Chemistry: Gases in our atmosphere, carbonates, pH, Indicators
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the composition of our air
Nitrogen - 78.1% (4/5)
Oxygen - 21% (1/5)
Argon - 0.9%
Carbon Dioxide - 0.04%
Describe the practical to find the amount of O2 in air
Use glass rod to poke some iron wool into bottom of a test tube. Use enough iron wool so that it is around 3 cm deep in the test tube.
Add a little water to the test tube and shake it, so that the iron wool is wet. Pour out any excess water.
Invert the test tube into a beaker that is half full of water.
With the test tube vertical, measure the height (in mm) of the air in the test tube. Record this in the observation section.
Arrange the test tube at an angle (see diagram), and leave for a week.
With the test tube vertical, measure the height of the air in the test tube.
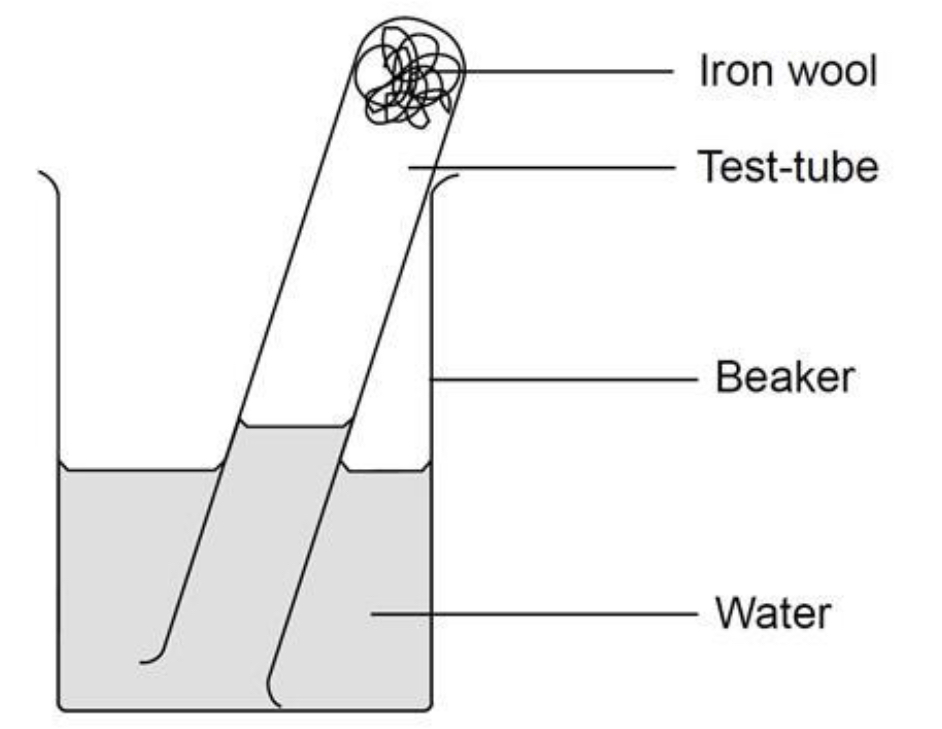
What is the equation to find amount of O2 in air
Percentage of O2 in air = (decrease in height of air ➗starting height of air) x100
What is rust
Iron (III) oxide
Iron + Oxygen = Iron Oxide
4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3 (s)
What happened to methane in early atmosphere?
Reacted with oxygen to form CO2
What happened to carbon dioxide in early atmosphere?
- Used up in photosynthesis reactions
- Some plants/organisms die and form fossil fuels trapping Carbon
- Dissolves in oceans
- Forms carbonates in sea creature shells
- Dead sea creatures form sedimentary rocks
What happened to ammonia in early atmosphere?
Reacted with oxygen and denitrifying bacteria in soil
What happened to water vapour in early atmosphere?
Condensed to form oceans as Earth cools
What is the word and symbol equation for combusting hydrogen (adding oxygen)?
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
2H2(g) + O2 → 2H2O
What is the word and symbol equation for combusting magnesium (adding oxygen)?
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide
2Mg(s) + O2 → 2MgO(s)
What is the word and symbol equation for combusting sulfur, O2 (adding oxygen)?
