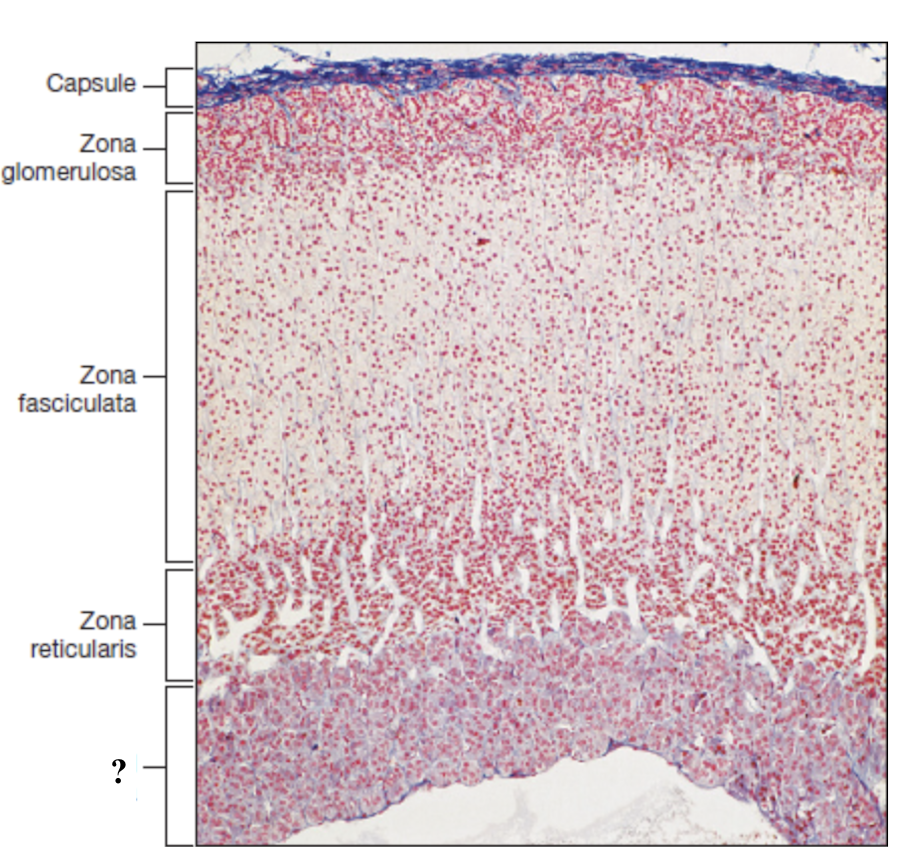
adrenal gland
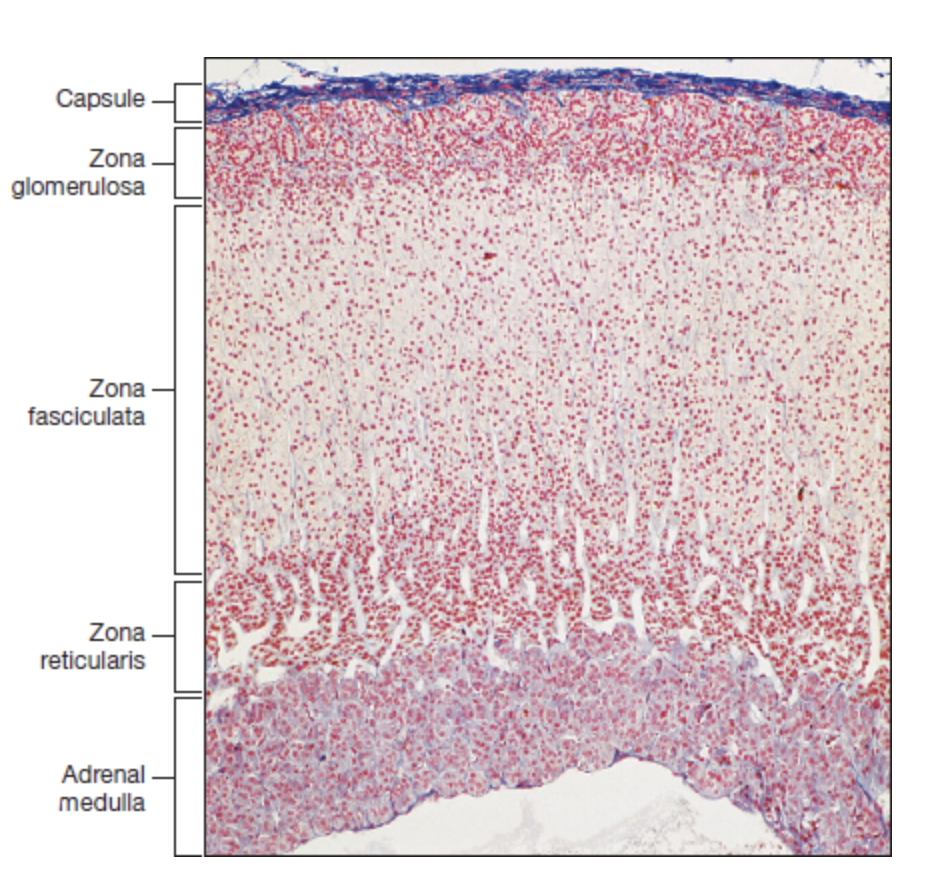
adrenal capsule
extremely thin and is the outermost layer
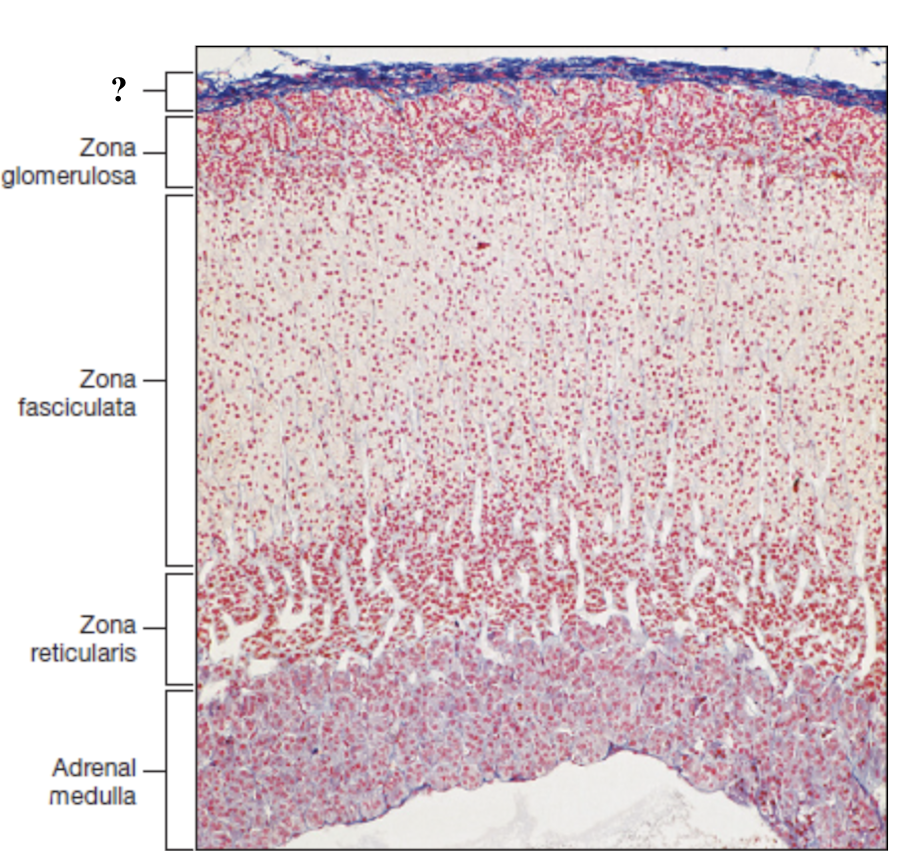
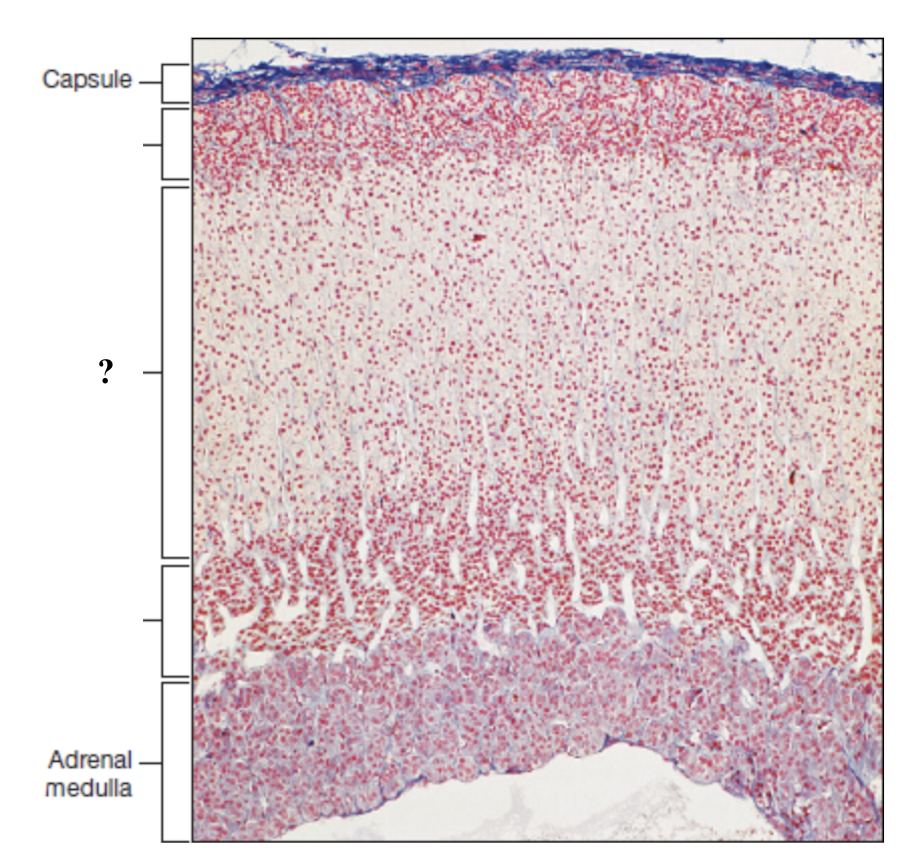
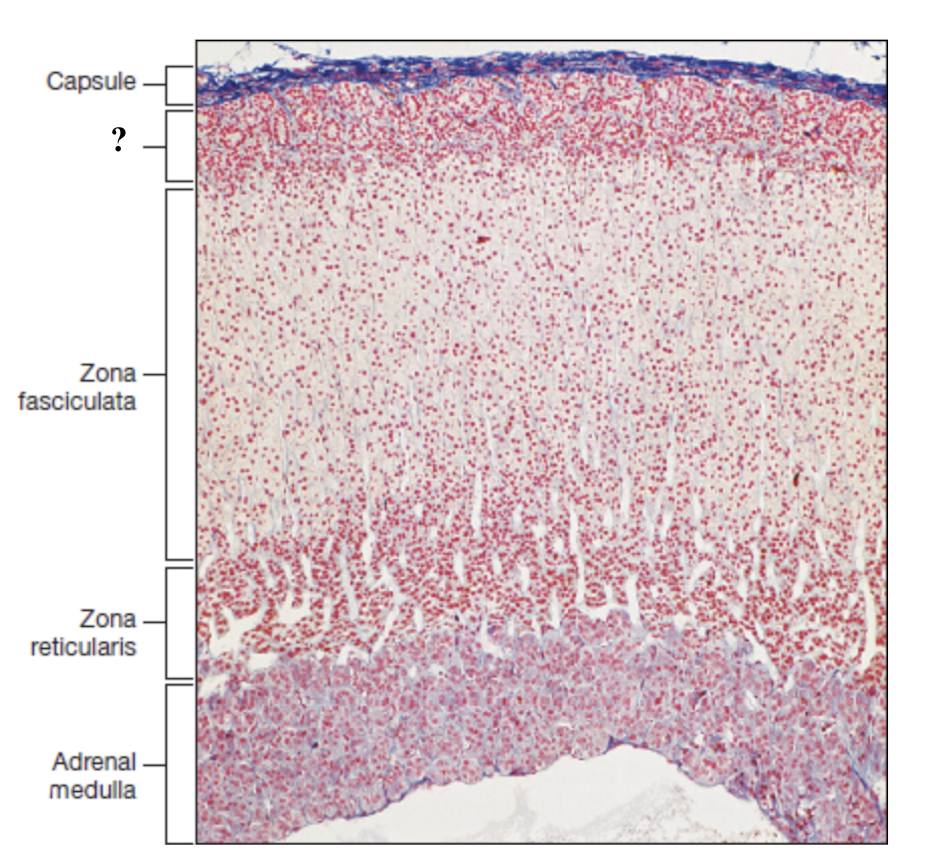
adrenal cortex
deep to the capsule and is made up of three distinct zones
zona glomerulosa
thin outer zone, cells arranged in small, round clusters nearest to the adrenal capsule
zona fasciculata
thick middle zone, lightly stained cells stacked in columns, foamy or sponge like cytoplasm
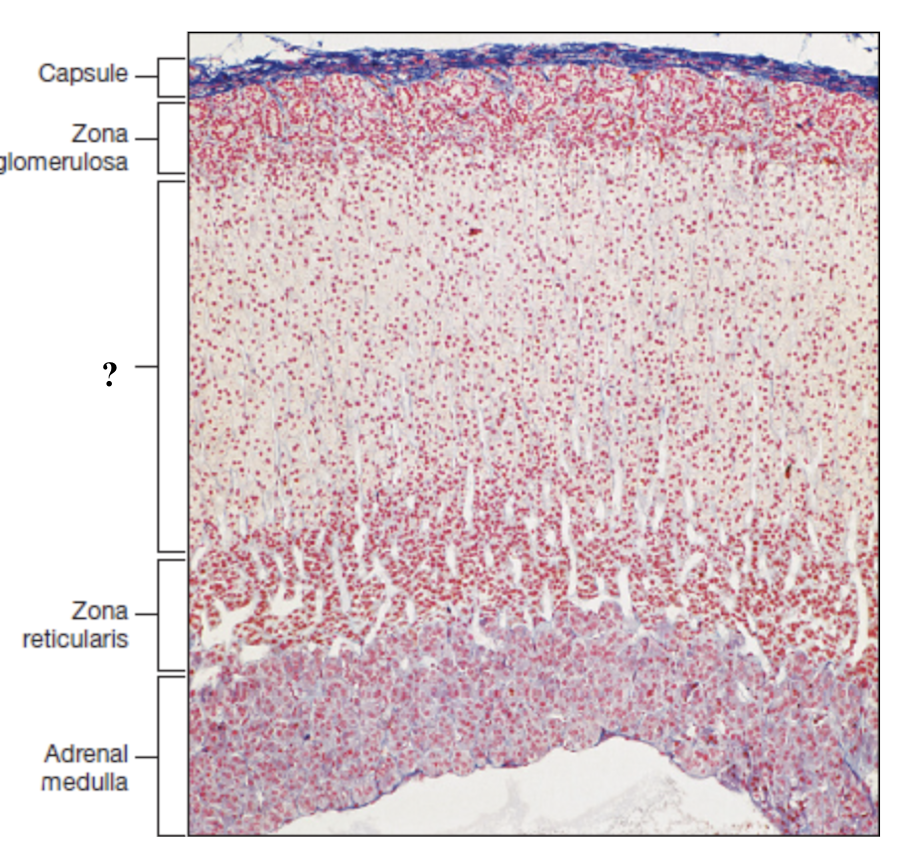
zona reticularis
thin inner zone, darkly stained, tightly packed cells in net like pattern
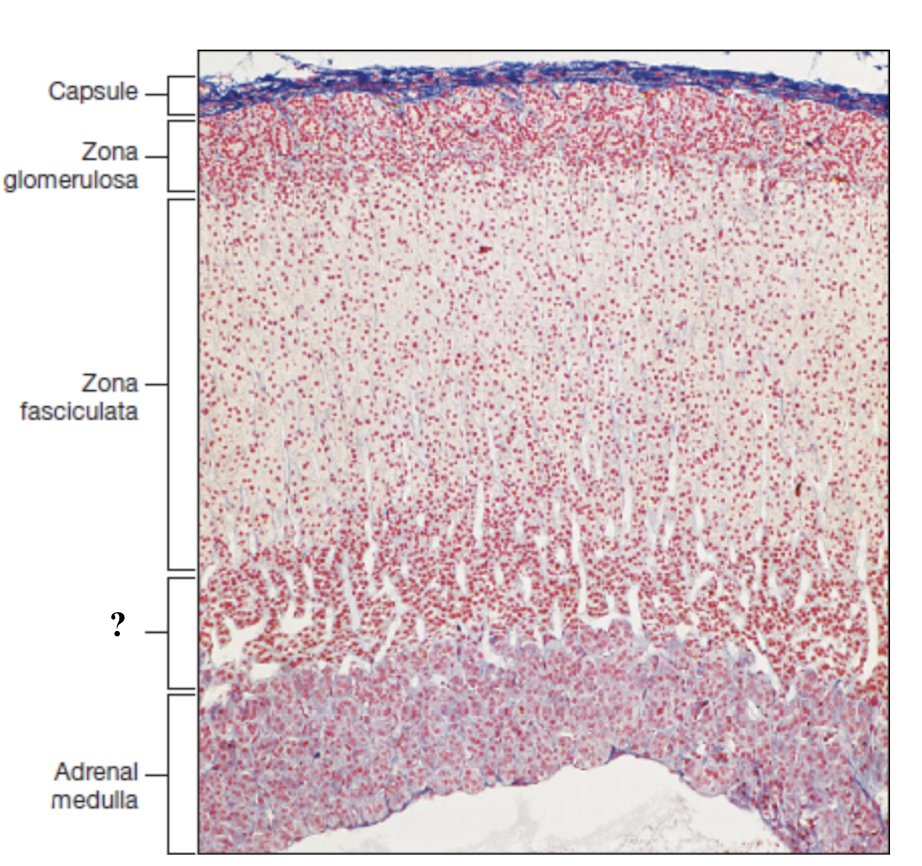
adrenal medulla
innermost region with numerous, loosely arranged blood vessels and clusters of hormone secreting cells
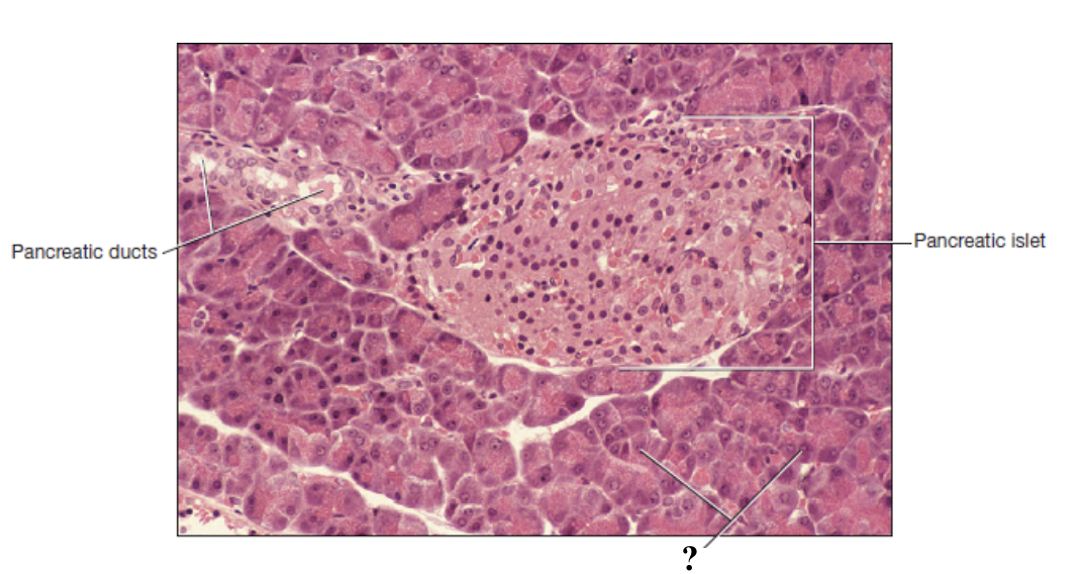
pancreas
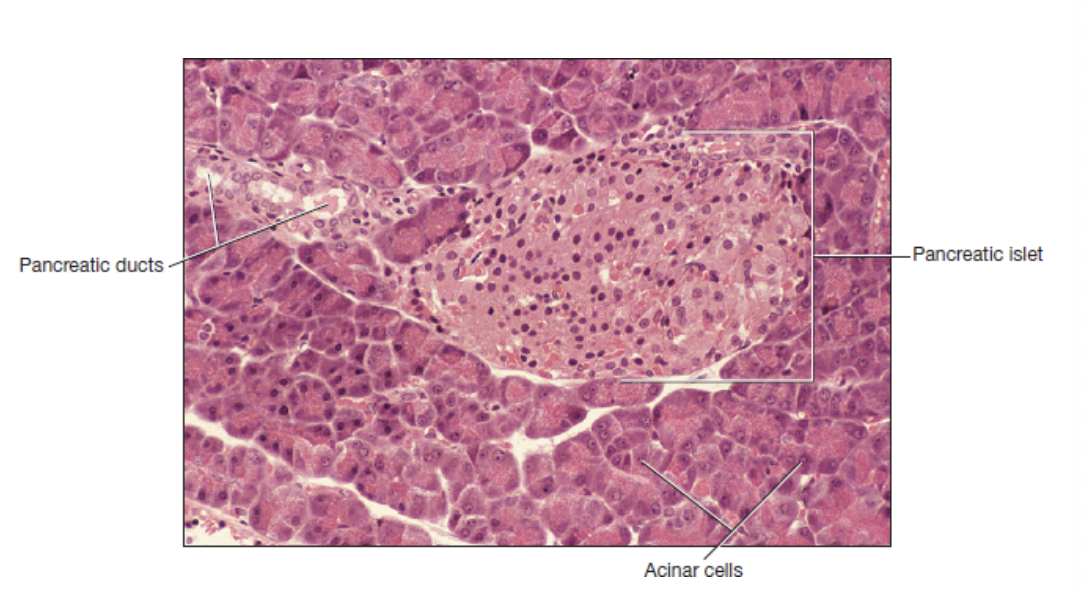
pancreatic ducts
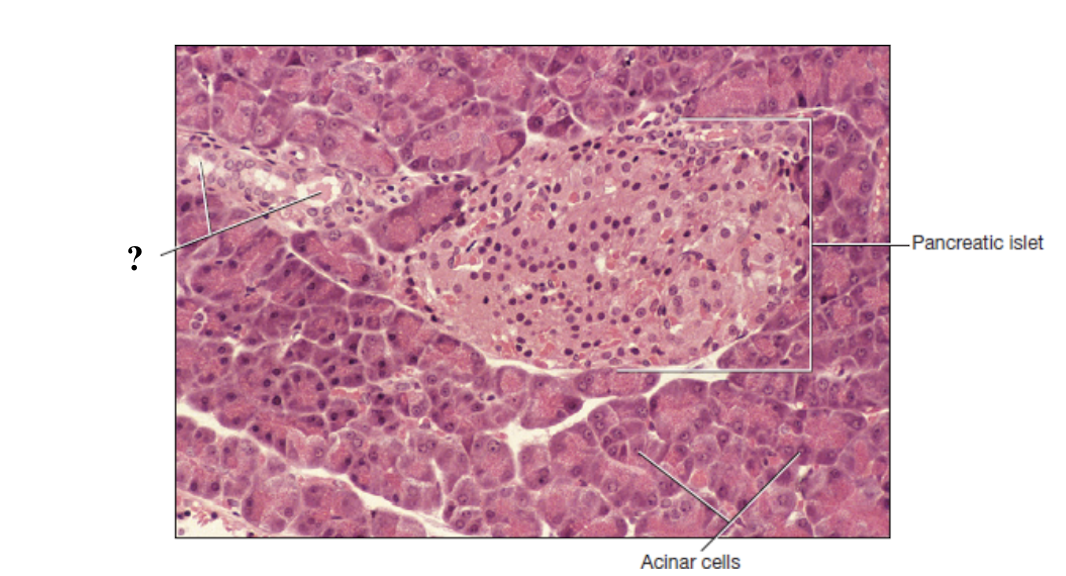
pancreatic islets
lighter in color, slightly cuboidal, arranged around a duct
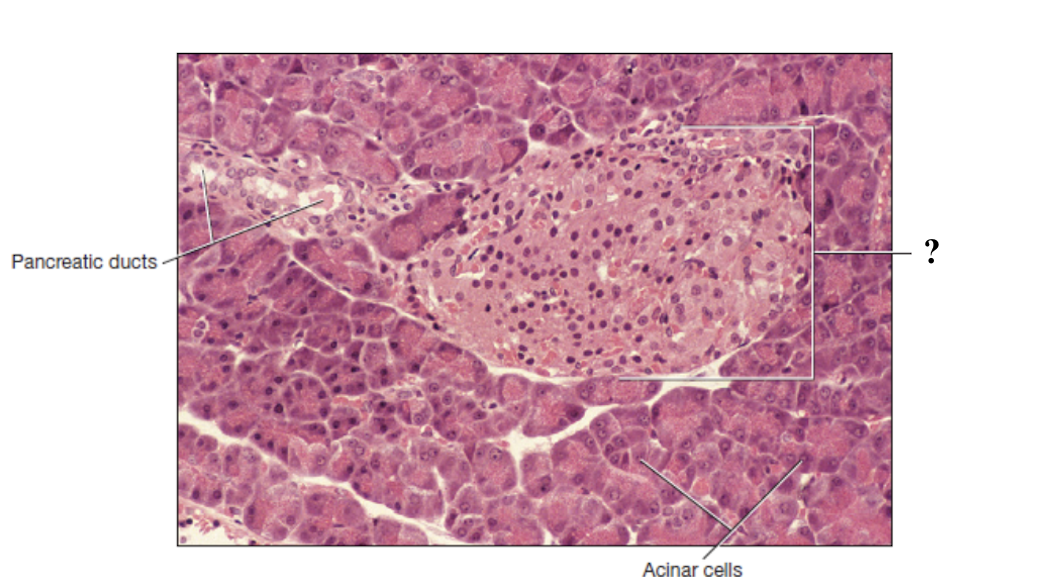
acinar cells
no distinct arrangement, may be larger, stain free spaces between them
negative feedback loop
