Unit 1A: Human Body System Functions, Homeostasis Mechanisms and Anatomy Orientation Terms (Honors and DE)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
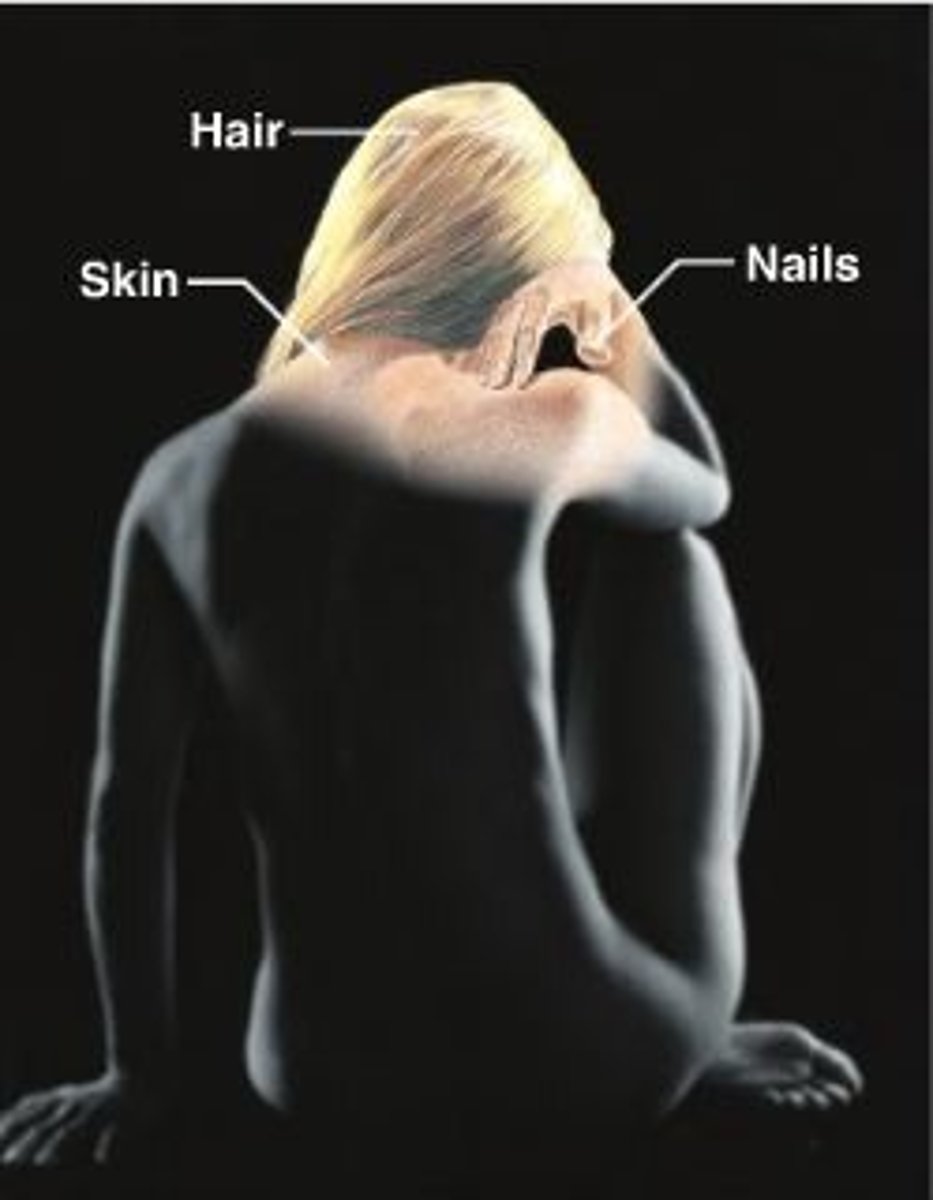
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, largest organ of the human body; separate internal from external environment
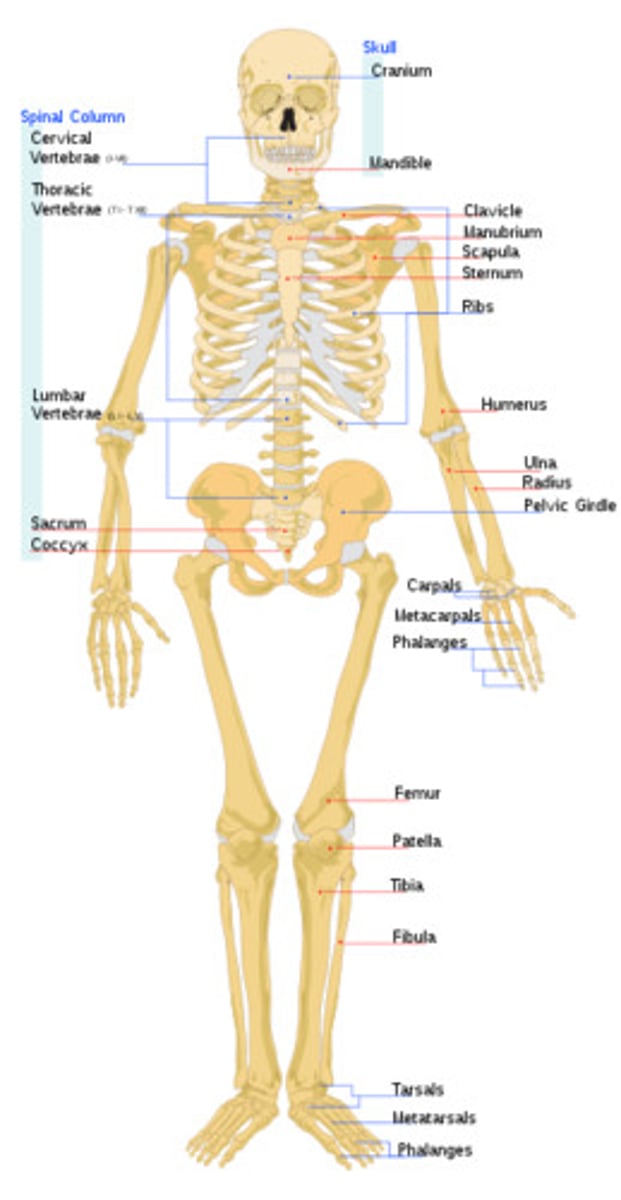
skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. Made up of bones and joints; bone marrow makes blood cells
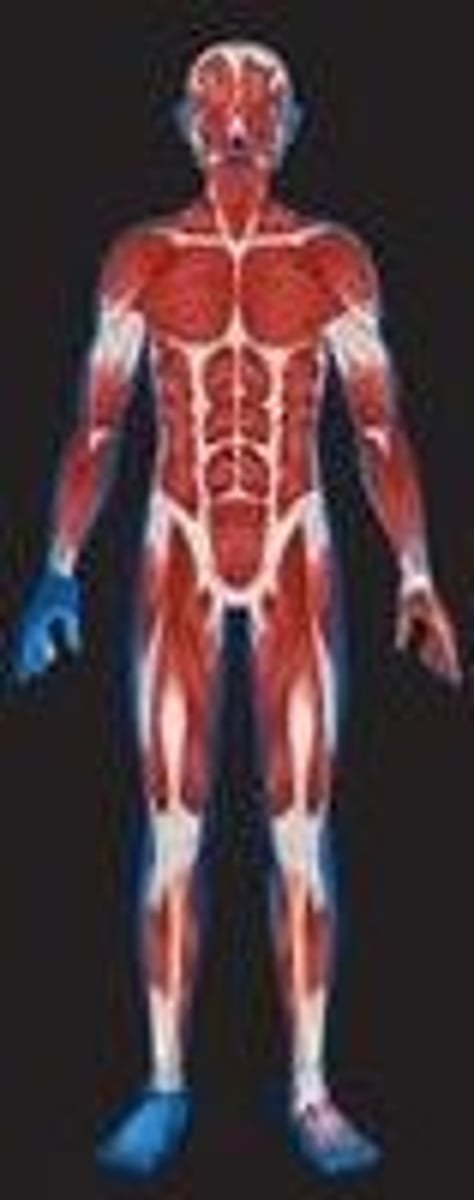
Muscular System
enables movement of the body and internal organs
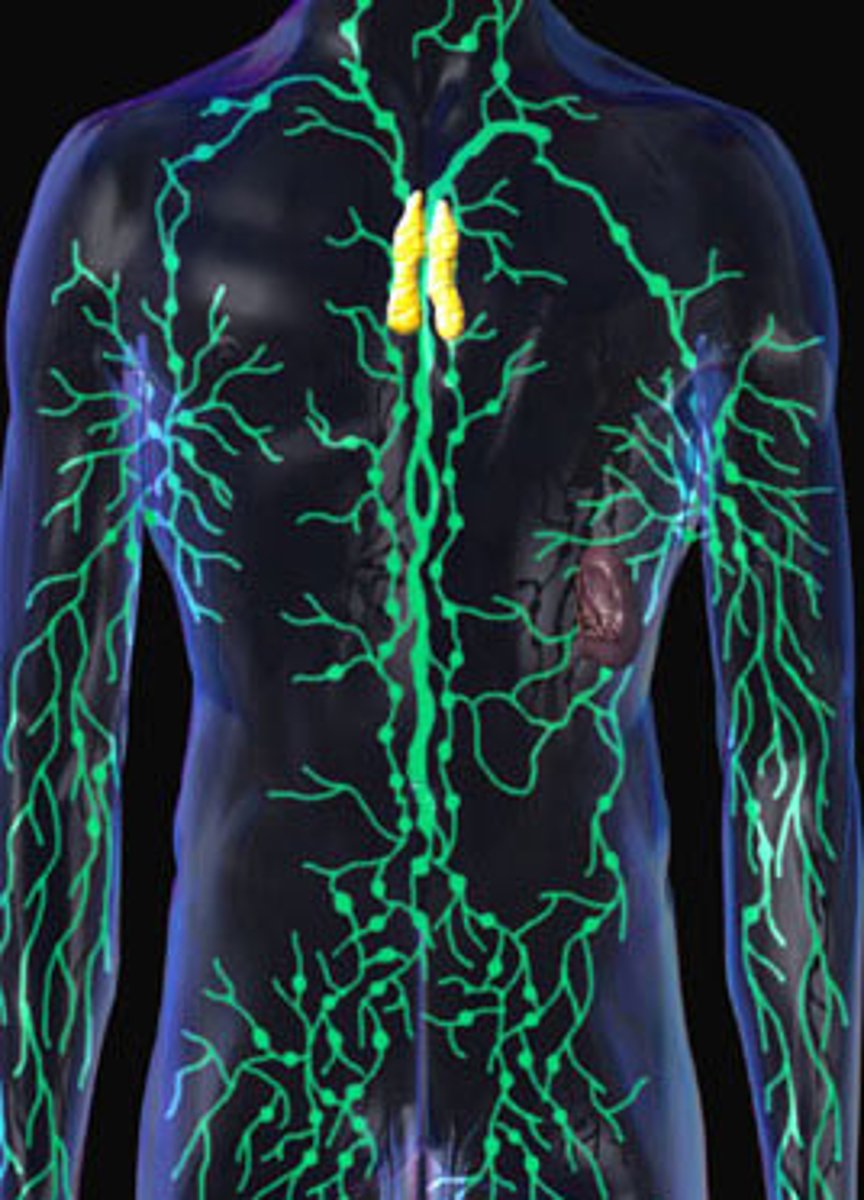
lymphatic system
Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defense against infection.
respiratory system
Brings oxygen into the body. Gets rid of carbon dioxide.

