Biology Exam Revision
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
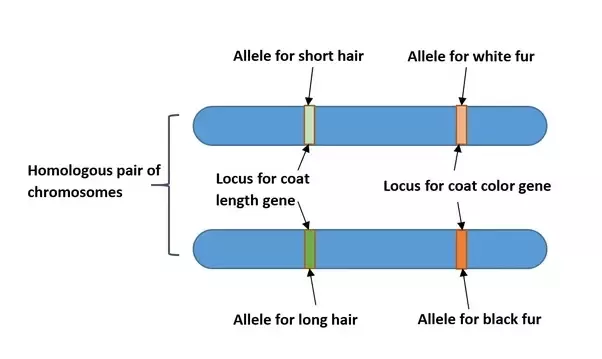
Alleles
Alternate forms of a gene for a particular characteristic
autosomes
non-sex chromosomes
carrier
an individual heterozygous for a characteristic who does not display the recessive trait
cell
the smallest unit of life and the building blocks of living things
centromere
section of a chromosome that links sister chromatids
Chargaff’s rule
a rule that states the pairing of adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine
chromatid
one identical half of a replicated chromosome
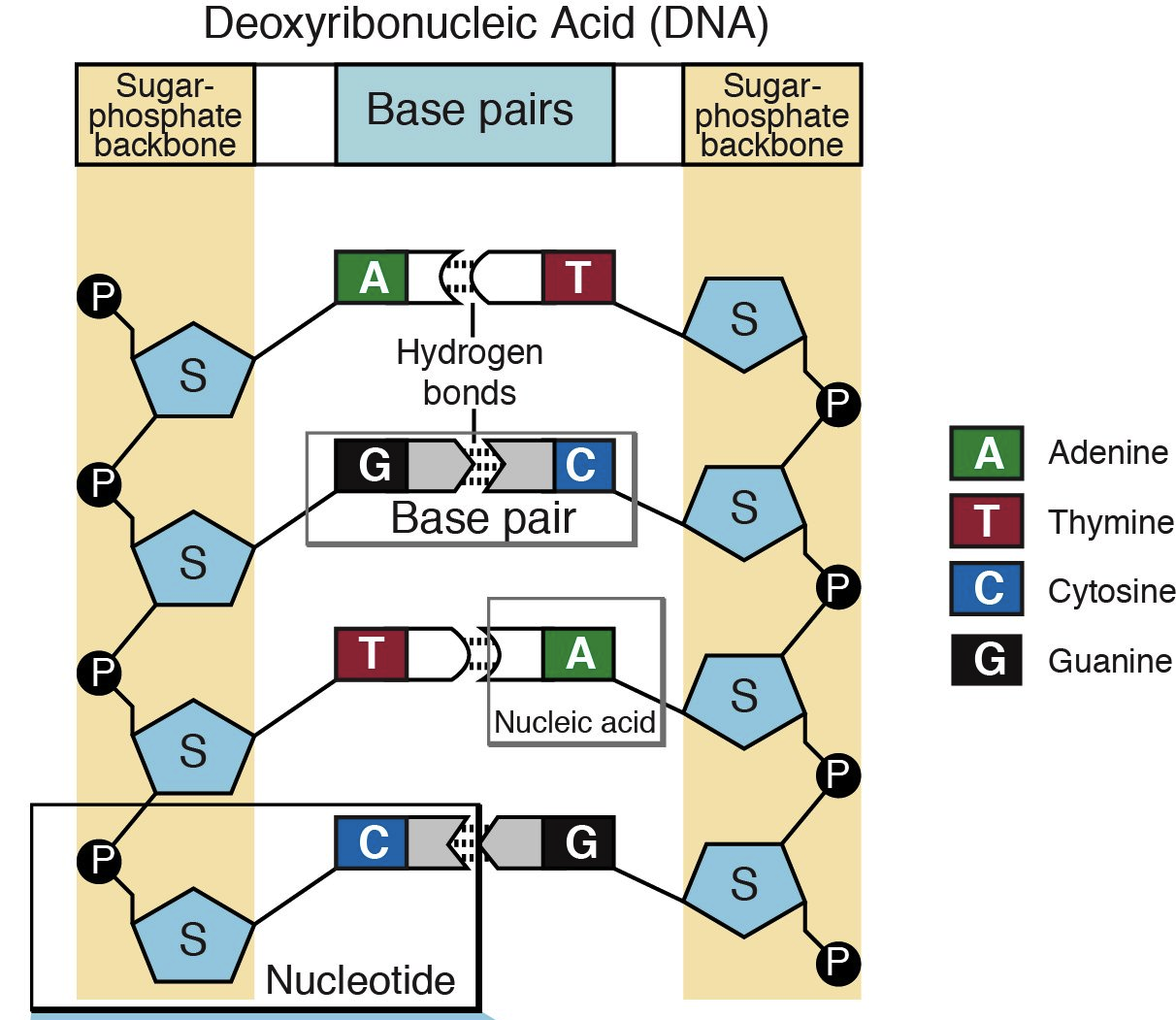
complementary base pairs
In DNA, specific base pairs will form between the nitrogenous bases adenine (A) and thymine (T) and between the bases cytosine (C) and guanine (G)
complete dominance
a type of inheritance where traits are either dominant or recessive
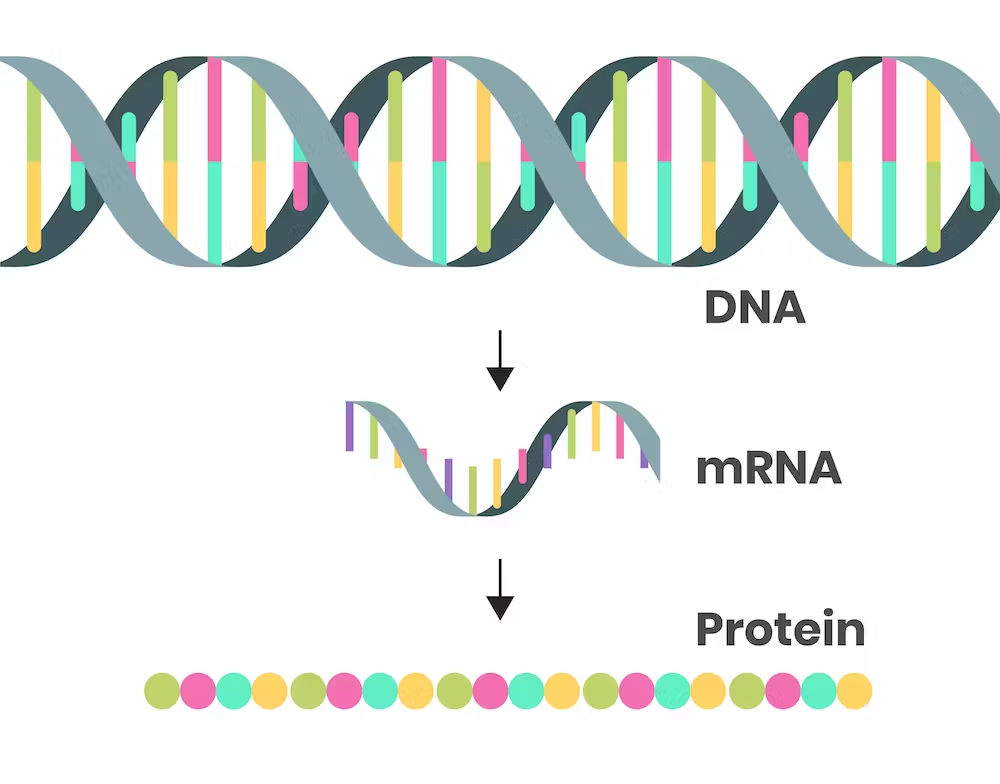
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
a substance found in all living things that contains its genetic information
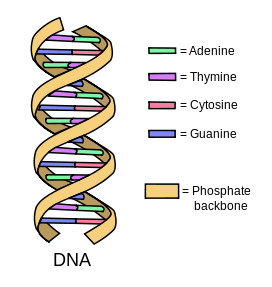
deoxyribose
the sugar in the nucleotides that make up DNA
diploid