automatic stabilizing mechanism in which hormones are released into bloodstream to act on target cells to correct disturbance to restore homeostasis, decrease gland activity, and decrease hormone concentration
thyroid hormone regulation
hypothalamus releases thyrotropin releasing hormone and stimulates anterior pituitary to release thyroid stimulating hormone
thyroid stimulating hormone stimulate thyroid gland to secrete T3 and T4
T3 and T4 levels rise in blood and inhibit thyrotropin and thyroid stimulating hormone
overproduction of thyroid hormones is prevented
cortisol regulation
hypothalamus releases corticotropin releasing hormone and stimulates the anterior pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic hormone
adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol
elevated cortisol levels inhibit corticotropin and adrenocorticotropic release
further cortisol production is reduced
blood glucose regulation
blood glucose levels fall and pancreas releases glucagon which stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver
blood glucose levels rise and pancreas releases insulin which promotes glucose uptake by cells
blood glucose levels return to normal and hormone secretion decreases
positive feedback loop
response that amplifies original stimulus to accelerate a process until an outcome is reached
childbirth
cervical stretching stimulates the release of oxytocin which causes stronger uterine contractions to further stretch the cervix more until baby is delivered
blood clotting
in a damaged vessel, platelets stick to injury site and release chemicals that attract more platelets that further release more chemicals until clot fully seals break
thermostat
negative feedback is like a _____ that works to bring the temperature back to normal
microphone
positive feedback is like a _____ that works to amplify a signal until a specific result is reached
viscosity
the resistance of a fluid to flow, caused by the cohesion between its particles
aka the thickness and stickiness of a fluid
4.5 to 5.5
blood is ____ times more viscous than water
osmolarity
total concentration of dissolved particles that cannot pass through the blood vessel wall
helps blood regulate fluid movement between blood and tissues
plasma and formed elements
two main components of whole blood
plasma
clear, light-yellow fluid portion of blood
55% of volume of whole blood
consists primary of water, proteins, nitrogenous wastes, hormones, gases, and other solutes
albumin
