OCHEM: Reaction Mechanisms
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
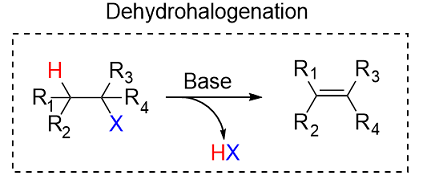
Dehydrohalogenation reaction
Reactants: KOH / ch3ch2oh
Elimination reaction, single step
What happens: a strong base, such as KOH or NaOH removes a proton (H+) and a halogen is removed, creating a pi bond
hydrohalogenation reaction
Reactants: H-Br or H-Cl
Carbocation rearrangement reaction
What happens:
Hydrophilic attack on alkene
Secondary carbocation remains and has a positive formal charge (+)
Hydride shift to second carbocation, becomes more stable tertiary carbon, leaving a positive formal charge (+) on the carbon that provided the hydrogen
Halogen attaches to more substituted carbon (the carbon mentioned in the previous step)
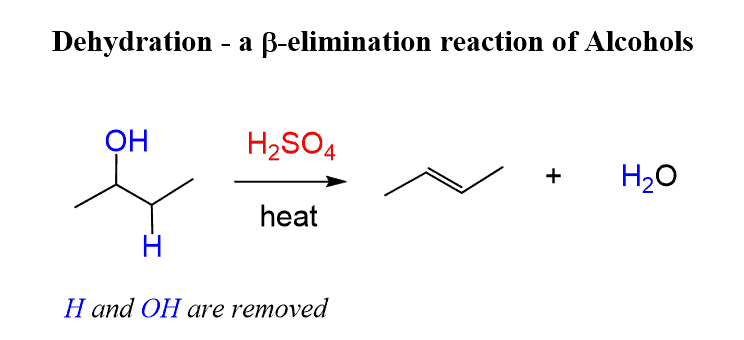
dehydration reaction
