Biochem Glycolysis/Krebs Cycle
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Rather than produce ATP, catabolic processes produce what?
A chemical gradient
NAD+/NADH can act as what?
Hydride donors/acceptors
FAD+/FADH2 can perform chemistry with how many electrons?
One or two.
What is ACTUAL free energy?
Describes the actual free energy that can be used to do work in real life
What does actual ΔG equal at equilibrium?
0
What is the equation for actual free energy?
ΔG = ΔG°’ + RTln(Q)
Is actual ΔG more favorable than ΔG°’? Why or why not?
Yes bc controlling [reactant] or [product] can provide an extra driving force to promote metabolic flux.
While ΔG’s are additive, Keq’s are…
multiplicative!
What are the three thermodynamic reasons as to why ATP is such a great energy source?
(1) high in energy bc it is destabilized by negative charges, (2) ADP and Pi are effectively hydrated, and (3) ATP hydrolysis produces resonance stabilized products
Unlike anhydrides, phospho-anhydrides significantly higher ____ for its hydrolysis.
Activation Energy
Why do phospho-anhydrides have higher activation energy for their hydrolysis compared to anhydrides?
Electron density surrounding phosphates makes it harder for nucleophiles to attack bc of electron repulsion
Compounds with very large ΔG°’ for hydrolysis can be used to do what?
Make ATP in a thermodynamically favorable process.
What is glycolysis?
The process by which glucose is oxidized to yield 2 pyruvate and 2 net ATP.
The first five reactions of glycolysis are the “preparatory phase,” which use ____ to produce _____.
2 ATP; 2 3-Carbon sugars
The second half of glycolysis is called the “payoff phase,” which grosses ___ and produces ____
4 ATP; 2 Pyruvates
What is the first step of glycolysis?
Phosphorylation of Glucose
What is the reaction of the first step of Glucose?
ATP + Glc —> G6P + ADP
What enzyme is involved in the Phosphorylation of Glucose?
Hexokinase (HK)
What is the purpose of glucose phosphorylation?
Make Glc no longer suitable for glucose transporter, trapping it in cell and maintaining Glc gradient. Sets up 1 of 2 phosphate groups for future reactions
Phosphorylation of glucose is a classic example of what?
Induced fit and energy coupling
Hexokinase exhibits a “hinge” mechanism, meaning what?
When no substrate is bound, enzyme is open. When substrate is bound, hinge closes to exclude water.
Xylose, due to its similarity in shape to Glucose, acts as a ____ for Hexokinase
Competitive Inhibitor
What is the second step of Glycolysis?
Isomerization of G6P to F6P
What is the reaction of step 2 of glycolysis?
G6P —> F6P
Is the first step of glycolysis favorable?
Very much so.
What enzyme is involved with G6P Isomerization?
Phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI)
What is the purpose of G6P Isomerization?
Sets up correct conformation for future reactions, namely, alcohol on C1 for creating F1,6BP and carbonyl on C2 for C3/C4 cleavage
How is Step 2 of Glycolysis regulated?
Mass Action, stays near equilibrium
What does it mean that catalysis of PGI has a bell shaped pH dependence?
PGI exhibits max rate at pH = 7 so that acidic component is protonated and basic component is not; suggests that these two groups are necessary to initiate catalysis
What is the third step of hydrolysis?
Phosphorylation of F6P
What is the reaction equation for the third step of hydrolysis?
ATP + F6P —> F1,6BP + ADP
What enzyme is involved in the third step of glycolysis?
Phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK)
What is the purpose of step 3 of glycolysis?
Sets up another Phosphate group that will have high phosphoryl transfer potential; ensures symmetry
Is step 2 of glycolysis favorable?
Very slightly —> dependent on mass action from previous step to drive reaction further
How is step 3 of glycolysis regulated?
Allosterically. Activated by AMP, signaling sugar F2,6BP; inhibited by ATP, citrate)
Phosphorylation of F6P is the first “committed step” of glycolysis, meaning what?
PFK is the key control point for regulation of glycolysis flux.
Is the third step of glycolysis favorable?
Very much so!
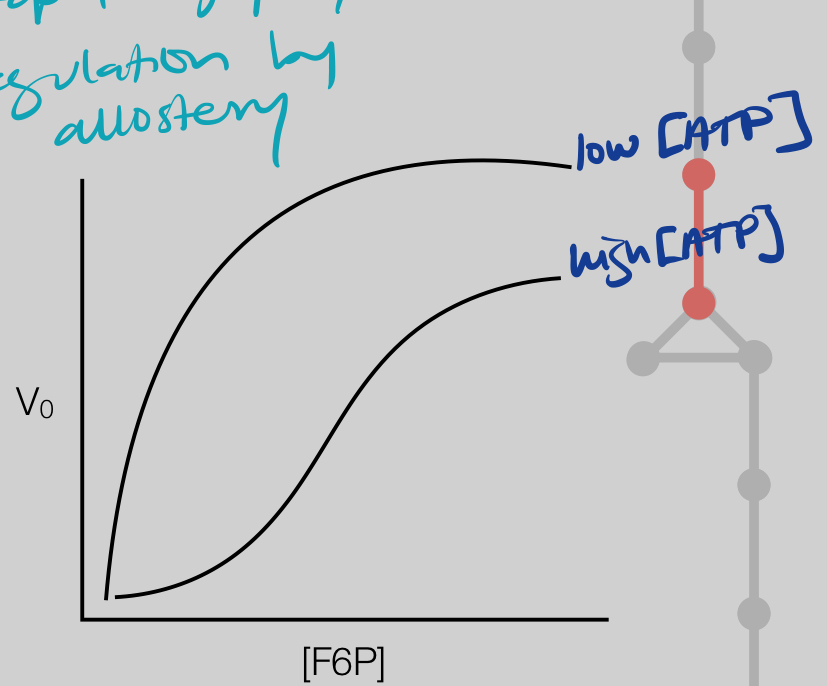
What explains this graph of the activity of the enzyme PFK?