smallest and most abundant plasma protein that transports solutes and buffers plasma pH
major contributor to blood viscosity and osmolarity
globulin
plasma protein that plays role in solute transport, clotting, and immunity
fibrinogen
plasma protein that is a soluble precursor of fibrin which is a sticky protein that forms framework of blood clots
serum
fluid that remains after blood clots and solids are removed
identical to plasma but lacks fibrinogen
formed elements
cellular portion of blood
accounts for 45% of volume of whole blood
includes erythrocytes, thrombocytes, and leukocytes
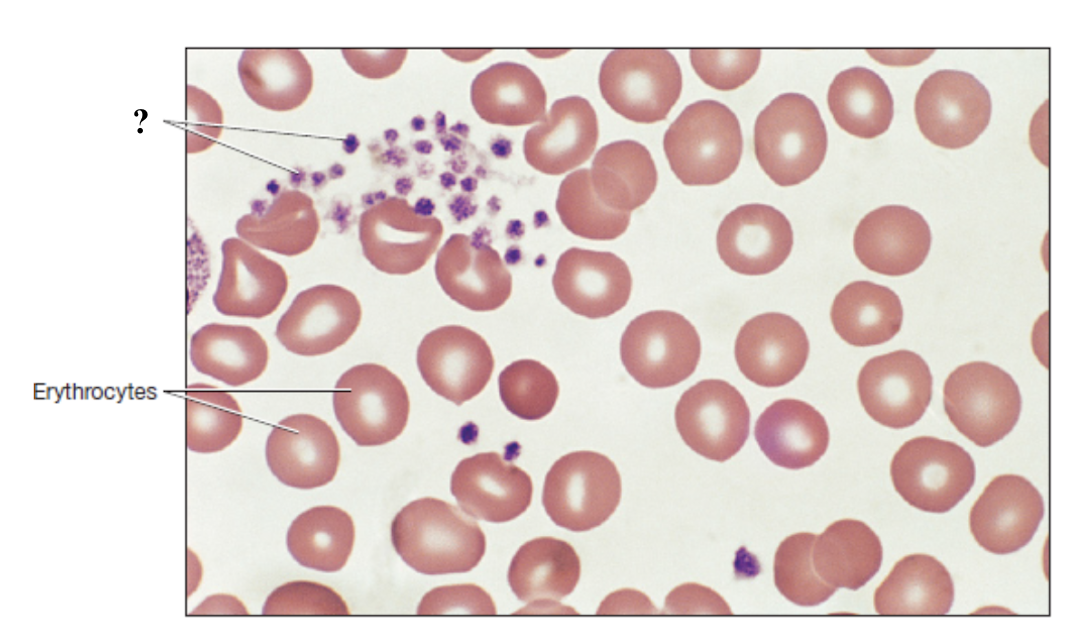
erythrocytes
red blood cells that function to carry oxygen throughout the body using hemoglobin and to pick up carbon dioxide
most numerous blood cells with average of 44% of total blood volume
biconcave shape, lack nucleus and most organelles
hemoglobin
iron-containing protein and red pigment that gives blood its color
hematocrit
packed cell volume
40 to 50% in males
36 to 44% in females
erythropoiesis
erythrocytes production which occurs in red bone marrow and takes 3 to 5 days
erythropoietin
hormone that stimulates the process of erythropoiesis
anemia
low hematocrit which may cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath
polycythemia
high hematocrit which can increase blood viscosity and raise risk of clotting and stroke
high, lower
at ___ altitudes, oxygen levels are ___ so kidneys release more erthyropoietin and increase RBC productions to improve oxygen delivery
blood doping
a performance-enhancing method where athletes artificially increase red blood cell count to boost oxygen delivery to muscle to improve endurance
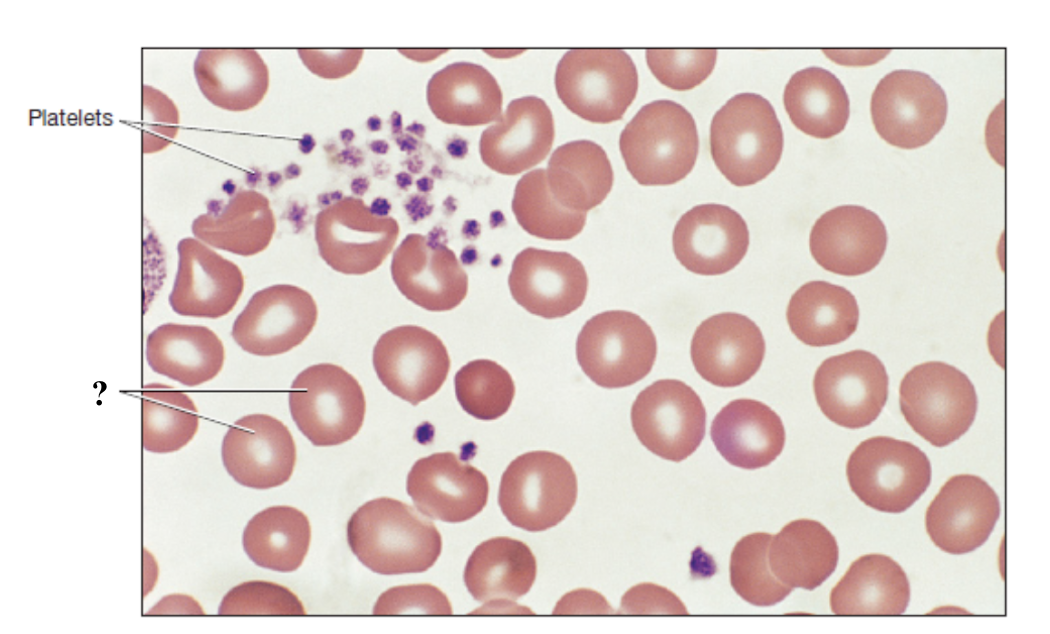
thrombocytes
platelets that function in hemostasis by forming platelet plugs and the initiating blood clotting process
make up less than 1% of total blood volume
not true cells, lack nucleus and most organelles
circulate for 5 to 6 days before removed by spleen or liver
hemostasis
process of stopping bleeding
megakaryocytes
extremely large bone marrow cells with multiobed nuclei from which thrombocytes originate from
thrombopoietin
hormone that stimulates thrombocyte production in red bone marrow
clotting cascade
chain reaction of chemical events involving clotting factors that lead to the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin to form a stable clot
clotting cascade step 1
vascular spasm: damaged blood vessel immediately constricts to slow down blood loss