Reactants: H2SO4, H2O / THF (solvent), 50 Celsius (heat)
Condensation reaction, multi-step
What happens:
a water molecule is eliminated from the reactant molecule using a strong acid catalyst (H2SO4)
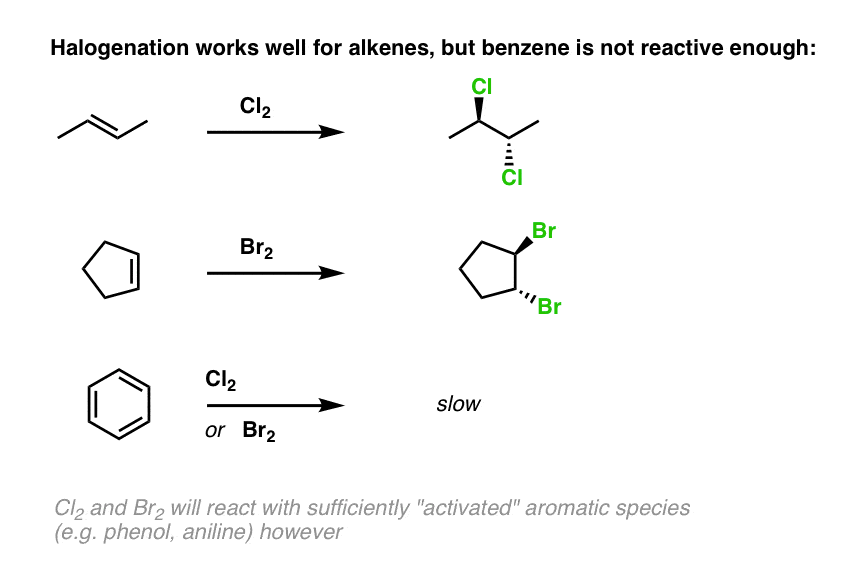
Halogenation reaction
Reactants: X2 (x= br or cl)
What happens:
alkene is treated with halogen which leads to the formation of two new C-halogen bonds on opposite faces of the compound
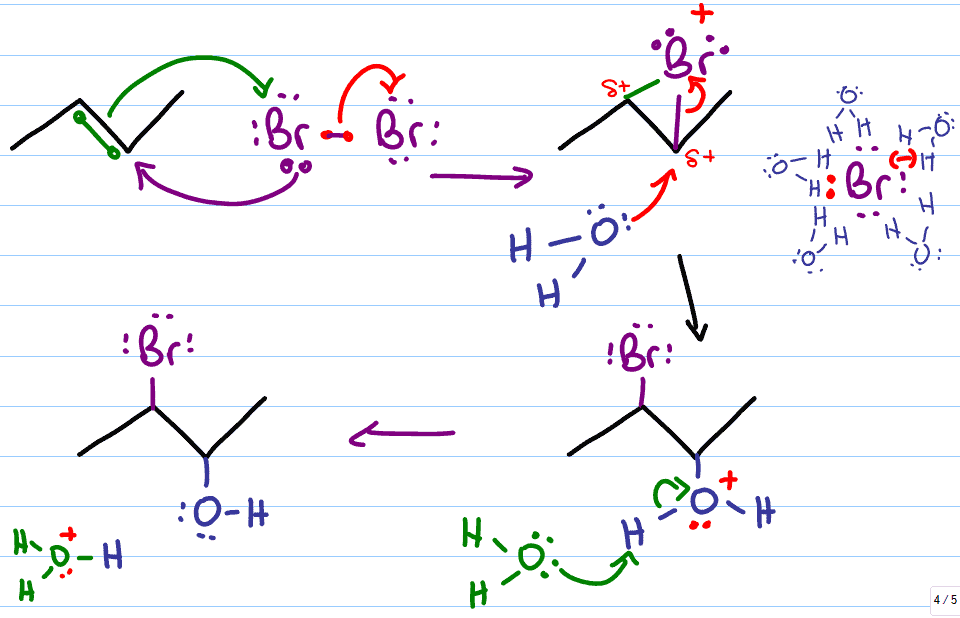
halohydrin reaction
Reactants: X2 / H2O (x=cl,br)
Anti-addition reaction
What happens:
Nucleophilic pi bond attacks halogen and breaks the bond
Halogen lone pair attacks carbon and forms halogen bridge
Second halogen breaks off, another water molecule acts as nucleophile and breaks the halide bridge
water attacks at the more substituted carbon and product is halohydrin with halogen on one carbon and OH group on adjacent carbon
