L8 Oxidation of Alcohols and Carbonyls
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Basic mechanism for oxidation of an alcohol
Reduction of E

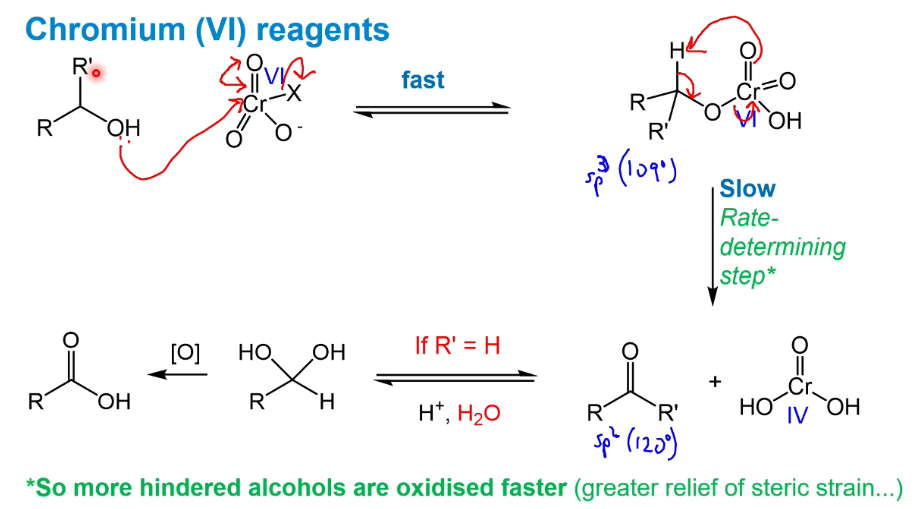
oxidation using Cr(VI) - CrO3
are more or less hindered alcohols oxidised faster
The slow rds has a greater release of steric strain as the transition from sp3 to sp2 occurs
An aldehyde forms an equilibrium with a hydrate which can then be oxidised further to a carboxylic acid (possibly unwanted)
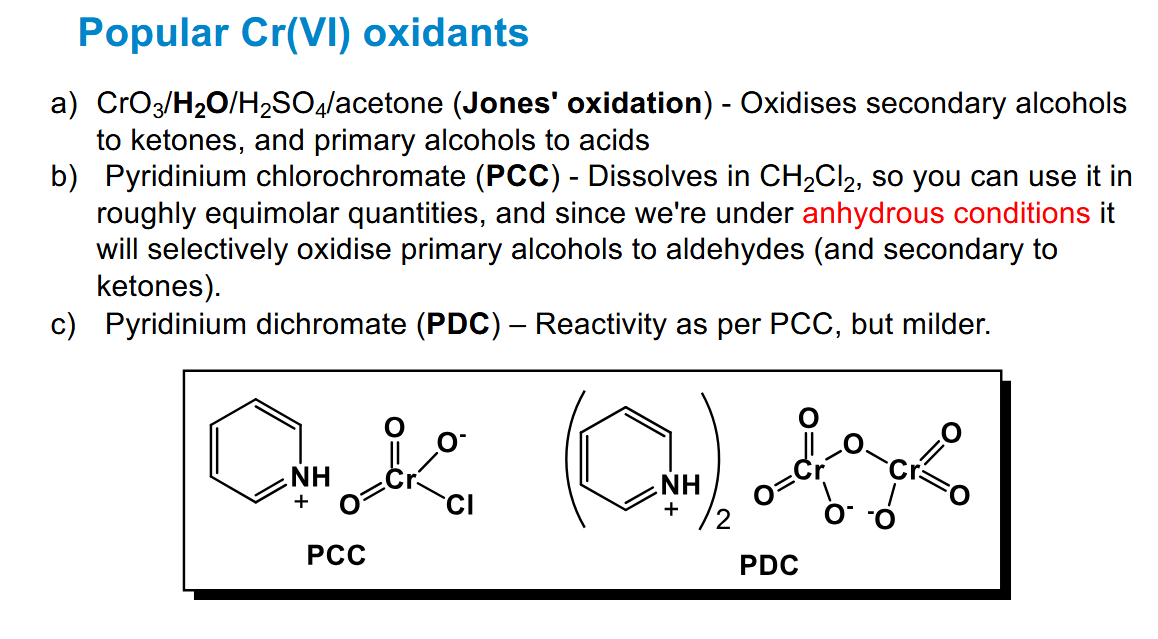
Cr(VI) oxidants
Jones reagent needs acetone to dissolve.
