ESS Topic 3 - Key Terms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Biodiversity
The variety of all life on Earth, including genetic, species, and habitat diversity.

Genetic diversity
The range of genetic material present in a population of a species.

Species diversity
The number of different species and their relative abundance in a community.

Habitat diversity
The range of different habitats in an ecosystem, biome, or the whole planet.

Evolution
The cumulative change in the heritable characteristics of a population over successive generations.
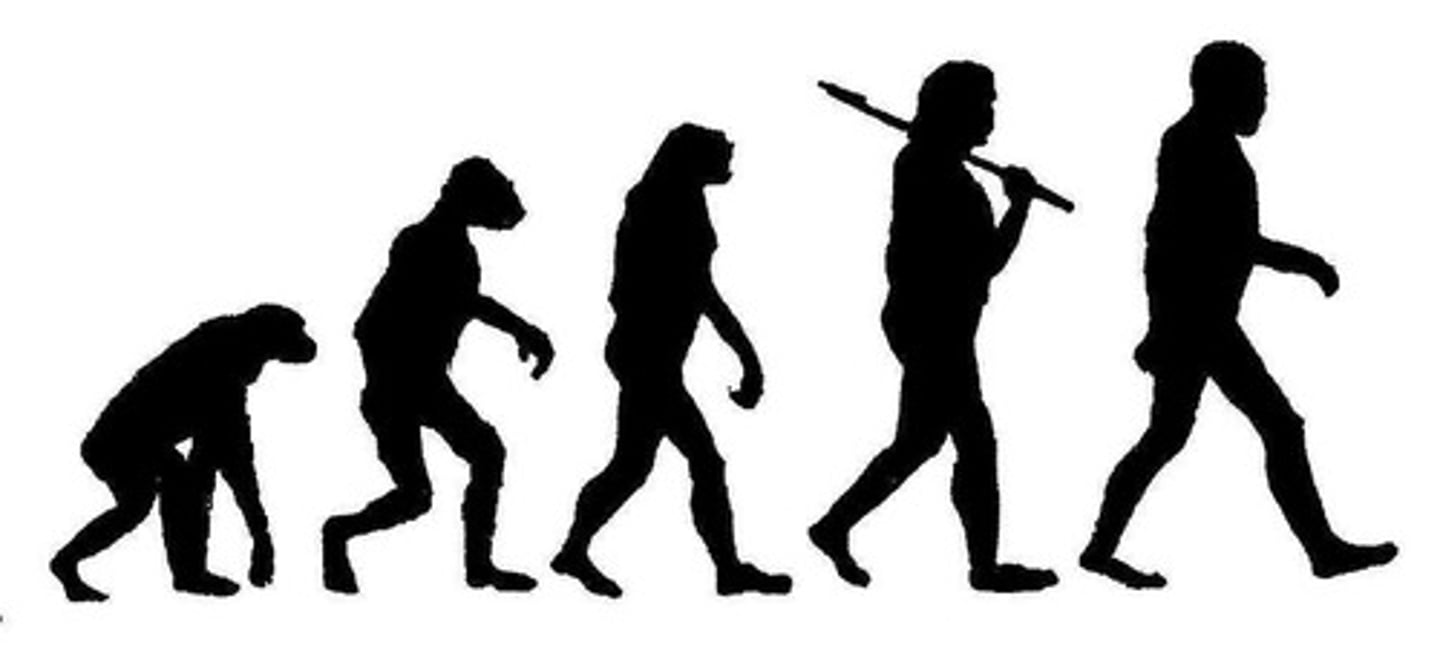
Natural selection
The process by which individuals with advantageous traits survive and reproduce more successfully.
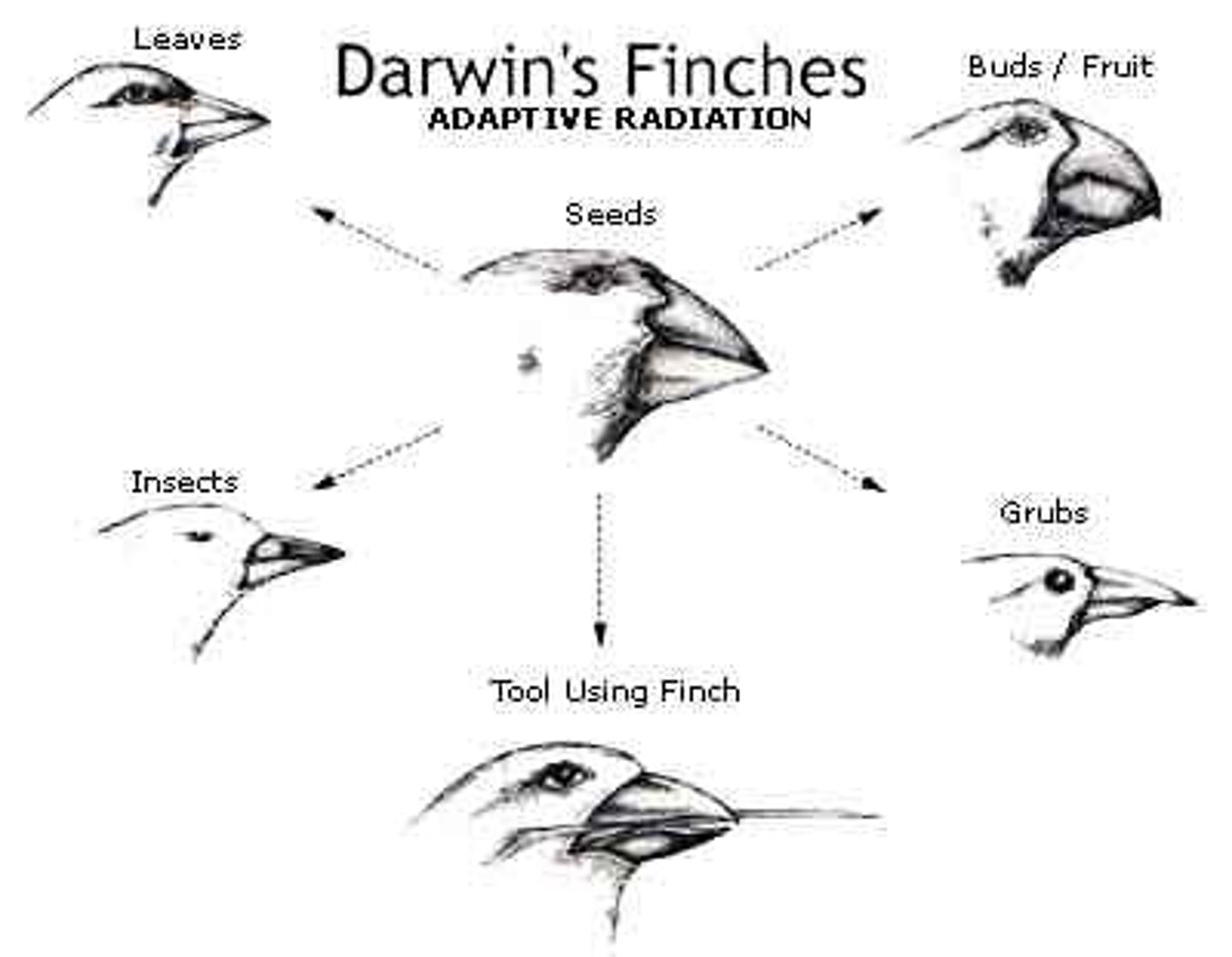
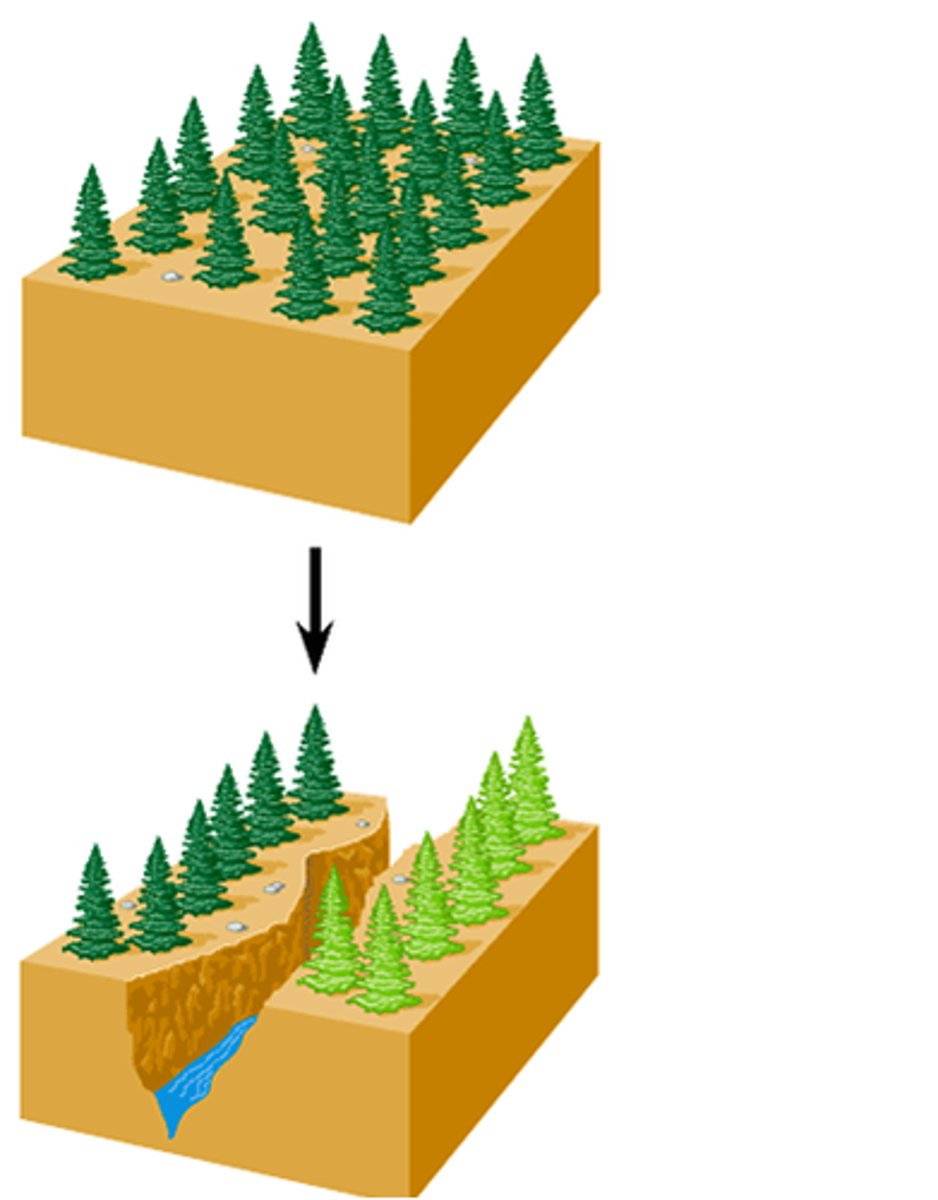
Speciation
The formation of new species when populations of a species become isolated and diverge genetically.
Direct threats
Human actions that immediately affect species (e.g., overharvesting, poaching, illegal trade).