the possession of two copies of each chromosome in a cell (2n) 46 in a human
DNA replication
process that results in DNA making a precise copy of itself
dominant
a trait (phenotype) that requires only one allele to be present for its expression in a heterozygote
gametes
reproductive or sex cells such as sperm or ova
gene
segment of a DNA molecule with a coded set of instructions in its base sequence for a specific protein product; when expressed, may determine the characteristics of an organism
genome
the complete set of genes present in a cell or organism
genotype
genetic instructions (contained in DNA) inherited from parents at a particular gene locus
haploid
the possession of one copy of each chromosome in a cell (n) 23 in a human
heterozygous
a genotype in which the two alleles are different
homologous
chromosomes with matching centromeres, gene locations, sizes and banding patterns
homozygous
a genotype in which the two alleles are identical
homozygous dominant
a genotype where both alleles for the dominant trait are present
homozygous recessive
a genotype where both alleles for the recessive trait are present
inheritance
genetic transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring
karyotype
an image that orders chromosomes based on their size
locus
position occupied by a gene on a chromosome
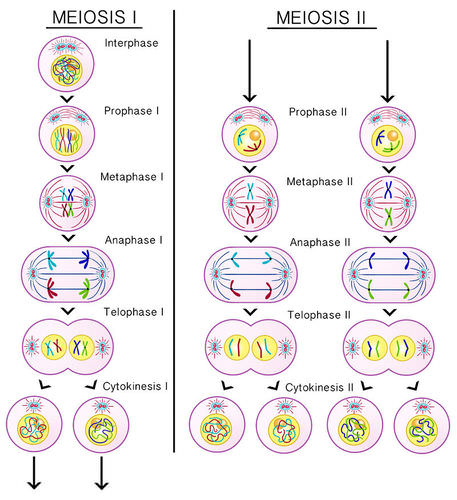
meiosis
cell division process that results in new cells with half the number of chromosomes of the original cell
transfer RNA (tRNA)
Molecules of tRNA are responsible for matching amino acids with the appropriate codons in mRNA.
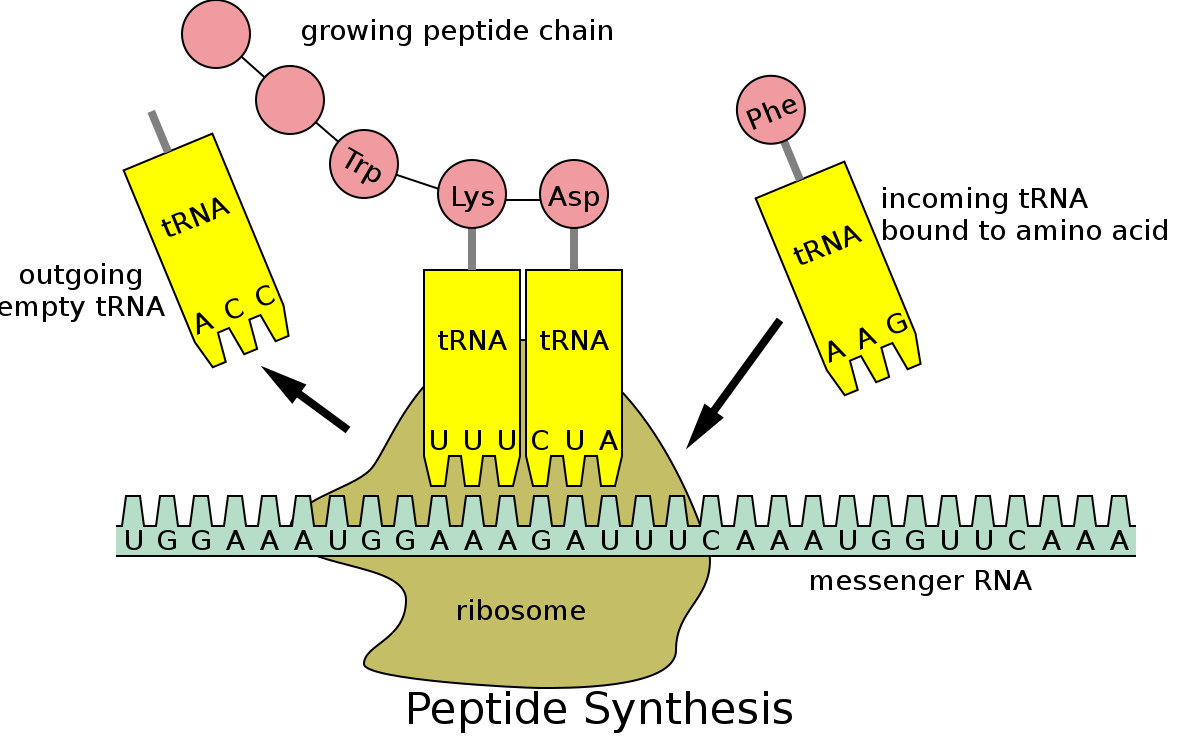
messenger RNA (mRNA)
single‑stranded RNA transcribed from a DNA template that then carries the genetic to a ribosome to be translated into a protein
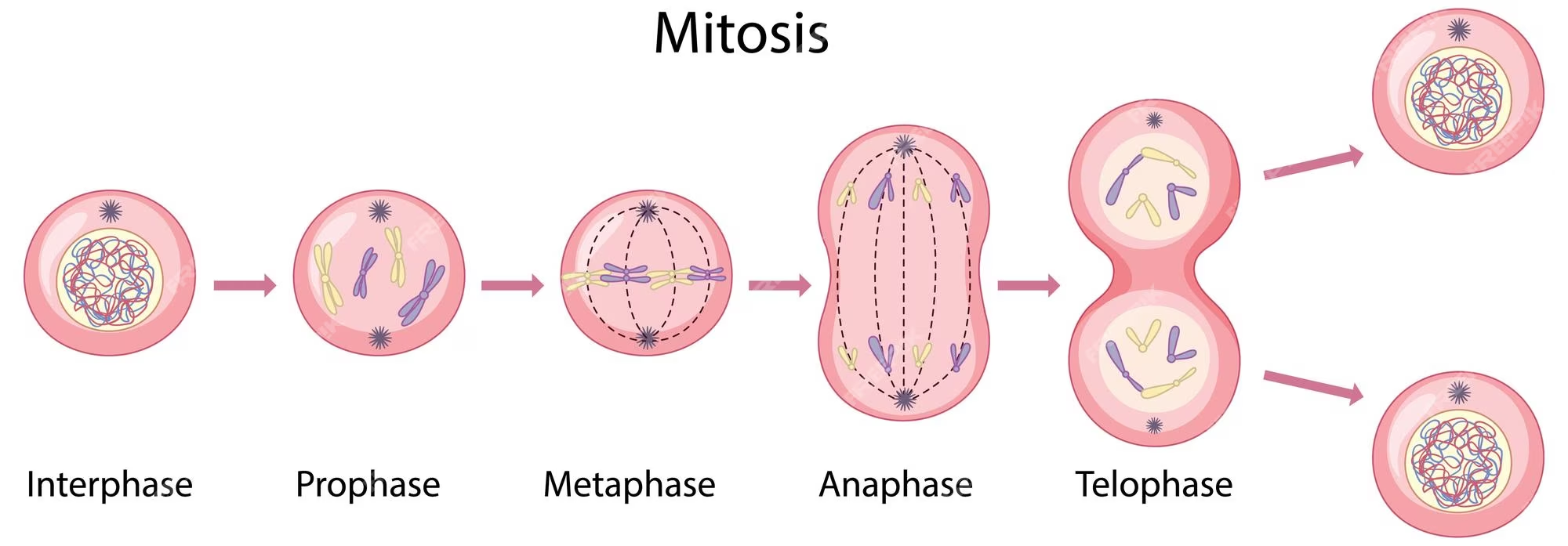
mitosis
cell division process that results in new genetically identical cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell, for non sex cells
monosomy
a condition where there is only one copy of a particular chromosome instead of two
mutations
changes to DNA sequence, at the gene or chromosomal level
nitrogenous base
a component of nucleotides that may be one of adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine or uracil
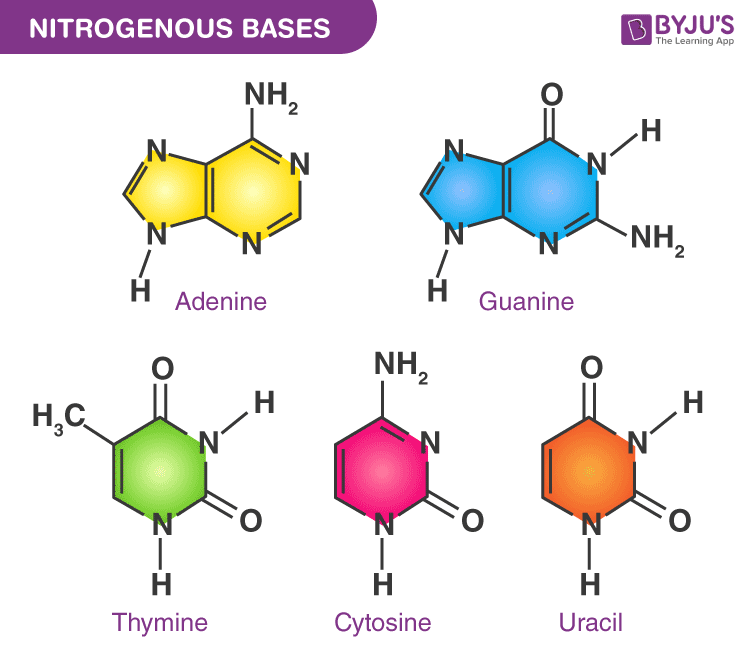
nucleic acids
molecules composed of building blocks called nucleotides, which are linked together in a chain
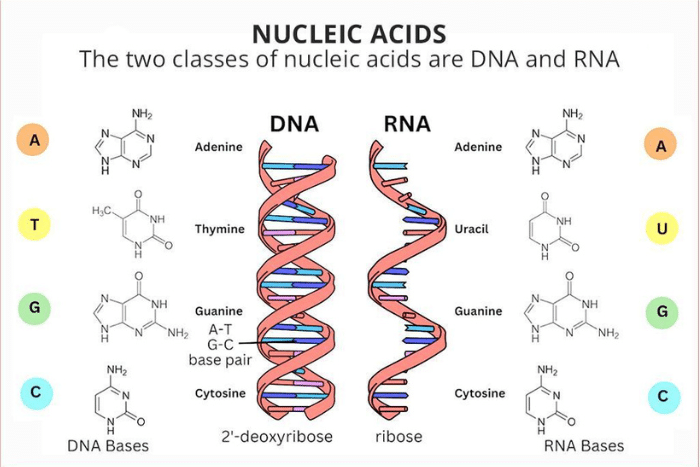
nucleotides