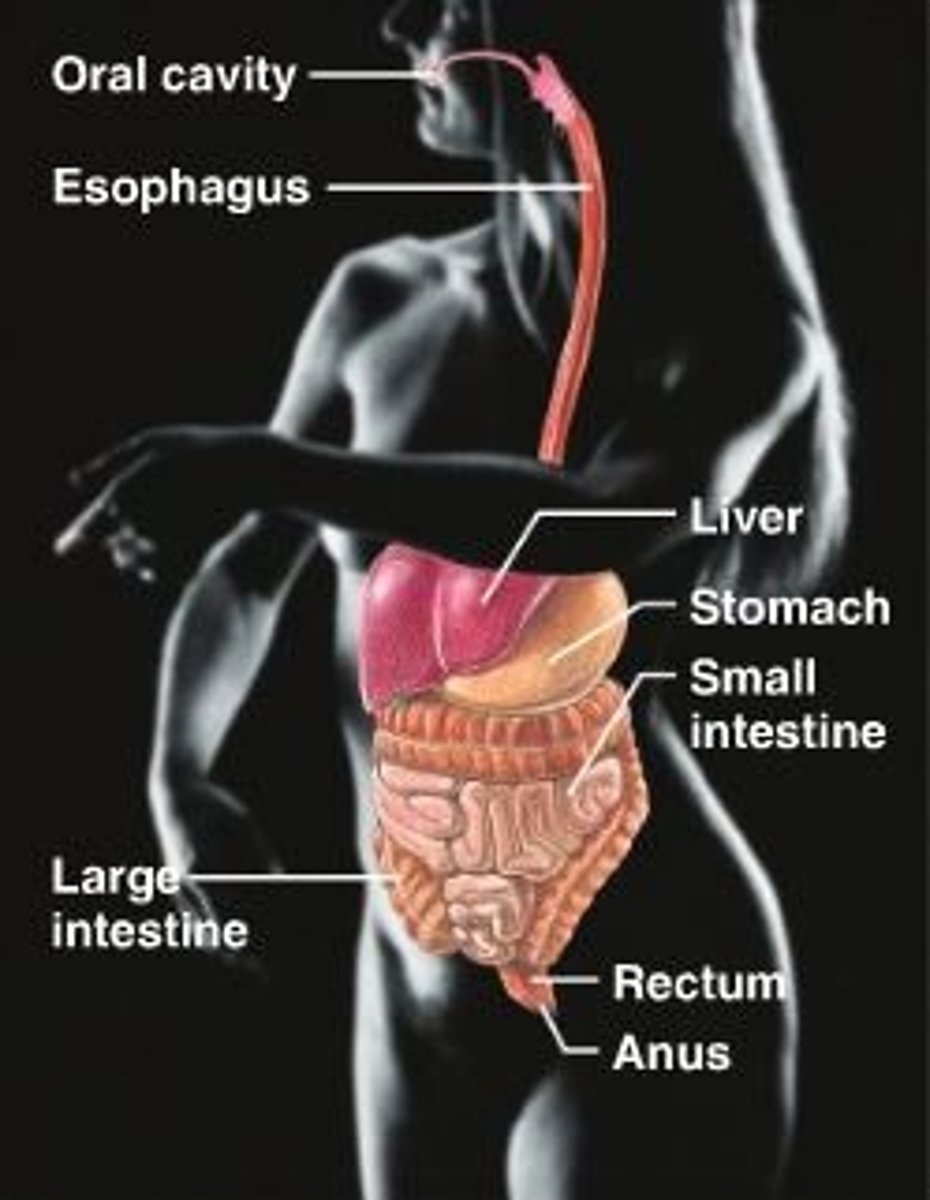
digestive system
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
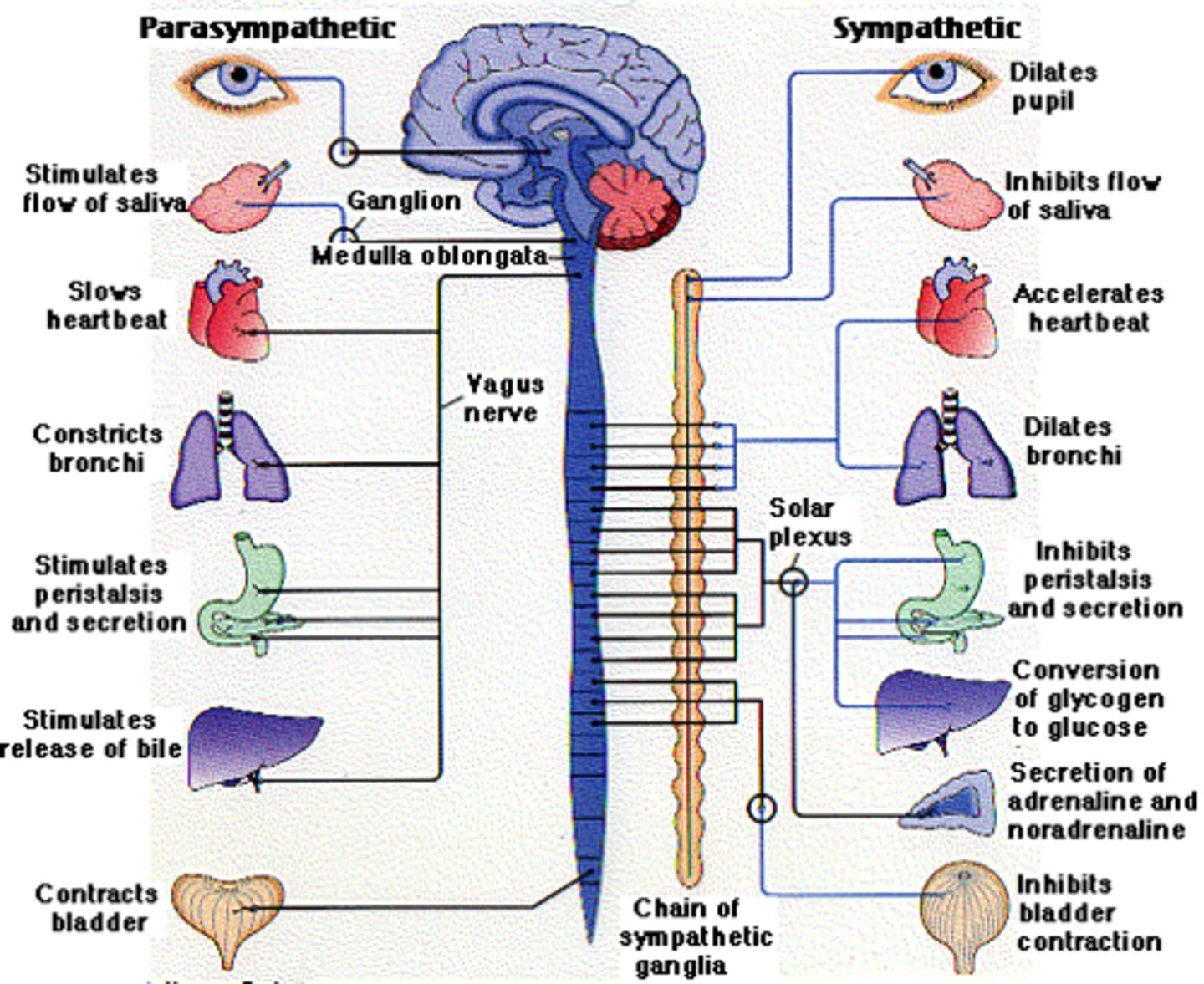
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
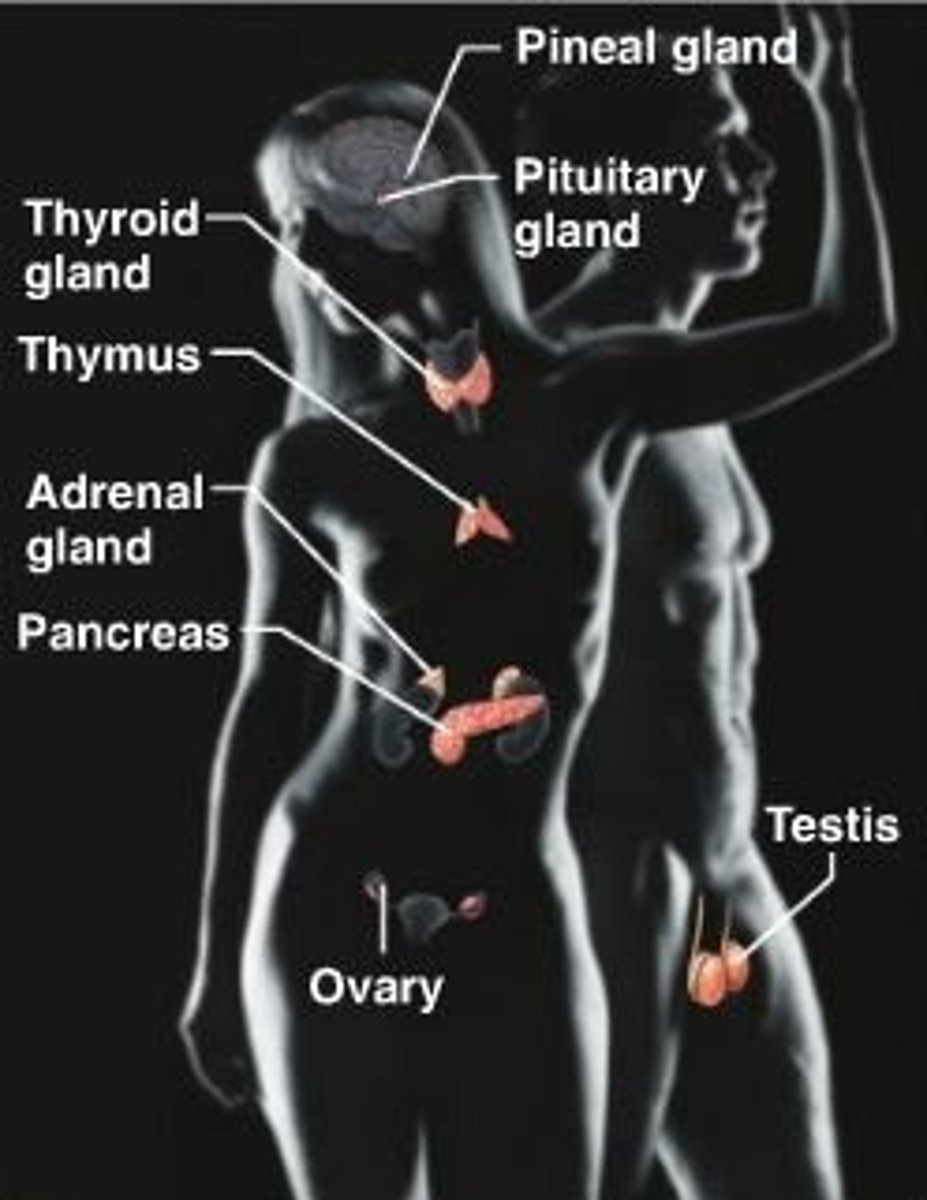
endocrine system
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells.
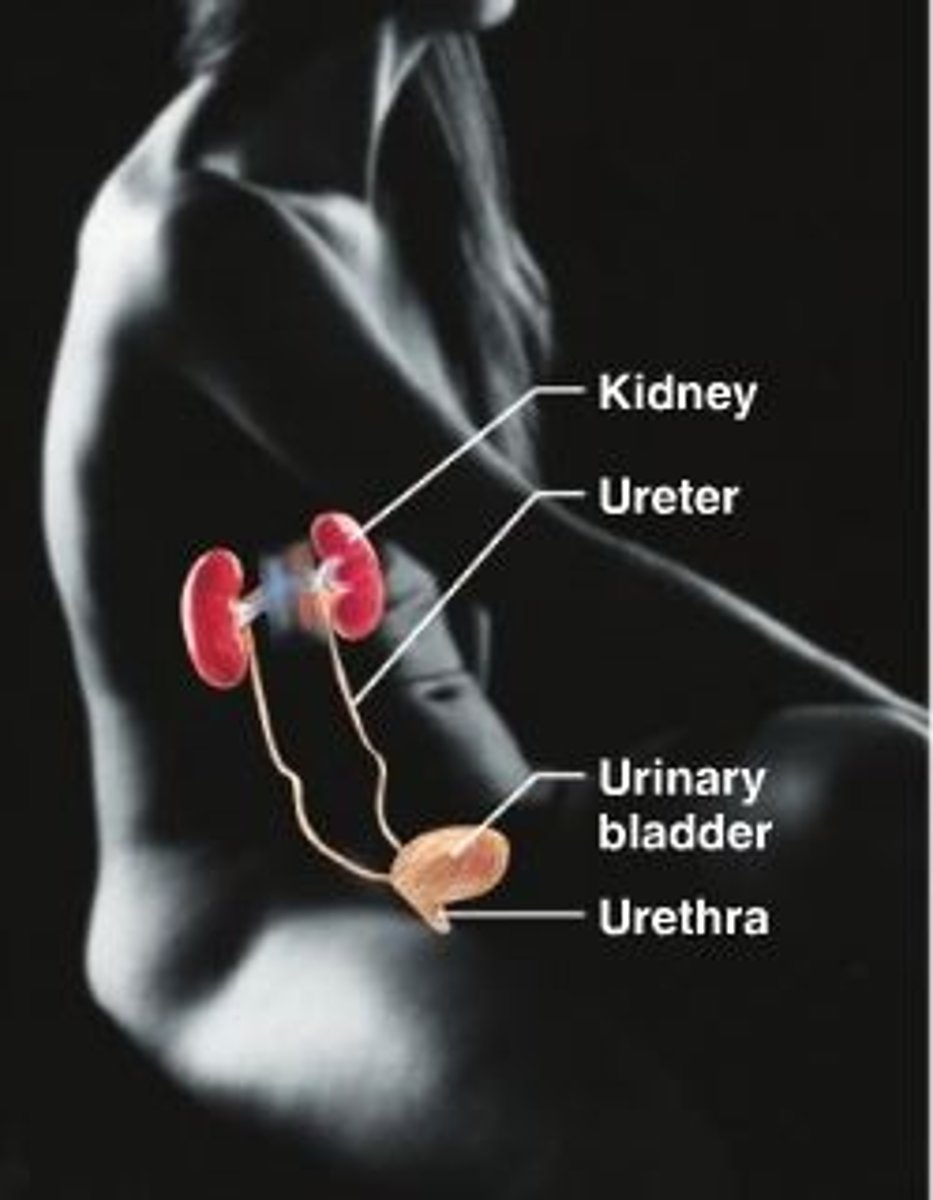
urinary system
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood.