When [energy] is high, you don’t need glycolysis to run.
What is the fourth step of glycolysis?
Splitting of 6 Carbon sugar to 3 Carbon sugar
What is the reaction equation for the fourth step of glycolysis?
F1,6BP —> DHAP + GAP
What enzyme is involved with the fourth step of glycolysis?
Aldolase
Is the fourth step of glycolysis favorable?
Just barely, thanks to mass action (high [reactant] and low [product])
What is the mechanism of the fourth step of glycolysis?
Retro-aldol reaction!
What is the purpose of the fourth step in glycolysis?
Splits the sugar into 2 (Phosphorylated) 3-Carbon fragments, each one has carbonyl group.
How does Aldolase in Glycolysis Step 4 circumvent the problem presented by high energy intermediate of enolate?
Uses Schiff base!
What is step 5 of glycolysis?
Conversion of DHAP to GAP
What is the reaction equation of step 5 of glycolysis?
DHAP —> GAP
What enzyme is involved with step 5 of glycolysis?
Triose Phosphate Isomerase
What is the purpose of step 5 of glycolysis?
Funnels DHAP to main glycolytic pathway; sets up phosphate to have high transfer potential following oxidation.
Is step 5 of glycolysis favorable?
Just barely UNfavorable; reaction stays near equilibrium unless Mass Action
TPI exhibits very high ____
catalytic efficiency
TPI exhibits a bell-shaped pH dependence, meaning what?
Functions best at pH = 7, needs to have both acidic and basic components in their correct forms for catalysis
What acidic component is used by TPI to catalyze its reaction?
Less acidic H of Histidine with pKa ~14, since more acidic H is tied up in H bond with another part of the enzyme.
What unwanted side reaction does TPI suppress?
Phosphate group elimination creating the toxic methylglyoxal molecules
How does TPI suppress the unwanted side reaction?
Prevents antiperiplanar conformation (relative to molecule’s orbitals) of Phosphate group through 10 reside loop which closes around substrate and rotates the bond.
What is step 6 of glycolysis?
Oxidation and Phosphorylation of GAP
What is the reaction equation for step 6 of glycolysis?
NAD+ + GAP —> 1,3-BPG + NADH
Is step 6 of glycolysis favorable?
No, but it is driven forward due to the very favorable next step, which keeps [product] low for this reaction and makes it proceed forward.
What enzyme is involved in step 6 of glycolysis?
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)
What problem is faced in step 6 of glycolysis?
If acid intermediate is used (COOH), reactant would remain as acid since conversion to RCOOP would have high Activation Energy.
How does GAPDH circumvent problem of Activation Energy in intermediate in step 6 of glycolysis?
Enzyme uses higher energy intermediate (Thioester) which has much lower Activation Energy for Phosphorylation.
What is step 7 of glycolysis?
Phosphoryl Transfer from 1,3BPG to ADP, forming ATP
What is the reaction equation of step 7 of glycolysis?
1,3-BPG + ADP —> 3-PG + ATP
Is step 7 of glycolysis favorable?
Just barely not, but proceeds through mass action. Occurs so long as [ATP] and [NADH] is low.
Step 7 of glycolysis involves substrate-level phosphorylation. What is that?
Generation of ATP directly from a chemical substrate.
What enzyme is involved in step 7 of glycolysis?
Phosphoglycerate Kinase (PGK)
What is step 8 of glycolysis?
Phosphate swap disguised as an isomerization
What is the reaction equation of step 8 of glycolysis?
3-PG —> 2-PG
What enzyme is involved in step 8 of glycolysis?
Phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM)
Is step 8 of glycolysis favorable?
Just barely not, stays near equilibrium; mass action
What is the purpose of the 8th step of glycolysis?
For the remaining Phosphate group to be transferred to ATP, it will leave behind a ketone (for pyruvate) rather than an aldehyde
The mechanism of step 8 of glycolysis also requires a catalytic amount of what molecule?
2,3-BPG
What is step 9 of glycolysis?
Elimination reaction which produces water.
What is the reaction equation of Step 9 of glycolysis?
2-PG —> PEP + H2O
What enzyme is involved in step 9 of glycolysis?
Enolase
What is the purpose of step 9 of glycolysis?
Converts a molecule with low phosphoryl transfer potential to one with high phosphoryl transfer potential (for next step!)
Is step 9 of glycolysis favorable?
Yes, but primarily remains at equilibrium; mass action
What kind of elimination reaction is step 9 of glycolysis?
E1CB
The mechanism of step 9 of glycolysis also requires the presence of which cation to maintain substrate stability?
Mg2+
What is the 10th and last step of glycolysis?
Synthesis of ATP from PEP
What is the purpose of the 10th step of glycolysis?
Transferring the phosphate from PEP to ATP
What enzyme is involved with the 10th step of glycolysis?
Pyruvate Kinase
Is the 10th step of glycolysis favorable?
Yes, very much so.
How is the 10th step of glycolysis regulated?
Allosterically —> inhibited by ATP + Ala, activated by F1,6-BP
Why is the 10th step of glycolysis so favorable?
Enolate protonation on top of already favorable phosphoryl transfer
What is the net reaction equation for glycolysis?
Glc + 2Pi + 2ADP + 2NAD+ —> 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O
What is the net gain of glycolysis?
2NADH, 2 ATP
What happens to pyruvate when O2 is not present?
Fermentation —> becomes alcohol and CO2
What happens to pyruvate when O2 IS present?
Proceeds through Krebs Cycle; Oxidative Phosphorylation