compounds (DNA building blocks) containing a sugar part (deoxyribose or ribose), a phosphate part and a nitrogen-containing base that varies
nucleus
roundish structure inside a cell that contains DNA and acts as the control centre for the cell
pedigree chart
diagram showing the family tree and a particular inherited characteristic for family members
phenotype
characteristics or traits expressed by an organism
Punnett square
a diagram used to predict the outcome of a genetic cross
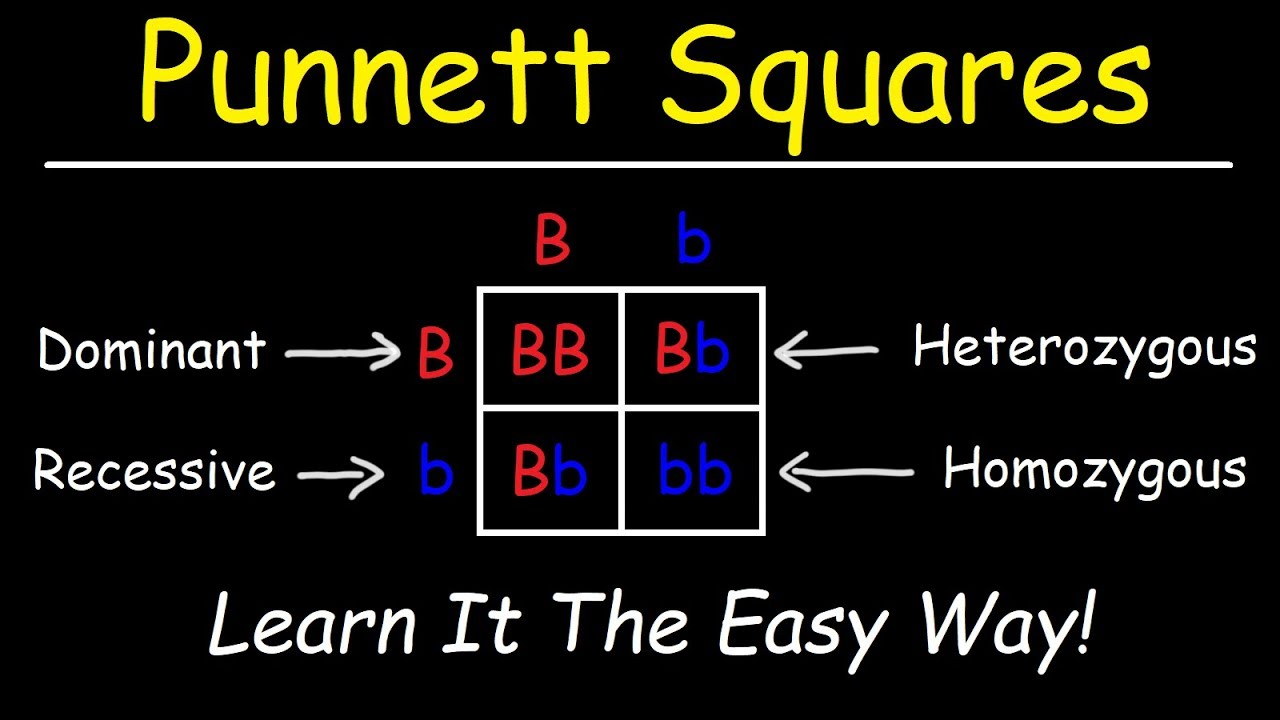
recessive
a trait (phenotype) that will only be expressed in the absence of the allele for the dominant trait
ribose
the sugar found in nucleotides of RNA
ribosome
organelle found in the cells of all organisms in which translation occurs, made of RNA and proteins
sex chromosomes
chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism
sex-linked inheritance
an inherited trait coded for by genes located on sex chromosomes
sister chromatids
identical chromatids on a replicated chromosome
somatic cells
cells of the body that are not sex cells
transcription
the process by which the genetic message in DNA is copied into a mRNA molecule
translation
the process by which mRNA is translated into proteins.