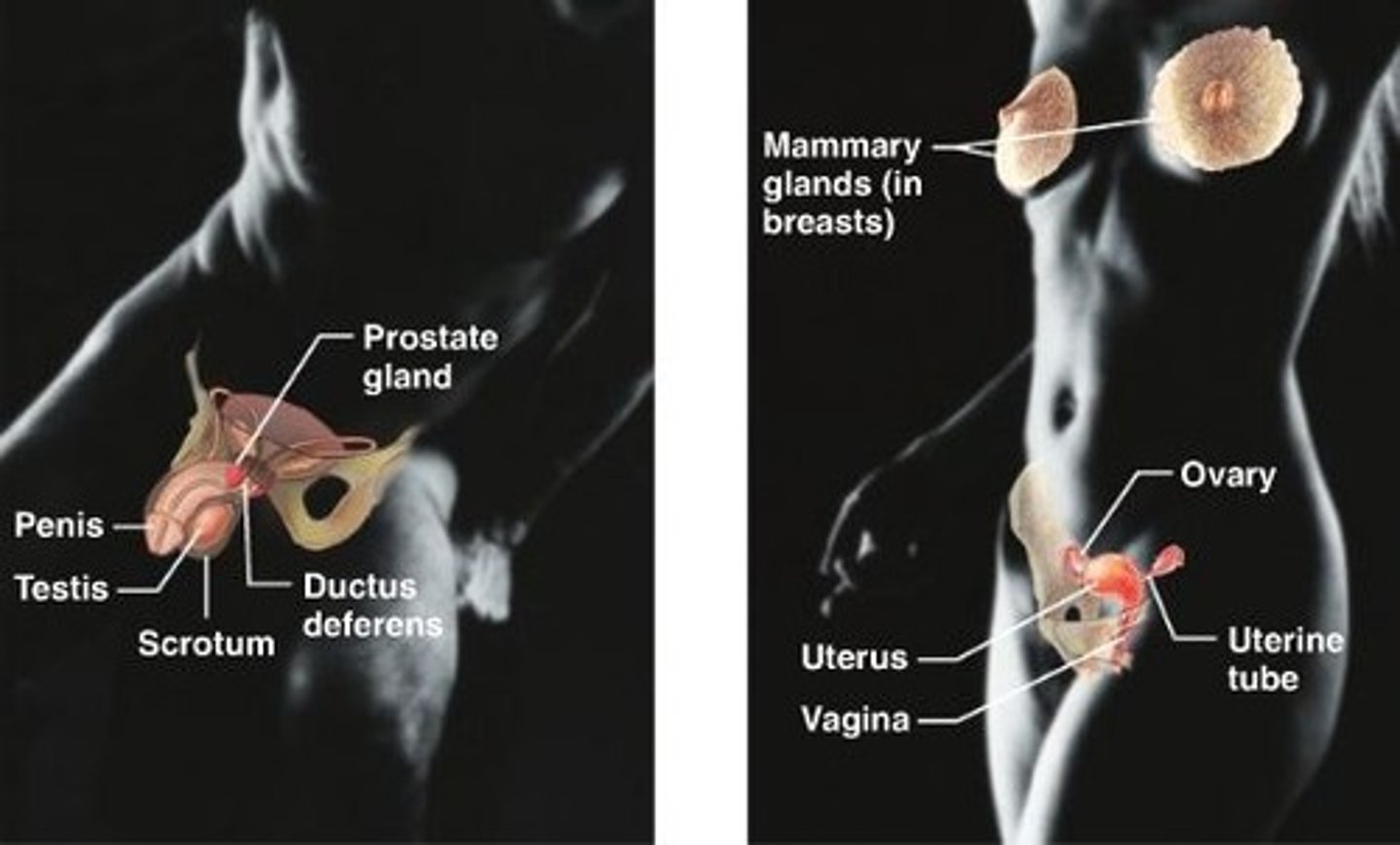
reproductive system
system of organs involved in producing offspring
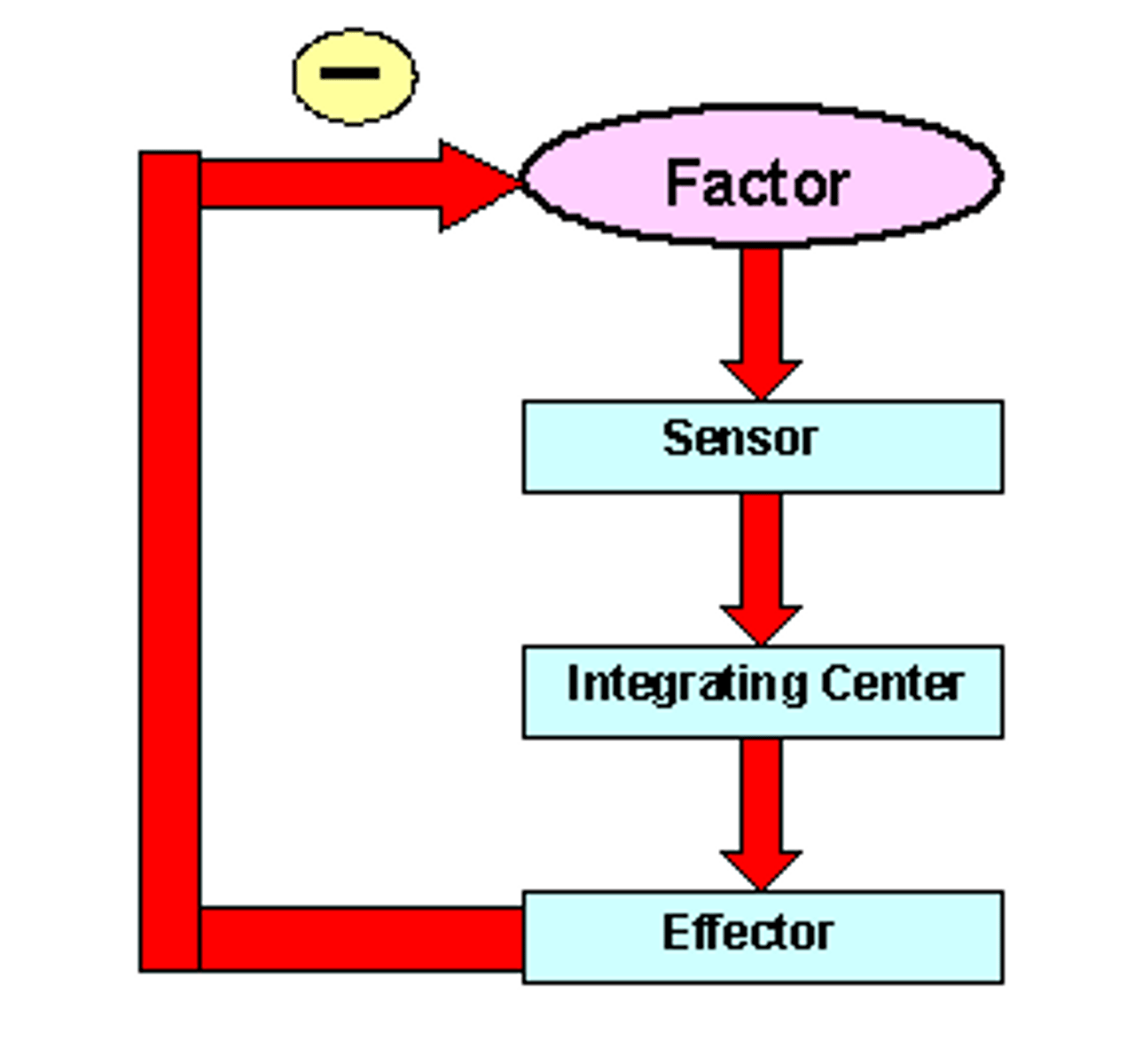
negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
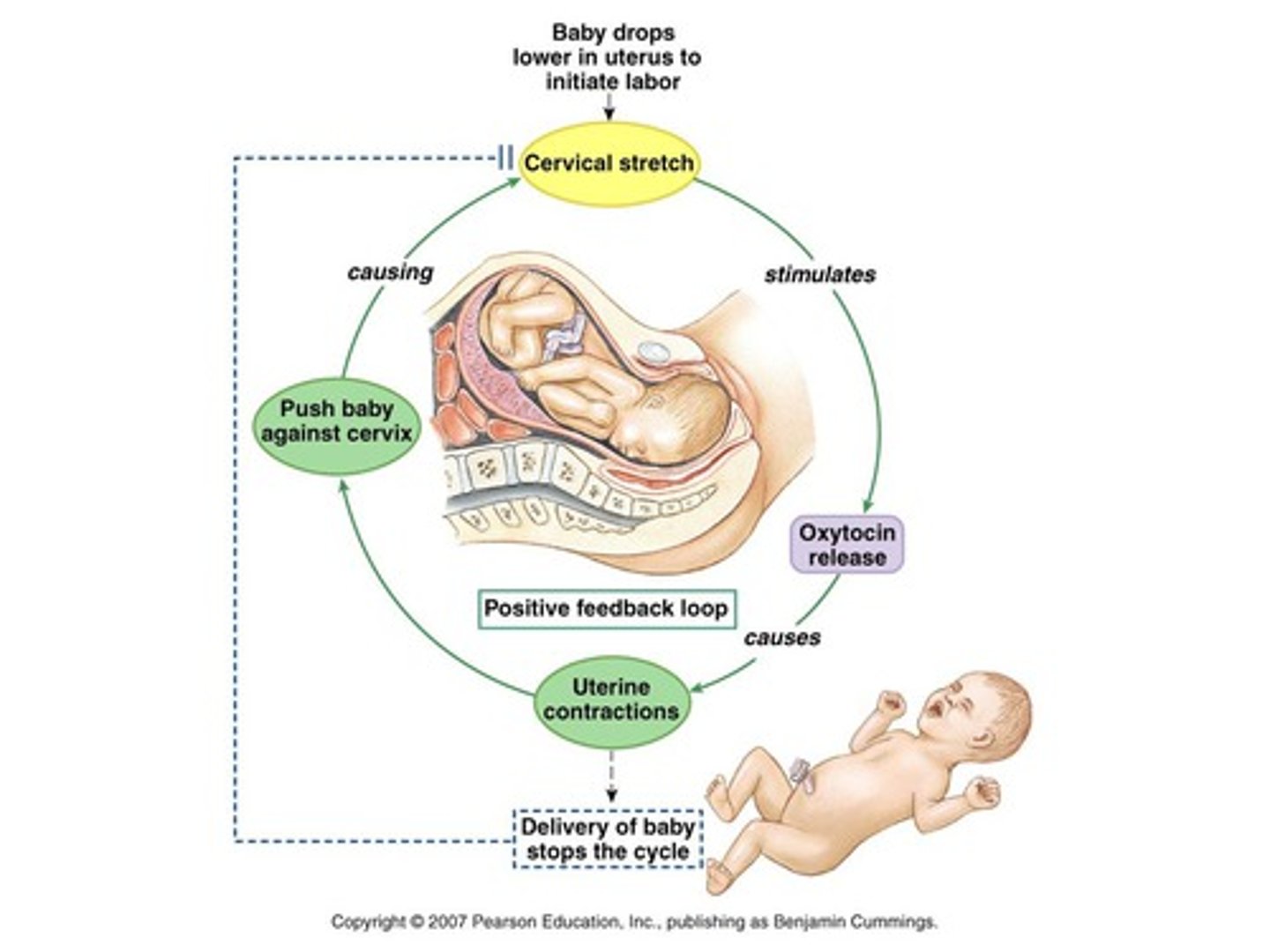
positive feedback
Feedback that tends to magnify a process or increase its output.