Sulfur + Oxygen → Sulfur Dioxide
S(s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
What is the word and symbol equation for combusting sulfur, 3O2 (adding oxygen)?
Sulfur + Oxygen → Sulfur Trioxide
2S(s) + 3O2(g) → 2SO3(g)
What is Nitrogen used for?
Fertilisers
What is argon used for?
Fill light bulbs
What is oxygen used for?
Make steel and for welding
What are the properties of metal oxides?
are ionic compounds containing O2- ions.
usually basic oxides react with acids to form salts).
usually insoluble in water (soluble ones react with it to form alkaline solutions with OH- ions).
What are the properties of non-metal oxides?
covalent compounds.
usually acidic oxides (react with bases to form salts).
often soluble in water (react with it to form acidic solutions with H+ ions).
What is carbon dioxide?
A colourless gad easily made in lab with hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate (marble chips)
Heating metals strongly can also produce CO2
How do you get carbon dioxide from heating metals?
Most carbonates split to give a metal oxide and carbon dioxide when you heat them.
What is thermal decomposition?
the decomposition reaction that requires heating to occur.
What is the greenhouse effect?
Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels burn.
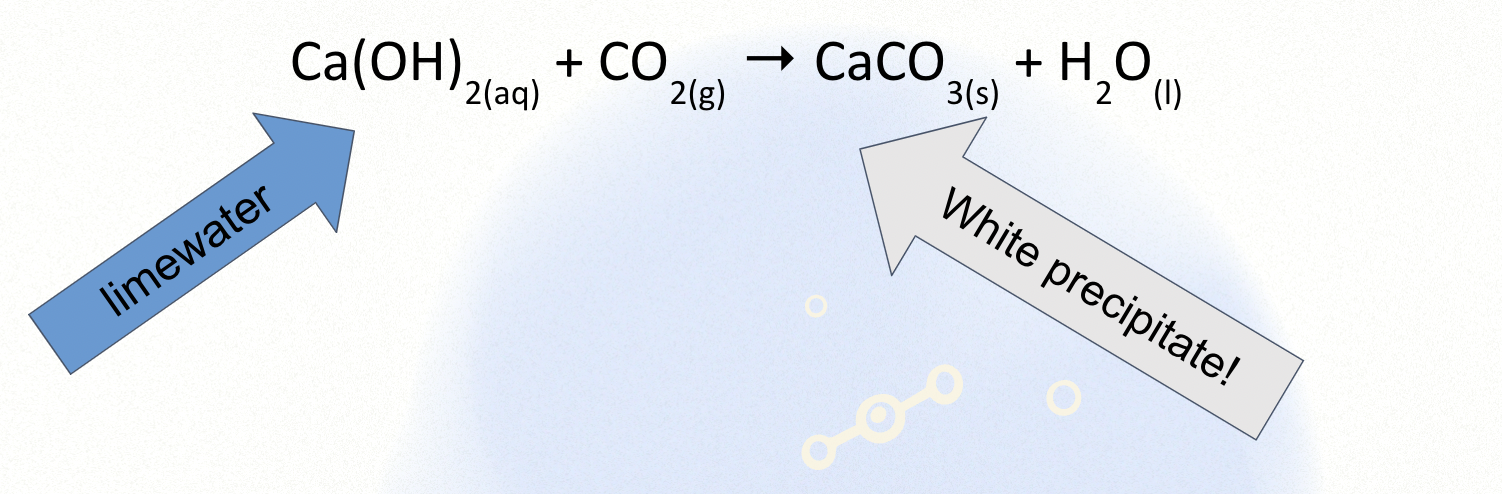
How do you test for Carbon dioxide?
When CO2 is bubbled through lime water it turns milky/chalky/cloudy.
What is a universal indicator?
Universal indicator is a mixture of different indicators which is able to detect multiple different pHs

What colours does litmus paper produce based on if the solution is acid or alkali?
red for acid, Blue for alkali
What colours does methyl orange produce based on if the solution is acid or alkali?
red for acid, Yellow for alkali
What colours does phenolphthalein produce based on if the solution is acid or alkali?
colourless for acid, Pink for alkali
What colours does universal indicator produce based on if the solution is acid or alkali?
Red for acid, Blue for alkali
What colour do neutral solution have?
An equal mixture of colours. (Litmus: Purple, Universal: Green)