Lower motor neurons
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
lower motor neurons definition
spinal ventral horn motor neurons and motor neurons located in cranial nerve somatic motor nuclei whose axons innervate skeletal muscle
activate skeletal muscle - final motor pathway
What are the two types of LMNs and what are the functional differences between them?
alpha motor neurons + gamma motor neurons
alpha motor neurons innervate
extrafusal fibers: tension generating fibers of skeletal muscle
In the AM (alpha motor) sometimes I feel TIGHT (tension/contraction) so i do a little EXTRA (extrafusal) stretching
gamma motor neurons innervate
intrafusal fibers: special type of skeletal muscle found within the muscle spindle (polar ends)
remember what muscle spindles do = detect changed in muscle length
interneurons
axons distribute locally in the spinal gray matter - regulate the activity of alpha and gamma motor neurons;
they can excite or inhibit these motor neurons
LMN pic
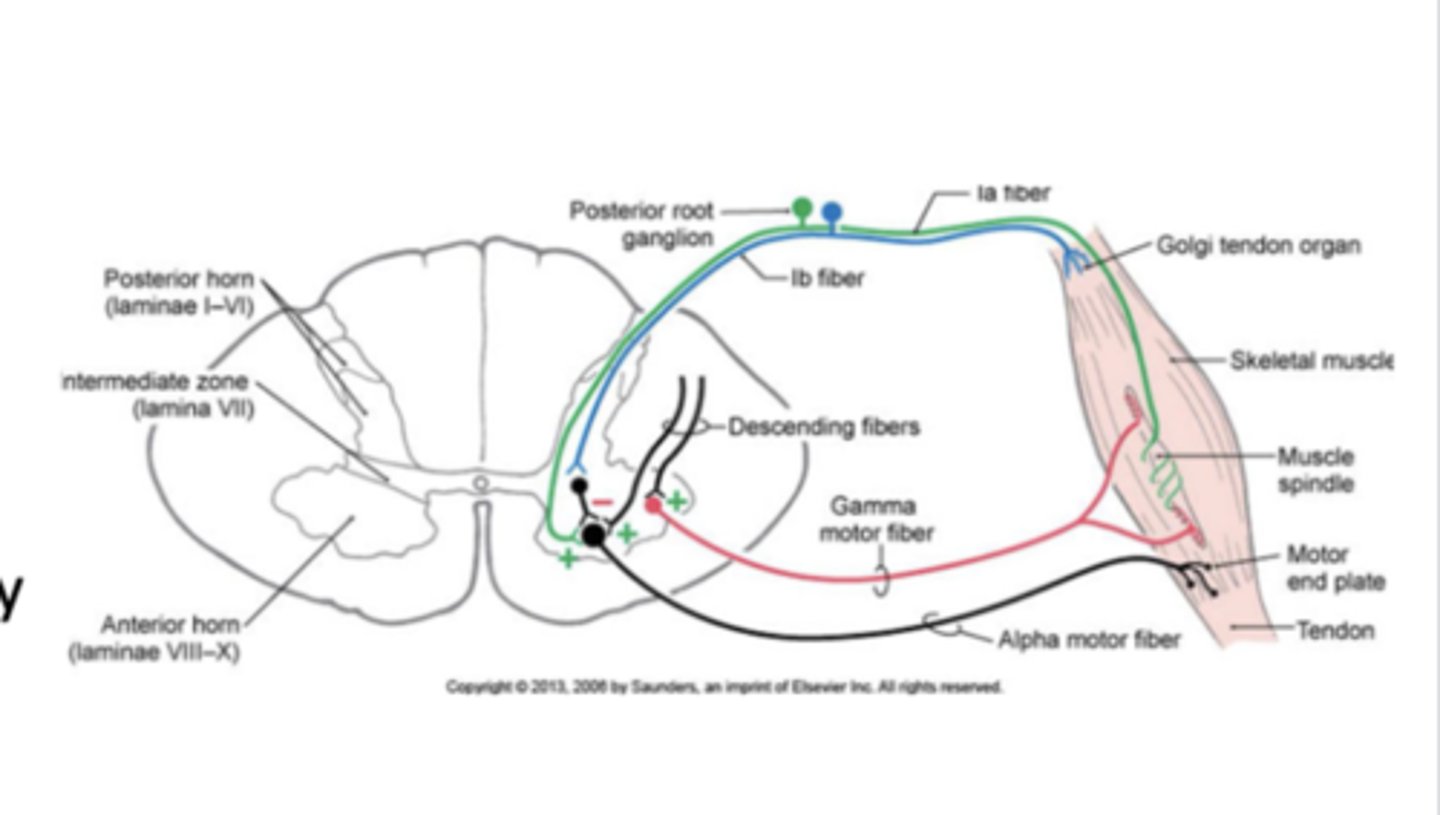
How are the local circuit neurons & LMNs topographically organized in the spinal cord?