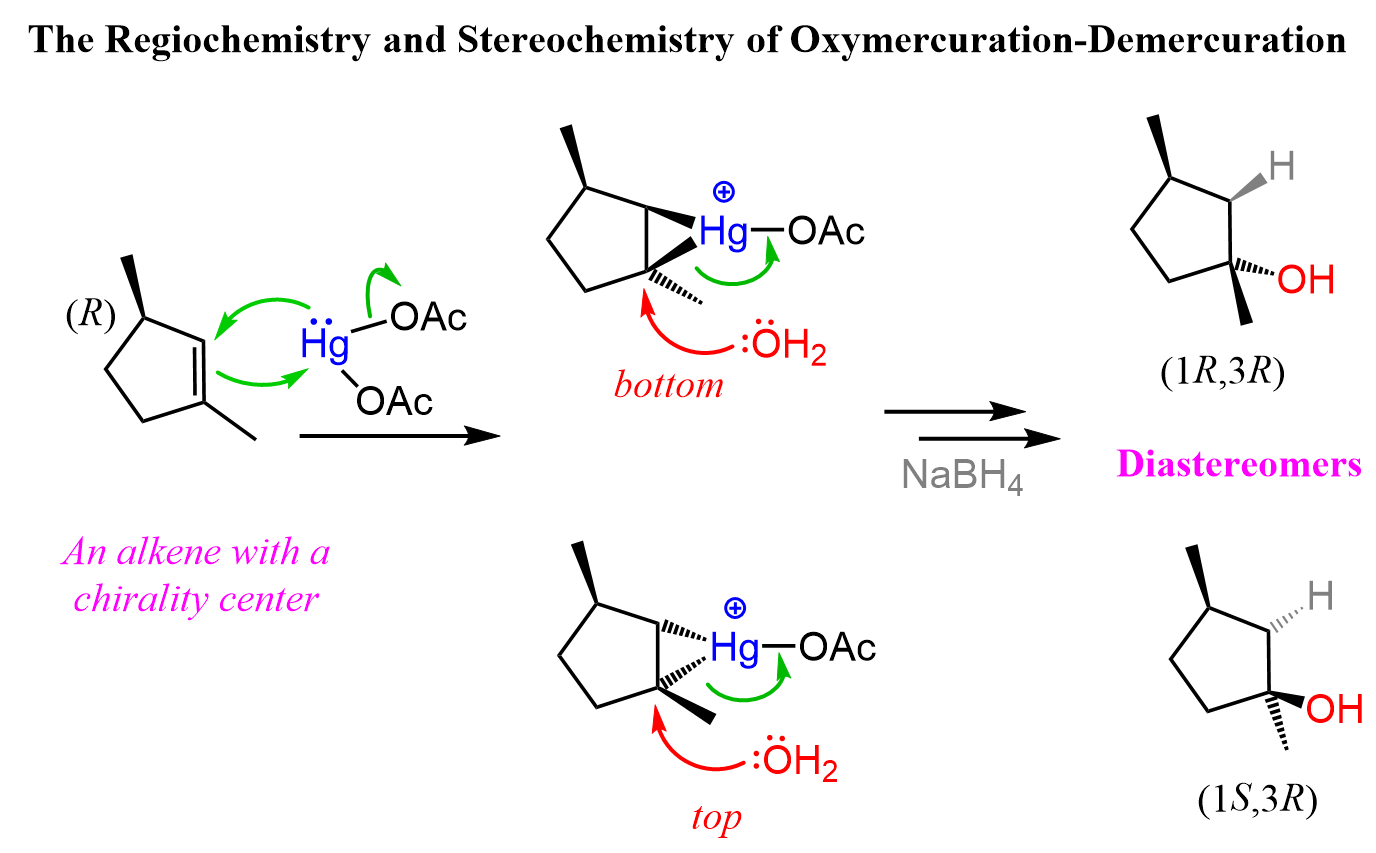
oxymercuration reaction
1. Hg(OAc)2, H2o
2. NaBH4
What happens:
a mercury acting as a reagent attacking the alkene double bond to form a Mercurinium Ion Bridge (weird triangle)
water molecule attacks the most substituted carbon —> opens the mercurium ion bridge, dashes followed by proton transfer to solvent water molecule.
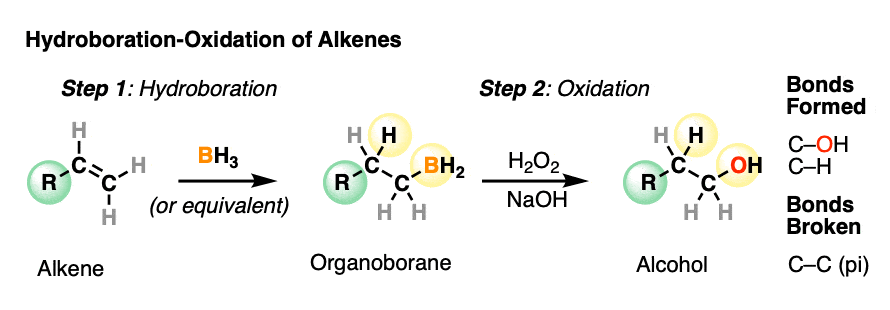
hydroboration reaction
Reactants:
1. BH3/THF (solvent, not important)
2.H2O2 / NaOH
two-step, Anti-Markovnikov
What happens:
alkene is treated with BH3 breaking the C=C pi bond and forms a C-H and C-B bond.
H2O2 (oxidant) is added in the presence of NaOH or KOH (strong base). A rearrangement occurs where the C-B bond is broken and a new C-OH bond is formed.