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
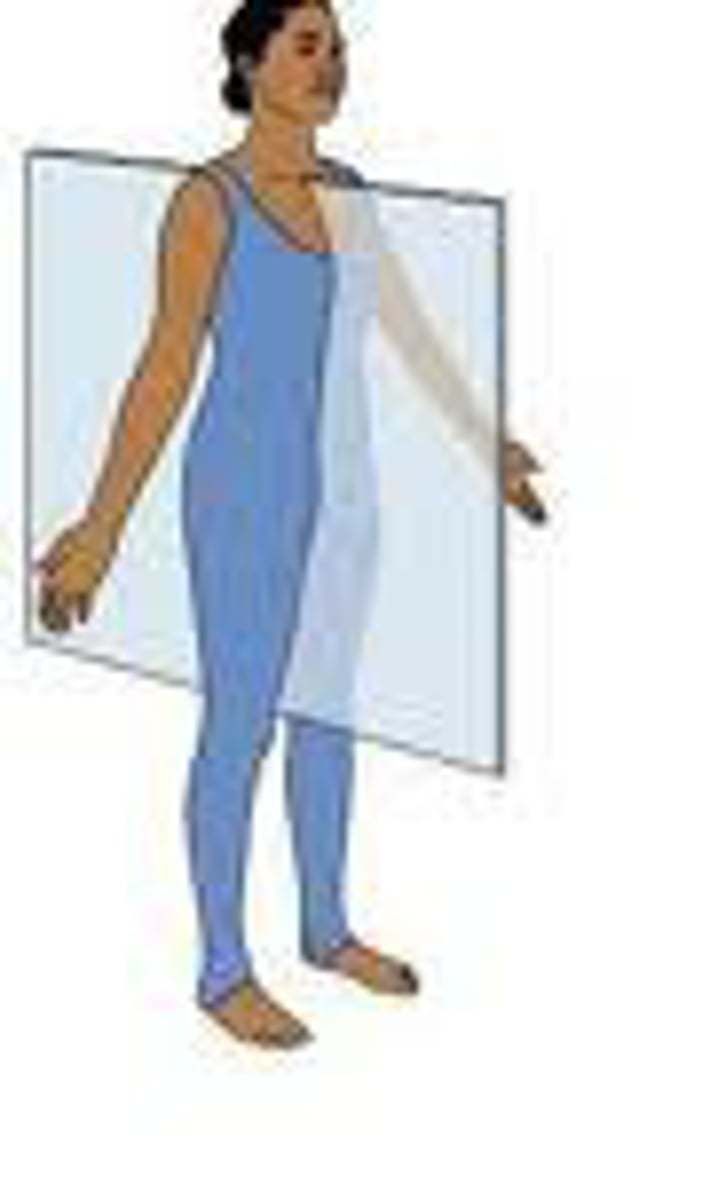
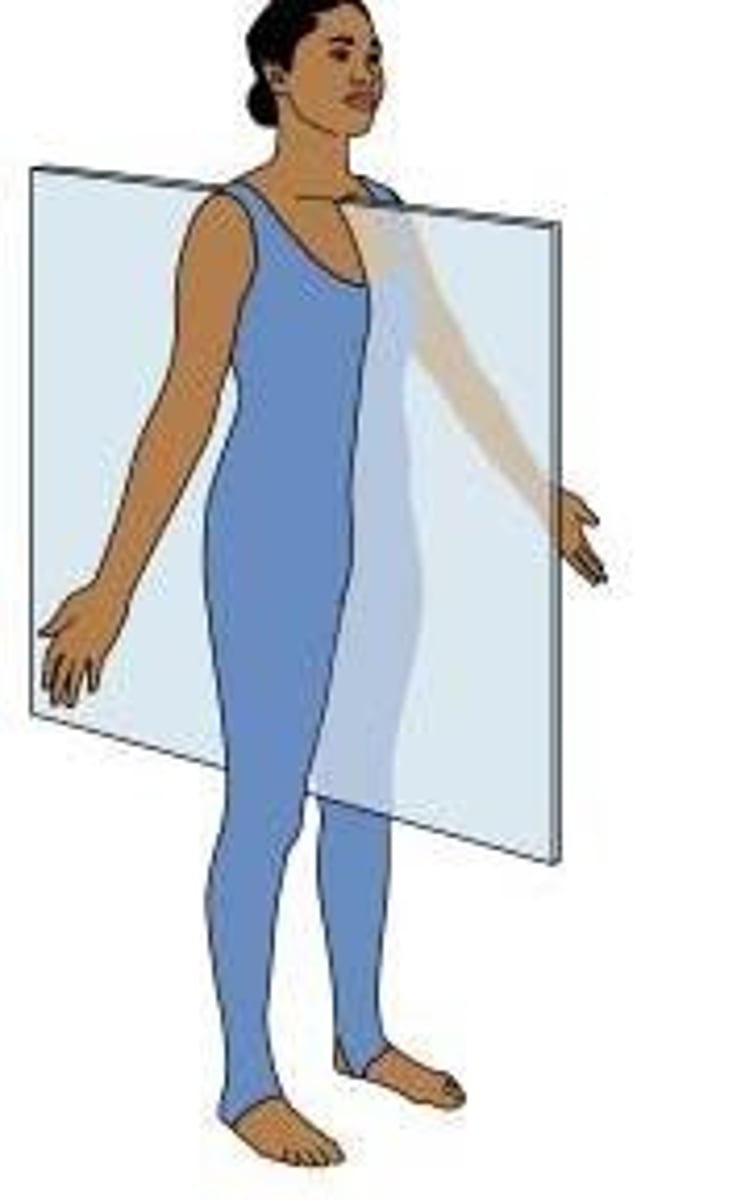
saggital/median plane
divides the body into left and right halves
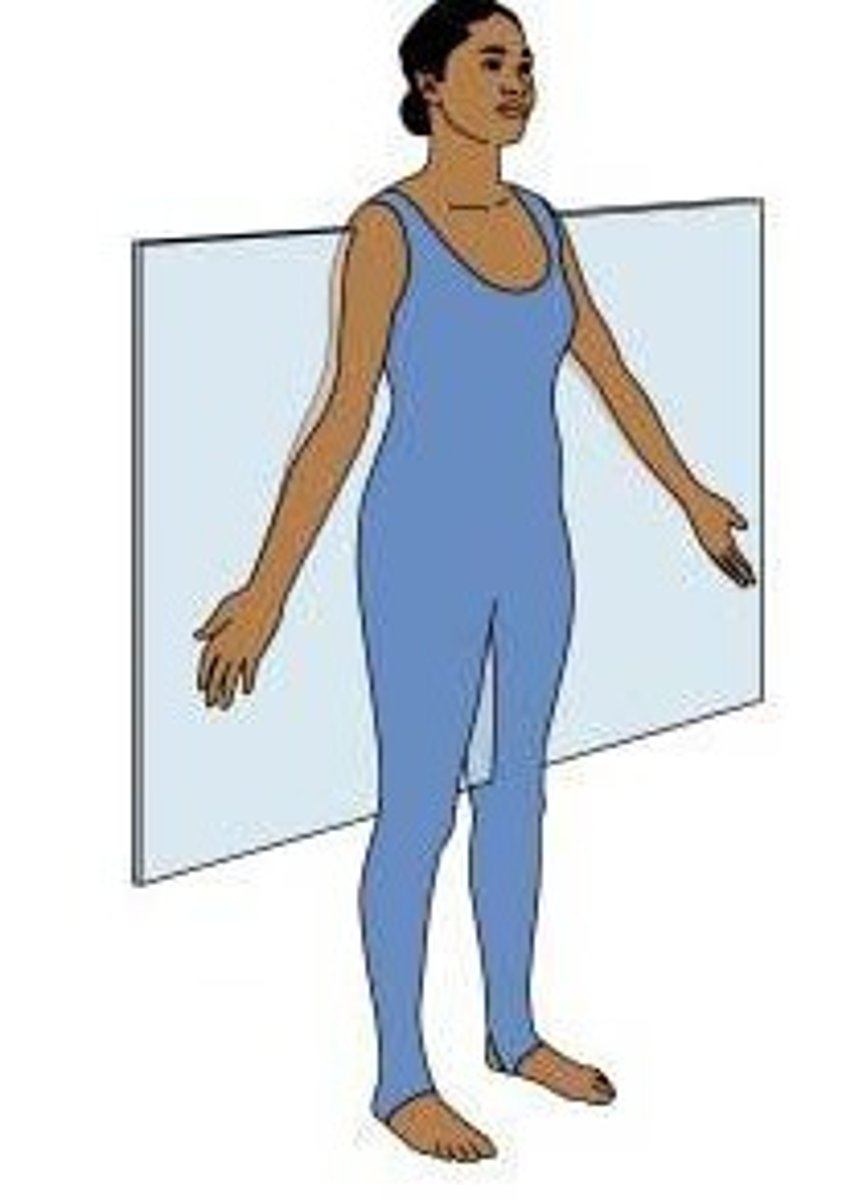
frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
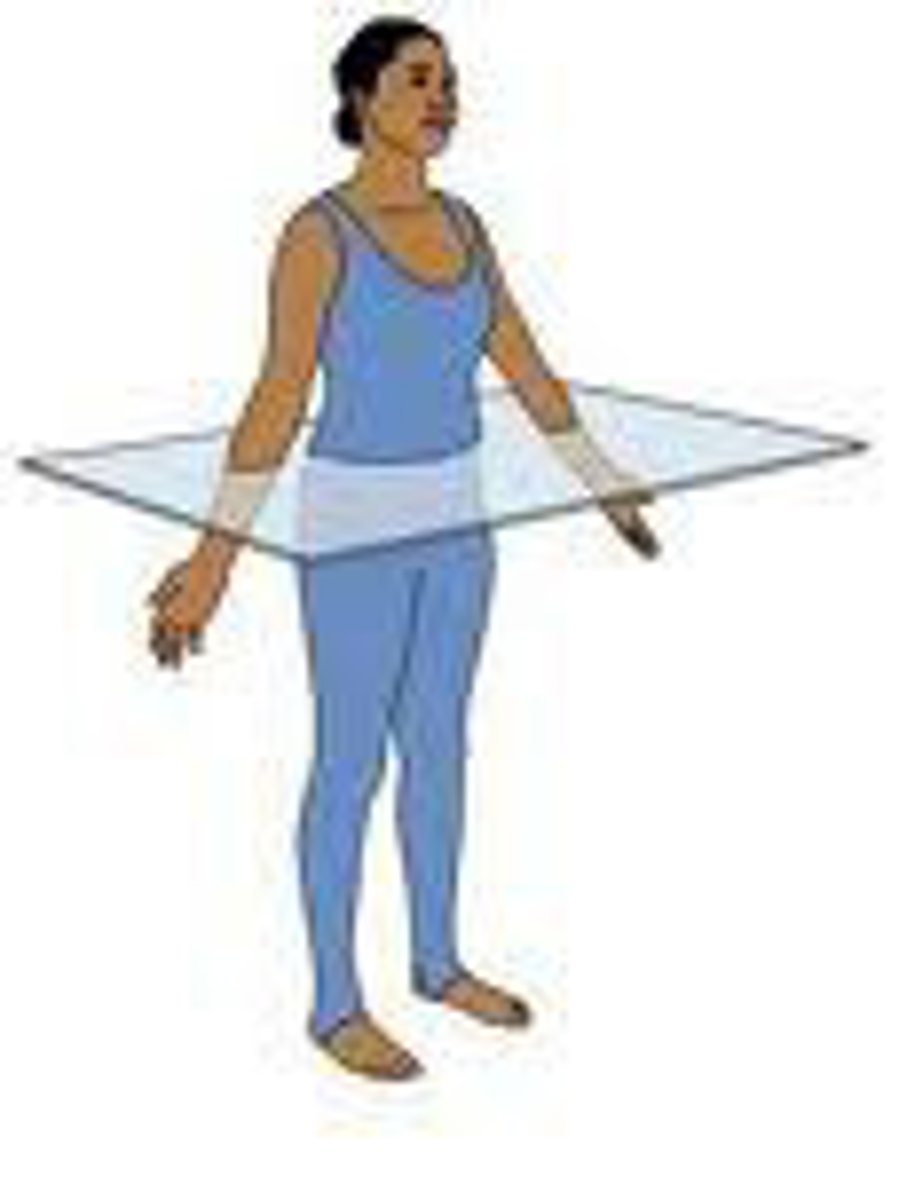
transverse
Divides body into upper and lower parts