orderly arrangement between LMN pools and the muscles they supply in the spinal cord
longitudinal arrangement
LMNs for
upper limb: located in the cervical enlargement of spinal cord
trunk: located in thoracic regions
lower limb: lumbar enlargement
Organization of LMNs in the Spinal Gray Matter
flexors are located ____ in the spinal cord
posterior
proximal muscles are located ___ in spinal cord
medial
extensors are located ______ in the spinal cord
anterior
distal muscles are located _____ in spinal cord
lateral
Organization of LMNs in the Spinal Gray Matter pic

medially located local circuit neurons project to ______ spinal segments and cross the midline ____ and communicate with ____ located LMNs for ____
multiple; bilaterally; medially; postural control
laterally located local circuit neurons project to ______ spinal segments and most are _____ and they communicate with ____ located LMNs for the control of _____
fewer; ipsilateral; laterally; skilled limb movement
What is the functional significance of this organization?
This organization allows for efficient control: medial areas manage posture and balance, while lateral areas specialize in skilled, voluntary movements of the limbs
idk CHECKKKKK
where are LMNs located in the brainstem?
in the motor cranial nerve nuclei
axons of LMN will contact skeletal muscle at specialized synapse called
motor end plate or neuromuscular junction
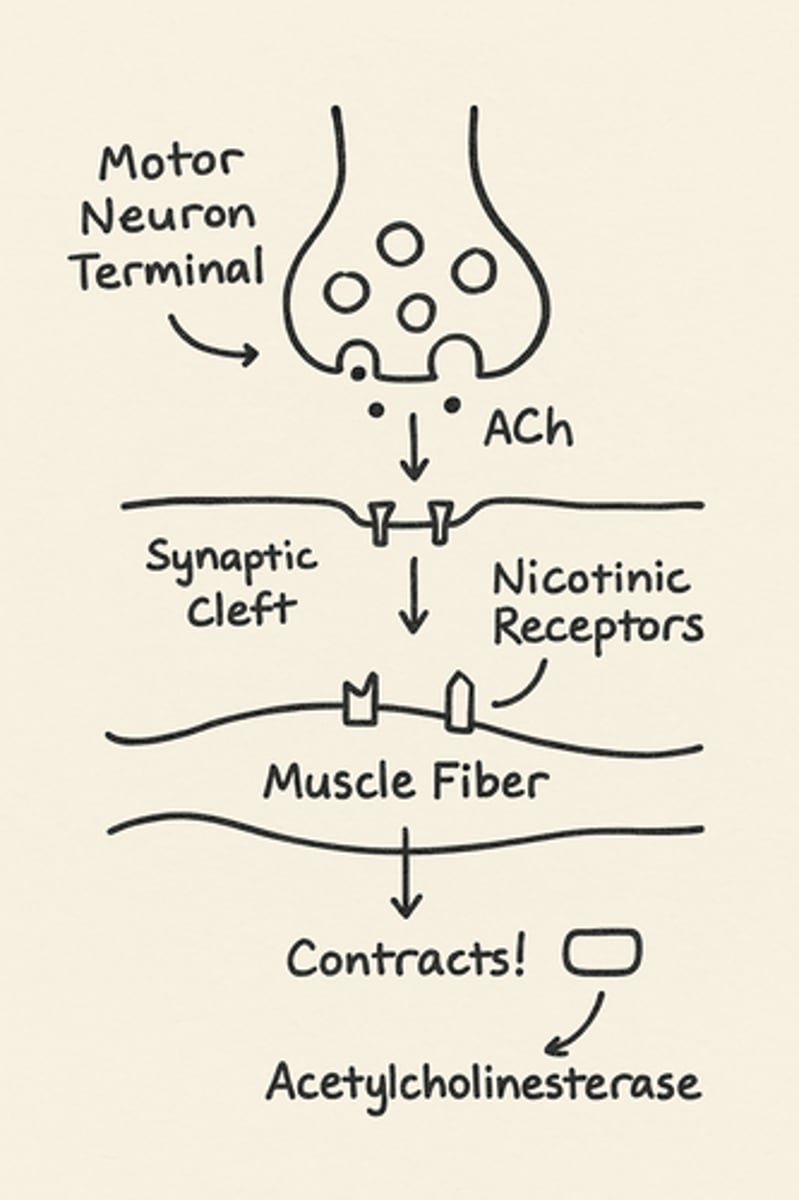
Be able to describe the NMJ and the synaptic transmission at this junction.