C-OH bond attaches to the less substituted carbon of the alkene with the C-H bond being formed on the more substituted carbon
hydrogenation reaction
Reactants: H2 & catalyst (Pd/C, Pt)
Syn addition, one-step
What happens: hydrogens are added to the same side of the double bond
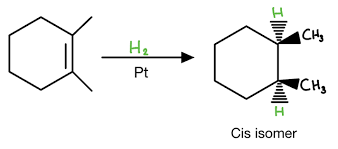
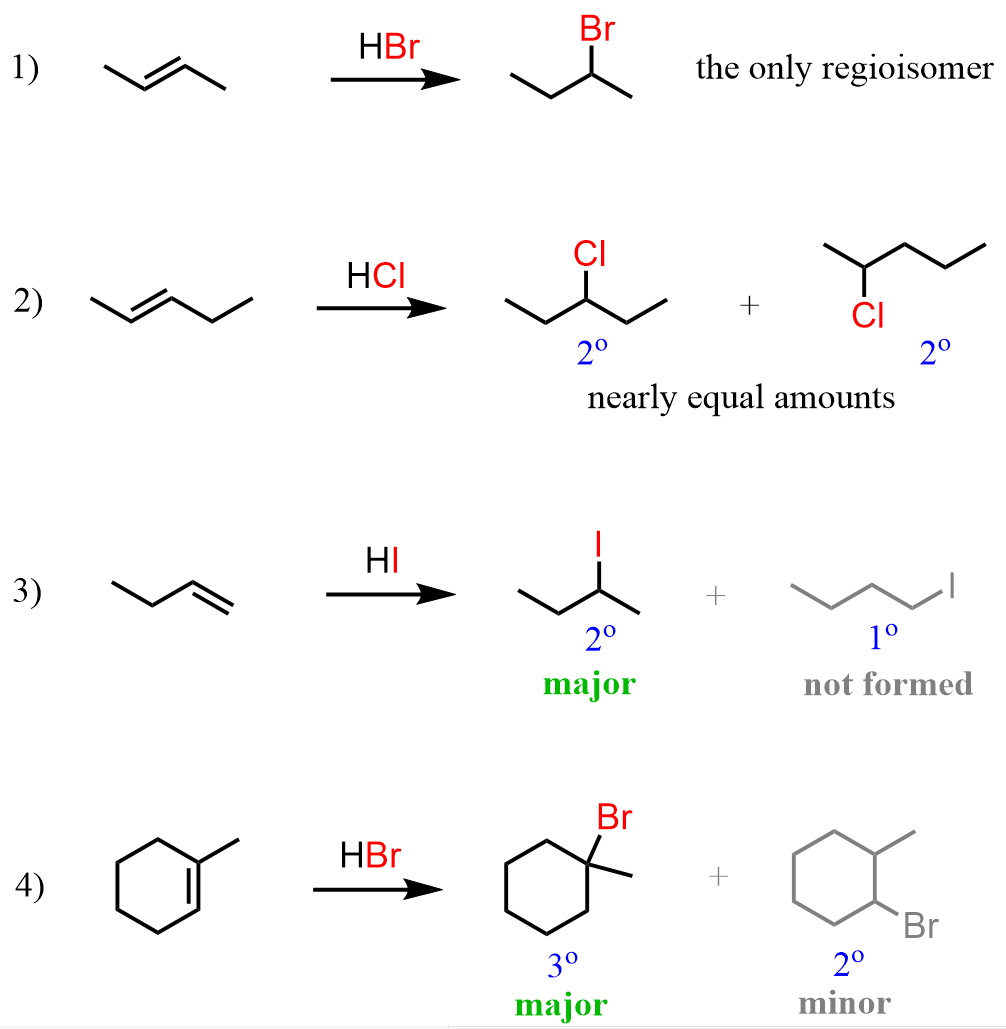
Markovnikov’s Rule
In the addition reaction of HX to an unsymmetrical alkene, the H adds to the carbon that already has the greater number of hydrogen atoms.
“H goes to more Hs”.
epoxidation reaction
Reactants: mCPBA / CH2Cl2 (solvent)
syn-addition, one-step
What happens:
The C=C pi bond breaks
Two new C–O single bonds form
The (weak) O–OH bond breaks
A carboxylic acid is transferred, a new C–O pi bond forms, while the existing C-O pi bond acts as a base to remove a proton from oxygen.