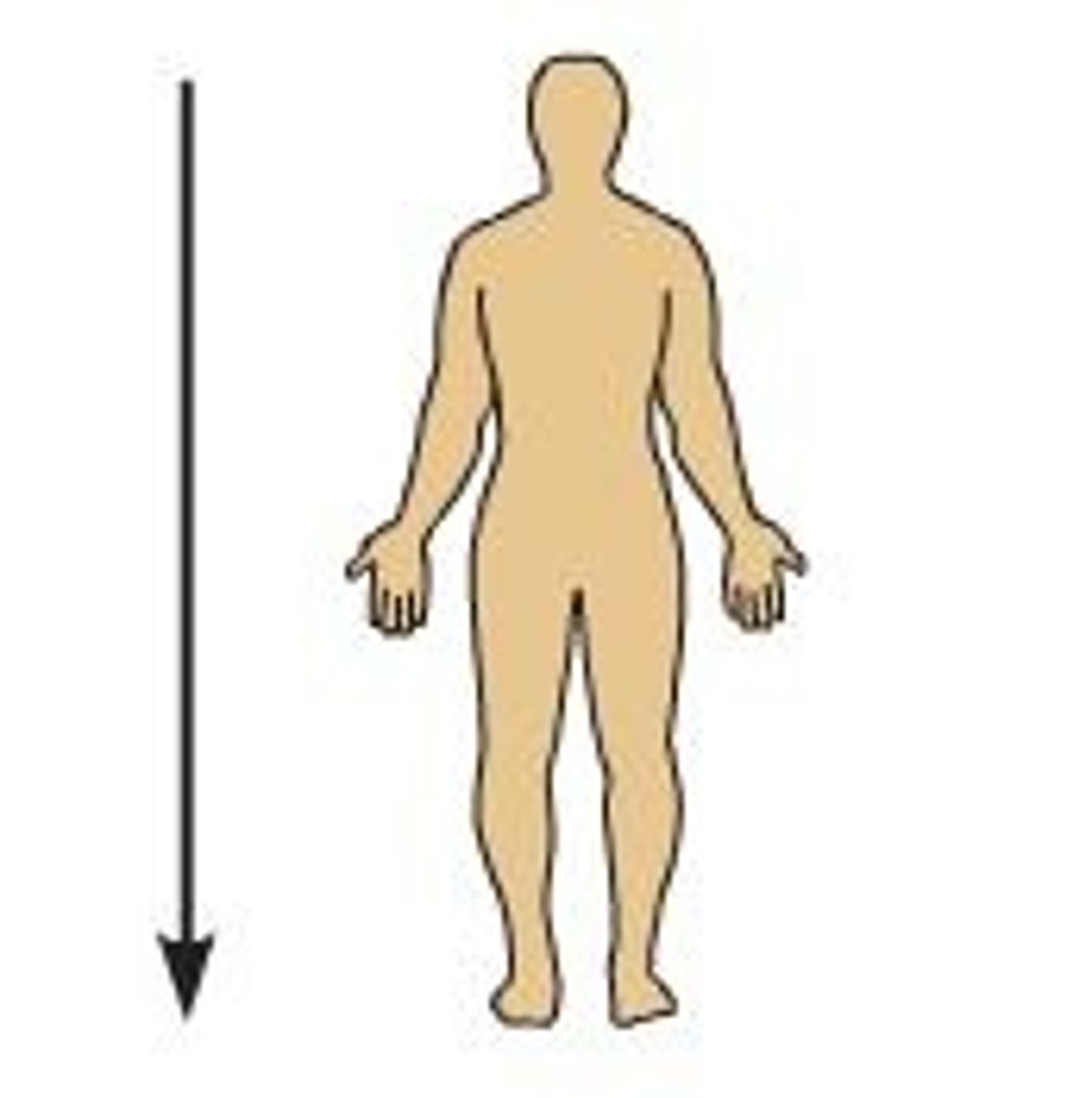
superior
toward the head
inferior
away from the head
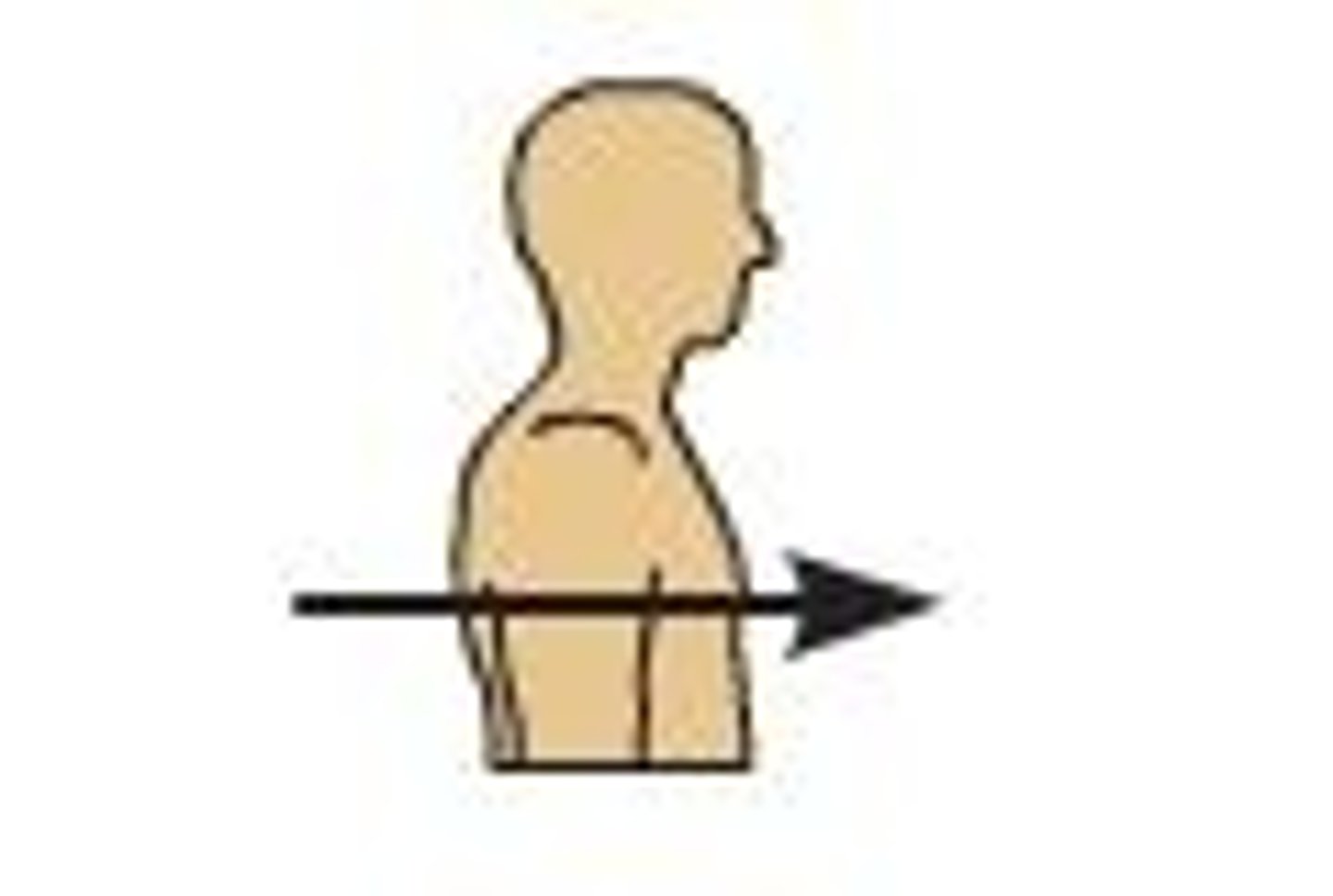
anterior (ventral)
front of the body
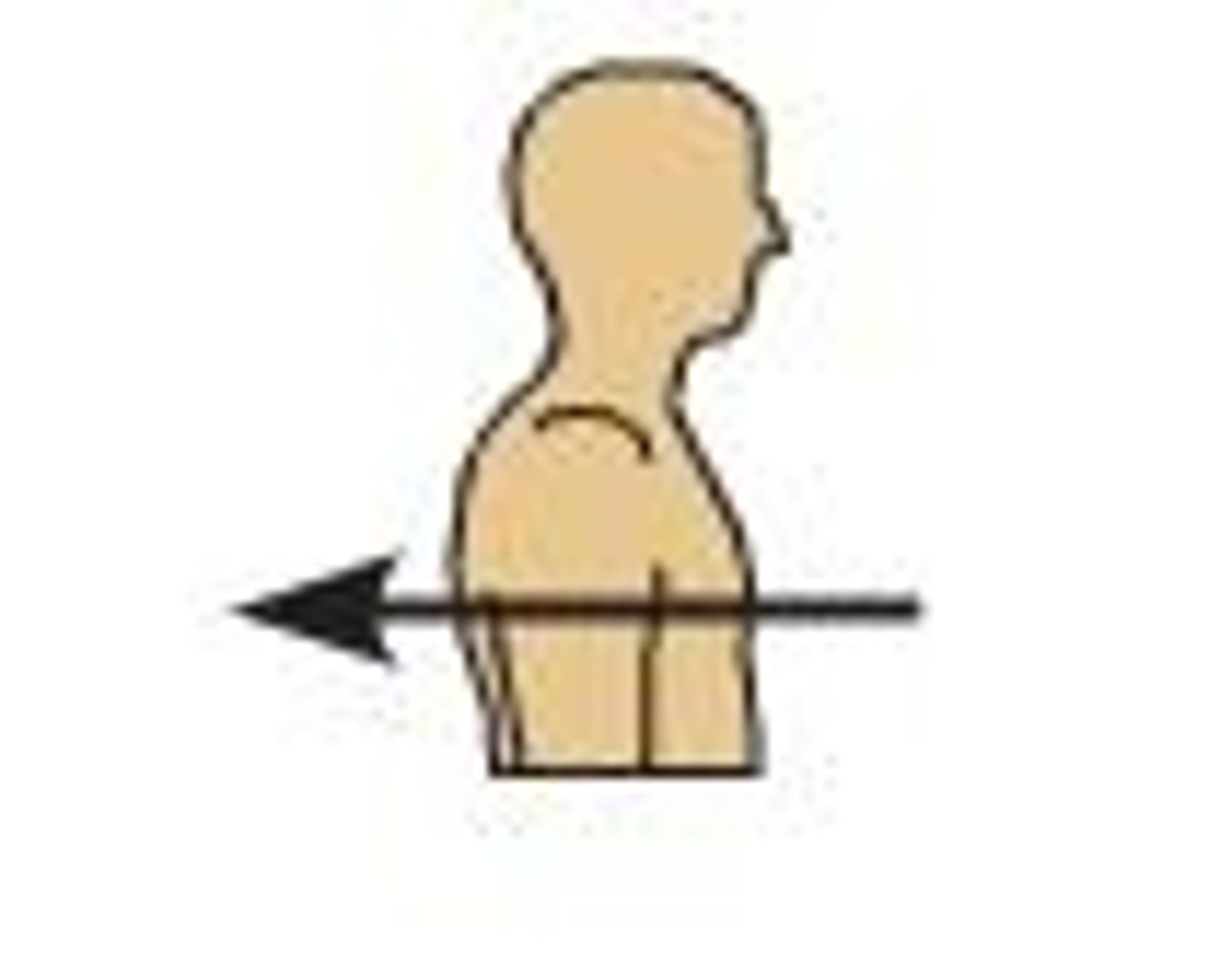
posterior (dorsal)
back of body
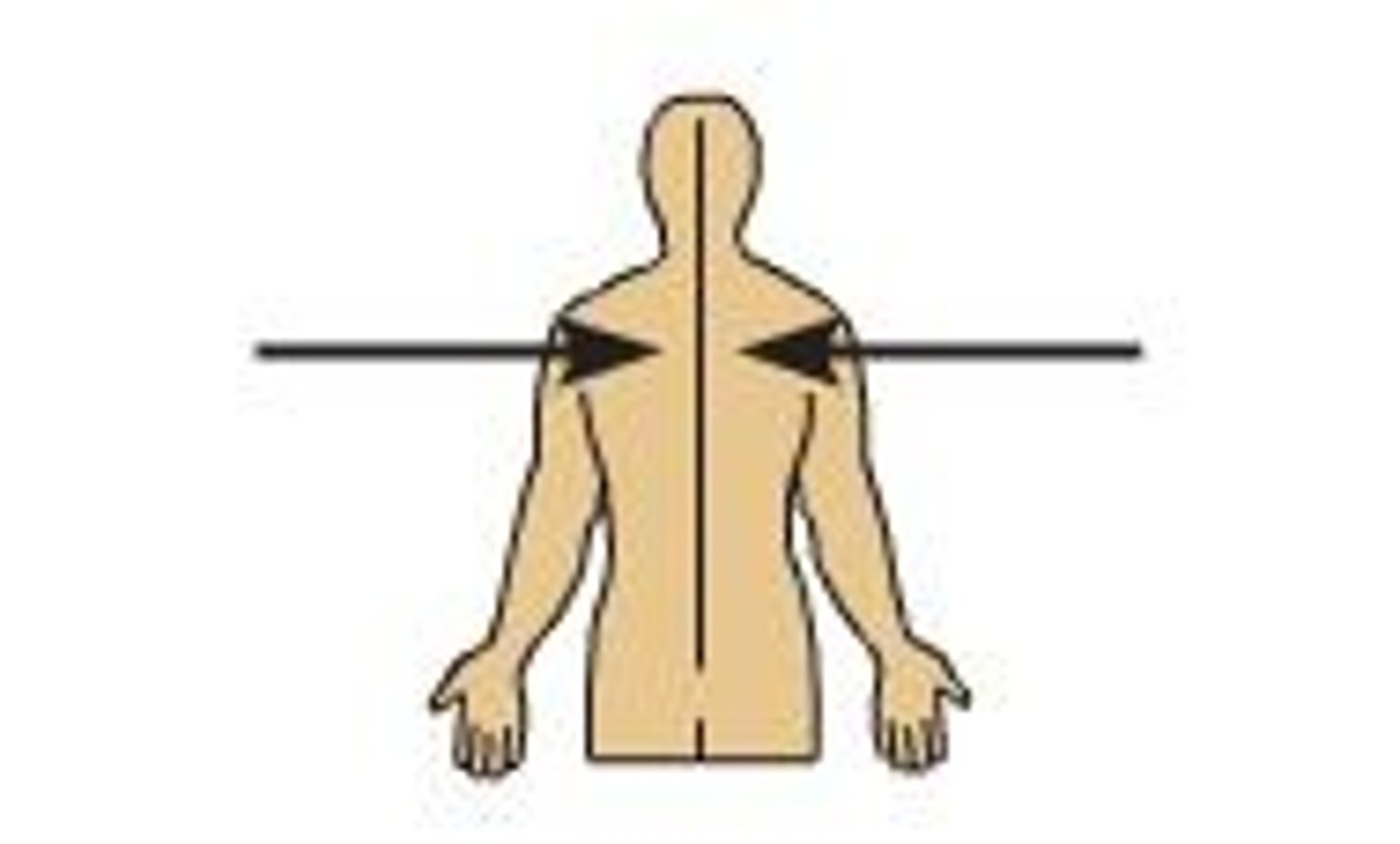
medial
Toward the midline of the body
lateral
Away from the midline of the body towards sides