trisomy
a condition where there are three copies of a particular chromosome instead of two
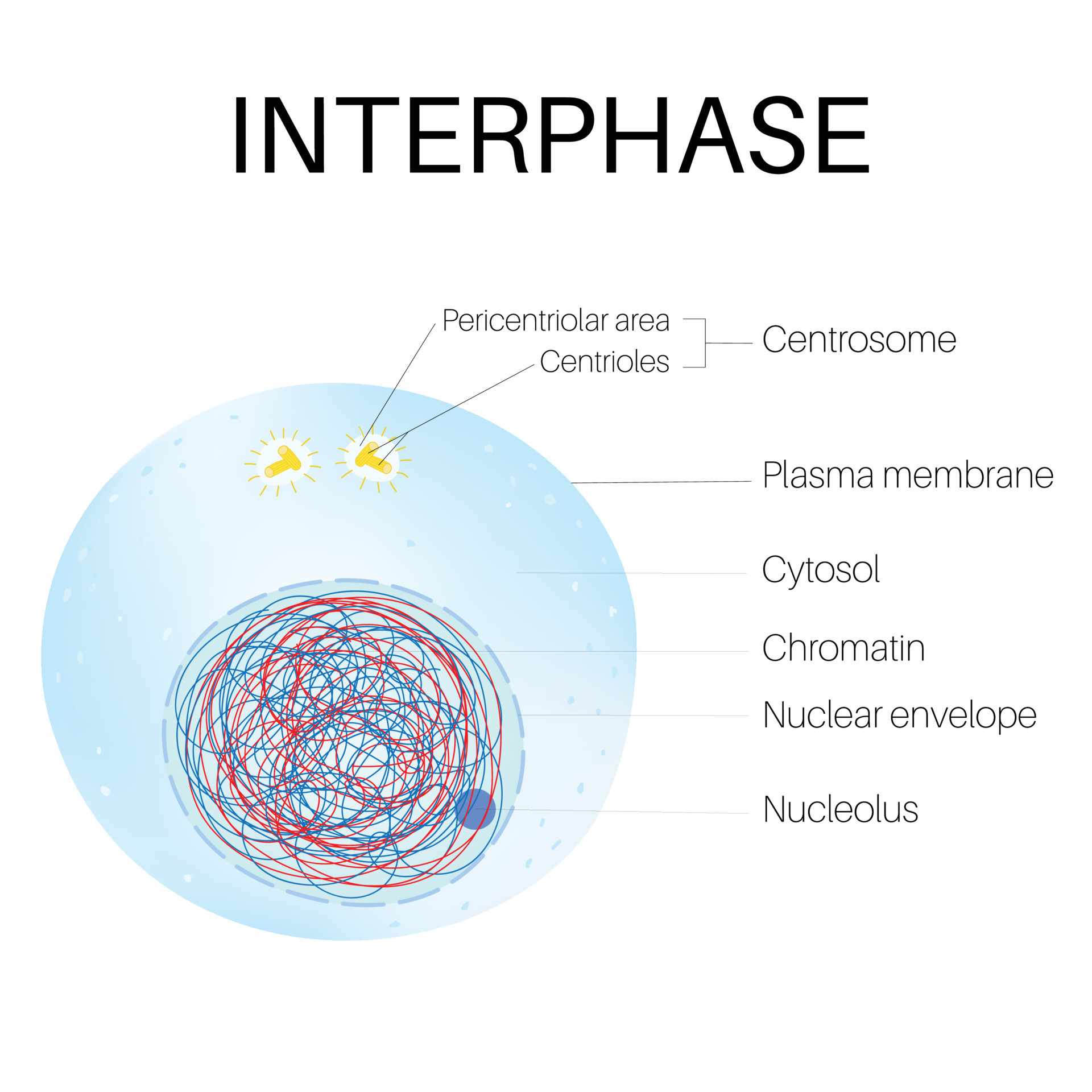
interphase
Stage of the cell cycles where the cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division including DNA replication; consists of G1 (organelles growth), S (DNA synthesis), and G2 (growth and preparation for mitosis, checks if everything is ready)
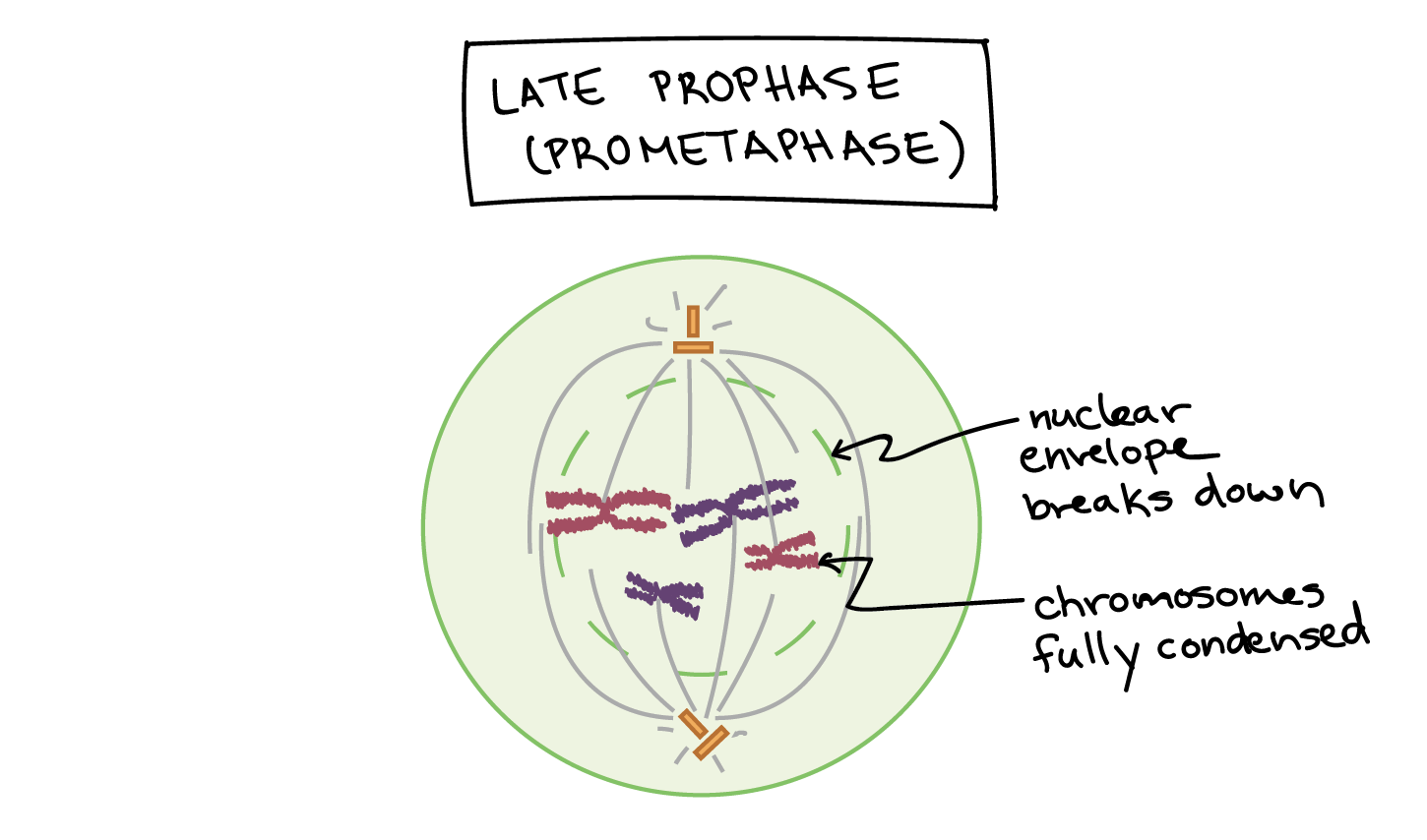
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus
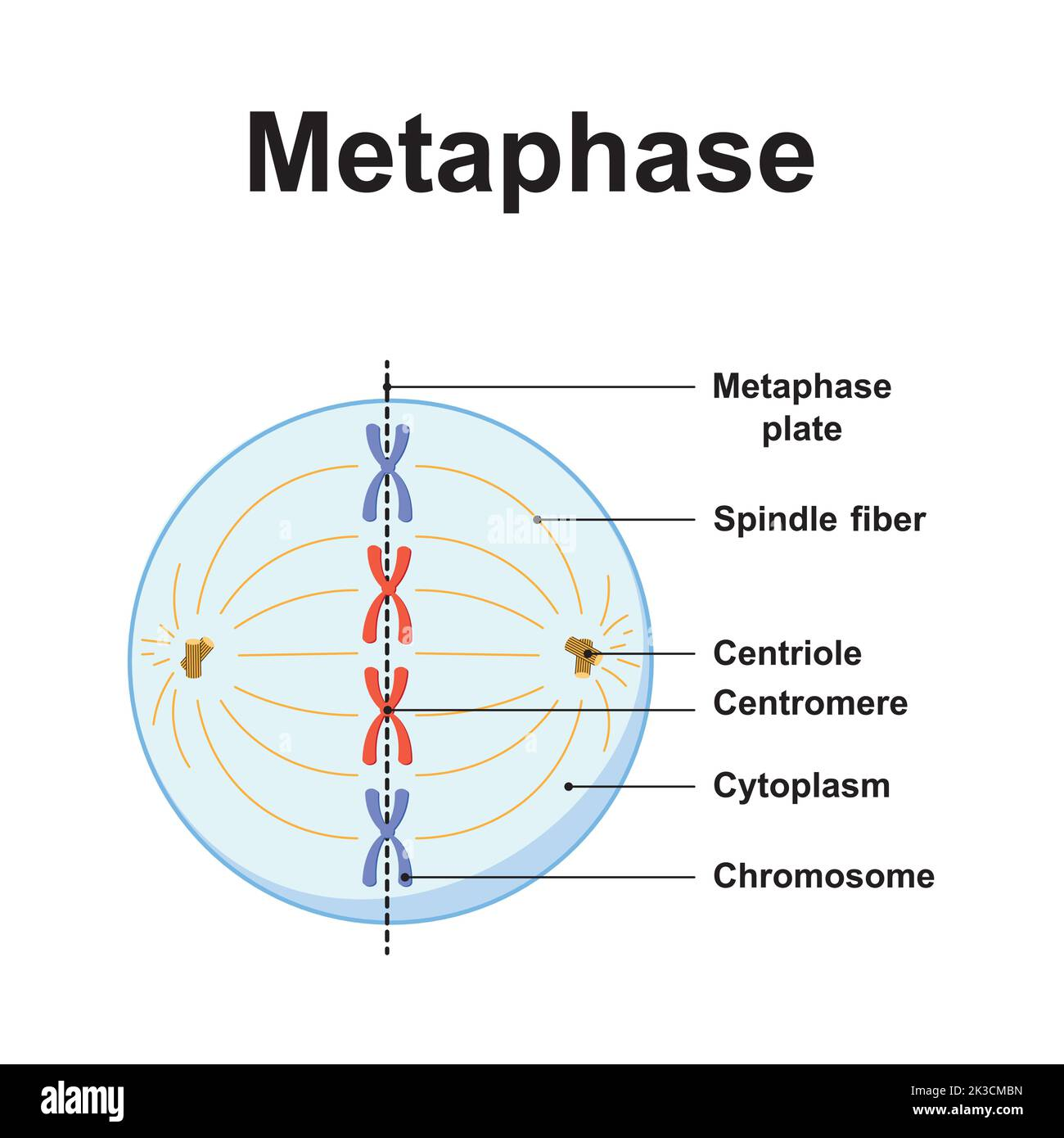
metaphase
phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes line up across the centre of the cell
