Sequences and Series
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Tests for finding monotonic increase or decrease
Difference Test
Quotient Test
Derivative Test
When to use monotonic difference test
On sequences with rational expressions
When to use monotonic quotient test
On sequences with factorials and expressions such that 2n/n!
When to use monotonic derivative test
On sequences with an easy derivative and easy sign
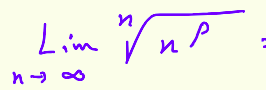
where p is any real number
= 1
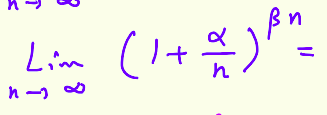
= eab, a,b /= 0

= 0 if -1 < r < 1
= inf if r > 1
DNE if r =< -1
When to use divergence test
Limit is easy to compute
To check for divergence (but not convergence)
When to use ratio test
If there are factorials or powers
When to use nth root test
If series contains powers (fixed or variable)
When to use comparison test
For determining absolute and conditional convergence
When to use limit comparison test
On polynomial expressions that can be replaced with their leading terms
Choices for the limit comparison test
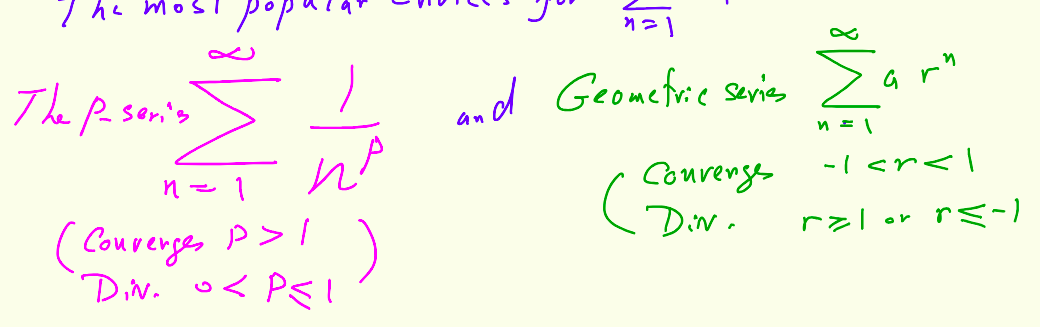
When to use limit integral test
If the following conditions are met:
1. f(x) > 0
2. f(x) is continuous on x > 1
3. f(x) is strictly decreasing on x > 1
Power Series: L
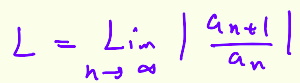
Power Series: R
R = 1/L
Power Series:Convergence
If R > 0, absolute convergence in the open interval (C-R, C+R) and diverges elsewhere
If R = 0, series only converges at x=c
If R = inf, series converges when x is real
Tests for finding series convergence
Divergence Test
Ratio Test
nth Root Test
Limit Comparison Test
Comparison Test
Integral Test
Alternating Series Test
When to use Alternating Test?
On series in the form (-1)nan or (-1)n-1an
Convergence condition for Alternating Test
Limit is 0
An is decreasing
Convergence condition for divergence test
Limit is 0 = we don’t know
Limit isn’t 0 = divergence
monotonic condition for derivative test
f’(x) > 0 = increase
f’(x) < 0 = decrease
monotonic condition for difference test
an+1-an > 0 = increase
an+1-an < 0 decrease
monotonic condition for quotient test
an+1/an > 1 = increase
an+1/an < 1 decrease
Convergence condition for ratio test and nth root test
0=< Limit < 1 = Converge
Limit > 1 = Diverge
Limit = 1 = we don’t know
Convergence condition for comparison test
If an is smaller than bn and bn converges, an converges too.
If an is larger than bn and bn diverges, an diverges too.
Convergence condition for limit comparison test
If the limit of an/bn /= 0 then an and bn have the same behaviour
Convergence condition for integral test
If integral J < inf, converges
if integral J = inf, diverges
Convergence condition for harmonic series
If P>1, converges
If 0< P =<1, diverges
Convergence condition for geometric series
-1 < r < 1, converges
r =< -1 or r >= 1