1:1 ratio of firing of motor neuron action potential and activation of muscle fiber
alpha motor neuron synapses with motor end plate
1. at active zones there are a large number of docking proteins and acetylcholine located in close proximity to voltage gated calcium channels
2. at subjunctional folds there are clusters of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors which are ionotropic receptors selective for cations
3. activation of the receptor causes influx of Na+ which depolarizes the muscle membrane (quick cross-bridge cycling)
4. acetylcholine is removed from synaptic space by enzymatic breakdown by acetylcholinesterase
NMJ and the synaptic transmission at this junction simple pic
What causes muscular fatigue and weakness in myasthenia gravis?
In myasthenia gravis, the body makes antibodies that block or destroy the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
Antibodies block ACh receptors → fewer signals reach the muscle → muscle gets weak and tired quickly.
IDK CHECKKK
What is a motor unit and what types of motor units do skeletal muscles contain?
answers after this
motor unit
is the single alpha motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates
small motor units
small muscles that generate lower levels of force
large motor units
large muscles that generate higher levels of force
type I motor unit
slow twitch: generate lower levels of tension but for longer periods of time (fatigue resistant) - postural control muscles
type II motor unit
generate higher levels of force but for shorter periods of time
-- IIa: fast twitch oxidative
-- IIb: fast twitch glycolytic
size principle - muscle contractions
grading force and muscle contractions motor unit
smaller motor units are recruited first followed by larger units
rate code - muscle contractions
grading force and muscle contractions motor unit
as the need for greater force and speed increases, synaptic input increases and the firing rate of neurons increase
How do alpha motor neurons encode the force of muscle contraction?
rate coding IDK CHECK
What is the role of peripheral sensory input in motor control?
activity of LMN influenced by what two sources ONE of them being peripheral sensory input
Peripheral sensory input provides feedback to the nervous system about body position, movement, and environment, helping to adjust and guide motor actions for coordination, balance, and accuracy.
IDK CHECKKK
reflex definition
is an automatic, involuntary response to a stimulus, that happens without conscious control. IDK CHECK
reflex pathways can produce
complex, coordinated activity at multiple joints
reflexive movements are ____ but descending input can
involuntary; alter the threshold for their activation or their gain (strength of response)
example: when think a plate is hot you pull your hand, or when a plate is hot and you carry it to the table instead of following instinct to drop it
muscle tone definition
steady level of tension in muscles - felt as a resistance of the muscle to passive stretch
function of the muscle spindle
proprioceptors that monitor muscle length and mediate monosynaptic stretch reflexes
structure of a muscle spindle
group 1a fibers = afferent endings that respond to small stretches and depend on velocity
group 2 fibers = afferent endings that respond to sustained stretch
intrafusal fibers of muscle spindle
nuclear bag and nuclear chain fiber innervated by gamma motor neurons (efferent)
sensory endings of muscle spindle
group Ia afferents: responsive to small, phasic stretches; velocity dependent
group II afferents: responsive to sustained stretch
What is alpha-gamma co-activation, and why is it important?
during voluntary movement both alpha and gamma motor neurons will be activated simultaneously
activation of the alpha motor neuron results in muscle fiber contraction
activation of the gamma motor neuron maintains the sensitivity of the muscle spindle during ongoing movement by keeping it tense enough to sense change (allows the system to provide feedback regarding muscle length during movement)
What is gamma bias?
(gain) amount of force generated in response to a muscle fiber stretch
*bias is modulated by UMN's to meet functional demands
high gain
small amount of stretch produces large increase in # of motor units recruited and increased firing rate resulting in large increases in tension
low gain
greater stretch needed to produce the same level of tension (experience during yoga)
What is the gamma loop and what happens to this loop when descending control is lost?
activation of gamma motor neurons can indirectly cause activation of an alpha motor neuron there by mediating muscle contraction
if descending control is lost = HYPERTONUS (muscle stiffness) + AREFLEXIA (diminished/absent reflexes)
Review the major brainstem reflex circuits covered in lecture.