cis alkene gives cis epoxide, trans alkene gives trans epoxide
NEVER gives anti addition products
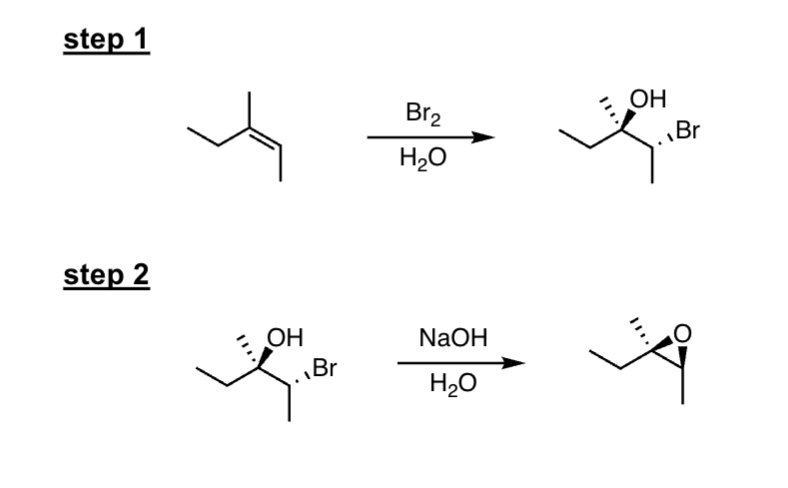
epoxides from halohydrins reaction
Reactants: 1. br2 / h2o 2. NaOH / H2O
two-step
What happens:
Preparation of a halohydrin by electrophilic addition of
HO-X to an alkeneTreatment of the halohydrin with a base (NaOH)
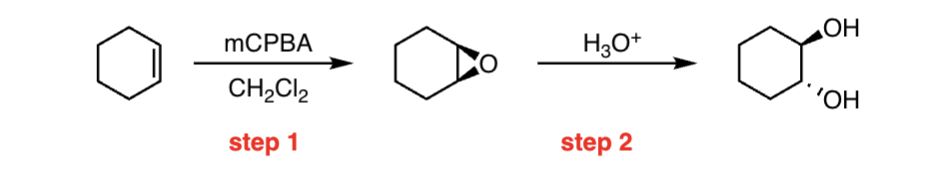
dihydroxylation of alkenes (two step)
1. mCPBA / ch2cl2 2. H3O+
two-step
What happens:
epoxidation followed by the acid catalyzed ring opening
reaction with water
dihydroxylation of alkenes reaction (one step)
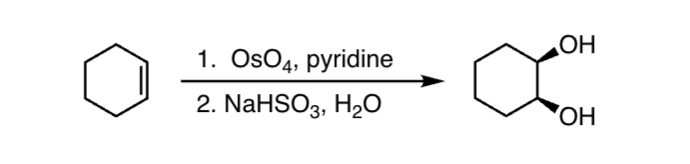
Reactants:1. OsO4, pyridine 2. NaHSO3, H2O
What happens:
treatment of the alkene directly with osmium tetraoxide
(OsO4)epoxides undergo an acid catalyzed reaction with water to give
the corresponding 1,2-diol
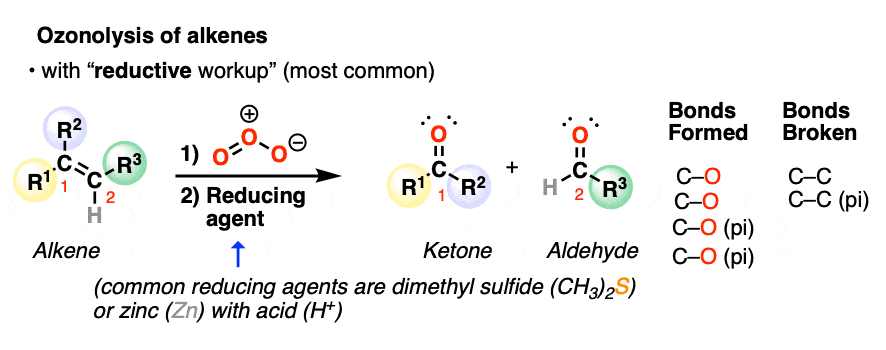
ozonolysis reaction
Reactants: 1. O3 2. Zn, ch3co2H
What happens:
The C=C bond is broken and two new C=O bonds are formed. The resulting C=O groups are known as carbonyl functional groups.