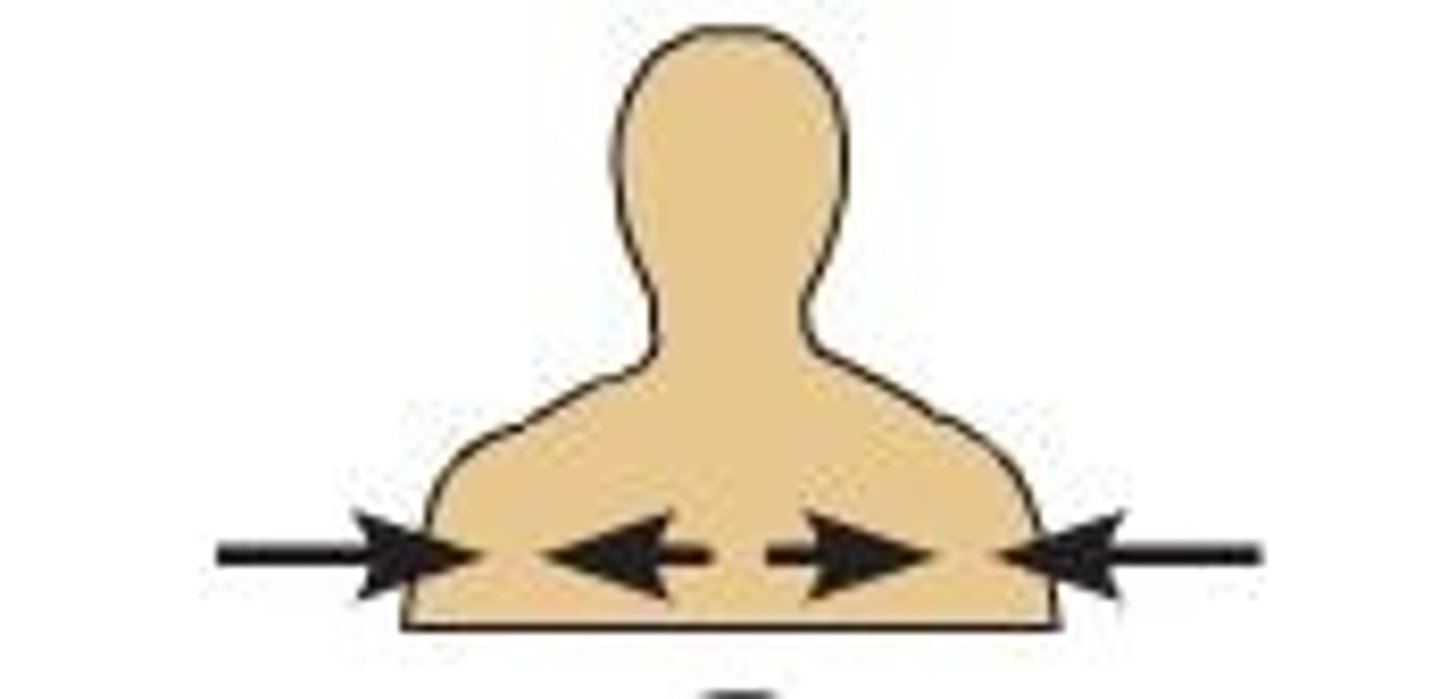
intermediate
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
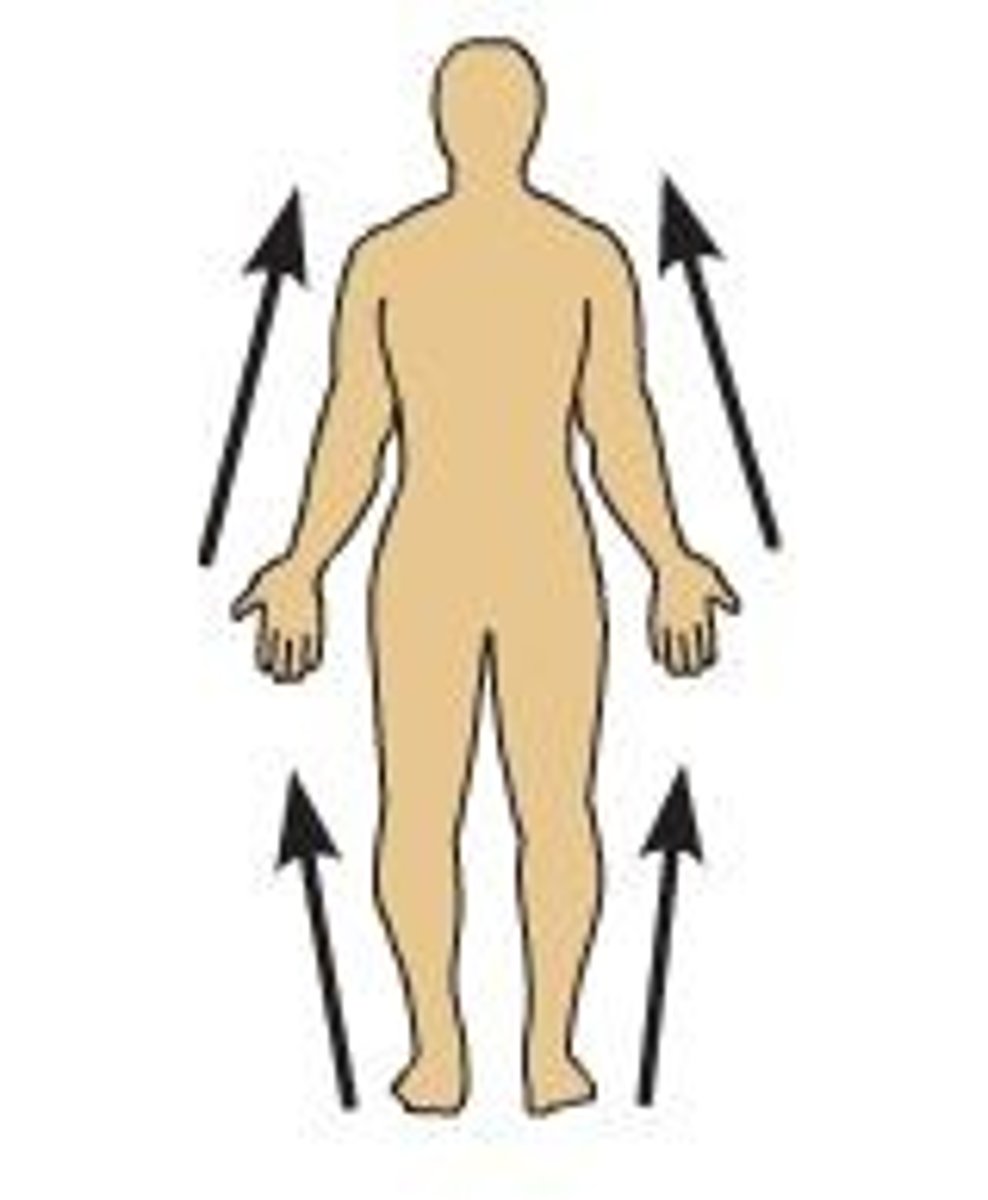
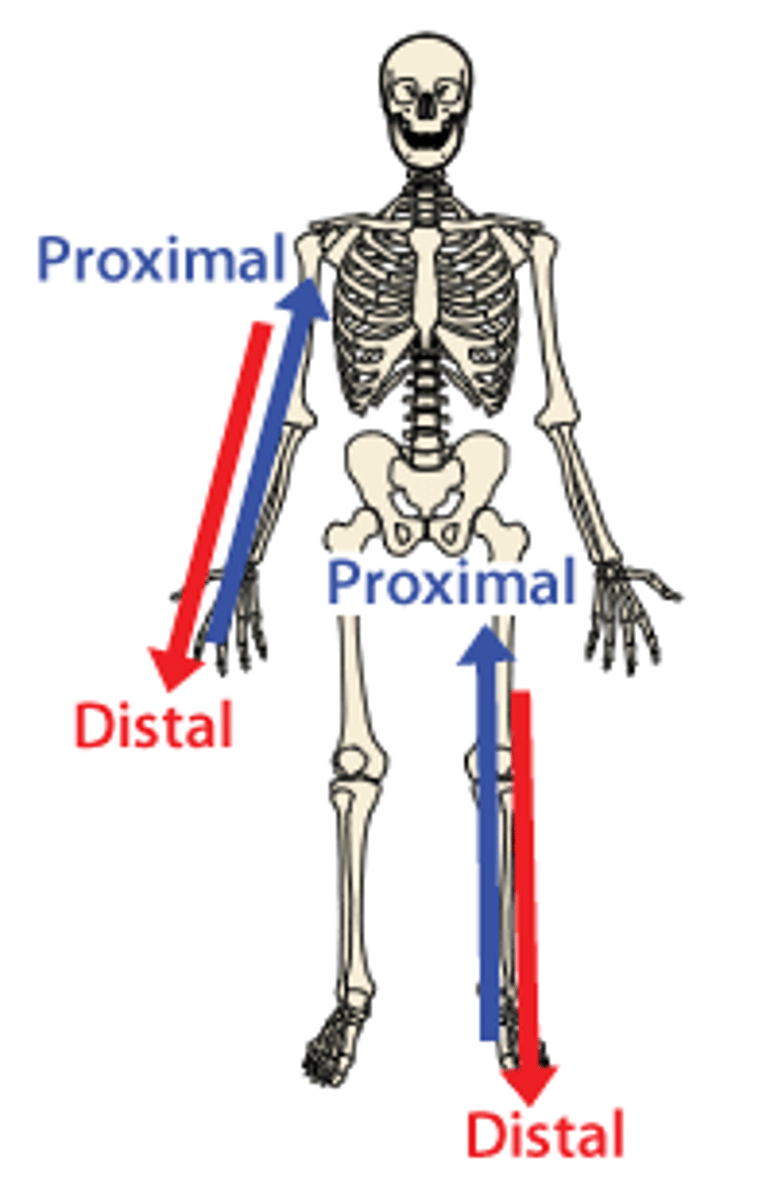
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
superficial
near the surface
deep
away from the surface
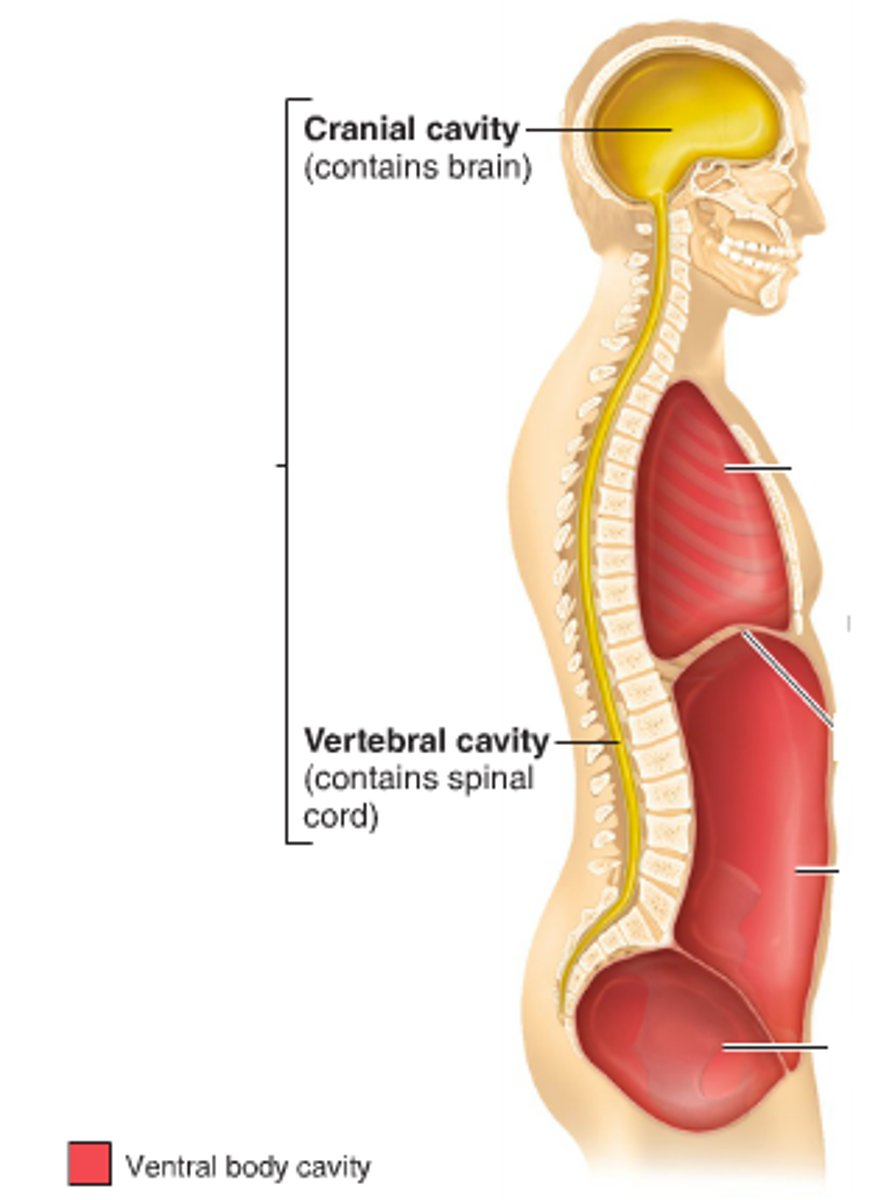
thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs
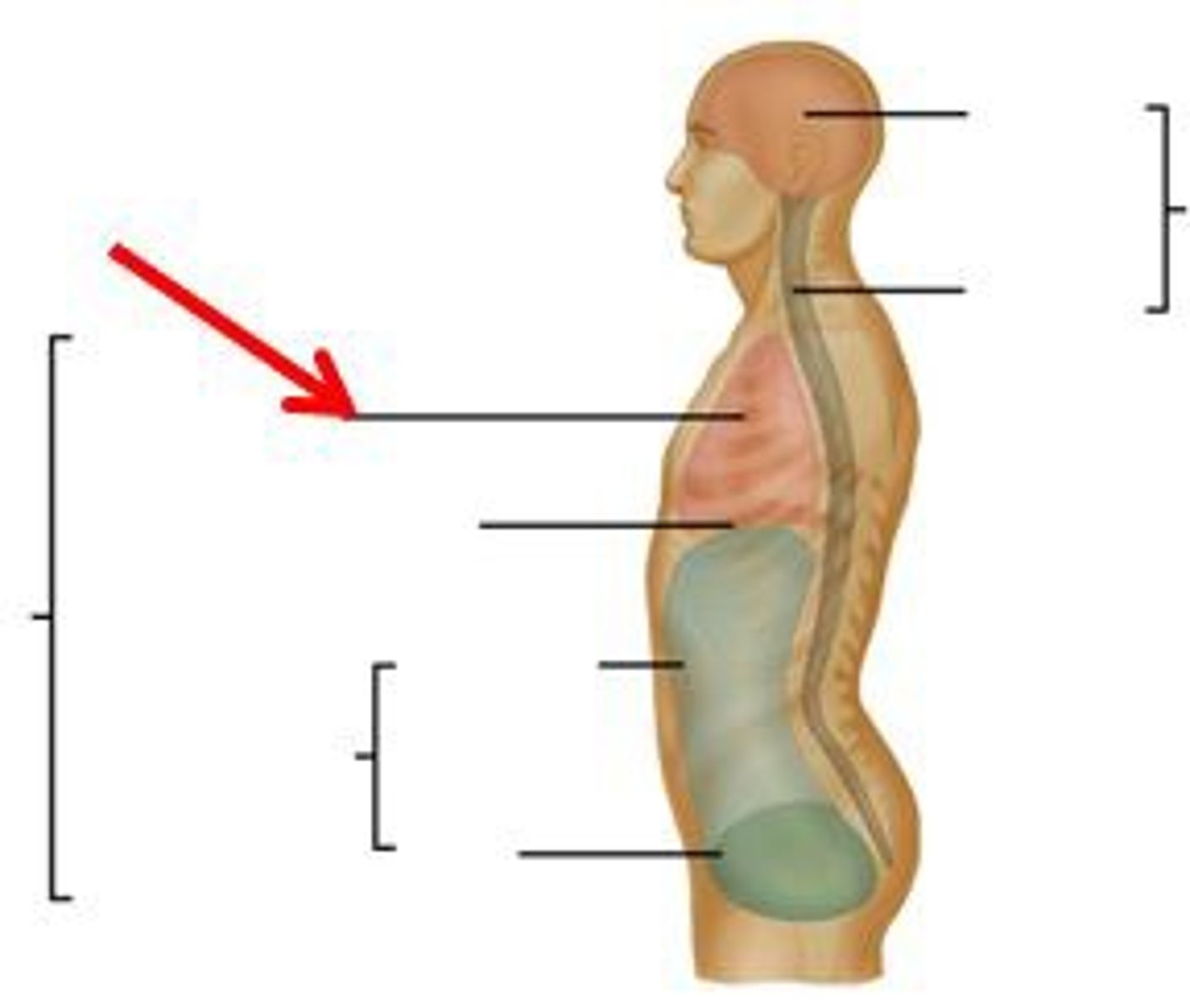
abdominal cavity
contains primarily the major organs of digestion
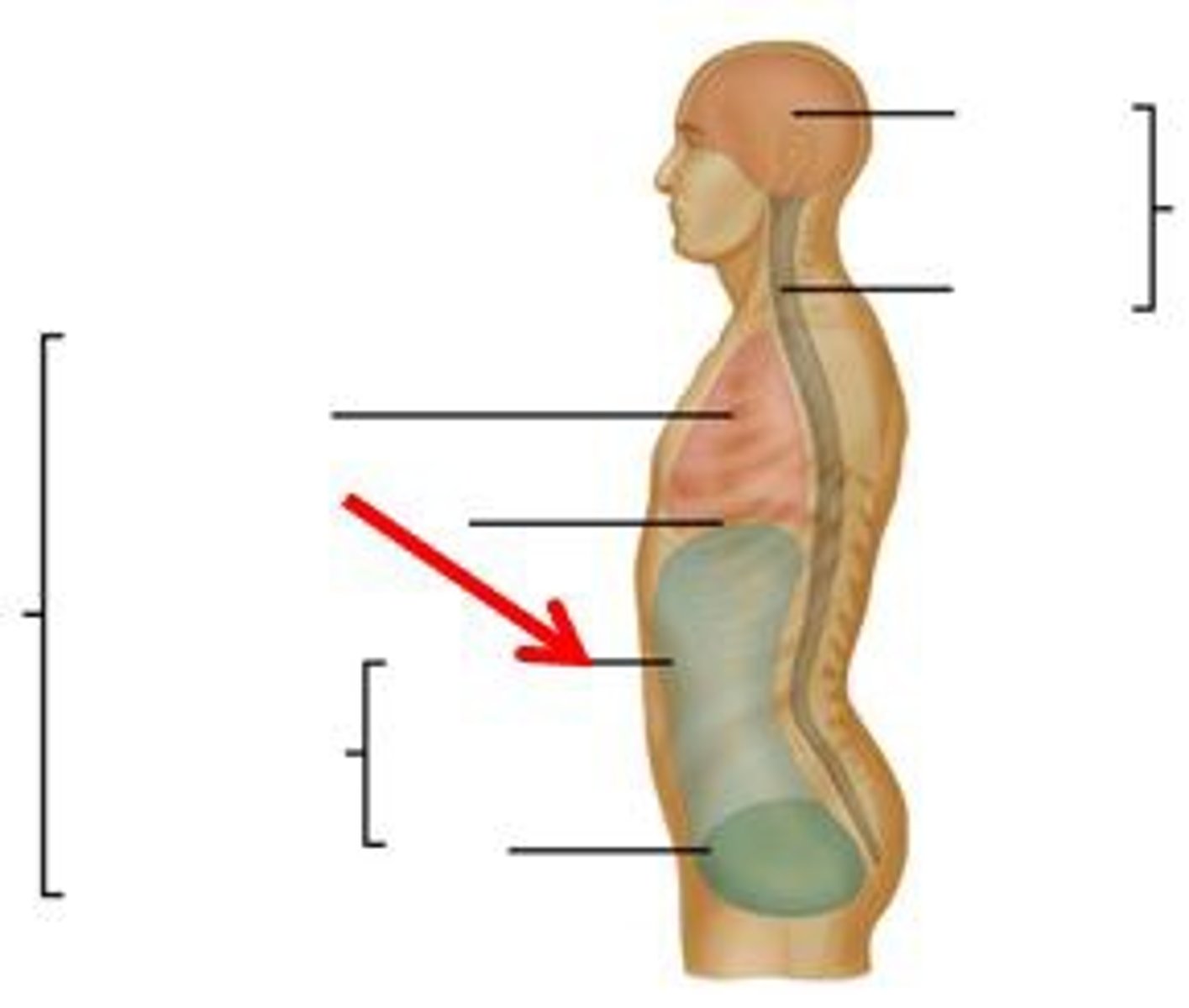
ventral cavity
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
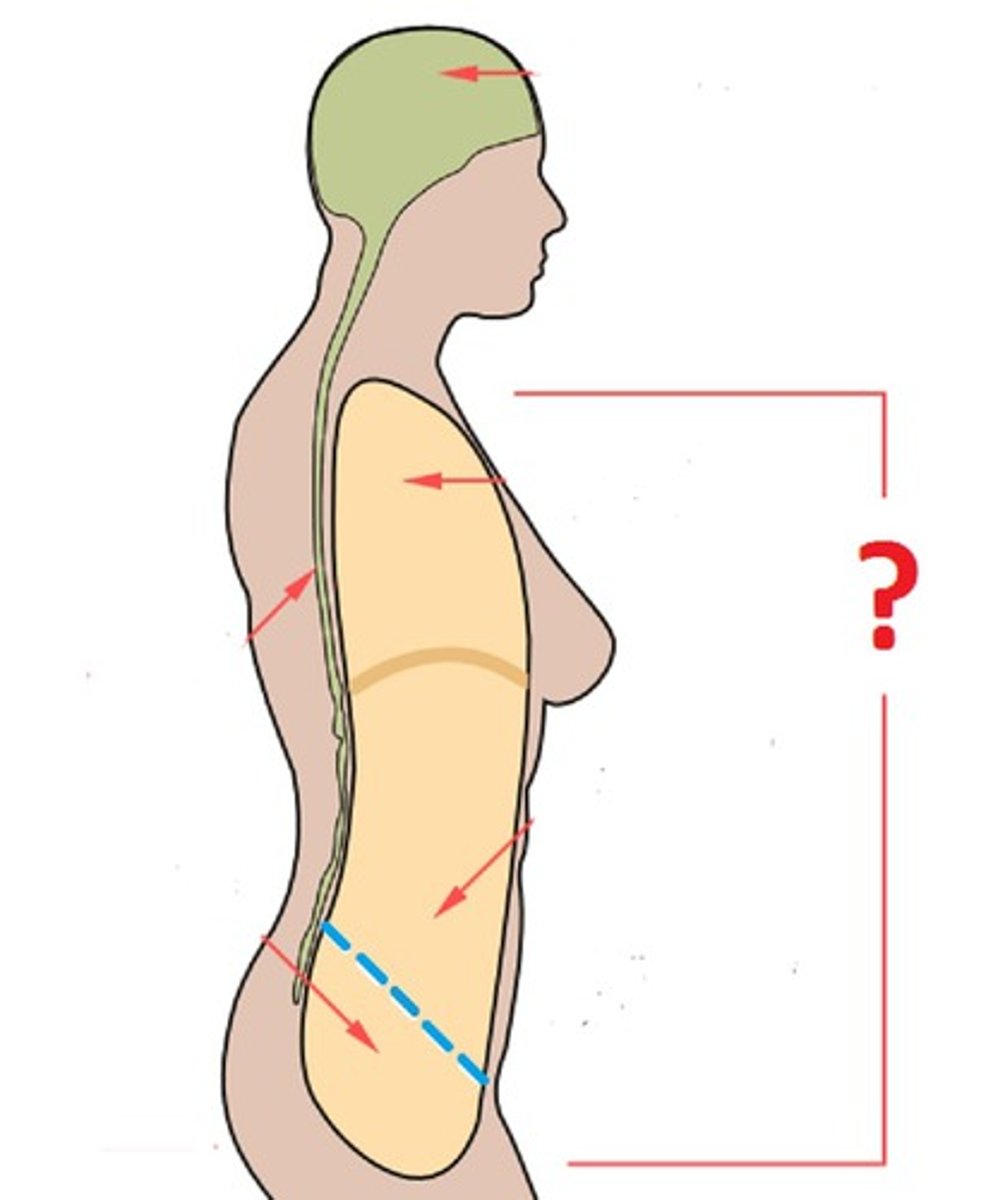
dorsal cavity
includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