Indirect threats
Human activities that indirectly affect biodiversity (e.g., habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, invasive species).

Invasive species
Non-native species that spread rapidly and outcompete or harm native species.

Keystone species
A species with a disproportionately large impact on its ecosystem relative to its abundance.

Umbrella species
A species whose protection indirectly protects many others in its ecosystem.

Flagship species
A charismatic species chosen to represent a conservation campaign and raise awareness.

Limiting factor
A factor (biotic or abiotic) that restricts the growth or distribution of a population.

Carrying capacity
The maximum population size an environment can sustainably support.

Conservation
The sustainable management of natural resources to maintain biodiversity.

In-situ conservation
Conserving species in their natural habitat (e.g., protected areas, national parks).
Ex-situ conservation
Conserving species outside their natural habitat (e.g., zoos, seed banks, captive breeding).
Protected area (National Park)
A designated region where human activity is limited to protect biodiversity.
UNESCO Biosphere Reserve
A protected area model with core, buffer, and transition zones balancing conservation and sustainable use.
Wildlife corridor
A natural strip of habitat connecting separated populations to reduce fragmentation.
IUCN Red List
A global inventory that categorizes species according to their risk of extinction.
CITES
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species, an international agreement regulating trade in endangered species.
CBD
Convention on Biological Diversity, a global treaty aimed at conserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable use.
NGO
Non-Governmental Organization, e.g., WWF, Greenpeace, that raise awareness and implement conservation projects.
IGO
Intergovernmental Organization, e.g., UNEP, FAO, UNESCO, that influence policy and conservation.
Simpson's Diversity Index (D)
A measure of biodiversity that accounts for species richness and relative abundance.