PCC and PDC stop at aldehydes (/ketones)
Cr residues are very toxic however
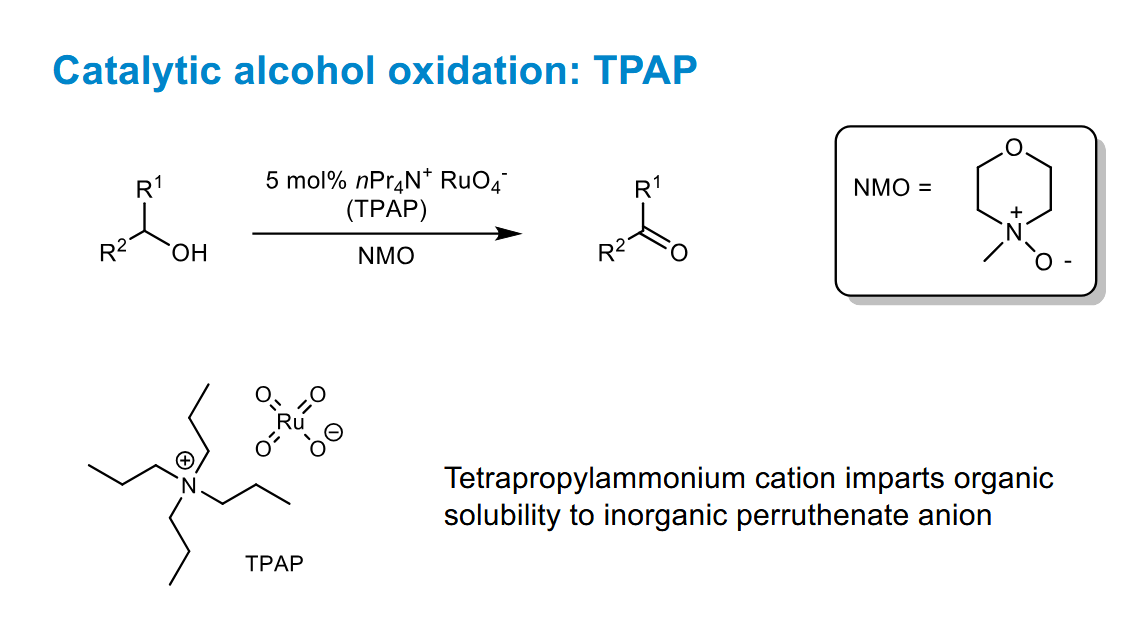
Catalytic alcohol oxidation using TPAP
TPAP mechanism for oxidation of alcohols
May need to use a desiccant to remove the water to prevent further oxidation.
The crucial step in the catalytic part is losing a lone pair of electrons on Ru

Activated DMSO oxidations
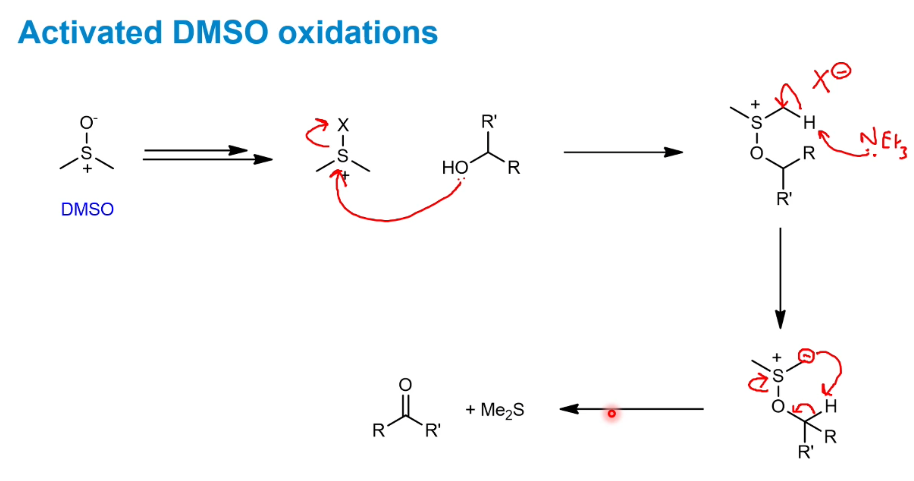
Swern oxidation using DMSO
Activated using a di acyl chloride.