clotting cascade step 2
platelet plug formation: platelets stick to exposed collagen fibers in the vessel wall and clump together to form temporary plug to cover injury
clotting cascade step 3
coagulation cascade activation: a chain reaction of clotting proteins begins
intrinsic pathway: triggered by damage inside a vessel
extrinsic pathway: triggered by damage to tissue outside the vessel
clotting cascade step 4
common pathway: both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways join together at a specific point called the activating factor X that leads to production of thrombin that converts fibrinogen into fibrin
clotting cascade step 5
stable clot formation: fibrin forms a mesh that traps blood cells to create a strong and stable clot to fully seal injury
partial thromboplastin time
clotting test that measures the intrinsic and common pathways and is used to monitor heparin therapy
prothrombin time
clotting test that measures the extrinsic and common pathways
international normalized ratio
clotting test used to monitor warfarin (coumadin) therapy
thrombocytopenia
low thrombocytes which can lead to easy bruising, prolonged bleeding after injury, and spontaneous internal bleeding
thrombocytosis
high thrombocytes which may result in bone marrow disorders, chronic inflammation, and can increase risk of abnormal blood clot formation, stroke, and heart attack
leukocytes
white blood cells that function to protect the body against infection, disease, and foreign invaders as part of the immune system
make up less than 1% of total blood volume
have nucleus and other organelles
classified into two main groups based on presence or absence of visible cytoplasmic granules when stained
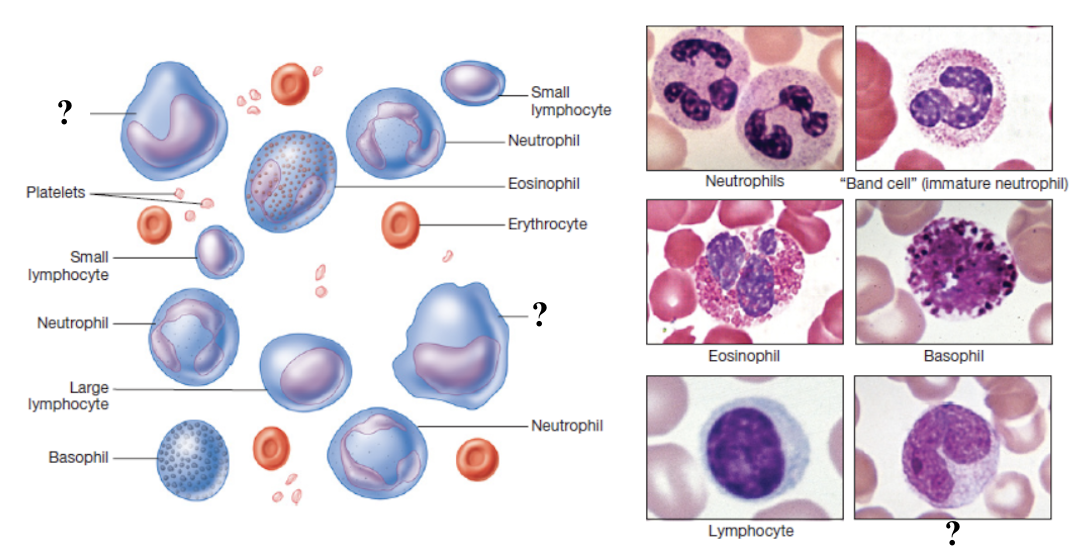
granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
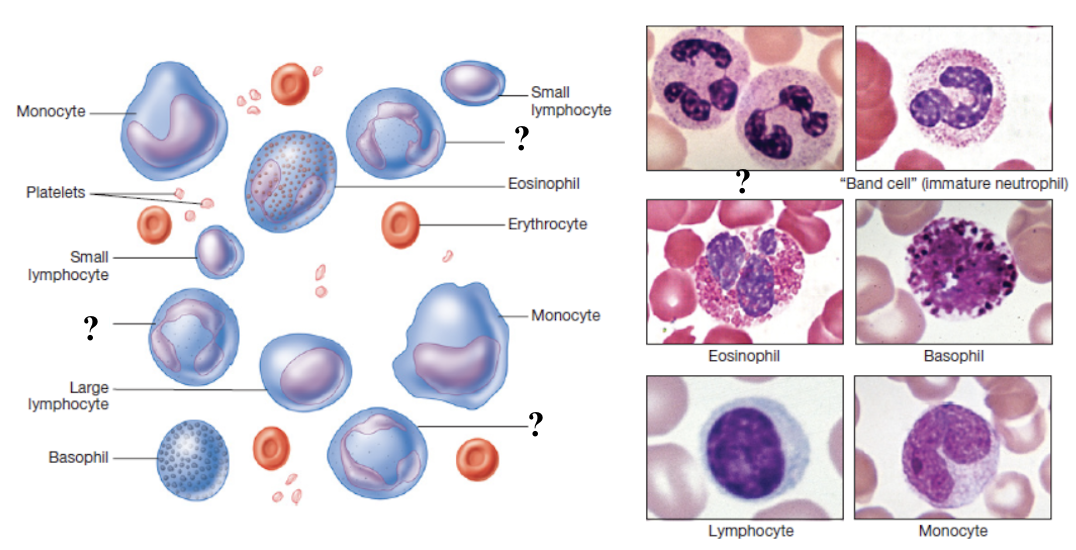
neutrophils
function as first responders to infection by ingesting and destroying bacteria and cellular debris using enzymes and antimicrobial chemicals
most numerous leukocyte, making up 60 to 70% of total white blood cells
multilobed
eosinophils
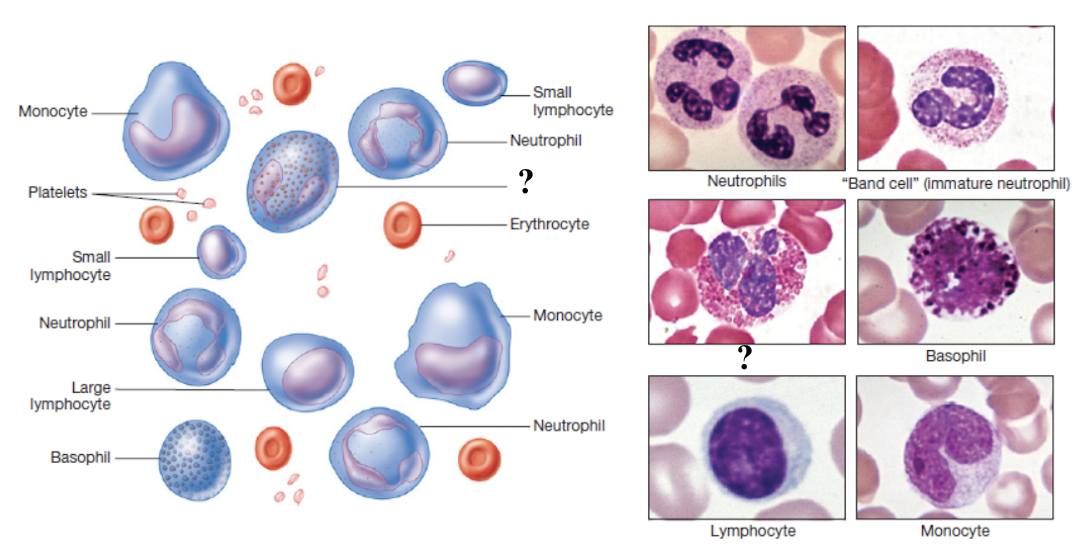
function to attack parasitic worms, participate in allergic reactions, and help regulate inflammation by phagocytizing antigen-antibody complexes
make up about 2 to 4% of total white blood cells
elevated in parasitic infections, allergies, autoimmune diseases, and certain skin disorders
stain hot pink/reddish color
basophils
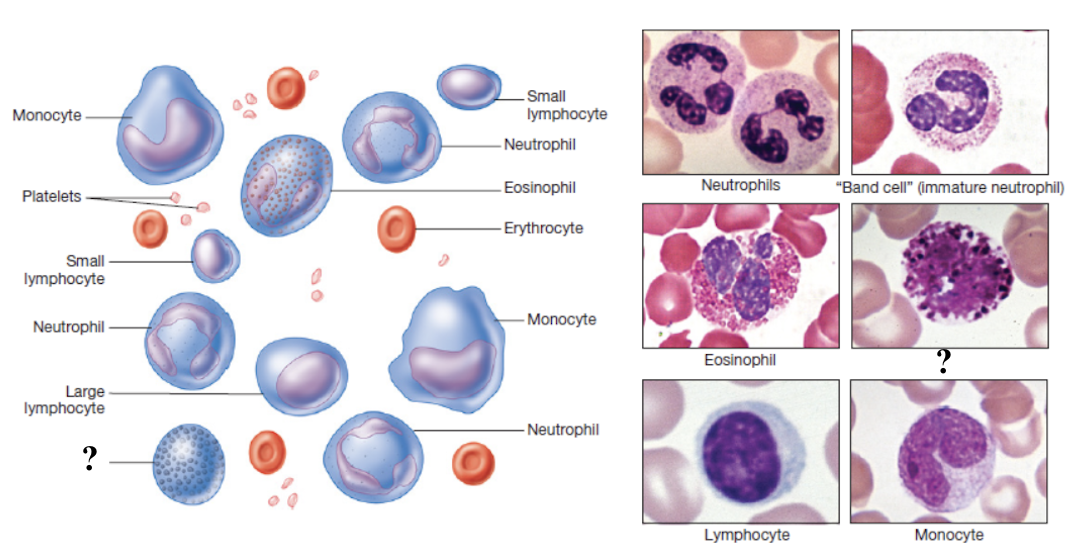