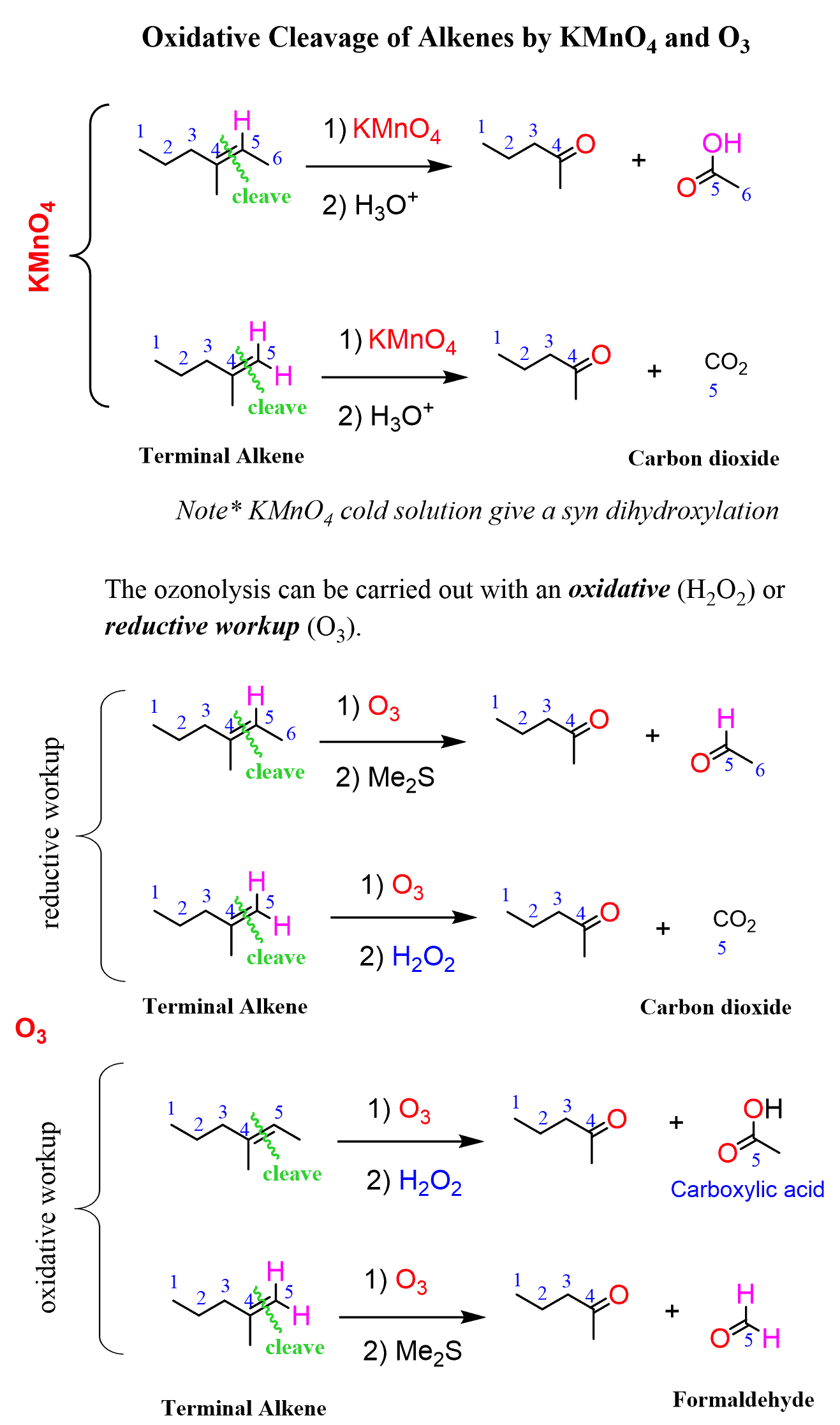
KMnO4 oxidation reaction
Reactants: KMnO4 / H3O+
What happens:
Alkene is cleaved down the middle splitting off into two products, one section being the left side of the alkene with a terminal oxygen
the right side:
if it is a terminal alkene, second product is carbon dioxide, if not, product is carboxylic acid
dihydroxylation / oxidation reaction
1. OsO4 / pyridine|NaHSO3 2. HIO
syn-addition
What happens:
always gives 1,2-diols (vicinal diols)
A C-C (pi) bond is broken
Two C-O bonds form on adjacent carbons
The two new C-O bonds are attached
cleavage of 1,2-diols reaction
HIO4 / H2O, THF(solvent)
What happens:
1,2- or vicinal diols are cleaved by periodic acid, HIO4, into two carbonyl compounds.