Quite mild and preserves the stereochemistry next to the aldehyde formed

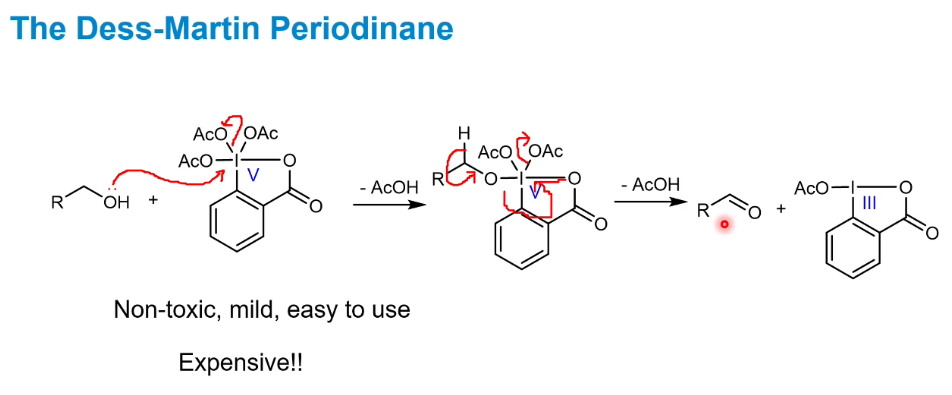
Dess-Martin Periodinane
Follows the same mechanism formula as usual
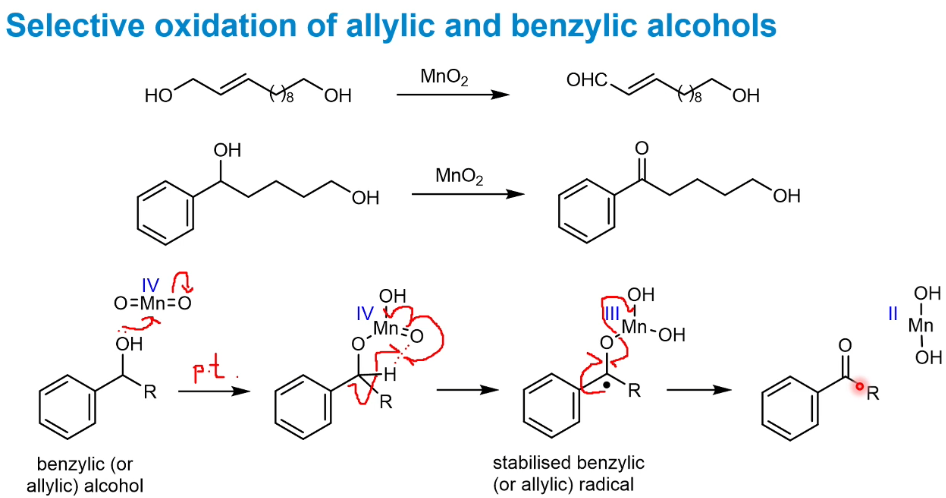
Selective oxidation of allylic and benzylic alcohols
Using MnO2 a radical is formed and the reaction only proceeds with allylic or benzylic stabilisation next to the OH, hence the other alcohols are untouched.
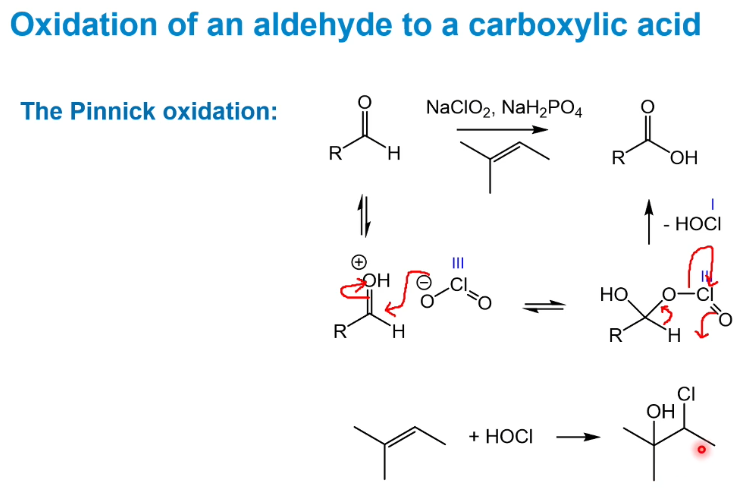
Pinnick oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids
The alkene is there to remove the HOCl - the resulitng compound is quite volatile and can be removed easily e.g. via evaporation.
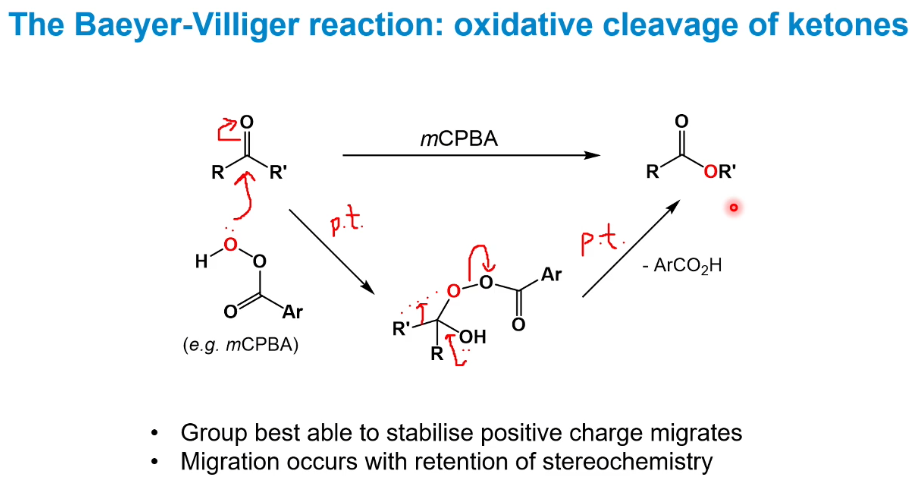
Baeyer-Villiger reaction - cleavage of ketones to form esters.
If R is H, it migrates and a carboxylic acid is produced - less useful as the side product is also a carboxylic acid so separation is harder.