function to release histamine and other inflammatory mediators when activated to contribute to allergy symptoms
least numerous white blood cells, making up less than 1% of total count
obscured in histology slide
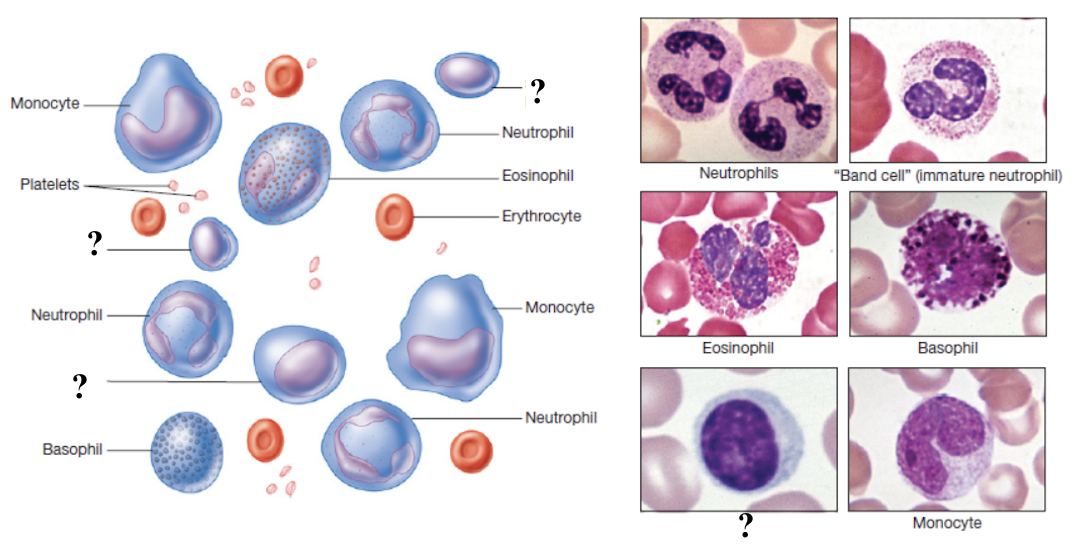
lymphocytes
function in adaptive immunity
make up about 20 to 25% of total white blood cells
elevated in viral infections and some chronic bacterial infections
low levels may occur in immune deficiencies or after chemotherapy
B lymphocytes
produce antibodies that bind to antigens
T lymphocytes
enhance other immune responses, destroy cancer cells, and kill virus-infected cells
monocytes
function to present antigens to lymphocytes to active the immune response and mature into macrophages which are active phagocytes that engulf bacteria, dead cells, and debris
largest sized white blood cell, make up 3 to 8% of total white blood cells
elevated in viral infections, chronic inflammation, and certain leukemias
leukocytosis
higher than normal white blood cell count
often indicates infection, inflammation, tissue injury, or leukemia
leukopenia
lower than normal white blood cell count
can result from bone marrow failure, autoimmune disorders, viral infections, or chemotherapy