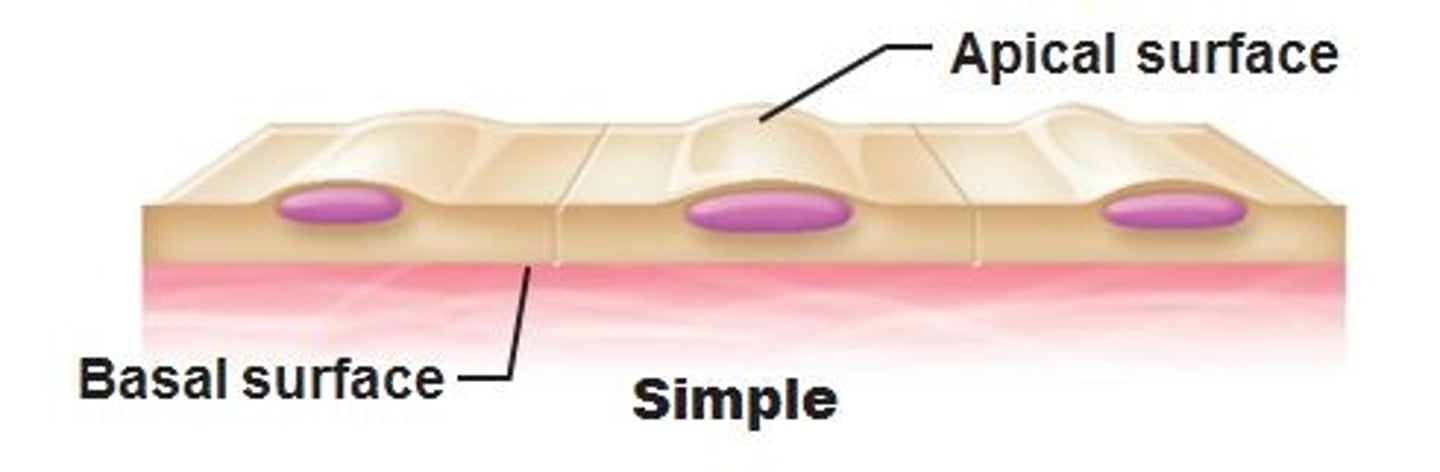
apical
tip
basal
bottom
contralateral
opposite side
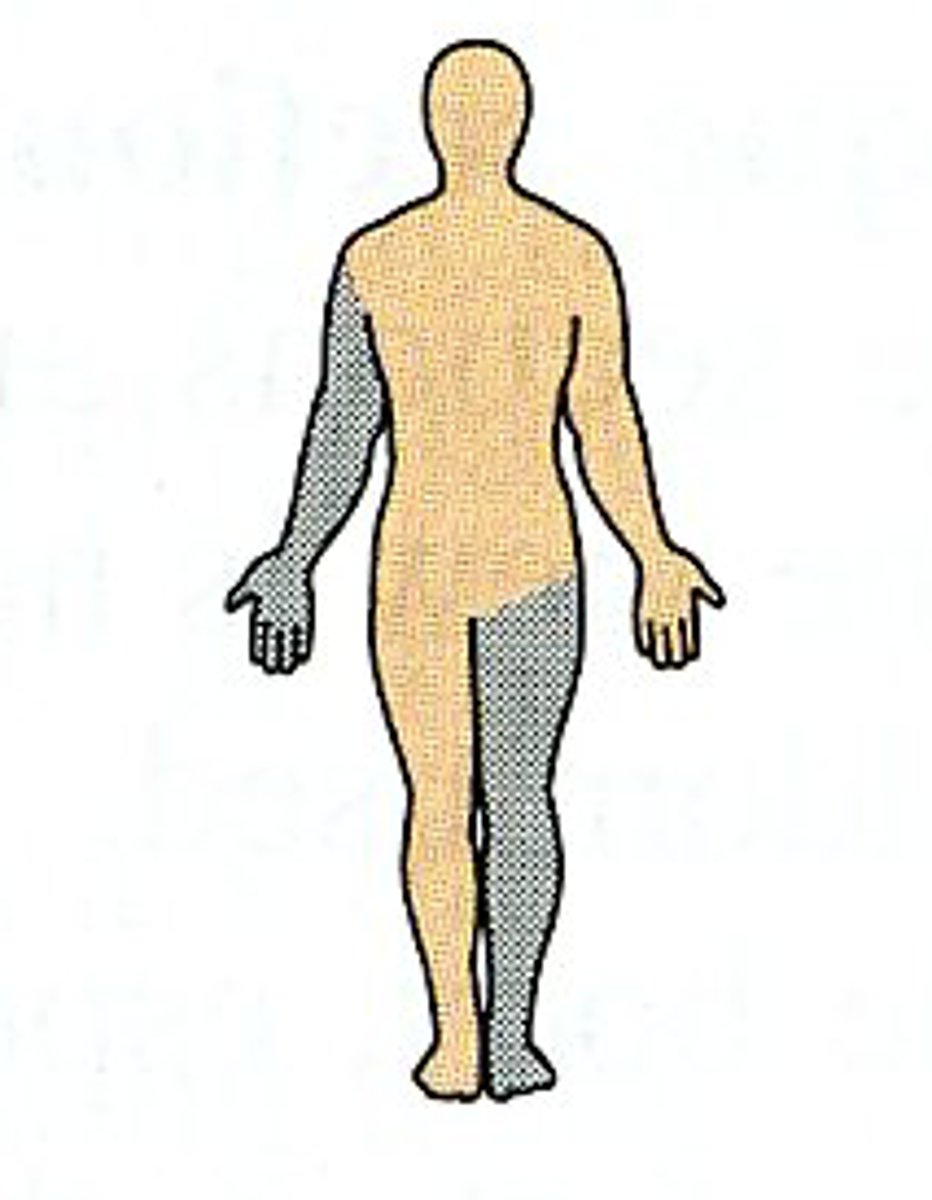
ipsilateral
same side
peripheral
on the edge
visceral
pertaining to the internal organs
parietal
pertaining to the outer wall of the body cavity
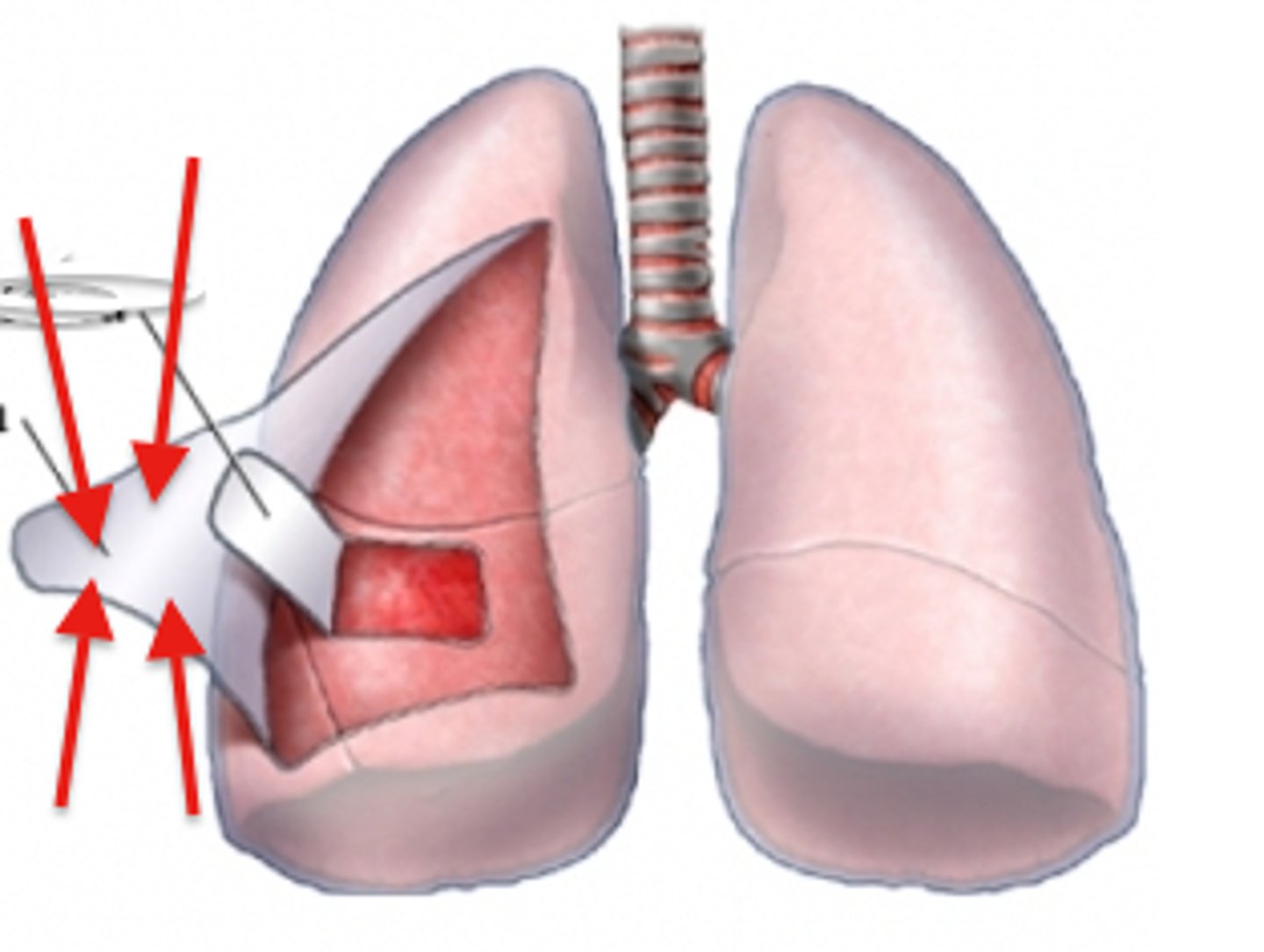
midsaggital
median = separates the body into equal right and left parts