Jaw jerk circuit
Corneal circuit
Pharyngeal circuit
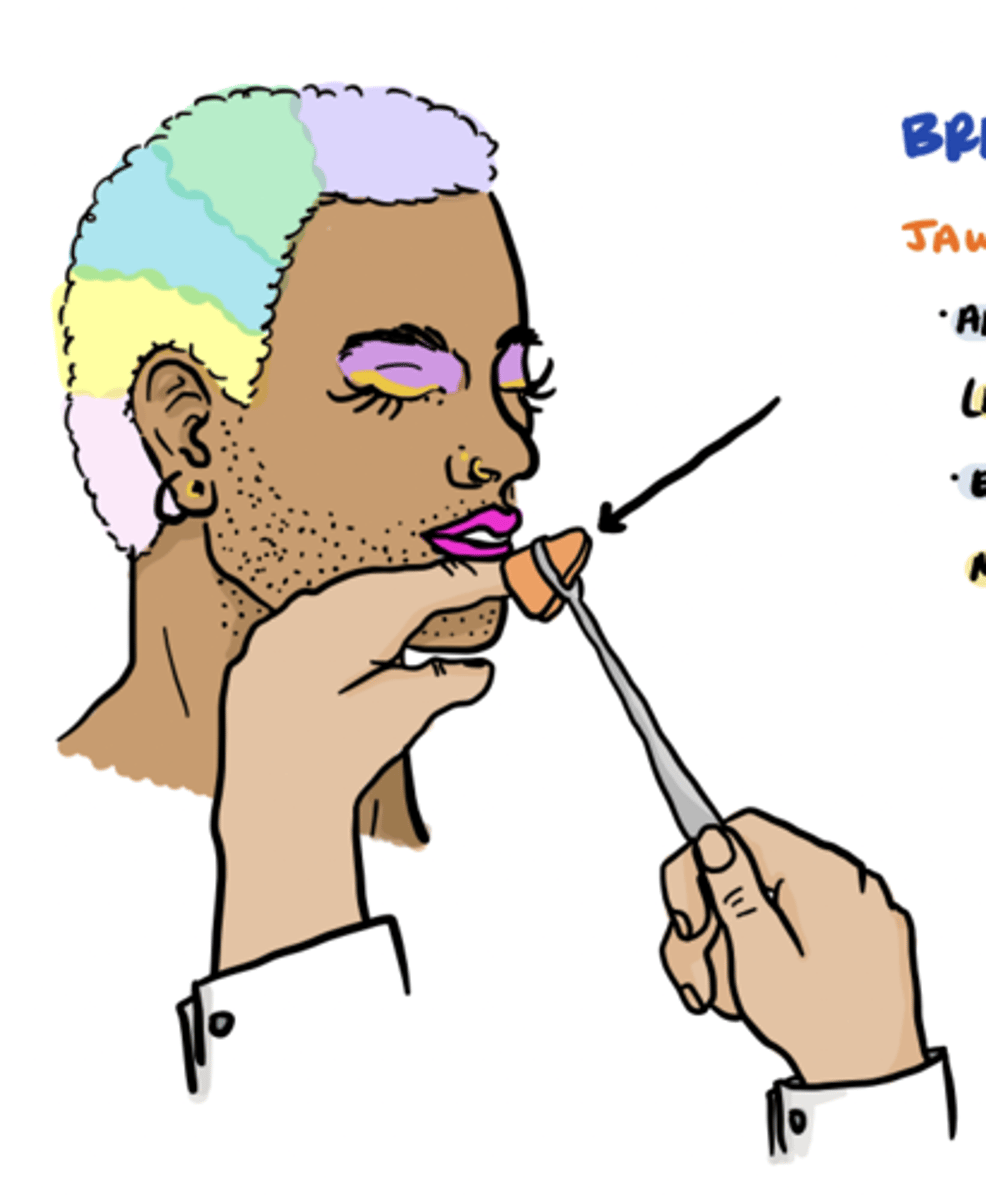
jaw jerk reflex circuit
afferent limb: proprioceptive fibers of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (mesencephalic nucleus)
efferent limb: motor fibers from the trigeminal motor nucleus traveling in the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
what CN does the jaw jerk reflex involve
CN V
jaw jerk reflex pic

corneal reflex circuit
afferent limb: nociceptive fibers of the opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve project to the spinal trigeminal nucelus (pain)
2nd order neurons of spinal trigeminal nucleus project to facial motor nuclei
efferent limb: motor fibers from the facial motor nuclei travelling in the facial nerves project to orbicularis oculi muscle
what CN are involved in the corneal reflex
CN V and CN VII
corneal reflex pic

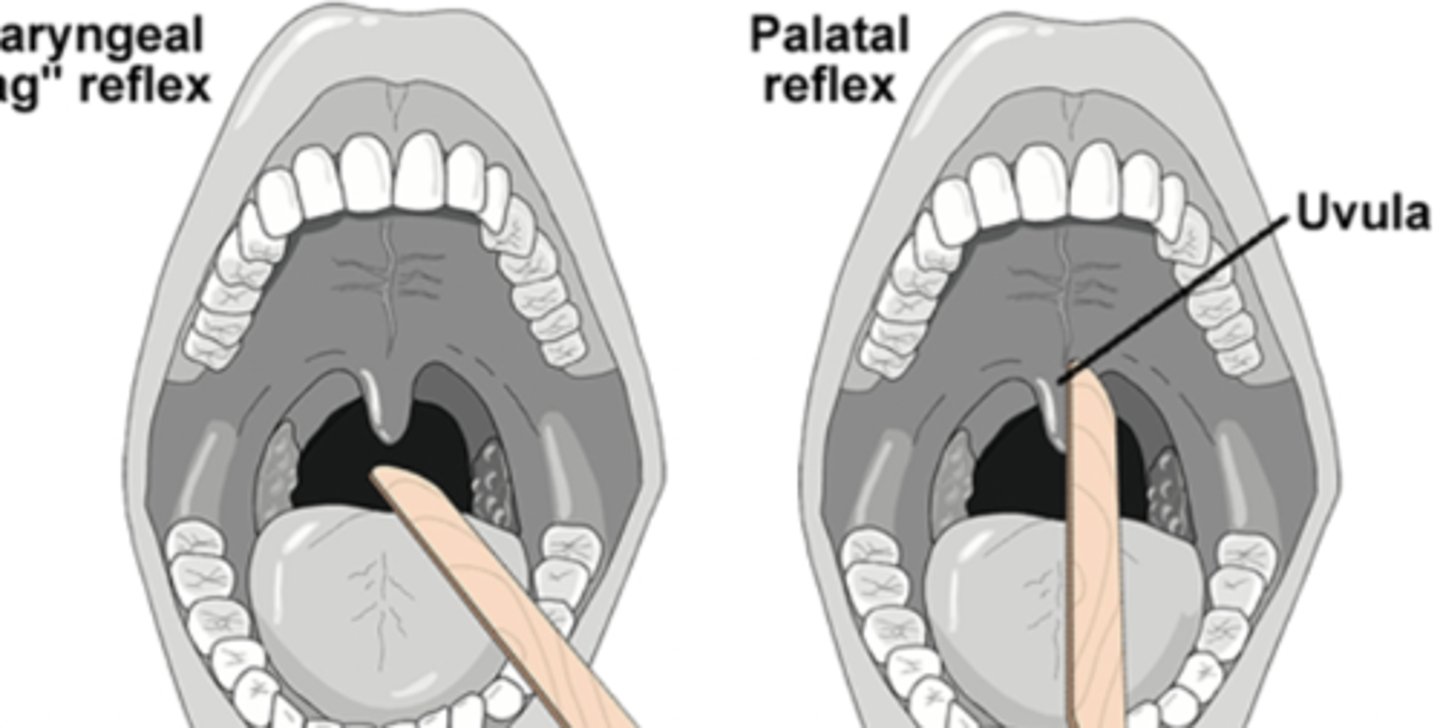
pharyngeal reflex circuit
afferent limb: nociceptive fibers of glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves project to the spinal trigeminal nucleus
2nd order neurons of spinal trigeminal project to the nucleus ambiguus bilaterally
efferent limb: motor fibers from nucleus ambiguus traveling in the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve project to posterior oral and pharyngeal muscle
what CN are involved in the pharyngeal reflex
CN IX and X
what is the purpose of the pharyngeal reflex
gag reflex, prevent choking
the corneal reflex and pharyngeal reflex are _____ and ______
direct and consensual
pharyngeal reflex pic
are lower motor signs seen on the ipsilateral or contralateral side?
ipsilateral
lower motor neuron signs
damage to the final motor pathway will cause some combination of the following
-weakness and eventual muscle atrophy
-fibrillations or fasciculations: spontaneous twitches due to -involuntary contractions of one motor unit (fibrillation) or group of motor units (fasciculation)
-hypotonia: decreased tone in skeletal muscles
-areflexia or hyporeflexia: lack of reflex activity or weak reflex activity
lower motor signs pic

f you have a lesion of a CN nuclei or a peripheral nerve (cranial or spinal), would the deficitsbe ipsilateral or contralateral to the lesion?
ipsilateral (same side as the lesion)
Because LMNs go directly from the brainstem or spinal cord to the muscles on the same side of the body or face. If the LMN is damaged, the muscles it serves on that same side are affected