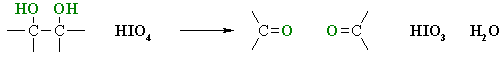
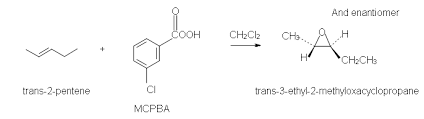
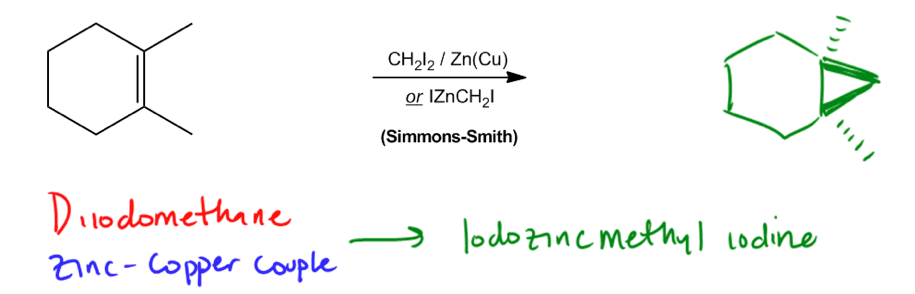
the simmons-smith reaction compounds
Reactants: CH2I2/ Zn(Cu) ether
What happens: The iodomethyl zinc iodide reacts with an alkene to give a cyclopropane. (creates CH2 triangle)
Anti-Markovnikov
addition reactions to unsymmetrical alkenes where the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon with less hydrogen atoms, and the other substituent (like a halogen or hydroxyl group) adds to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms
anti-Markovnikov's rule is observed only in H-Br
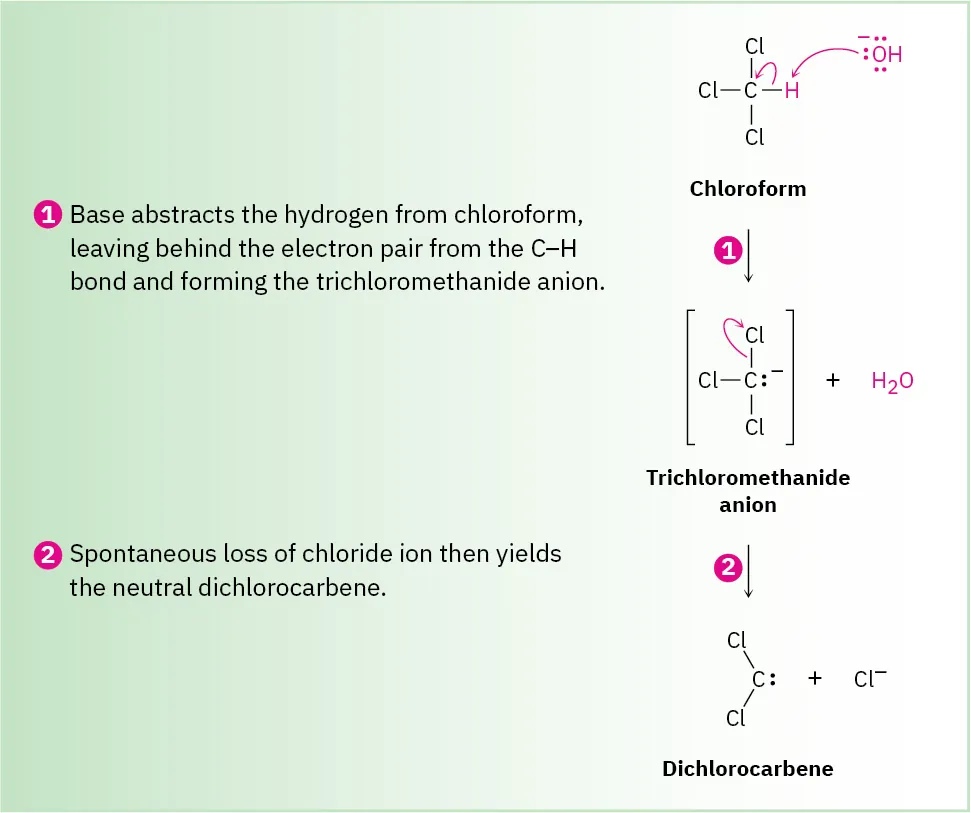
Dichlorocarbene reaction
Reactants: CHCl3, KOH
Deprotonation of CHCl3 gives the trichloromethanide anion, −:CCl3, which spontaneously expels a Cl– ion.