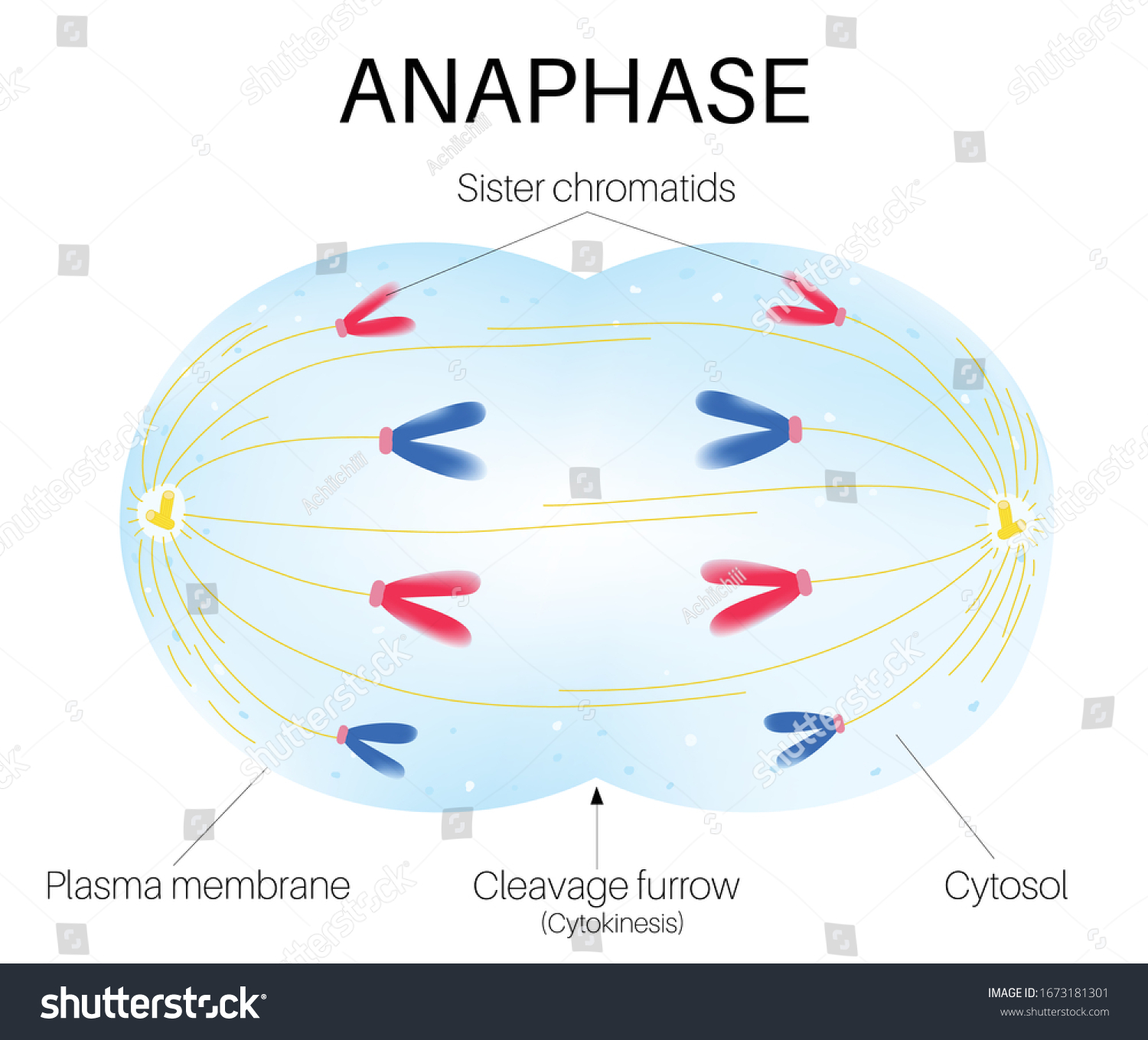
anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
telophase
the final phase of mitosis, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
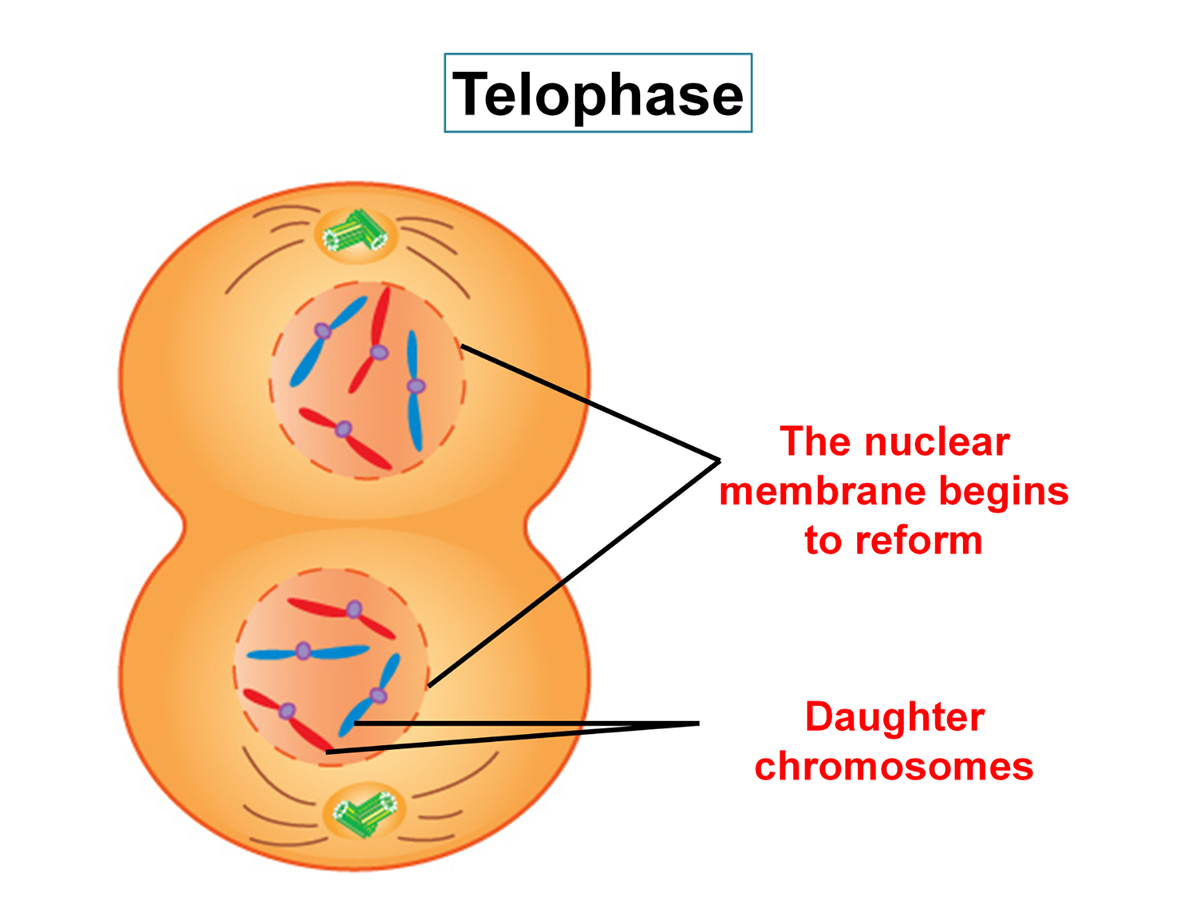
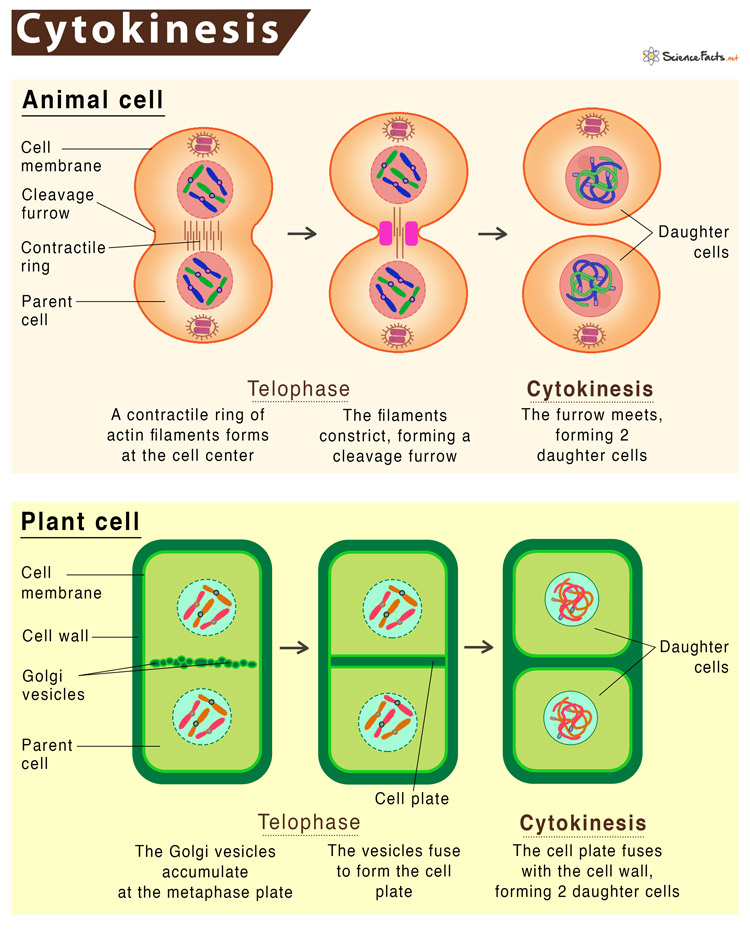
cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
independent assortment
the random distribution of the pairs of genes on different chromosomes to the gametes
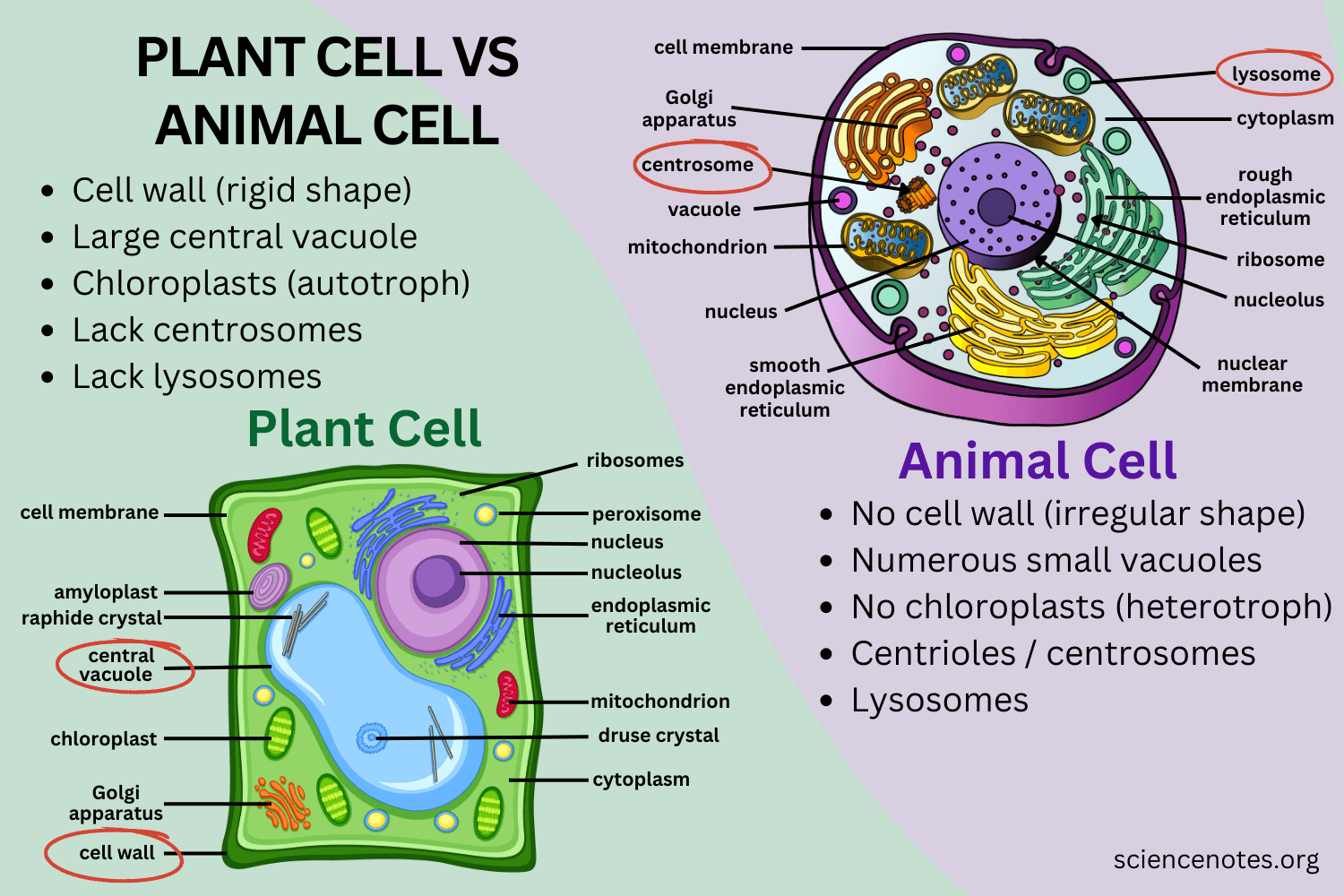
differences between animal and plant cells
plant cells have a cell wall, and a much larger vacuole.